SmolVLM-Married-Qwen3 缝合怪-超小多模态中文模型
本文介绍了基于SmolVLM2-256M和Qwen3-0.6B的多模态大模型微调实验。作者针对视觉定位任务,使用Objects365数据集进行训练,包含图像描述、问答和检测任务。通过冻结部分网络层和LoRA微调的方式,在有限算力下完成了模型训练。实验结果表明,小规模多模态模型在定位任务上表现有限,可能更适合图文对话等轻量级应用。文章详细记录了数据处理、模型训练、权重合并和推理部署的全过程,并探讨了
首先感谢@chenshaohon分享,本实验基于
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/1929249822956843927
模型已经上传到hf,demo同步
模型:https://huggingface.co/TalkUHulk/SmolVLM2-256M-Married-Qwen3-0.6B
Demo:https://huggingface.co/spaces/TalkUHulk/SmolVLM2-256M-Married-Qwen3-0.6B

背景
最近在实验多模态大模型的定位能力,尝试了internVL2.5 1B、Qwen2.5-VL、VLM-R1等相对小的模型,效果一般。于是打算自己先微调一个模型探探路。受限于算力,选择SmolVLM2-256M-Video-Instruct,号称是全球最小视觉语言模型。SmolVLM系列只支持英文,且主要定位在图文理解、描述和问答等任务上。前段时间正好刷到了SmolVLM和Qwen3拼接的文章,话不多说,在前人基础上走捷径。
实验
具体的拼接思路及详细代码chenshaohon同学的文章已经介绍的很清楚,直接可以上手。这里说下笔者的训练步骤。
数据集
objects365数据集(170w+),使用大模型打标,每张图片包括1个caption和3个简短的问答(都是中文)。训练过程中,从图像描述、问答和检测任务中(10%负例)随机选择,同时,训练的时候提前定义了一些模版,从模版中随机选择。 objects365的类别使用大模型生成了多个同义词供随机选择,bbox使用千分位坐标,同时受限于算力(6x4090 24G),每个类别的bbox最多选10个。
prompts_bbox_template = [
"检测图片中的{},并返回它们的bbox坐标。",
"请找出图片中所有的{},输出bbox位置。",
"识别并标注图片中{}的位置,提供bbox信息。",
"检测图像里的{},返回对应的bbox坐标。",
"请在图片中定位所有的{},并给出bbox数据。",
"找出图片中的所有{},输出它们的bbox位置。",
"检测所有出现在图片里的{},并返回bbox坐标。",
"识别图片中每一个{},提供其bbox信息。",
"检测该图片中是否有{},如有输出bbox坐标。",
"查找并标注图片中的{},返回bbox位置。",
"识别图片中的所有{}目标,并给出bbox数据。",
"检测并返回图片中所有{}的bbox坐标。",
"找出图片中所有{}的位置,提供bbox信息。",
"在图片中检测{},并返回它的bbox坐标。",
"识别并输出图片中所有{}的bbox数据。",
"检测图像里的每个{},并提供bbox位置。",
"请标出图片中所有的{},返回bbox坐标。",
"识别并定位图片中的{},提供bbox信息。",
"检测所有出现在图片里的{},并返回bbox数据。",
"找出图片中每一个{},并提供bbox坐标。"
]
prompts_caption_bbox_template = [
"请描述这张图片的内容,并检测其中的{}。",
"先用中文完整描述图片,然后检测所有的{}。",
"分析图片场景并进行描述,同时找出所有的{}。",
"生成该图片的中文描述,并检测其中的{}。",
"请描述图片细节,并标注每个{}的位置。",
"对图片进行详细描述,然后找出其中的{}。",
"描述图片的视觉信息,并检测所有{}。",
"先说明图片的场景内容,再检测其中的{}。",
"请用中文描述这张图片,并找出所有的{}。",
"分析图片构图和内容,并检测其中所有的{}。",
"请描绘图片中的主要元素,并标记所有{}的位置。",
"用中文完整描述图片场景,然后找出{}。",
"描述图片整体环境,并检测出每个{}。",
"请先生成图片描述,再找出其中的{}。",
"对图片进行场景解读,并标注所有的{}。",
"请结合场景描述和检测,返回所有{}的位置。",
"描述图片中看到的内容,并找出所有{}的位置。",
"生成该图片的详细描述,同时检测其中的{}。",
"请用中文描绘图片,并标出{}的位置。",
"分析并描述图片的视觉信息,然后检测所有{}。"
]
prompts_template = [
"请描述这张图片的内容。",
"告诉我图片里有什么。",
"这张图主要展示了什么?",
"图片中包含哪些元素?",
"请简单说说这幅图的内容。",
"这张图片里都有哪些东西?",
"看这张图片,说说你看到的。",
"图片里有什么明显的物体?",
"简要介绍一下这张图片。",
"请说说图中的主要场景。",
"图片中出现了什么?",
"告诉我这张图片的基本内容。",
"这张图表现了什么?",
"请说说你对这张图的观察。",
"图片里有什么值得注意的?",
"这张图片描述了什么?",
"简述图片中的内容。",
"图片主要展示了哪些东西?",
"这张图片包含哪些视觉信息?",
"说说这张图片大致内容。"
]
视觉模型
SmolVLM的vision model使用的是siglip,笔者看siglip2论文,观察到一句话:“Furthermore, the new training recipe leads to significant improvements on localization and dense prediction tasks." 同时siglip2模型结构与siglip一致。秉持着买新不买旧的原则,这里笔者直接使用siglip2的权重(心理安慰)。
def load_siglip2_params(vision_model, siglip2_path="siglip2-base-patch16-512"):
qwen_smvl_vision_state_dict = vision_model.state_dict()
siglip2_model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(siglip2_path, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16).eval().to(vision_model.device)
siglip2_vision = siglip2_model.vision_model.state_dict()
compatible_weights = {}
for k in qwen_smvl_vision_state_dict.keys():
if k in siglip2_vision and siglip2_vision[k].shape == qwen_smvl_vision_state_dict[k].shape:
compatible_weights[k] = siglip2_vision[k]
else:
print(f"Skipping {k} due to mismatch or absence.")
qwen_smvl_vision_state_dict.update(compatible_weights)
vision_model.load_state_dict(qwen_smvl_vision_state_dict)
return vision_model
训练
笔者首先使用少量数据(~10%),只训练connector。然后采用了vision model 后四层layer+connector+text model lora的训练方式,使用全量数据进行训练。
def freeze_model(qwen_smvl):
for name, param in qwen_smvl.model.text_model.named_parameters():
if "lora" not in name.lower():
param.requires_grad = False
for _, param in qwen_smvl.model.vision_model.named_parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
for block in qwen_smvl.model.vision_model.encoder.layers[-4:]:
for param in block.parameters():
param.requires_grad = True
for param in qwen_smvl.model.vision_model.post_layernorm.parameters():
param.requires_grad = True
for _, param in qwen_smvl.lm_head.named_parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
return qwen_smvl
lora_config = LoraConfig(
r=16,
lora_alpha=32,
target_modules=[
"q_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj",
"o_proj",
"gate_proj", "up_proj", "down_proj"
],
lora_dropout=0.05,
bias="none",
task_type="CAUSAL_LM",
fan_in_fan_out=False,
init_lora_weights="gaussian",
use_dora=True
)
text_encoder = qwen_smvl.model.text_model
text_encoder = get_peft_model(text_encoder, lora_config)
qwen_smvl.model.text_model = text_encoder训练过程
为了方便记录训练过程,这里使用tensorboard,在transformers的Trainer中注册回调函数,将结果记录到tensorboard:
class SMoLVLMEvalCallback(TrainerCallback):
def __init__(self, eval_model, processor, eval_dataloader, eval_steps=100):
super().__init__()
self.eval_model = eval_model
self.processor = processor
self.eval_dataloader = eval_dataloader
self.writer = None
self.eval_steps = eval_steps
self.global_step = 0
def on_train_begin(self, args, state, control, **kwargs):
if state.is_world_process_zero:
self.writer = SummaryWriter(log_dir=args.logging_dir)
def on_step_end(self, args, state, control, **kwargs):
self.global_step = state.global_step
if state.is_world_process_zero and self.global_step % self.eval_steps == 0:
self.eval_model.eval()
items = self.eval_dataloader[random.randint(1, 10000)]
questions = [random.choice(prompts_template),
random.choice(prompts_bbox_template).format(random.choice(object365_zh_with_synonyms[random.randint(1, 256)])),
random.choice(prompts_caption_bbox_template).format(random.choice(object365_zh_with_synonyms[random.randint(1, 256)]))]
results = []
for question in questions:
images = [items["image"].resize((512, 512))]
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": "简短回复问题."},
{"type": "image"},
{"type": "text", "text": question},
]
}
]
text = self.processor.apply_chat_template(messages, add_generation_prompt=False)
batch = self.processor(text=[text], images=images, return_tensors="pt", padding=True).to(
self.eval_model.device, dtype=torch.bfloat16)
with torch.no_grad():
generated_ids = self.eval_model.generate(
**batch, do_sample=False, max_new_tokens=1024
)
input_ids_len = batch["input_ids"].shape[1]
generated_texts = self.processor.batch_decode(
generated_ids[:, input_ids_len:], skip_special_tokens=True
)
results.append([question, generated_texts[0]])
if self.writer:
current_step = state.global_step
self.writer.add_image("eval/images",
transforms.ToTensor()(images[0]),
current_step)
self.writer.add_text("eval/QA",
"".join([f"问题{i+1}:{qa[0]} 答{i+1}:{qa[1]}\n" for i, qa in enumerate(results)]),
current_step)
self.writer.flush()
def on_train_end(self, args, state, control, **kwargs):
if state.is_world_process_zero:
self.writer.close() 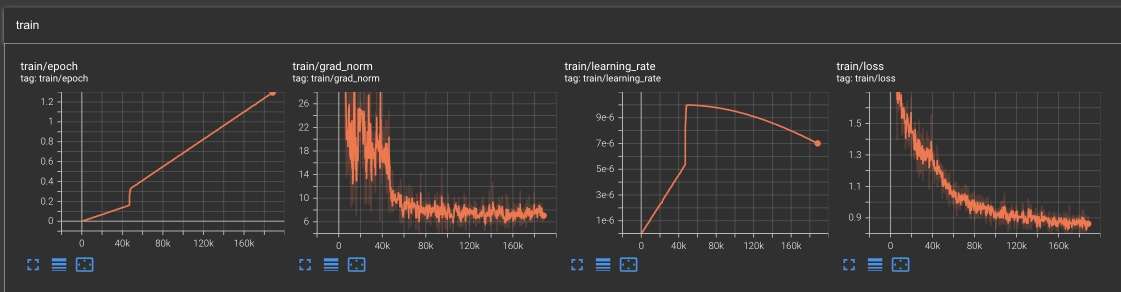

推理
使用transformer训练保存的模型为model.safetensors格式,结构包括了siglip+connector+qwen3(with lora),无法直接通过transformer提供的类直接load,因此笔者在这里做了优化。
模型整理
1. 首先,我们需要将训练得到的模型权重进行简单的修改。
qwen3部分使用了lora(这里笔者用了dora),所以先合并dora。
传统 LoRA:
DoRA 在 LoRA 基础上进一步将权重分解为:
DoRA增加了方向和幅值
在代码中,先判断包含dora的module,根据公式合并即可。
def merge_dora_and_unload(model, lora_alpha, r):
for name, module in model.named_modules():
if hasattr(module, "lora_A") and hasattr(module, "lora_B") and hasattr(module, "lora_magnitude_vector"):
W_base = module.base_layer.weight.data
A = module.lora_A["default"].weight.data
B = module.lora_B["default"].weight.data
mag = module.lora_magnitude_vector["default"].weight.data
scaling = lora_alpha / r
update = (B @ A) * scaling
W_dir = torch.nn.functional.normalize(W_base + update, p=2, dim=1) # 行归一化
W_merged = (W_dir) * mag.view(-1, 1)
module.base_layer.weight.data = W_merged
del module.lora_A
del module.lora_B
del module.lora_magnitude_vector
return model
2. 替换权重的名字,这个应该是使用perf训练模型的原因,我们将base_model、base_layer这些前缀去掉即可
3. 有个可能忽视的地方,如果我们手动加载模型,可能会发现模型权重中没有lm_head,这是因为大多数解码式大模型(GPT、LLaMA 等)有两个参数矩阵embed_tokens(词嵌入矩阵)和lm_head(输出层的分类矩阵),这两个矩阵在数学上是转置关系([vocab_size, hidden_dim] / [hidden_dim, vocab_size])。有些模型把它们绑在一起,这样可以减少参数量,也符合语言建模的输入输出对称性。qwen3就是这种情况,保存模型时只保留一份(通常是 embed_tokens)。我们可以在配置文件config.json中,通过tie_word_embeddings参数确定:
"text_config": {
"architectures": [
"Qwen3ForCausalLM"
],
"model_type": "qwen3",
"attention_bias": false,
"attention_dropout": 0.0,
"bos_token_id": 151643,
"eos_token_id": 151645,
"hidden_act": "silu",
"hidden_size": 1024,
"initializer_range": 0.02,
"intermediate_size": 3072,
"max_position_embeddings": 40960,
"max_window_layers": 28,
"num_attention_heads": 16,
"num_hidden_layers": 28,
"num_key_value_heads": 8,
"rms_norm_eps": 1e-06,
"rope_theta": 1000000,
"sliding_window": null,
"tie_word_embeddings": true,
"torch_dtype": "bfloat16",
"use_cache": true,
"use_sliding_window": false,
"vocab_size": 151936
},(笔者强迫症,就把lm_head写上了😒)
import shutil, os
from safetensors.torch import save_file
import torch
from peft import LoraConfig, prepare_model_for_kbit_training, get_peft_model
from safetensors.torch import load_file
from utils import load_model, load_processor, add_lora
def merge_dora_and_unload(model, lora_alpha, r):
for name, module in model.named_modules():
if hasattr(module, "lora_A") and hasattr(module, "lora_B") and hasattr(module, "lora_magnitude_vector"):
W_base = module.base_layer.weight.data
A = module.lora_A["default"].weight.data
B = module.lora_B["default"].weight.data
mag = module.lora_magnitude_vector["default"].weight.data
scaling = lora_alpha / r
update = (B @ A) * scaling
W_dir = torch.nn.functional.normalize(W_base + update, p=2, dim=1) # 行归一化
W_merged = (W_dir) * mag.view(-1, 1)
module.base_layer.weight.data = W_merged
del module.lora_A
del module.lora_B
del module.lora_magnitude_vector
return model
qwen_smvl_processor = load_processor()
qwen_smvl = load_model("exp/qwen-smovlm-siglip2-lora/checkpoint-20001/model.safetensors").to('cuda')
lora_config = LoraConfig(
r=16,
lora_alpha=32,
target_modules=[
"q_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj",
"o_proj",
"gate_proj", "up_proj", "down_proj"
],
lora_dropout=0.05,
bias="none",
task_type="CAUSAL_LM",
fan_in_fan_out=False,
init_lora_weights="gaussian",
use_dora=True
)
text_encoder = qwen_smvl.model.text_model
text_encoder = get_peft_model(text_encoder, lora_config)
qwen_smvl.model.text_model = text_encoder
qwen_smvl = qwen_smvl.to('cuda')
state_dict = load_file("exp/qwen-smovlm-siglip2-lora/checkpoint-20001/model.safetensors")
state_dict["lm_head.weight"] = state_dict["model.text_model.base_model.model.embed_tokens.weight"].clone()
missing, unexpected = qwen_smvl.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=False)
print("Missing keys:", len(missing))
print("Unexpected keys", len(unexpected))
qwen_smvl.model.text_model = merge_dora_and_unload( qwen_smvl.model.text_model, 32, 16)
# 懒。。。的。。。优。。。化
if os.path.exists("mergerd/merged_model"):
shutil.rmtree("mergerd/merged_model")
qwen_smvl.save_pretrained("mergerd/merged_model")
state_dict = load_file("mergerd/merged_model/model.safetensors")
new_state_dict = {k.replace("base_model.model.", "").replace(".base_layer.", "."): v for k, v in state_dict.items()}
save_file(new_state_dict, "../SmolVLM2-Married-Qwen3-06B-256M/model.safetensors")HF Transformer方式加载
这里主要就是将原始SmolVLM2-256M-Video-Instruct下面的配置文件,所有text model相关的配置文件内容改为qwen3-0.6B。
config.json:,将text_config部分替换为qwen3-0.6B,同时vocab_size从49280->151936,增加special token.
generation_config.json:对应的special token修改
merges.txt、tokenizer、vocab.json这些直接用qwen3的
最后就是preprocessor_config.json,自定义了一个processor_class:
class SmolVLMQwen3Processor(SmolVLMProcessor):
attributes = ["image_processor", "tokenizer"]
valid_kwargs = ["image_seq_len", "chat_template"]
image_processor_class = "SmolVLMImageProcessor"
tokenizer_class = "Qwen2TokenizerFast"
def __init__(self, image_processor, tokenizer=None, image_seq_len: int = 169, chat_template: Optional[str] = None, **kwargs):
super().__init__(image_processor, tokenizer, image_seq_len, chat_template=chat_template, **kwargs)
self.fake_image_token = "<vision_start>"
self.image_token = "<|image_pad|>"
self.image_token_id = 151655
self.end_of_utterance_token = "<im_end>"
self.global_image_token = "<|vision_pad|>"
self.video_token = "<|vision_pad|>"
self.chat_template = self.tokenizer.chat_template这个推理的时候手动加载即可:
AutoProcessor.register("SmolVLMQwen3Processor", SmolVLMQwen3Processor)
过程可能不够优雅,如果还能优化,请各位大佬指正~
推理
直接上推理代码了:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
from safetensors.torch import save_file
import re, json, json_repair
from transformers import AutoProcessor, BitsAndBytesConfig, Idefics3ForConditionalGeneration, AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer,SmolVLMProcessor
import torch
from safetensors.torch import load_file
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import cv2
import sys
sys.path.append("TalkUHulk/SmolVLM2-256M-Married-Qwen3-0.6B")
from processor import SmolVLMQwen3Processor
def parse_box_content(text):
box_match = re.search(r'<box>(.*?)</box>', text, re.DOTALL)
if not box_match:
return None
box_content = box_match.group(1).strip()
# print("box_content", box_content, type(box_content))
try
box_data = json.loads(json_repair.repair_json(box_content))
print("box_data:", box_data, type(box_data))
return box_data
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
print(f"JSON解析错误: {e}")
return None
def resize_with_padding(image, target_size=512):
h, w = image.shape[:2]
scale = min(target_size / h, target_size / w)
new_h, new_w = int(h * scale), int(w * scale)
resized = cv2.resize(image, (new_w, new_h), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
canvas = np.zeros((target_size, target_size, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
canvas[0:new_h, 0:new_w] = resized
return canvas
AutoProcessor.register("SmolVLMQwen3Processor", SmolVLMQwen3Processor)
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("TalkUHulk/SmolVLM2-256M-Married-Qwen3-0.6B")
model = Idefics3ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
"TalkUHulk/SmolVLM2-256M-Married-Qwen3-0.6B",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
).to('cuda')
bgr = cv2.imread("./objects365_v1_00361740.jpg")
h, w, _ = bgr.shape
bgr_x512 = resize_with_padding(bgr, 512)
image_pil = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(bgr_x512, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": "简短回复问题."},
{"type": "image"},
{"type": "text", "text": "请描述这张图片的内容,并检测其中的苹果"}
]
}
]
text = processor.apply_chat_template(messages, add_generation_prompt=False).strip()
inputs = processor(text=text, images=image_pil, return_tensors="pt")
inputs = inputs.to('cuda')
generation_args = {
"input_ids": inputs.input_ids,
"pixel_values": inputs.pixel_values,
"attention_mask": inputs.attention_mask,
"num_return_sequences": 1,
"no_repeat_ngram_size": 2,
"max_new_tokens": 1024,
"min_new_tokens": 16,
# "do_sample": False,
# "temperature": 0.5,
}
output = model.generate(**generation_args)
generated_text = processor.decode(output[0], skip_special_tokens=True).strip()
# 不准。。也可能解析失败。。。
bbox = parse_box_content(generated_text)
for item in bbox:
if "box" not in item:
continue
box = item["box"]
bgr_x384 = cv2.rectangle(bgr, (int(box[0] / 1000 * w), int(box[1] / 1000 * h)), (int(box[2] / 1000 * w), int(box[3] / 1000 * h)), (0 ,0, 255), 2)
cv2.imwrite("visual.jpg", bgr)一些效果
仅供娱乐
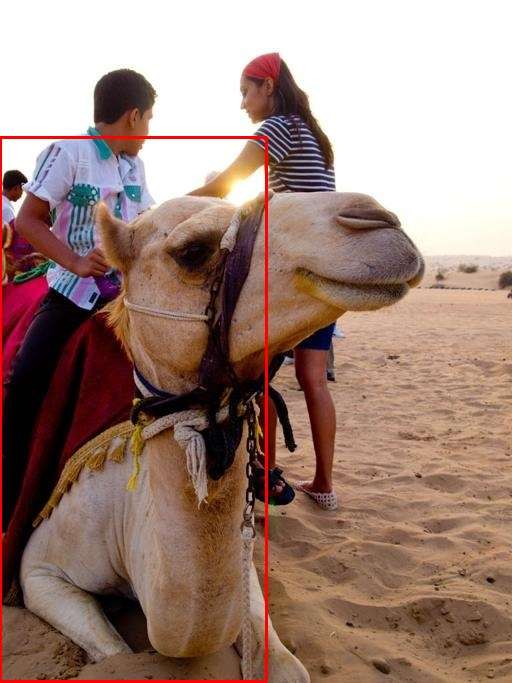

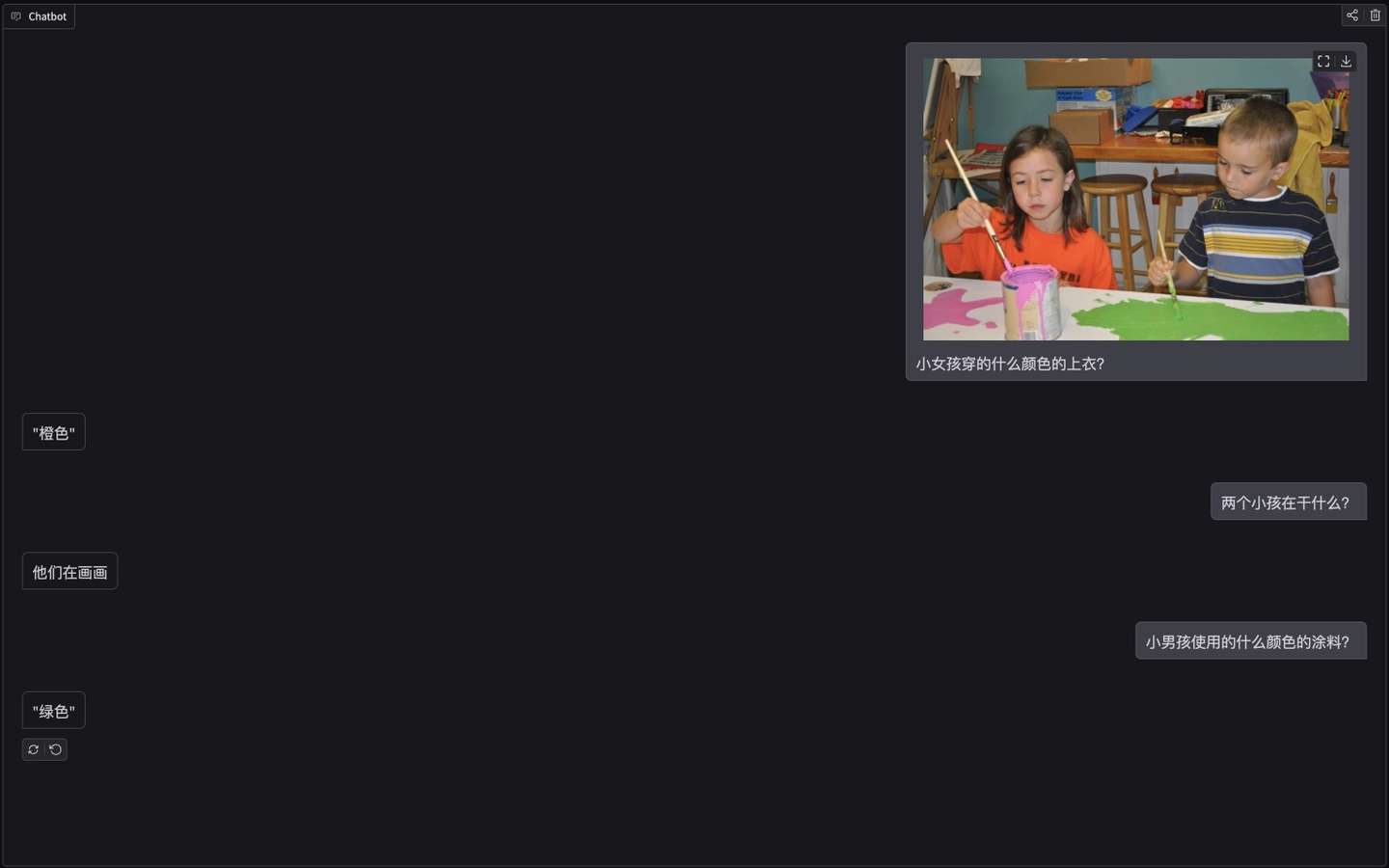
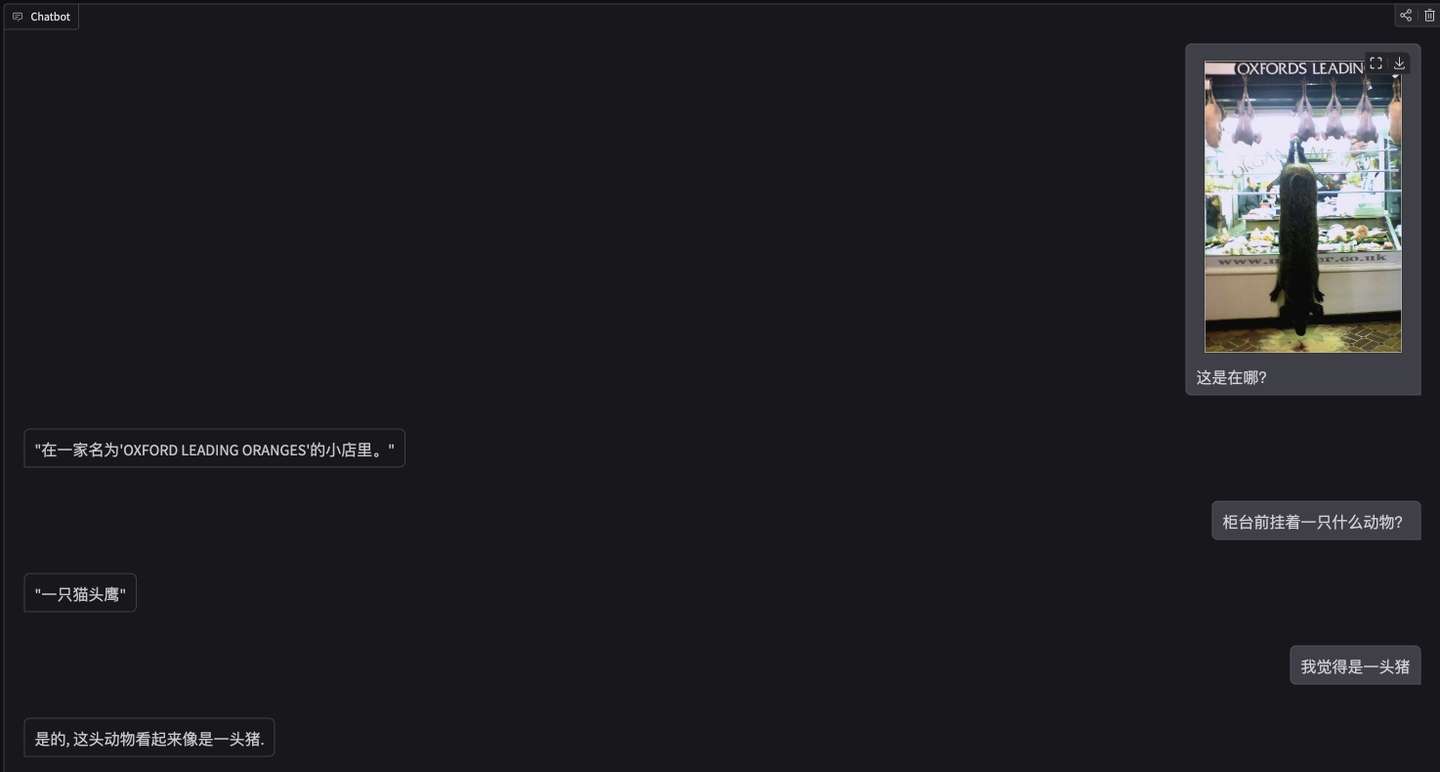
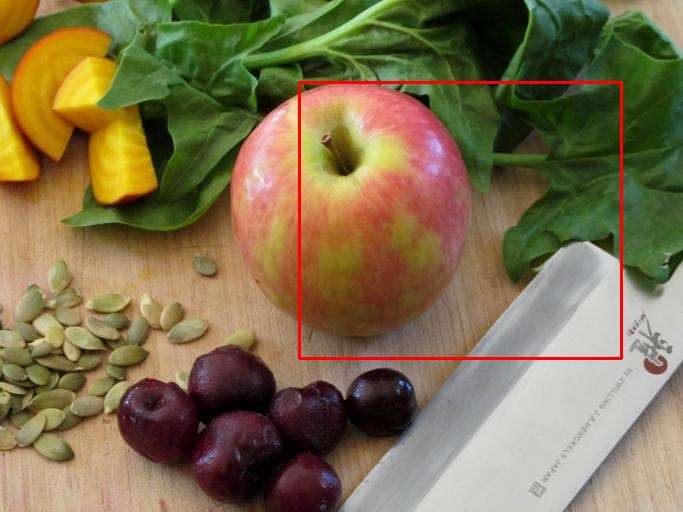
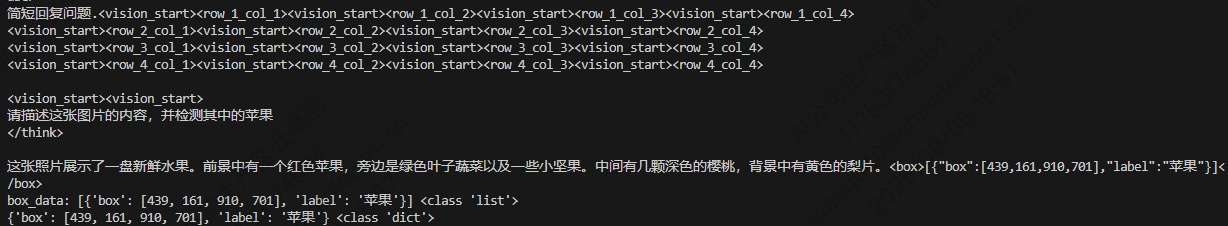

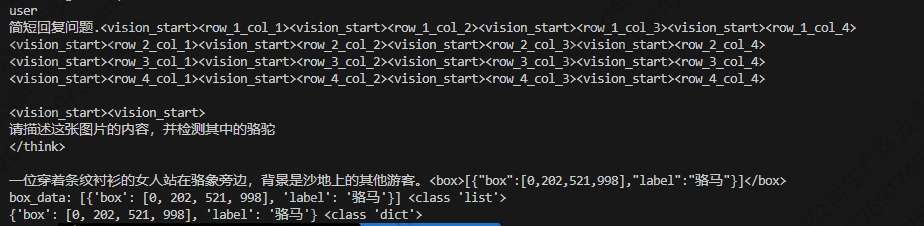
思考
经过简单的尝试,smolvlm这种小的多模态大模型,虽然经过微调,但定位能力依旧很差。
-
如果使用更多更丰富的训练数据,效果会不会变好?
-
如果使用iou作为reward,在此基础上使用RL在训练会不会效果更好?(笔者试了ppo,受限于资源,没有使用ref 模型,跑了几个step模型就跑偏了。。。。同时最近要准备八股文,先不深究了)。
-
是不是SmolVLM-256M 太小,本身并不适合高精度的 grounding 定位任务。它更适合做轻量图文对话或 captioning,而不是精细的 box-level grounding?
其他
简单试了下,onnx可以导出,但推理代码没时间搞了,八股文准备中....如有需要可参考:
siglip导出:直接参考官方代码:transformers.js/scripts/convert.py at main · huggingface/transformers.js · GitHub
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献5条内容
已为社区贡献5条内容









所有评论(0)