FastLIO For ROS2源码解读
删除laserMapping.cpp中原有main函数,新增定义类。
·
整体框架
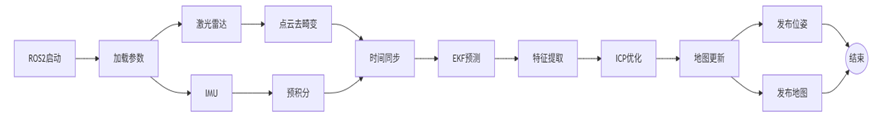 步骤关键代码
步骤关键代码
参数加载及初始化
源码:LaserMappingNode()
// 参数声明与获取
this->declare_parameter<bool>("publish.path_en", true);
this->declare_parameter<string>("map_file_path", "");
this->declare_parameter<string>("common.lid_topic", "/livox/lidar");
this->get_parameter_or<bool>("mapping.extrinsic_est_en", extrinsic_est_en, true);
//各项初始化工作
_featsArray.reset(new PointCloudXYZI()); // 储存当前帧的有效特征点
memset(point_selected_surf, true, sizeof(point_selected_surf)); // 初始化所有点为选中状态
memset(res_last, -1000.0f, sizeof(res_last)); // 初始化残差
//……主处理函数
源码://处理流程:数据同步→IMU预测→激光雷达更新→发布全局地图更新结果各种参数
timer_callback()
数据同步
源码:sync_packages()
目的:同步激光雷达和IMU数据,确保两者时间对齐,为后续的紧耦合优化提供一致的传感器数据包。
//同步IMU数据(确保时间戳覆盖激光雷达扫描周期)
while ((!imu_buffer.empty()) && (imu_time < lidar_end_time)) {
// 更新当前IMU时间戳
imu_time = get_time_sec(imu_buffer.front()->header.stamp);
// 时间超出当前LiDAR帧范围时停止
if (imu_time > lidar_end_time)
break;
// 将IMU数据存入测量组
meas.imu.push_back(imu_buffer.front());
// 从缓冲区移除已使用数据
imu_buffer.pop_front();
}点云去畸变
源码:// IMU前向传播 + 预积分(基于IMU数据预测状态,并去畸变点云)
standard_pcl_cbk() / livox_pcl_cbk()
具体:
PointCloudXYZI::Ptr ptr(new PointCloudXYZI());
//msg为订阅的ROS2发布的话题,此处为/livox/lidar
p_pre->process(msg, ptr); // 调用预处理器(去畸变、降采样)
lidar_buffer.push_back(ptr); // 存入缓冲区IMU前向传播+预积分
源码:
// IMU前向传播 + 预积分(基于IMU数据预测状态,并去畸变点云)
p_imu->Process(Measures, kf, feats_undistort);
state_point = kf.get_x();// 获取当前状态
pos_lid = state_point.pos + state_point.rot * state_point.offset_T_L_I; // lidar position in world system
// feats_undistort去畸变后雷达帧点云
if (feats_undistort->empty() || (feats_undistort == NULL))
{
RCLCPP_WARN(this->get_logger(), "No point, skip this scan!\n");
return;
}
flg_EKF_inited = (Measures.lidar_beg_time - first_lidar_time) < INIT_TIME ? false : true;分割点云
在有效扫描区域以外的点云会产生较大畸变和误差,因此在主处理流程中需要添加一步,分割FOV下的雷达点云,确保只处理视场内的点云。
源码:lasermap_fov_segment()
降采样
去畸变后点云->降采样后点云
/*** downsample the feature points in a scan/降采样 ***/
downSizeFilterSurf.setInputCloud(feats_undistort);
downSizeFilterSurf.filter(*feats_down_body);
t1 = omp_get_wtime();
feats_down_size = feats_down_body->points.size();构建全局点云kdTree
两种情况:第一帧点云/非第一帧点云,只有在第一帧时需要构建全局kdTree。
// 针对第一帧点云初始化全局kdtree
if (ikdtree.Root_Node == nullptr)
{
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Initialize the map kdtree");
if (feats_down_size > 5)
{
ikdtree.set_downsample_param(filter_size_map_min); // 降kdtree降采样参数
feats_down_world->resize(feats_down_size);
for (int i = 0; i < feats_down_size; i++)
{
pointBodyToWorld(&(feats_down_body->points[i]), &(feats_down_world->points[i]));
}
ikdtree.Build(feats_down_world->points);
}
return;
}迭代卡尔曼滤波状态估计
/*** iterated state estimation ***/
double t_update_start = omp_get_wtime(); // 计时
double solve_H_time = 0;
kf.update_iterated_dyn_share_modified(LASER_POINT_COV, solve_H_time);
// 迭代卡尔曼滤波update lidar
state_point = kf.get_x(); // 提取更新后状态
euler_cur = SO3ToEuler(state_point.rot); // 欧拉角
pos_lid = state_point.pos + state_point.rot * state_point.offset_T_L_I; // new lidar position in world system
geoQuat.x = state_point.rot.coeffs()[0];
geoQuat.y = state_point.rot.coeffs()[1];
geoQuat.z = state_point.rot.coeffs()[2];
geoQuat.w = state_point.rot.coeffs()[3];
double t_update_end = omp_get_wtime();核心实现函数
h_share_model()//降采样+平面特征点提取+ICP匹配ROS2发布位姿参数
/******* Publish odometry *******/
// 在已经进行了IMU预测和全局kd树建立的情况下发布激光雷达在世界坐标系下的最终位姿
publish_odometry(pubOdomAftMapped_, tf_broadcaster_);增量式更新全局地图
前文介绍了针对第一帧点云的全局kdTree,此处为针对非第一帧点云的动态更新全局地图,并且基于 ikd-Tree 的体素网格下采样与动态更新策略对每一帧都要判断点云是否为重复特征点,最大程度的优化内存。
/*** add the feature points to map kdtree ***/
map_incremental();
// 动态网格化下采样,增量式更新全局kdtree,对于第一帧,在前文中完成建树,并在此处直接全部添加建图、定位功能封装
原始代码:
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
RCLCPP_INFO(rclcpp::get_logger("test"), "still here wdf");
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
signal(SIGINT, SigHandle);
rclcpp::spin(std::make_shared<LaserMappingNode>());
if (rclcpp::ok())
rclcpp::shutdown();
/**************** save map ****************/
/* 1. make sure you have enough memories
/* 2. pcd save will largely influence the real-time performences **/
cout<<"pcl_wait_pub=:"<<pcl_wait_pub->size()<<endl;
if (pcl_wait_pub->size() > 0 && pcd_save_en)
{
string file_name = string("scans.pcd");
string all_points_dir(string(string(ROOT_DIR) + "PCD/") + file_name);
pcl::PCDWriter pcd_writer;
cout << "current scan saved to /PCD/" << file_name<<endl;
pcd_writer.writeBinary(all_points_dir, *pcl_wait_pub);
}
/**************** save path ****************/
cout<<"lidar_path=:"<<lidar_path.size()<<endl;
if (lidar_path.size() > 0 && path_en)
{
std::cout << "\nSaving path data to lidar_path.txt...\n";
std::ofstream outfile(string(ROOT_DIR)+"Path/path_pos.txt");
if (outfile.is_open()) {
for (const auto& pose : lidar_path) {
// 提取位置和姿态四元数
const auto& position = pose.pose.position;
const auto& orientation = pose.pose.orientation;
// 写入文件:x y z qx qy qz qw
outfile << position.x << " "
<< position.y << " "
<< position.z << " "
<< orientation.x << " " // qx
<< orientation.y << " " // qy
<< orientation.z << " " // qz
<< orientation.w << "\n"; // qw
}
}
outfile.close();
std::cout << "Path data saved!\n";
}
else
{
std::cerr << "Failed to open path_pos.txt!\n";
}
if (runtime_pos_log)
{
vector<double> t, s_vec, s_vec2, s_vec3, s_vec4, s_vec5, s_vec6, s_vec7;
FILE *fp2;
string log_dir = root_dir + "/Log/fast_lio_time_log.csv";
fp2 = fopen(log_dir.c_str(),"w");
fprintf(fp2,"time_stamp, total time, scan point size, incremental time, search time, delete size, delete time, tree size st, tree size end, add point size, preprocess time\n");
for (int i = 0;i<time_log_counter; i++){
fprintf(fp2,"%0.8f,%0.8f,%d,%0.8f,%0.8f,%d,%0.8f,%d,%d,%d,%0.8f\n",T1[i],s_plot[i],int(s_plot2[i]),s_plot3[i],s_plot4[i],int(s_plot5[i]),s_plot6[i],int(s_plot7[i]),int(s_plot8[i]), int(s_plot10[i]), s_plot11[i]);
t.push_back(T1[i]);
s_vec.push_back(s_plot9[i]);
s_vec2.push_back(s_plot3[i] + s_plot6[i]);
s_vec3.push_back(s_plot4[i]);
s_vec5.push_back(s_plot[i]);
}
fclose(fp2);
}
return 0;
}原始代码中对全局地图和定位信息的输出依赖的全局变量pcl_wait_pub、lidar_path,导致外部程序无法获取实时位置或实时全局地图,需要借助ROS2的发布和订阅工具进行实时的信息流交互。
定义ros_run_SLAM类
删除laserMapping.cpp中原有main函数,新增定义ros_run_SLAM类。
class ros_run_SLAM
{
public:
ros_run_SLAM();
~ros_run_SLAM();
void build_map();
void save_map();
void save_path();
};定义PosSubscriber节点
// Subscribe to the stream published by real-time coordinates through nodes
class PosSubscriber : public rclcpp::Node
{
public:
PosSubscriber() : Node("pos_subscriber")
{
subscription_ = this->create_subscription<geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped>(
"/pos", 10,
[this](const geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped::SharedPtr msg)
{
this->pos_callback(msg);
});
}
void pos_callback(const geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped::SharedPtr msg)
// deal with the current position
{
const auto &pose = msg->pose; // 获取最新位姿...
// 提取位置和姿态四元数
const auto &position = pose.position;
const auto &orientation = pose.orientation;
const auto &scanTime = msg->header.stamp;
double timestamp = rclcpp::Time(scanTime).seconds();
// 使用ROS内置时间格式化(UTC时间)
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(),
"位姿信息:\n"
" 位置: x=%.9f, y=%.9f, z=%.9f\n"
" 姿态: qx=%.9f, qy=%.9f, qz=%.9f, qw=%.9f\n"
" 时间: %s", // 纳秒级时间戳
position.x, position.y, position.z,
orientation.x, orientation.y, orientation.z, orientation.w,
unixTimestampToReadableTime(timestamp).c_str());
}
private:
rclcpp::Subscription<geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped>::SharedPtr subscription_;
};LaserMappingNode():新增对公共变量pubPos的定义
pubPos_ = this->create_publisher<geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped>("/pos", 20);publish_path():新增对实时位姿数据的发布
// 发布current position
pubPos->publish(msg_body_pose);void build_map():新增传感器实时定位的订阅节点
auto pos_subscriber = std::make_shared<PosSubscriber>();//订阅节点新建main.cpp文件夹
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
//初始化 ROS2 上下文
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
//创建实例
ros_run_SLAM slam_controller;
//启动建图流程
try {
slam_controller.build_map(); // 阻塞式运行,直到节点结束
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(rclcpp::get_logger("main"), "SLAM crashed: %s", e.what());
}
// 4. 保存结果(可选)
slam_controller.save_map(); // 保存点云地图
slam_controller.save_path(); // 保存运动轨迹
return 0;
}运行结果
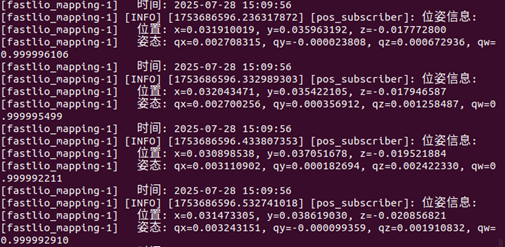
在控制台中以ROS信息的形式输出传感器实时位姿数据,可用于之后特征提取应用。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)