手写 Tomcat
使用 Socket 简单实现ResponseHttpServer03 动态 Response : 按照规范构造返回流04 各司其职的 Server : 拆分响应模块与处理模块#mermaid-svg-2INa1N7vV9JzTK1K {font-family:"trebuchet ms",verdana,arial,sans-serif;font-size:16px;fill:#333;}#mer
文章目录
- 02 初出茅庐:构造一个极简的 HttpServer
- 03 动态 Response : 按照规范构造返回流
- 04 各司其职的 Server : 拆分响应模块与处理模块
- 05 Server 性能提升: 设计多个 Processor
- 06 规范化: 引入 HttpRequest 与 HttpResponse
- 07 对内的保护: 引入门面模式封装内部实现类
- 08 解析参数:通过引入 Cookie 和 Session 避免反复登录
- 09 有状态的 Response: 实现 Session 传递与 keep-alive
- 10 Servlet Wrapper: 如何维护 Servlet 生命周期及实现容器管理?
- 11 多层容器:如何通过实现 Context 与 Wrapper 形成多层容器?
- 12 Pipeline 与 Valve: 如何实现容器间的调用、事务管理、权限验证?
- Filter 与 Listener: 如何实现过滤和持续监听?
02 初出茅庐:构造一个极简的 HttpServer
使用 Socket 简单实现
Request
public class Request {
InputStream input;
String uri;
public Request(InputStream input) {
this.input = input;
}
public void parse() {
int i = 0;
byte[] buffer = new byte[2024];
try {
i = input.read(buffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
i = -1;
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
sb.append((char) buffer[j]);
}
uri = parseUir(sb.toString());
}
public String parseUir(String str) {
int index1 = 0, index2 = 0;
index1 = str.indexOf(' ');
index2 = str.indexOf(' ', index1 + 1);
if (index1 == -1 || index2 == -1) {
throw new RuntimeException("请求格式异常");
}
return str.substring(index1 + 1, index2);
}
public String getUri() {
return uri;
}
}
Response
public class Response {
Request request;
OutputStream out;
int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024;
public Response(Request request, OutputStream out) {
this.request = request;
this.out = out;
}
public void sendStaticResource() {
byte[] bytes = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE];
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
File file = new File(HttpServer.WEB_ROOT, request.getUri());
if (file.exists()) {
// 在发送文件内容前,先发送成功的HTTP响应头
String successHeader = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n"
+ "Content-Type: text/html\r\n" // 注意: 这里可以根据文件类型动态改变
+ "Content-Length: " + file.length() + "\r\n"
+ "\r\n"; // 重要的空行,分隔头和体
out.write(successHeader.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
int ch = fis.read(bytes, 0, BUFFER_SIZE);
while (ch != -1) {
out.write(bytes, 0, ch);
ch = fis.read(bytes, 0, BUFFER_SIZE);
}
out.flush();
} else {
// file not found
String errorMessage = """
HTTP/1.1 404 File Not Found\r
Content-Type: text/html\r
Content-Length: 23\r
\r
<h1>File Not Found</h1>""";
out.write(errorMessage.getBytes());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// thrown if cannot instantiate a File object
System.out.println(e.toString());
} finally {
if (fis != null){
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException ignored) {
}
}
}
}
}
HttpServer
public class HttpServer {
public static final String WEB_ROOT = System.getProperty("user.dir") + File.separator + "webroot";
public static void main(String[] args) {
HttpServer httpServer = new HttpServer();
System.out.println(WEB_ROOT);
httpServer.await();
}
public void await() {
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
int port = 8080;
try {
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port, 1, InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
while (true) {
Socket socket = null;
InputStream inputStream = null;
OutputStream outputStream = null;
try {
socket = serverSocket.accept();
inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
Request request = new Request(inputStream);
request.parse();
outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
Response response = new Response(request, outputStream);
response.sendStaticResource();
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
03 动态 Response : 按照规范构造返回流
private String composeResponseHead() {
HashMap<String, String> headers = new HashMap<>();
headers.put("StatusCode", "200");
headers.put("StatusName", "ok");
headers.put("ContentType", "text/html;charset=utf-8");
headers.put("ZonedDateTime", DateTimeFormatter.ISO_ZONED_DATE_TIME.format(ZonedDateTime.now()));
return new StrSubstitutor(headers).replace(OKMessage);
}
//下面的字符串是当文件没有找到时返回的 404 错误描述
private final static String fileNotFoundMessage = """
HTTP/1.1 404 File Not Found\r
Content-Type: text/html\r
\r
<h1>File Not Found</h1>
""";
//下面的字符串是正常情况下返回的,根据http协议,里面包含了相应的变量。
private final static String OKMessage = """
HTTP/1.1 ${StatusCode} ${StatusName}\r
Content-Type: ${ContentType}\r
Server: miniTomcat\r
Date: ${ZonedDateTime}\r
\r
""";
04 各司其职的 Server : 拆分响应模块与处理模块
把 HttpServer 拆分成两个部分
- HttpConnector : 负责与客户端进行连接
- HttpProcessor : 负责分发与处理连接
HttpConnector
public class HttpConnector implements Runnable {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HttpConnector.class);
@Override
public void run() {
ServerSocket serverSocket;
int port = 8080;
try {
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port, 1, InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"));
log.info("服务器启动成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
while (true) {
try {
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
HttpProcessor httpProcessor = new HttpProcessor();
httpProcessor.process(socket);
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
public void start() {
Thread thread = new Thread(this);
thread.start();
}
}
HttpConnector 实现 Runnable 接口,可以创建多个 HttpConnector 线程,提高并发量
HttpProcessor
public class HttpProcessor {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HttpProcessor.class);
public void process(Socket socket) {
try {
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
Request request = new Request(inputStream);
request.parse();
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
Response response = new Response(request, outputStream);
if (request.getUri().startsWith("/servlet/")) {
log.info("访问动态资源");
ServletProcessor servletProcessor = new ServletProcessor();
servletProcessor.process(request, response);
} else {
StaticResourceProcessor staticResourceProcessor = new StaticResourceProcessor();
staticResourceProcessor.process(request, response);
}
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
05 Server 性能提升: 设计多个 Processor
在上一节中,虽然可以开多个 HttpConnector 线程,但是一个 HttpConnector 只能处理一个 HttpProcessor
在这一节要将 HttpProcessor 异步化
HttpConnector
public class HttpConnector implements Runnable {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HttpConnector.class);
int minProcessors = 3;
int maxProcessors = 10;
int curProcessor = 0;
final Deque<HttpProcessor> processors = new ArrayDeque<>();
@Override
public void run() {
ServerSocket serverSocket;
int port = 8080;
try {
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port, 1, InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"));
for (int i = 0; i < minProcessors; i++) {
HttpProcessor processor = new HttpProcessor(this);
processor.start();
processors.add(processor);
}
curProcessor = minProcessors;
log.info("服务器启动成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
while (true) {
try {
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
HttpProcessor processor = getProcessor();
if (processor == null) {
socket.close();
log.error("processor 已耗尽");
} else {
processor.assign(socket);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
public HttpProcessor getProcessor() {
synchronized (processors) {
if (!processors.isEmpty()) {
return processors.poll();
} else {
if (curProcessor < maxProcessors) {
curProcessor++;
return new HttpProcessor(this);
}
}
}
return null;
}
void recycle(HttpProcessor processor) {
processors.push(processor);
}
public void start() {
Thread thread = new Thread(this);
thread.start();
}
}
HttpProcessor
public class HttpProcessor implements Runnable {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HttpProcessor.class);
Socket socket;
boolean available = false;
HttpConnector connector;
public HttpProcessor(HttpConnector connector) {
this.connector = connector;
}
public void start() {
Thread thread = new Thread(this);
thread.start();
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
Socket socket = await();
if (socket == null) {
continue;
}
process(socket);
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
connector.recycle(this);
}
}
public void process(Socket socket) {
try {
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
Request request = new Request(inputStream);
request.parse();
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
Response response = new Response(request, outputStream);
if (request.getUri().startsWith("/servlet/")) {
log.info("访问动态资源");
ServletProcessor servletProcessor = new ServletProcessor();
servletProcessor.process(request, response);
} else {
StaticResourceProcessor staticResourceProcessor = new StaticResourceProcessor();
staticResourceProcessor.process(request, response);
}
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
synchronized void assign(Socket socket) {
while (available) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
this.socket = socket;
available = true;
notifyAll();
}
private synchronized Socket await() {
while (!available) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
Socket socket = this.socket;
available = false;
notifyAll();
return (socket);
}
}
首先看 assign(socket) 方法,在这里,我们用一个标志available来标记,如果标志为true, Connetor线程就继续死等。到了某个时候,Processor线程把这个标志设置为false,Connector线 程就跳出死等的循环,然后把接收到的Socket交给Processor。然后要立刻重新把available标志设 置为true,再调用 notifyAll() 通知其他线程。
再看 await() ,这是作为接收者Processor的线程使用的方法。反过来,如果avaliable标志为 false,那么Processor线程继续死等。到了某个时候,Connector线把这个标志设置为true,那么 Processor线程就跳出死等的循环,拿到Socket。然后要立刻重新把avaiable标志设置为false,再调 用 notifyAll() 通知其他线程。 这个线程互锁机制保证了两个线程之间的同步协调。图示如下:
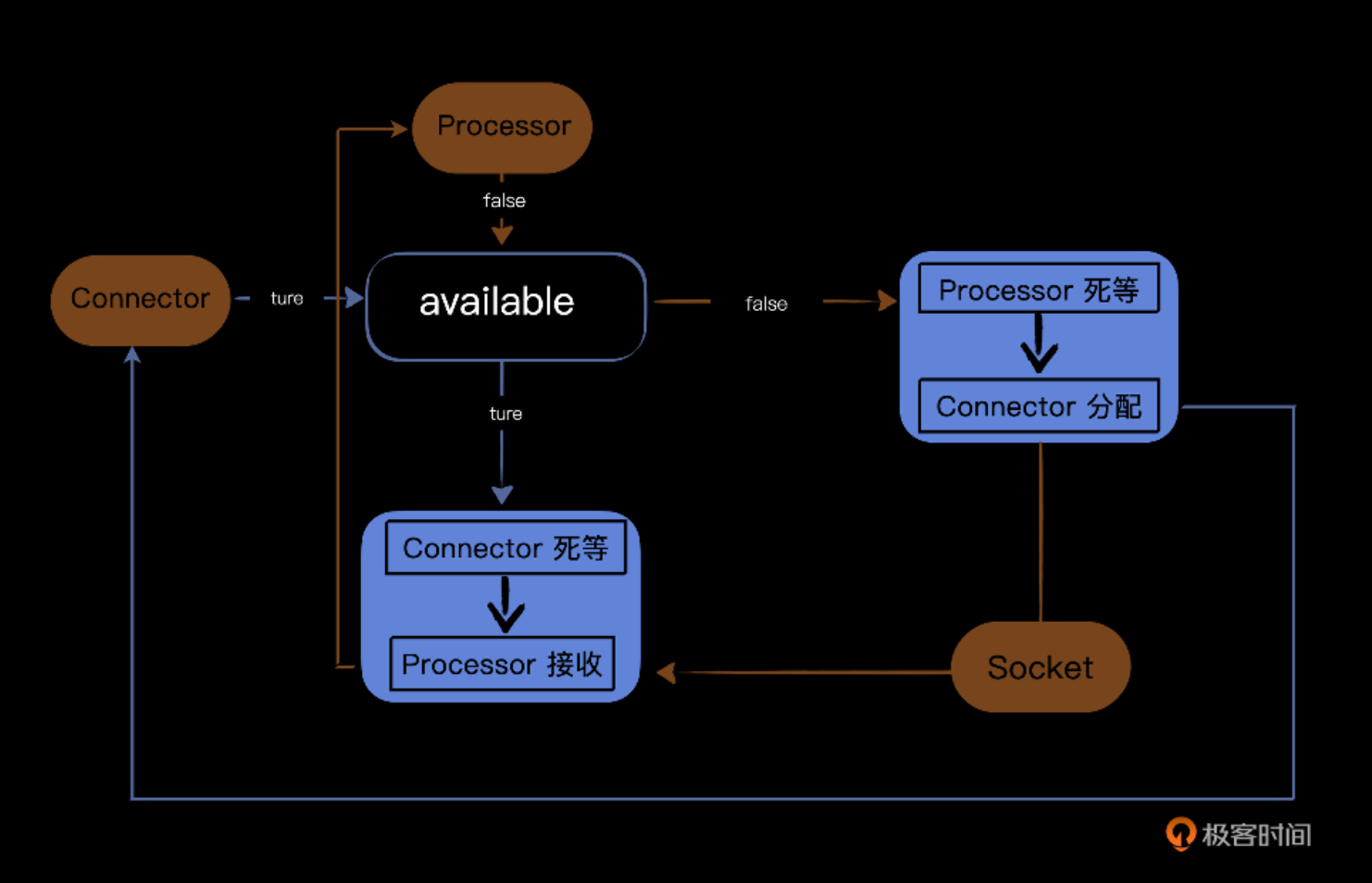
我们再回顾一下HttpProcessor类中的assign方法与await方法。在HttpProcessor的线程启动之后, available的标识一直是false,这个时候这个线程会一直等待。在HttpConnector类里构造 Processor,并且调用 processor.assign(socket) 给HttpProcessor分配Socket之后,标识符 available改成true,并且调用notifyAll这个本地方法通知唤醒所有等待的线程。
而在await方法里,HttpProcessor拿到HttpConnector传来的Socket之后,首先会接收Socket,并 且立即把available由true改为false,最后以拿到的这个Socket为基准继续进行Processor中的处理 工作。
这也意味着,一旦Connector分配了一个Socket给到Processor,后者就能立即结束等待,拿到 Socket后调用Process方法继续后面的工作。这时available的状态立刻修改,进而用notifyAll方法唤 醒 Connector的等待线程,Connector就可以全身而退,去处理下一个HttpProcessor了。
T omcat中两个线程互锁的这种机制很经典,在后续版本的NIO和Servlet协调的设计中都用到了。
这样也就做到了HttpProcessor的异步化,也正因为做到了异步化,我们就不能再利用Connector去 关闭Socket了,因为Connector是不知道Processor何时处理完毕的,Socket的关闭任务就交给 Processor自己处理了。
06 规范化: 引入 HttpRequest 与 HttpResponse
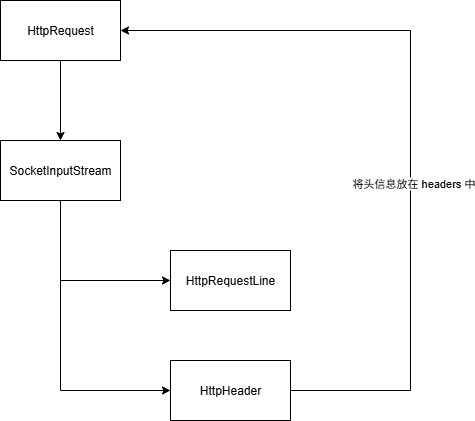
HttpRequestLine 负责 method 、 uri、 protocol
eq:GET /hello.txt HTTP/1.1
HttpHeader 负责其他请求头
SocketInputStream 负责解析请求头
HttpRequest 负责存储请求头
HttpRequest
public class HttpRequest implements HttpServletRequest {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HttpRequest.class);
private InputStream input;
private SocketInputStream sis;
private String uri;
InetAddress address;
int port;
protected HashMap<String, String> headers = new HashMap<>();
protected Map<String, String> parameters = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
HttpRequestLine requestLine = new HttpRequestLine();
public HttpRequest(InputStream input) {
this.input = input;
this.sis = new SocketInputStream(this.input, 2048);
}
public void parse(Socket socket) {
try {
parseConnection(socket);
this.sis.readRequestLine(requestLine);
parseHeaders();
} catch (IOException | ServletException e) {
log.error(e.getMessage());
}
this.uri = new String(requestLine.uri, 0, requestLine.uriEnd);
}
private void parseConnection(Socket socket) {
address = socket.getInetAddress();
port = socket.getPort();
}
private void parseHeaders() throws IOException, ServletException {
while (true) {
HttpHeader header = new HttpHeader();
sis.readHeader(header);
if (header.nameEnd == 0) {
if (header.valueEnd == 0) {
return;
} else {
throw new ServletException("httpProcessor.parseHeaders.colon");
}
}
String name = new String(header.name,0, header.nameEnd);
String value = new String(header.value, 0, header.valueEnd);
// Set the corresponding request headers
if (name.equals(DefaultHeaders.ACCEPT_LANGUAGE_NAME)) {
headers.put(name, value);
} else if (name.equals(DefaultHeaders.CONTENT_LENGTH_NAME)) {
headers.put(name, value);
} else if (name.equals(DefaultHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE_NAME)) {
headers.put(name, value);
} else if (name.equals(DefaultHeaders.HOST_NAME)) {
headers.put(name, value);
} else if (name.equals(DefaultHeaders.CONNECTION_NAME)) {
headers.put(name, value);
} else if (name.equals(DefaultHeaders.TRANSFER_ENCODING_NAME)) {
headers.put(name, value);
} else {
headers.put(name, value);
}
}
}
}
SocketInputStream
public class SocketInputStream extends InputStream {
private static final byte CR = (byte) '\r';
private static final byte LF = (byte) '\n';
private static final byte SP = (byte) ' ';
private static final byte HT = (byte) '\t';
private static final byte COLON = (byte) ':';
private static final int LC_OFFSET = 'A' - 'a';
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SocketInputStream.class);
protected byte[] buf;
protected int count;
protected int pos;
protected InputStream is;
public SocketInputStream(InputStream is, int bufferSize) {
this.is = is;
this.buf = new byte[bufferSize];
}
public void readRequestLine(HttpRequestLine requestLine)
throws IOException {
int chr = 0;
do {
try {
chr = read();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
} while ((chr == CR) || (chr == LF));
pos--;
int maxRead = requestLine.method.length;
int readStart = pos;
int readCount = 0;
boolean space = false;
while (!space) {
if (pos >= count) {
int val = read();
if (val == -1) {
throw new IOException("requestStream.readline.error");
}
pos = 0;
readStart = 0;
}
if (buf[pos] == SP) {
space = true;
}
requestLine.method[readCount] = (char) buf[pos];
readCount++;
pos++;
}
requestLine.methodEnd = readCount - 1;
maxRead = requestLine.uri.length;
readStart = pos;
readCount = 0;
space = false;
boolean eol = false;
while (!space) {
if (pos >= count) {
int val = read();
if (val == -1)
throw new IOException("requestStream.readline.error");
pos = 0;
readStart = 0;
}
if (buf[pos] == SP) {
space = true;
}
requestLine.uri[readCount] = (char) buf[pos];
readCount++;
pos++;
}
requestLine.uriEnd = readCount - 1;
maxRead = requestLine.protocol.length;
readStart = pos;
readCount = 0;
while (!eol) {
if (pos >= count) {
int val = read();
if (val == -1)
throw new IOException("requestStream.readline.error");
pos = 0;
readStart = 0;
}
if (buf[pos] == CR) {
// Skip CR.
} else if (buf[pos] == LF) {
eol = true;
} else {
requestLine.protocol[readCount] = (char) buf[pos];
readCount++;
}
pos++;
}
requestLine.protocolEnd = readCount;
}
public void readHeader(HttpHeader header)
throws IOException {
int chr = read();
if ((chr == CR) || (chr == LF)) { // Skipping CR
if (chr == CR)
read(); // Skipping LF
header.nameEnd = 0;
header.valueEnd = 0;
return;
} else {
pos--;
}
// Reading the header name
int maxRead = header.name.length;
int readStart = pos;
int readCount = 0;
boolean colon = false;
while (!colon) {
// We're at the end of the internal buffer
if (pos >= count) {
int val = read();
if (val == -1) {
throw new IOException("requestStream.readline.error");
}
pos = 0;
readStart = 0;
}
if (buf[pos] == COLON) {
colon = true;
}
char val = (char) buf[pos];
if ((val >= 'A') && (val <= 'Z')) {
val = (char) (val - LC_OFFSET);
}
header.name[readCount] = val;
readCount++;
pos++;
}
header.nameEnd = readCount - 1;
// Reading the header value (which can be spanned over multiple lines)
maxRead = header.value.length;
readStart = pos;
readCount = 0;
int crPos = -2;
boolean eol = false;
boolean validLine = true;
while (validLine) {
boolean space = true;
// Skipping spaces
// Note : Only leading white spaces are removed. Trailing white
// spaces are not.
while (space) {
// We're at the end of the internal buffer
if (pos >= count) {
// Copying part (or all) of the internal buffer to the line
// buffer
int val = read();
if (val == -1)
throw new IOException("requestStream.readline.error");
pos = 0;
readStart = 0;
}
if ((buf[pos] == SP) || (buf[pos] == HT)) {
pos++;
} else {
space = false;
}
}
while (!eol) {
// We're at the end of the internal buffer
if (pos >= count) {
// Copying part (or all) of the internal buffer to the line
// buffer
int val = read();
if (val == -1)
throw new IOException("requestStream.readline.error");
pos = 0;
readStart = 0;
}
if (buf[pos] == CR) {
} else if (buf[pos] == LF) {
eol = true;
} else {
// FIXME : Check if binary conversion is working fine
int ch = buf[pos] & 0xff;
header.value[readCount] = (char) ch;
readCount++;
}
pos++;
}
int nextChr = read();
if ((nextChr != SP) && (nextChr != HT)) {
pos--;
validLine = false;
} else {
eol = false;
header.value[readCount] = ' ';
readCount++;
}
}
header.valueEnd = readCount;
}
@Override
public int available() throws IOException {
return (count - pos) + is.available();
}
@Override
public void close() throws IOException {
if (is == null) {
return;
}
is.close();
is = null;
buf = null;
}
@Override
public int read() throws IOException {
if (pos >= count) {
fill();
if (pos >= count) {
return -1;
}
}
return buf[pos++] & 0xFF;
}
protected void fill() {
int nRead;
try {
nRead = is.read(buf, 0, buf.length);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
pos = 0;
count = 0;
if (nRead > 0) {
count = nRead;
}
}
}
pos:在 buf 中要读的位置
count: 在 buf 的末尾
buf 是一个缓存,is 会不断将数据输入到 buf 中
在 read() 方法中,当 pos >= count 时,说明 buf 中的数据已经使用完毕,通过 is 读取下一批数据并缓存在 buf 中,否则会将返回当前位置的数据,并将 pos++
07 对内的保护: 引入门面模式封装内部实现类
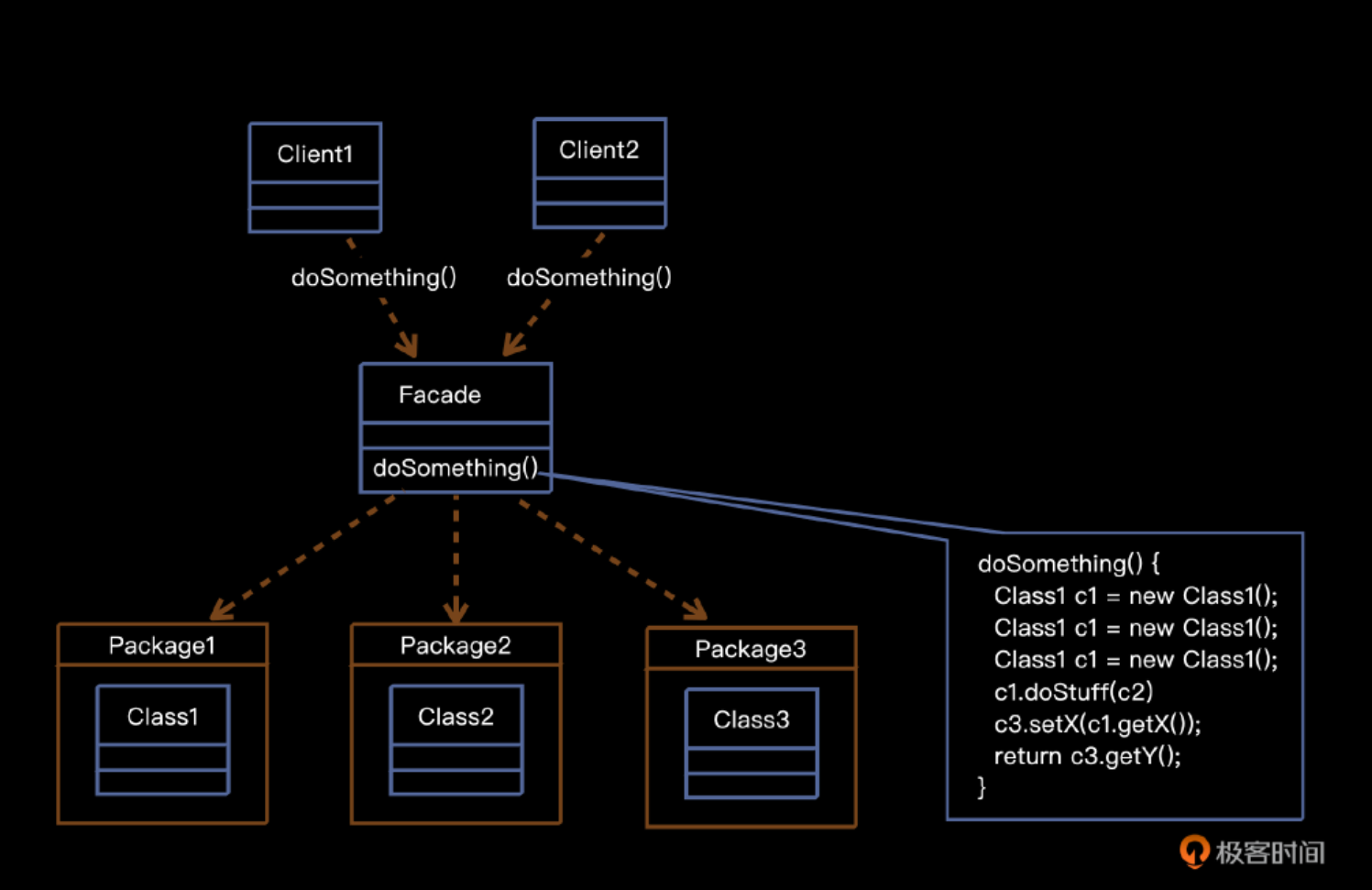
在HttpProcessor类里,我们直接使用的是HttpRequest与HttpResponse, 这两个对象要传入Servlet里,但在这两个类中我们也定义了许多内部的方法,一旦被用户知晓我们 的实现类,那么这些内部方法就暴露在用户面前了,这是我们不愿看到的,也是我们需要规避的。 因此这节课我们计划用⻔面(Facade)设计模式来解决这个问题
HttpRequestFacade
public class HttpRequestFacade implements HttpServletRequest {
private HttpServletRequest request;
public HttpRequestFacade(HttpRequest request) {
this.request = request;
}
/* implementation of the HttpServletRequest*/
public Object getAttribute(String name) {
return request.getAttribute(name);
}
public Enumeration getAttributeNames() {
return request.getAttributeNames();
}
public String getAuthType() {
return request.getAuthType();
}
public String getCharacterEncoding() {
return request.getCharacterEncoding();
}
public int getContentLength() {
return request.getContentLength();
}
public String getContentType() {
return request.getContentType();
}
public String getContextPath() {
return request.getContextPath();
}
public Cookie[] getCookies() {
return request.getCookies();
}
public long getDateHeader(String name) {
return request.getDateHeader(name);
}
public Enumeration getHeaderNames() {
return request.getHeaderNames();
}
public String getHeader(String name) {
return request.getHeader(name);
}
public Enumeration getHeaders(String name) {
return request.getHeaders(name);
}
public ServletInputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
return request.getInputStream();
}
public int getIntHeader(String name) {
return request.getIntHeader(name);
}
public Locale getLocale() {
return request.getLocale();
}
public Enumeration getLocales() {
return request.getLocales();
}
public String getMethod() {
return request.getMethod();
}
public String getParameter(String name) {
return request.getParameter(name);
}
public Map getParameterMap() {
return request.getParameterMap();
}
public Enumeration getParameterNames() {
return request.getParameterNames();
}
public String[] getParameterValues(String name) {
return request.getParameterValues(name);
}
public String getPathInfo() {
return request.getPathInfo();
}
public String getPathTranslated() {
return request.getPathTranslated();
}
public String getProtocol() {
return request.getProtocol();
}
public String getQueryString() {
return request.getQueryString();
}
public BufferedReader getReader() throws IOException {
return request.getReader();
}
public String getRealPath(String path) {
return request.getRealPath(path);
}
}
HttpResponseFacade
public class HttpResponseFacade implements HttpServletResponse {
private HttpServletResponse response;
public HttpResponseFacade(HttpResponse response) {
this.response = response;
}
public void addDateHeader(String name, long value) {
response.addDateHeader(name, value);
}
public void addHeader(String name, String value) {
response.addHeader(name, value);
}
public void addIntHeader(String name, int value) {
response.addIntHeader(name, value);
}
public boolean containsHeader(String name) {
return response.containsHeader(name);
}
public String encodeRedirectURL(String url) {
return response.encodeRedirectURL(url);
}
public String encodeRedirectUrl(String url) {
return response.encodeRedirectUrl(url);
}
public String encodeUrl(String url) {
return response.encodeUrl(url);
}
public String encodeURL(String url) {
return response.encodeURL(url);
}
public void flushBuffer() throws IOException {
response.flushBuffer();
}
public int getBufferSize() {
return response.getBufferSize();
}
public String getCharacterEncoding() {
return response.getCharacterEncoding();
}
}
最后修改 ServletProcessor
public void process(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response) {
String uir = request.getUri();
String ServletName = uir.substring(uir.lastIndexOf('/') + 1);
URLClassLoader loader;
try {
URL[] urls = new URL[1];
File classPath = new File(HttpServer.WEB_ROOT);
String repository = (new URL("file", null, classPath.getCanonicalPath() + File.separator)).toString();
URLStreamHandler urlStreamHandler = null;
urls[0] = new URL(null, repository, urlStreamHandler);
loader = new URLClassLoader(urls);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
ServletName = "com.lbwxxc.test.HelloServlet";
Class<?> servletClass;
ClassLoader classLoader = this.getClass().getClassLoader();
try {
servletClass = classLoader.loadClass(ServletName);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
PrintWriter writer;
try {
writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println(composeResponseHead());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
HttpRequestFacade httpRequestFacade = new HttpRequestFacade(request);
HttpResponseFacade httpResponseFacade = new HttpResponseFacade(response);
Servlet servlet;
try {
servlet = (Servlet) servletClass.newInstance();
servlet.service(httpRequestFacade, httpResponseFacade);
} catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException | ServletException | IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
这样在Servlet中,我们看到的只是Facade,看不⻅内部方法,应用程序员想进行强制转化也不行, 这样既简单又安全。
还有,按照Servlet的规范,客户自定义的Servlet是要继承HttpServlet的,在调用的service方法 内,它的实际行为是通过method判断调用的是哪一个方法,如果是Get方法就调用doGet(),如果是 Post方法调用的就是doPost(),其他的方法也是一样的道理。
所以在我们自定义的HttpRequest里,一定要实现getMethod方法,我们来调整一下。
public String getMethod() {
return new String(requestLine.method, 0, requestLine.methodEnd);
}
08 解析参数:通过引入 Cookie 和 Session 避免反复登录
Cookie 可能存放在请求行或者请求头,所以在解析 HttpRequest 时,要分别处理
public void parseRequestLine() {
int queryStart = requestLine.indexOf("?");
if (queryStart >= 0) {
queryString = new String(requestLine.uri, queryStart + 1, requestLine.uriEnd - queryStart - 1);
uri = new String(requestLine.uri, 0, queryStart);
int semicolon = uri.indexOf(DefaultHeaders.JSESSIONID_NAME);
if (semicolon >= 0) {
sessionid = uri.substring(semicolon + DefaultHeaders.JSESSIONID_NAME.length());
uri = uri.substring(0, semicolon);
}
} else {
queryString = null;
uri = new String(requestLine.uri, 0, requestLine.uriEnd);
int semicolon = uri.indexOf(DefaultHeaders.JSESSIONID_NAME);
if (semicolon >= 0) {
sessionid = uri.substring(semicolon + DefaultHeaders.JSESSIONID_NAME.length());
uri = uri.substring(0, semicolon);
}
}
}
private void parseHeaders() throws IOException, ServletException {
while (true) {
HttpHeader header = new HttpHeader();
sis.readHeader(header);
if (header.nameEnd == 0) {
if (header.valueEnd == 0) {
return;
} else {
throw new ServletException("httpProcessor.parseHeaders.colon");
}
}
String name = new String(header.name,0, header.nameEnd);
String value = new String(header.value, 0, header.valueEnd);
// Set the corresponding request headers
if (name.equals(DefaultHeaders.ACCEPT_LANGUAGE_NAME)) {
headers.put(name, value);
} else if (name.equals(DefaultHeaders.CONTENT_LENGTH_NAME)) {
headers.put(name, value);
} else if (name.equals(DefaultHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE_NAME)) {
headers.put(name, value);
} else if (name.equals(DefaultHeaders.HOST_NAME)) {
headers.put(name, value);
} else if (name.equals(DefaultHeaders.CONNECTION_NAME)) {
headers.put(name, value);
} else if (name.equals(DefaultHeaders.TRANSFER_ENCODING_NAME)) {
headers.put(name, value);
} else if (name.equals(DefaultHeaders.COOKIE_NAME)) {
headers.put(name, value);
this.cookies = parseCookieHeader(value);
for (int i = 0; i < cookies.length; i++) {
if (cookies[i].getName().equals("jsessionid")) {
this.sessionid = cookies[i].getValue();
}
}
} else {
headers.put(name, value);
}
}
}
解析完 HttpRequest,会尝试获取 session,如果没有最会创建,并存放在 HttpConnect
public void process(Socket socket) {
try {
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
HttpRequest httpRequest = new HttpRequest(inputStream);
httpRequest.parse(socket);
if (httpRequest.getSessionid() == null || httpRequest.getSessionid().isEmpty()) {
// 尝试获取 session,如果没有则创建
httpRequest.getSession(true);
}
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
HttpResponse httpResponse = new HttpResponse(outputStream);
httpResponse.setRequest(httpRequest);
if (httpRequest.getUri().startsWith("/servlet/")) {
log.info("访问动态资源");
ServletProcessor servletProcessor = new ServletProcessor();
servletProcessor.process(httpRequest, httpResponse);
} else {
StaticResourceProcessor staticResourceProcessor = new StaticResourceProcessor();
staticResourceProcessor.process(httpRequest, httpResponse);
}
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public HttpSession getSession(boolean b) {
if (sessionFacade != null)
return sessionFacade;
if (sessionid != null) {
session = HttpConnector.sessions.get(sessionid);
if (session != null) {
sessionFacade = new SessionFacade(session);
return sessionFacade;
} else {
session = HttpConnector.createSession();
sessionFacade = new SessionFacade(session);
return sessionFacade;
}
} else {
session = HttpConnector.createSession();
sessionFacade = new SessionFacade(session);
sessionid = session.getId();
return sessionFacade;
}
}
public static Session createSession() {
Session session = new Session();
session.setValid(true);
session.setCreationTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
String sessionId = generateSessionId();
session.setId(sessionId);
sessions.put(sessionId, session);
return (session);
}
09 有状态的 Response: 实现 Session 传递与 keep-alive
public void sendHeaders() throws IOException {
PrintWriter outputWriter = getWriter();
outputWriter.print(this.getProtocol());
outputWriter.print(" ");
outputWriter.print(status);
if (message != null) {
outputWriter.print(" ");
outputWriter.print(message);
}
outputWriter.print("\r\n");
if (getContentType() != null) {
outputWriter.print("Content-Type: " + getContentType() + "\r\n");
}
if (getContentLength() >= 0) {
outputWriter.print("Content-Length: " + getContentLength() + "\r\n");
}
Iterator<String> names = headers.keySet().iterator();
while (names.hasNext()) {
String name = names.next();
String value = headers.get(name);
outputWriter.print(name);
outputWriter.print(": ");
outputWriter.print(value);
outputWriter.print("\r\n");
}
HttpSession session = this.request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Cookie cookie = new Cookie(DefaultHeaders.JSESSIONID_NAME, session.getId());
cookie.setMaxAge(-1);
addCookie(cookie);
}
synchronized (cookies) {
Iterator<Cookie> items = cookies.iterator();
while (items.hasNext()) {
Cookie cookie = items.next();
outputWriter.print(CookieTools.getCookieHeaderName(cookie));
outputWriter.print(": ");
StringBuffer sbValue = new StringBuffer();
CookieTools.getCookieHeaderValue(cookie, sbValue);
log.info("set cookie jsessionid string : {}", sbValue);
outputWriter.print(sbValue);
outputWriter.print("\r\n");
}
}
outputWriter.print("\r\n");
outputWriter.flush();
}
在正式处理请求前,会先把 response 头写入到流中
bug
在 ServletProcessor 多添加了一个响应头
public void process(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response) {
String uir = request.getUri();
String ServletName = uir.substring(uir.lastIndexOf('/') + 1);
URLClassLoader loader = HttpConnector.loader;
ServletName = "com.lbwxxc.test.HelloServlet";
Class<?> servletClass;
ClassLoader classLoader = this.getClass().getClassLoader();
try {
servletClass = classLoader.loadClass(ServletName);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
// PrintWriter writer;
// try {
// writer = response.getWriter();
// writer.println(composeResponseHead());
// } catch (IOException e) {
// throw new RuntimeException(e);
// }
HttpRequestFacade httpRequestFacade = new HttpRequestFacade(request);
HttpResponseFacade httpResponseFacade = new HttpResponseFacade(response);
Servlet servlet;
try {
servlet = (Servlet) servletClass.newInstance();
servlet.service(httpRequestFacade, httpResponseFacade);
} catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException | ServletException | IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
10 Servlet Wrapper: 如何维护 Servlet 生命周期及实现容器管理?
Wrapper 是对 Servlet 的封装
public class ServletWrapper {
private Servlet instance = null;
private String servletClass;
private ClassLoader loader;
private String name;
protected ServletContainer parent = null;
public ServletWrapper(String servletClass, ServletContainer parent) {
this.parent = parent;
this.servletClass = servletClass;
//loadServlet();
}
public ClassLoader getLoader() {
if (loader != null)
return loader;
return parent.getLoader();
}
public String getServletClass() {
return servletClass;
}
public void setServletClass(String servletClass) {
this.servletClass = servletClass;
}
public ServletContainer getParent() {
return parent;
}
public void setParent(ServletContainer container) {
parent = container;
}
public Servlet getServlet(){
return this.instance;
}
public Servlet loadServlet() throws ServletException {
if (instance!=null)
return instance;
Servlet servlet = null;
String actualClass = servletClass;
if (actualClass == null) {
throw new ServletException("servlet class has not been specified");
}
ClassLoader classLoader = getLoader();
Class classClass = null;
try {
if (classLoader!=null) {
classClass = classLoader.loadClass(actualClass);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new ServletException("Servlet class not found");
}
try {
servlet = (Servlet) classClass.newInstance();
}
catch (Throwable e) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate servlet");
}
try {
servlet.init(null);
}
catch (Throwable f) {
throw new ServletException("Failed initialize servlet.");
}
instance = servlet;
return servlet;
}
public void invoke(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (instance != null) {
instance.service(request, response);
}
}
}
创建 ServletContainer 专门管理 Wrapper
public class ServletContainer {
HttpConnector connector;
ClassLoader loader;
Map<String, String> servletClsMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
Map<String, ServletWrapper> servletInstanceMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public ServletContainer() {
URL[] urls = new URL[1];
URLStreamHandler streamHandler = null;
File classPath = new File("target/classes/com/lbwxxc/test");
try {
String repository = (new URL("file", null, classPath.getCanonicalPath() + File.separator)).toString();
urls[0] = new URL(null, repository, streamHandler);
loader = new URLClassLoader(urls);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void invoke(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response) {
ServletWrapper servlet = null;
ClassLoader loader = getLoader();
String uri = request.getUri();
String servletName = uri.substring(uri.lastIndexOf("/") + 1);
String servletClassName = servletName;
servlet = servletInstanceMap.get(servletName);
if (servlet == null) {
Class<?> servletClass = null;
try {
servletClass = loader.loadClass("com.lbwxxc.test.HelloServlet");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
servlet = new ServletWrapper(servletClassName, this);
servlet.setInstance((Servlet) servletClass.newInstance());
} catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
servletClsMap.put(servletName, servletClassName);
servletInstanceMap.put(servletName, servlet);
}
try {
HttpRequestFacade requestFacade = new HttpRequestFacade(request);
HttpResponseFacade responseFacade = new HttpResponseFacade(response);
System.out.println("Call service()");
servlet.invoke(requestFacade, responseFacade);
} catch (ServletException | IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
让 HttpConnector 与 ServletContainer 相互引用
HttpConnector httpConnector = new HttpConnector();
ServletContainer servletContainer = new ServletContainer();
httpConnector.setContainer(servletContainer);
servletContainer.setConnector(httpConnector);
httpConnector.start();
在 ServletProcessor 直接调用 ServletContainer ,实现责任分离
private HttpConnector connector;
public ServletProcessor(HttpConnector connector) {
this.connector = connector;
}
11 多层容器:如何通过实现 Context 与 Wrapper 形成多层容器?
public abstract class ContainerBase implements Container {
protected Map<String, Container> children = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
protected ClassLoader loader = null;
protected String name = null;
protected Container parent = null;
public abstract String getInfo();
public ClassLoader getLoader() {
if (loader != null)
return (loader);
if (parent != null)
return (parent.getLoader());
return (null);
}
public synchronized void setLoader(ClassLoader loader) {
ClassLoader oldLoader = this.loader;
if (oldLoader == loader) {
return;
}
this.loader = loader;
}
public String getName() {
return (name);
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Container getParent() {
return (parent);
}
public void setParent(Container container) {
Container oldParent = this.parent;
this.parent = container;
}
public void addChild(Container child) {
addChildInternal(child);
}
private void addChildInternal(Container child) {
synchronized(children) {
if (children.get(child.getName()) != null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("addChild: Child name '" +
child.getName() +
"' is not unique");
child.setParent((Container) this); // May throw IAE
children.put(child.getName(), child);
}
}
public Container findChild(String name) {
if (name == null)
return (null);
synchronized (children) { // Required by post-start changes
return ((Container) children.get(name));
}
}
public Container[] findChildren() {
synchronized (children) {
Container results[] = new Container[children.size()];
return ((Container[]) children.values().toArray(results));
}
}
public void removeChild(Container child) {
synchronized(children) {
if (children.get(child.getName()) == null)
return;
children.remove(child.getName());
}
child.setParent(null);
多层容器
12 Pipeline 与 Valve: 如何实现容器间的调用、事务管理、权限验证?
使用责任链

Filter 与 Listener: 如何实现过滤和持续监听?
过滤器
final class ApplicationFilterChain implements FilterChain {
public ApplicationFilterChain() {
super();
}
private ArrayList<ApplicationFilterConfig> filters = new ArrayList<>();
private Iterator<ApplicationFilterConfig> iterator = null;
private Servlet servlet = null;
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("FilterChain doFilter()");
internalDoFilter(request,response);
}
private void internalDoFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Construct an iterator the first time this method is called
if (this.iterator == null)
this.iterator = filters.iterator();
// Call the next filter if there is one
if (this.iterator.hasNext()) {
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig =
(ApplicationFilterConfig) iterator.next();
Filter filter = null;
try {
filter = filterConfig.getFilter();
System.out.println("Filter doFilter()");
filter.doFilter(request, response, this);
} catch (IOException | ServletException | RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new ServletException("filterChain.filter", e);
}
return;
}
// We fell off the end of the chain -- call the servlet instance
try {
HttpServletRequest requestFacade = new HttpRequestFacade((HttpRequestImpl) request);
HttpServletResponse responseFacade = new HttpResponseFacade((HttpResponseImpl) response);
servlet.service(requestFacade, responseFacade);
} catch (IOException | ServletException | RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new ServletException("filterChain.servlet", e);
}
}
void addFilter(ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig) {
this.filters.add(filterConfig);
}
void release() {
this.filters.clear();
this.iterator = iterator;
this.servlet = null;
}
void setServlet(Servlet servlet) {
this.servlet = servlet;
}
}
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)