LangGraph 基础知识教程-跟我一起学构建agent(二),大模型入门到精通,收藏这篇就足够了!
下面继续开始第一部分-基础知识;下面演示完整的示例代码及输出的结果;详细的概念定义可以参考每小节对应的官方描述,
下面继续开始第一部分-基础知识;下面演示完整的示例代码及输出的结果;详细的概念定义可以参考每小节对应的官方描述,本文在这里就不在详细描述了;
LangGraph基础知识学习-从零搭建agent
本文介绍4-6个小结的基础教程,完整代码已经上传到github上;文末自取;
4添加human-in-the-loop
5自定义状态
6时间旅行
4添加human-in-the-loop
参考文档教程:
https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/tutorials/get-started/4-human-in-the-loop/
# https://python.langchain.com/docs/integrations/tools/tavily_search/
# 获取密钥的地址: https://app.tavily.com/sign-in
import os
TAVILY_API_KEY="tvly-dev-123"
os.environ["TAVILY_API_KEY"] = TAVILY_API_KEY
from langchain_tavily import TavilySearch
tool = TavilySearch(max_results=5)
tools = [tool]
tool.invoke("What's a 'node' in LangGraph?")
{'query': "What's a 'node' in LangGraph?",
'follow_up_questions': None,
'answer': None,
'images': [],
'results': [{'title': 'LangGraph Basics: Understanding State, Schema, Nodes, and Edges',
'url': 'https://medium.com/@vivekvjnk/langgraph-basics-understanding-state-schema-nodes-and-edges-77f2fd17cae5',
'content': 'LangGraph Basics: Understanding State, Schema, Nodes, and Edges | by Story_Teller | Medium LangGraph Basics: Understanding State, Schema, Nodes, and Edges LangGraph Basics: Understanding State, Schema, Nodes, and Edges These predefined structures in the messaging app are synonymous with the schema of the state in LangGraph. Just as a messaging app ensures all interactions (messages) follow a consistent format, the schema in LangGraph ensures the state passed along edges is structured and interpretable. This static schema allows nodes to rely on a consistent state format, ensuring seamless communication along edges throughout the graph. In this article, we explored the foundational concepts of graph-based systems, drawing parallels to familiar messaging applications to illustrate how edges, nodes, and state transitions function seamlessly in dynamic workflows.',
'score': 0.98525,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': 'LangGraph Tutorial for Beginners - Analytics Vidhya',
'url': 'https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2025/05/langgraph-tutorial-for-beginners/',
'content': 'Now that we have built the simplest graph in the above section, in this section,\xa0I will show you how to use LangGraph to build a support chatbot, starting with basic functionality and progressively adding features like web search, memory, and human-in-loop. A. LangGraph offers:– State management which keeps track of data as the agent performs tasks.– Multi-agent support which allows multiple agents to work together within a graph.– Persistence with checkpointers as it saves the state at each step which enable error recovery and debudding.– Human-in-the-loop which helps in pausing the workflow for human review and approval. It allows us to build applications that use the power of LLMs, such as chatbots and AI assistants, while managing complex workflows and state across multiple agents.',
'score': 0.98138,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': 'LangGraph Tutorial: What Is LangGraph and How to Use It?',
'url': 'https://www.datacamp.com/tutorial/langgraph-tutorial',
'content': 'LangGraph is a library within the LangChain ecosystem that provides a framework for defining, coordinating, and executing multiple LLM agents (or chains) in a structured and efficient manner. By managing the flow of data and the sequence of operations, LangGraph allows developers to focus on the high-level logic of their applications rather than the intricacies of agent coordination. Whether you need a chatbot that can handle various types of user requests or a multi-agent system that performs complex tasks, LangGraph provides the tools to build exactly what you need. LangGraph significantly simplifies the development of complex LLM applications by providing a structured framework for managing state and coordinating agent interactions.',
'score': 0.97647,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': 'LangGraph - LangChain',
'url': 'https://www.langchain.com/langgraph',
'content': "[LangGraph](https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/tutorials/introduction/)[LangSmith](https://docs.smith.langchain.com/)[LangChain](https://python.langchain.com/docs/introduction/)  [Read a conceptual guide](https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/concepts/agentic_concepts/#human-in-the-loop) .gif) [See different agent architectures](https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/concepts/agentic_concepts/) [Learn about agent memory](https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/concepts/memory/)  [](https://academy.langchain.com/courses/intro-to-langgraph) Design agent-driven user experiences with LangGraph Platform's APIs. Quickly deploy and scale your application with infrastructure built for agents. The next chapter in building complex production-ready features with LLMs is agentic, and with LangGraph and LangSmith, LangChain delivers an out-of-the-box solution to iterate quickly, debug immediately, and scale effortlessly.” The next chapter in building complex production-ready features with LLMs is agentic, and with LangGraph and LangSmith, LangChain delivers an out-of-the-box solution to iterate quickly, debug immediately, and scale effortlessly.” LangGraph Platform is a service for deploying and scaling LangGraph applications, with an opinionated API for building agent UXs, plus an integrated developer studio.",
'score': 0.97456,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': 'Nodes and Edges | langchain-ai/langgraph-101 | DeepWiki',
'url': 'https://deepwiki.com/langchain-ai/langgraph-101/2.2-nodes-and-edges',
'content': 'Nodes and Edges | langchain-ai/langgraph-101 | DeepWiki Nodes and Edges Nodes and Edges What are Nodes and Edges? In LangGraph, a graph is composed of nodes connected by edges to form a directed workflow. Nodes are the workhorses of LangGraph - they are Python functions that receive the current graph state as input, perform operations, and return updates to that state. Edges define the flow of execution between nodes in a LangGraph. graph_builder.add_edge("retrieve_documents", "generate_response") Conditional edges use a function to determine the next node based on the current state. Building a Graph with Nodes and Edges graph_builder.add_node("retrieve_documents", retrieve_documents) graph_builder.add_edge("retrieve_documents", "generate_response") When designing nodes and edges in LangGraph: Nodes and Edges What are Nodes and Edges? Building a Graph with Nodes and Edges',
'score': 0.96957,
'raw_content': None}],
'response_time': 0.96}
import os
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
API_KEY = "sk-123"
BASE_URL = "https://api.deepseek.com"
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = API_KEY
os.environ["OPENAI_API_BASE"] = BASE_URL
llm = init_chat_model("openai:deepseek-chat")
#我们现在可以将它合并到 :StateGraph
from typing import Annotated
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
classState(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)
# Modification: tell the LLM which tools it can call
# highlight-next-line
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
defchatbot(state: State):
return {"messages": [llm_with_tools.invoke(state["messages"])]}
graph_builder.add_node("chatbot", chatbot)
<langgraph.graph.state.StateGraph at 0x193a56a3560>
from typing import Annotated
from langchain_tavily import TavilySearch
from langchain_core.messages import BaseMessage
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode, tools_condition
from langgraph.types import Command, interrupt
classState(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)
@tool
defhuman_assistance(query: str) -> str:
"""Request assistance from a human."""
human_response = interrupt({"query": query})
return human_response["data"]
tool = TavilySearch(max_results=2)
tools = [tool,human_assistance] # 添加human_assistance工具
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
defchatbot(state: State):
return {"messages": [llm_with_tools.invoke(state["messages"])]}
graph_builder.add_node("chatbot", chatbot)
tool_node = ToolNode(tools=tools)
graph_builder.add_node("tools", tool_node)
graph_builder.add_conditional_edges(
"chatbot",
tools_condition,
)
# Any time a tool is called, we return to the chatbot to decide the next step
graph_builder.add_edge("tools", "chatbot")
graph_builder.add_edge(START, "chatbot")
graph = graph_builder.compile()
# 添加内存功能
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import MemorySaver
memory = MemorySaver()
graph = graph_builder.compile(checkpointer=memory)
from IPython.display import Image, display
try:
display(Image(graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))
except Exception:
# This requires some extra dependencies and is optional
pass
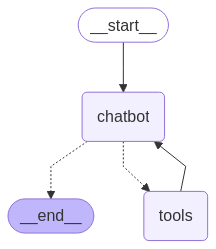
#与您的聊天机器人互动
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "2"}}
user_input = "I need some expert guidance for building an AI agent. Could you request assistance for me?"
# The config is the **second positional argument** to stream() or invoke()!
events = graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": user_input}]},
config,
stream_mode="values",
)
for event in events:
if"messages"in event:
event["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
================================[1m Human Message [0m=================================
I need some expert guidance for building an AI agent. Could you request assistance for me?
==================================[1m Ai Message [0m==================================
Tool Calls:
human_assistance (call_0_b8540b0e-65d5-4ea6-99d4-33e14342b9fc)
Call ID: call_0_b8540b0e-65d5-4ea6-99d4-33e14342b9fc
Args:
query: I need expert guidance for building an AI agent.
snapshot = graph.get_state(config)
snapshot.next
('tools',)
# 恢复执行
human_response = (
"We, the experts are here to help! We'd recommend you check out LangGraph to build your agent."
" It's much more reliable and extensible than simple autonomous agents."
)
human_command = Command(resume={"data": human_response})
events = graph.stream(human_command, config, stream_mode="values")
for event in events:
if"messages"in event:
event["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
==================================[1m Ai Message [0m==================================
Tool Calls:
human_assistance (call_0_b8540b0e-65d5-4ea6-99d4-33e14342b9fc)
Call ID: call_0_b8540b0e-65d5-4ea6-99d4-33e14342b9fc
Args:
query: I need expert guidance for building an AI agent.
=================================[1m Tool Message [0m=================================
Name: human_assistance
We, the experts are here to help! We'd recommend you check out LangGraph to build your agent. It's much more reliable and extensible than simple autonomous agents.
==================================[1m Ai Message [0m==================================
It looks like the experts have provided a helpful recommendation! They suggest using **LangGraph** to build your AI agent, as it is more reliable and extensible compared to simple autonomous agents.
If you'd like further details or assistance with LangGraph or any other aspect of building your AI agent, feel free to ask!
5自定义状态
参考文档教程:
https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/tutorials/get-started/5-customize-state/
# https://python.langchain.com/docs/integrations/tools/tavily_search/
# 获取密钥的地址: https://app.tavily.com/sign-in
import os
TAVILY_API_KEY="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"
os.environ["TAVILY_API_KEY"] = TAVILY_API_KEY
from langchain_tavily import TavilySearch
tool = TavilySearch(max_results=5)
tools = [tool]
tool.invoke("What's a 'node' in LangGraph?")
{'query': "What's a 'node' in LangGraph?",
'follow_up_questions': None,
'answer': None,
'images': [],
'results': [{'title': 'What is LangGraph? - IBM',
'url': 'https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/langgraph',
'content': 'LangGraph, created by LangChain, is an open source AI agent framework designed to build, deploy and manage complex generative AI agent workflows. At its core, LangGraph uses the power of graph-based architectures to model and manage the intricate relationships between various components of an AI agent workflow. LangGraph illuminates the processes within an AI workflow, allowing full transparency of the agent’s state. By combining these technologies with a set of APIs and tools, LangGraph provides users with a versatile platform for developing AI solutions and workflows including chatbots, state graphs and other agent-based systems. Nodes: In LangGraph, nodes represent individual components or agents within an AI workflow. LangGraph uses enhanced decision-making by modeling complex relationships between nodes, which means it uses AI agents to analyze their past actions and feedback.',
'score': 0.90907925,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': 'Nodes and Edges | langchain-ai/langgraph-101 | DeepWiki',
'url': 'https://deepwiki.com/langchain-ai/langgraph-101/2.2-nodes-and-edges',
'content': 'Nodes and Edges | langchain-ai/langgraph-101 | DeepWiki Nodes and Edges Nodes and Edges What are Nodes and Edges? In LangGraph, a graph is composed of nodes connected by edges to form a directed workflow. Nodes are the workhorses of LangGraph - they are Python functions that receive the current graph state as input, perform operations, and return updates to that state. Edges define the flow of execution between nodes in a LangGraph. graph_builder.add_edge("retrieve_documents", "generate_response") Conditional edges use a function to determine the next node based on the current state. Building a Graph with Nodes and Edges graph_builder.add_node("retrieve_documents", retrieve_documents) graph_builder.add_edge("retrieve_documents", "generate_response") When designing nodes and edges in LangGraph: Nodes and Edges What are Nodes and Edges? Building a Graph with Nodes and Edges',
'score': 0.8559598,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': "An Absolute Beginner's Guide to LangGraph.js",
'url': 'https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/blog/educatordeveloperblog/an-absolute-beginners-guide-to-langgraph-js/4212496',
'content': "We'll add the name and isHuman properties to our State object and update the sayHello and sayBye nodes to use these State object properties. Update the Graph's nodes and edges: We'll build a graph that returns a random fact or joke based on the user's input. Finally, inside src/index.ts, import and execute the Graph with a user input, inside the /joke-or-fact route: In this guide, we've covered the basics of LangGraph.js, building a simple graph that returns a random fact or joke based on user input. We've learned how to define nodes, edges, and state objects and how to add conditional routing to our Graph. LangGraph.js is a powerful tool for building complex workflows and managing State in your applications.",
'score': 0.59457535,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': 'LangGraph cheatsheet · GitHub',
'url': 'https://gist.github.com/razhangwei/631a799e6bd69b26ce9c118c624cd80d',
'content': 'This is an excellent LangGraph cheat sheet! LangGraph Cheat Sheet 3. Create Nodes Example Node Function: 4. Create the Graph 5. Add Nodes to the Graph 9. Compile the Graph Invoke the Graph StateGraph | Main class for creating a graph add_node() | Adds a node to the graph add_edge() | Adds a direct edge between two nodes add_conditional_edges() | Adds conditional edges based on a routing function set_entry_point() | Sets the starting node of the graph compile() | Compiles the graph into a RunnableGraph invoke() | Executes the graph with an initial state Send() | Dispatches tasks to multiple nodes in parallel This cheat sheet provides you with all essential steps, best practices, and examples for building LangGraph workflows efficiently! Footer Footer navigation',
'score': 0.5654673,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': 'How to Build AI Agents with LangGraph: A Step-by-Step Guide',
'url': 'https://medium.com/@lorevanoudenhove/how-to-build-ai-agents-with-langgraph-a-step-by-step-guide-5d84d9c7e832',
'content': 'In this step, we’ll define how the AI agent manages its state (the ongoing context of the conversation) and ensure it responds appropriately to the user’s input and tool output. This involves creating a template for the conversation, specifying the tools that the assistant will use, and configuring how the AI agent will respond to user input and trigger different functions (like calculating solar savings). This step ensures that the AI assistant can access and trigger the tools as needed during the conversation, creating a seamless interaction between the user and the assistant. By following these steps, you have successfully created an AI assistant using LangGraph that can calculate solar panel energy savings based on user inputs.',
'score': 0.092532046,
'raw_content': None}],
'response_time': 1.66}
import os
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
API_KEY = "sk-123"
BASE_URL = "https://api.deepseek.com"
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = API_KEY
os.environ["OPENAI_API_BASE"] = BASE_URL
llm = init_chat_model("openai:deepseek-chat")
from typing import Annotated
from langchain_tavily import TavilySearch
from langchain_core.messages import BaseMessage
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode, tools_condition
from langgraph.types import Command, interrupt
from langchain_core.messages import ToolMessage
from langchain_core.tools import InjectedToolCallId, tool
from langgraph.types import Command, interrupt
classState(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]
name: str
birthday: str
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)
@tool
# Note that because we are generating a ToolMessage for a state update, we
# generally require the ID of the corresponding tool call. We can use
# LangChain's InjectedToolCallId to signal that this argument should not
# be revealed to the model in the tool's schema.
defhuman_assistance(
name: str, birthday: str, tool_call_id: Annotated[str, InjectedToolCallId]
) -> str:
"""Request assistance from a human."""
human_response = interrupt(
{
"question": "Is this correct?",
"name": name,
"birthday": birthday,
},
)
# If the information is correct, update the state as-is.
if human_response.get("correct", "").lower().startswith("y"):
verified_name = name
verified_birthday = birthday
response = "Correct"
# Otherwise, receive information from the human reviewer.
else:
verified_name = human_response.get("name", name)
verified_birthday = human_response.get("birthday", birthday)
response = f"Made a correction: {human_response}"
# This time we explicitly update the state with a ToolMessage inside
# the tool.
state_update = {
"name": verified_name,
"birthday": verified_birthday,
"messages": [ToolMessage(response, tool_call_id=tool_call_id)],
}
# We return a Command object in the tool to update our state.
return Command(update=state_update)
tool = TavilySearch(max_results=2)
tools = [tool,human_assistance] # 添加human_assistance工具
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
defchatbot(state: State):
return {"messages": [llm_with_tools.invoke(state["messages"])]}
graph_builder.add_node("chatbot", chatbot)
tool_node = ToolNode(tools=tools)
graph_builder.add_node("tools", tool_node)
graph_builder.add_conditional_edges(
"chatbot",
tools_condition,
)
# Any time a tool is called, we return to the chatbot to decide the next step
graph_builder.add_edge("tools", "chatbot")
graph_builder.add_edge(START, "chatbot")
graph = graph_builder.compile()
# 添加内存功能
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import MemorySaver
memory = MemorySaver()
graph = graph_builder.compile(checkpointer=memory)
from IPython.display import Image, display
try:
display(Image(graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))
except Exception:
# This requires some extra dependencies and is optional
pass

#与您的聊天机器人互动
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "1"}}
user_input = (
"Can you look up when LangGraph was released? "
"When you have the answer, use the human_assistance tool for review."
)
# The config is the **second positional argument** to stream() or invoke()!
events = graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": user_input}]},
config,
stream_mode="values",
)
for event in events:
if"messages"in event:
event["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
================================[1m Human Message [0m=================================
Can you look up when LangGraph was released? When you have the answer, use the human_assistance tool for review.
==================================[1m Ai Message [0m==================================
Tool Calls:
tavily_search (call_0_4f41d3f3-0512-440f-b690-56b476b58855)
Call ID: call_0_4f41d3f3-0512-440f-b690-56b476b58855
Args:
query: LangGraph release date
=================================[1m Tool Message [0m=================================
Name: tavily_search
{"query": "LangGraph release date", "follow_up_questions": null, "answer": null, "images": [], "results": [{"title": "Releases · langchain-ai/langgraph - GitHub", "url": "https://github.com/langchain-ai/langgraph/releases", "content": "Releases · langchain-ai/langgraph GitHub Copilot Write better code with AI GitHub Advanced Security Find and fix vulnerabilities Code Search Find more, search less * Why GitHub * GitHub Advanced Security Enterprise-grade security features Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests... Releases: langchain-ai/langgraph Releases · langchain-ai/langgraph github-actions github-actions [docs] LangGraph / LangGraph Platform docs updates (#4479) Add clear cache methods github-actions Changes since checkpoint==2.0.25 checkpoint: release 2.0.26 (#4708) docs(reference): filter class methods and add missing docstrings (#4463) github-actions Update python SDK docstrings (#4602) github-actions github-actions feat: CLI: Add main.py (#4637) github-actions github-actions fix for langgraph docstring fixes for libs/langgraph docs: update add_messages API ref (#4495) github-actions Release checkpoint-sqlite (#4509) docstrings for checkpoint-sqlite Add delete_thread method to Checkpointer class (#4328) github-actions", "score": 0.57035583, "raw_content": null}, {"title": "Announcing LangGraph v0.1 & LangGraph Cloud: Running agents at scale ...", "url": "https://blog.langchain.dev/langgraph-cloud/", "content": "Announcing LangGraph v0.1 & LangGraph Cloud: Running agents at scale, reliably Our new infrastructure for running agents at scale, LangGraph Cloud, is available in beta. Separate from the langchain package, LangGraph’s core design philosophy is to help developers add better precision and control into agentic workflows, suitable for the complexity of real-world systems. LangGraph Cloud, currently in closed beta, is infrastructure for deploying your LangGraph agents in a scalable, fault tolerant way. LangGraph Cloud: Scalable agent deployment with integrated monitoring To complement the LangGraph framework, we also have a new runtime, LangGraph Cloud, now available in beta, which provides infrastructure purpose-built for deploying agents at scale. LangGraph Cloud also brings a more integrated experience for collaborating on, deploying, and monitoring your agentic app.", "score": 0.30856565, "raw_content": null}], "response_time": 0.46}
==================================[1m Ai Message [0m==================================
Tool Calls:
human_assistance (call_0_7a301df6-bb5a-41da-8af3-6e55f3999bed)
Call ID: call_0_7a301df6-bb5a-41da-8af3-6e55f3999bed
Args:
name: LangGraph Release Date Review
birthday: 2023-01-01
snapshot = graph.get_state(config)
snapshot.next
('tools',)
# 添加人工协助
human_command = Command(
resume={
"name": "LangGraph",
"birthday": "Jan 17, 2024",
},
)
events = graph.stream(human_command, config, stream_mode="values")
for event in events:
if"messages"in event:
event["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
==================================[1m Ai Message [0m==================================
Tool Calls:
human_assistance (call_0_7a301df6-bb5a-41da-8af3-6e55f3999bed)
Call ID: call_0_7a301df6-bb5a-41da-8af3-6e55f3999bed
Args:
name: LangGraph Release Date Review
birthday: 2023-01-01
=================================[1m Tool Message [0m=================================
Name: human_assistance
Made a correction: {'name': 'LangGraph', 'birthday': 'Jan 17, 2024'}
==================================[1m Ai Message [0m==================================
It appears that LangGraph was released on **January 17, 2024**. Let me know if you'd like any additional details!
# 查看当前状态
snapshot = graph.get_state(config)
{k: v for k, v in snapshot.values.items() if k in ("name", "birthday")}
{'name': 'LangGraph', 'birthday': 'Jan 17, 2024'}
# 自定义修改状态
# 打印状态值
print(snapshot.values.items())
graph.update_state(config, {"name": "LangGraph (library)"})
# 打印值
{k: v for k, v in snapshot.values.items() if k in ("name", "birthday")}
dict_items([('messages', [HumanMessage(content='Can you look up when LangGraph was released? When you have the answer, use the human_assistance tool for review.', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={}, id='1f81e5da-c9ed-4b6f-b7a2-ddb15bf48724'), AIMessage(content='', additional_kwargs={'tool_calls': [{'id': 'call_0_4f41d3f3-0512-440f-b690-56b476b58855', 'function': {'arguments': '{"query":"LangGraph release date"}', 'name': 'tavily_search'}, 'type': 'function', 'index': 0}], 'refusal': None}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 23, 'prompt_tokens': 1362, 'total_tokens': 1385, 'completion_tokens_details': None, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'audio_tokens': None, 'cached_tokens': 1216}, 'prompt_cache_hit_tokens': 1216, 'prompt_cache_miss_tokens': 146}, 'model_name': 'deepseek-chat', 'system_fingerprint': 'fp_8802369eaa_prod0425fp8', 'id': '6b78d8a8-4db3-453f-9375-b38e524194c0', 'service_tier': None, 'finish_reason': 'tool_calls', 'logprobs': None}, id='run--fb61661f-0460-47d7-adb9-d4f85d900f26-0', tool_calls=[{'name': 'tavily_search', 'args': {'query': 'LangGraph release date'}, 'id': 'call_0_4f41d3f3-0512-440f-b690-56b476b58855', 'type': 'tool_call'}], usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 1362, 'output_tokens': 23, 'total_tokens': 1385, 'input_token_details': {'cache_read': 1216}, 'output_token_details': {}}), ToolMessage(content='{"query": "LangGraph release date", "follow_up_questions": null, "answer": null, "images": [], "results": [{"title": "Releases · langchain-ai/langgraph - GitHub", "url": "https://github.com/langchain-ai/langgraph/releases", "content": "Releases · langchain-ai/langgraph GitHub Copilot Write better code with AI GitHub Advanced Security Find and fix vulnerabilities Code Search Find more, search less * Why GitHub * GitHub Advanced Security Enterprise-grade security features Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests... Releases: langchain-ai/langgraph Releases · langchain-ai/langgraph github-actions github-actions [docs] LangGraph / LangGraph Platform docs updates (#4479) Add clear cache methods github-actions Changes since checkpoint==2.0.25 checkpoint: release 2.0.26 (#4708) docs(reference): filter class methods and add missing docstrings (#4463) github-actions Update python SDK docstrings (#4602) github-actions github-actions feat: CLI: Add main.py (#4637) github-actions github-actions fix for langgraph docstring fixes for libs/langgraph docs: update add_messages API ref (#4495) github-actions Release checkpoint-sqlite (#4509) docstrings for checkpoint-sqlite Add delete_thread method to Checkpointer class (#4328) github-actions", "score": 0.57035583, "raw_content": null}, {"title": "Announcing LangGraph v0.1 & LangGraph Cloud: Running agents at scale ...", "url": "https://blog.langchain.dev/langgraph-cloud/", "content": "Announcing LangGraph v0.1 & LangGraph Cloud: Running agents at scale, reliably Our new infrastructure for running agents at scale, LangGraph Cloud, is available in beta. Separate from the langchain package, LangGraph’s core design philosophy is to help developers add better precision and control into agentic workflows, suitable for the complexity of real-world systems. LangGraph Cloud, currently in closed beta, is infrastructure for deploying your LangGraph agents in a scalable, fault tolerant way. LangGraph Cloud: Scalable agent deployment with integrated monitoring To complement the LangGraph framework, we also have a new runtime, LangGraph Cloud, now available in beta, which provides infrastructure purpose-built for deploying agents at scale. LangGraph Cloud also brings a more integrated experience for collaborating on, deploying, and monitoring your agentic app.", "score": 0.30856565, "raw_content": null}], "response_time": 0.46}', name='tavily_search', id='f4fbb8e8-f7d7-4ca5-969a-0f1d7941a069', tool_call_id='call_0_4f41d3f3-0512-440f-b690-56b476b58855'), AIMessage(content='', additional_kwargs={'tool_calls': [{'id': 'call_0_7a301df6-bb5a-41da-8af3-6e55f3999bed', 'function': {'arguments': '{"name":"LangGraph Release Date Review","birthday":"2023-01-01"}', 'name': 'human_assistance'}, 'type': 'function', 'index': 0}], 'refusal': None}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 33, 'prompt_tokens': 1940, 'total_tokens': 1973, 'completion_tokens_details': None, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'audio_tokens': None, 'cached_tokens': 1344}, 'prompt_cache_hit_tokens': 1344, 'prompt_cache_miss_tokens': 596}, 'model_name': 'deepseek-chat', 'system_fingerprint': 'fp_8802369eaa_prod0425fp8', 'id': 'fe865043-9bb9-4a2a-a725-033bf140d6d1', 'service_tier': None, 'finish_reason': 'tool_calls', 'logprobs': None}, id='run--004e940b-d255-4a14-8f12-fc1e49f5bb93-0', tool_calls=[{'name': 'human_assistance', 'args': {'name': 'LangGraph Release Date Review', 'birthday': '2023-01-01'}, 'id': 'call_0_7a301df6-bb5a-41da-8af3-6e55f3999bed', 'type': 'tool_call'}], usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 1940, 'output_tokens': 33, 'total_tokens': 1973, 'input_token_details': {'cache_read': 1344}, 'output_token_details': {}}), ToolMessage(content="Made a correction: {'name': 'LangGraph', 'birthday': 'Jan 17, 2024'}", name='human_assistance', id='c02a55a8-b41c-4ba9-b438-612dfafb370e', tool_call_id='call_0_7a301df6-bb5a-41da-8af3-6e55f3999bed'), AIMessage(content="It appears that LangGraph was released on **January 17, 2024**. Let me know if you'd like any additional details!", additional_kwargs={'refusal': None}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 28, 'prompt_tokens': 2005, 'total_tokens': 2033, 'completion_tokens_details': None, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'audio_tokens': None, 'cached_tokens': 1920}, 'prompt_cache_hit_tokens': 1920, 'prompt_cache_miss_tokens': 85}, 'model_name': 'deepseek-chat', 'system_fingerprint': 'fp_8802369eaa_prod0425fp8', 'id': '20e374eb-f0ef-478a-add2-6eb137e22d0e', 'service_tier': None, 'finish_reason': 'stop', 'logprobs': None}, id='run--218fa197-b63a-4830-a015-0edbf4c846cd-0', usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 2005, 'output_tokens': 28, 'total_tokens': 2033, 'input_token_details': {'cache_read': 1920}, 'output_token_details': {}})]), ('name', 'LangGraph'), ('birthday', 'Jan 17, 2024')])
{'name': 'LangGraph', 'birthday': 'Jan 17, 2024'}
6时间旅行
参考文档教程:
https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/tutorials/get-started/6-time-travel/
# https://python.langchain.com/docs/integrations/tools/tavily_search/
# 获取密钥的地址: https://app.tavily.com/sign-in
import os
TAVILY_API_KEY="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"
os.environ["TAVILY_API_KEY"] = TAVILY_API_KEY
from langchain_tavily import TavilySearch
tool = TavilySearch(max_results=5)
tools = [tool]
tool.invoke("What's a 'node' in LangGraph?")
{'query': "What's a 'node' in LangGraph?",
'follow_up_questions': None,
'answer': None,
'images': [],
'results': [{'title': 'What is LangGraph? - IBM',
'url': 'https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/langgraph',
'content': 'LangGraph, created by LangChain, is an open source AI agent framework designed to build, deploy and manage complex generative AI agent workflows. At its core, LangGraph uses the power of graph-based architectures to model and manage the intricate relationships between various components of an AI agent workflow. LangGraph illuminates the processes within an AI workflow, allowing full transparency of the agent’s state. By combining these technologies with a set of APIs and tools, LangGraph provides users with a versatile platform for developing AI solutions and workflows including chatbots, state graphs and other agent-based systems. Nodes: In LangGraph, nodes represent individual components or agents within an AI workflow. LangGraph uses enhanced decision-making by modeling complex relationships between nodes, which means it uses AI agents to analyze their past actions and feedback.',
'score': 0.90907925,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': 'Nodes and Edges | langchain-ai/langgraph-101 | DeepWiki',
'url': 'https://deepwiki.com/langchain-ai/langgraph-101/2.2-nodes-and-edges',
'content': 'Nodes and Edges | langchain-ai/langgraph-101 | DeepWiki Nodes and Edges Nodes and Edges What are Nodes and Edges? In LangGraph, a graph is composed of nodes connected by edges to form a directed workflow. Nodes are the workhorses of LangGraph - they are Python functions that receive the current graph state as input, perform operations, and return updates to that state. Edges define the flow of execution between nodes in a LangGraph. graph_builder.add_edge("retrieve_documents", "generate_response") Conditional edges use a function to determine the next node based on the current state. Building a Graph with Nodes and Edges graph_builder.add_node("retrieve_documents", retrieve_documents) graph_builder.add_edge("retrieve_documents", "generate_response") When designing nodes and edges in LangGraph: Nodes and Edges What are Nodes and Edges? Building a Graph with Nodes and Edges',
'score': 0.8559598,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': "An Absolute Beginner's Guide to LangGraph.js",
'url': 'https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/blog/educatordeveloperblog/an-absolute-beginners-guide-to-langgraph-js/4212496',
'content': "We'll add the name and isHuman properties to our State object and update the sayHello and sayBye nodes to use these State object properties. Update the Graph's nodes and edges: We'll build a graph that returns a random fact or joke based on the user's input. Finally, inside src/index.ts, import and execute the Graph with a user input, inside the /joke-or-fact route: In this guide, we've covered the basics of LangGraph.js, building a simple graph that returns a random fact or joke based on user input. We've learned how to define nodes, edges, and state objects and how to add conditional routing to our Graph. LangGraph.js is a powerful tool for building complex workflows and managing State in your applications.",
'score': 0.59457535,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': 'LangGraph cheatsheet · GitHub',
'url': 'https://gist.github.com/razhangwei/631a799e6bd69b26ce9c118c624cd80d',
'content': 'This is an excellent LangGraph cheat sheet! LangGraph Cheat Sheet 3. Create Nodes Example Node Function: 4. Create the Graph 5. Add Nodes to the Graph 9. Compile the Graph Invoke the Graph StateGraph | Main class for creating a graph add_node() | Adds a node to the graph add_edge() | Adds a direct edge between two nodes add_conditional_edges() | Adds conditional edges based on a routing function set_entry_point() | Sets the starting node of the graph compile() | Compiles the graph into a RunnableGraph invoke() | Executes the graph with an initial state Send() | Dispatches tasks to multiple nodes in parallel This cheat sheet provides you with all essential steps, best practices, and examples for building LangGraph workflows efficiently! Footer Footer navigation',
'score': 0.5654673,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': 'How to Build AI Agents with LangGraph: A Step-by-Step Guide',
'url': 'https://medium.com/@lorevanoudenhove/how-to-build-ai-agents-with-langgraph-a-step-by-step-guide-5d84d9c7e832',
'content': 'In this step, we’ll define how the AI agent manages its state (the ongoing context of the conversation) and ensure it responds appropriately to the user’s input and tool output. This involves creating a template for the conversation, specifying the tools that the assistant will use, and configuring how the AI agent will respond to user input and trigger different functions (like calculating solar savings). This step ensures that the AI assistant can access and trigger the tools as needed during the conversation, creating a seamless interaction between the user and the assistant. By following these steps, you have successfully created an AI assistant using LangGraph that can calculate solar panel energy savings based on user inputs.',
'score': 0.092532046,
'raw_content': None}],
'response_time': 1.71}
import os
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
API_KEY = "sk-123"
BASE_URL = "https://api.deepseek.com"
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = API_KEY
os.environ["OPENAI_API_BASE"] = BASE_URL
llm = init_chat_model("openai:deepseek-chat")
# 主程序
from typing import Annotated
from langchain_tavily import TavilySearch
from langchain_core.messages import BaseMessage
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode, tools_condition
from langgraph.types import Command, interrupt
from langchain_core.messages import ToolMessage
from langchain_core.tools import InjectedToolCallId, tool
from langgraph.types import Command, interrupt
classState(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)
tool = TavilySearch(max_results=2)
tools = [tool] # 添加human_assistance工具
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
defchatbot(state: State):
return {"messages": [llm_with_tools.invoke(state["messages"])]}
graph_builder.add_node("chatbot", chatbot)
tool_node = ToolNode(tools=tools)
graph_builder.add_node("tools", tool_node)
graph_builder.add_conditional_edges(
"chatbot",
tools_condition,
)
# Any time a tool is called, we return to the chatbot to decide the next step
graph_builder.add_edge("tools", "chatbot")
graph_builder.add_edge(START, "chatbot")
graph = graph_builder.compile()
# 添加内存功能
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import MemorySaver
memory = MemorySaver()
graph = graph_builder.compile(checkpointer=memory)
from IPython.display import Image, display
try:
display(Image(graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))
except Exception:
# This requires some extra dependencies and is optional
pass

#与您的聊天机器人互动
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "2"}}
user_input = (
"I'm learning LangGraph. "
"Could you do some research on it for me?"
)
# The config is the **second positional argument** to stream() or invoke()!
events = graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": user_input}]},
config,
stream_mode="values",
)
for event in events:
if"messages"in event:
event["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
================================[1m Human Message [0m=================================
I'm learning LangGraph. Could you do some research on it for me?
==================================[1m Ai Message [0m==================================
Tool Calls:
tavily_search (call_0_1124b302-9f52-4688-85e8-e016349dc888)
Call ID: call_0_1124b302-9f52-4688-85e8-e016349dc888
Args:
query: LangGraph
search_depth: advanced
=================================[1m Tool Message [0m=================================
Name: tavily_search
{"query": "LangGraph", "follow_up_questions": null, "answer": null, "images": [], "results": [{"url": "https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/langgraph", "title": "What is LangGraph? - IBM", "content": "LangGraph, created by LangChain, is an open source AI agent framework designed to build, deploy and manage complex generative AI agent workflows. It provides a set of tools and libraries that enable users to create, run and optimize large language models (LLMs) in a scalable and efficient manner. At its core, LangGraph uses the power of graph-based architectures to model and manage the intricate relationships between various components of an AI agent workflow. [...] Agent systems: LangGraph provides a framework for building agent-based systems, which can be used in applications such as robotics, autonomous vehicles or video games.\n\nLLM applications: By using LangGraph’s capabilities, developers can build more sophisticated AI models that learn and improve over time. Norwegian Cruise Line uses LangGraph to compile, construct and refine guest-facing AI solutions. This capability allows for improved and personalized guest experiences. [...] By using a graph-based architecture, LangGraph enables users to scale artificial intelligence workflows without slowing down or sacrificing efficiency. LangGraph uses enhanced decision-making by modeling complex relationships between nodes, which means it uses AI agents to analyze their past actions and feedback. In the world of LLMs, this process is referred to as reflection.", "score": 0.9353998, "raw_content": null}, {"url": "https://github.com/langchain-ai/langgraph", "title": "langchain-ai/langgraph: Build resilient language agents as graphs.", "content": "LangGraph — used by Replit, Uber, LinkedIn, GitLab and more — is a low-level orchestration framework for building controllable agents. While langchain provides integrations and composable components to streamline LLM application development, the LangGraph library enables agent orchestration — offering customizable architectures, long-term memory, and human-in-the-loop to reliably handle complex tasks.\n\n```\npip install -U langgraph\n```", "score": 0.8884594, "raw_content": null}], "response_time": 0.16}
==================================[1m Ai Message [0m==================================
Here's what I found about LangGraph:
1. **IBM's Overview**:
- LangGraph is an open-source AI agent framework developed by LangChain. It is designed to build, deploy, and manage complex generative AI agent workflows.
- It uses graph-based architectures to model relationships between components in AI workflows, making it scalable and efficient.
- Applications include agent-based systems (e.g., robotics, autonomous vehicles) and large language model (LLM) applications. For example, Norwegian Cruise Line uses LangGraph to enhance guest-facing AI solutions.
- LangGraph supports reflection, allowing AI agents to analyze past actions and feedback for improved decision-making.
Read more: [IBM on LangGraph](https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/langgraph)
2. **GitHub Repository**:
- LangGraph is a low-level orchestration framework for building controllable agents. It is used by companies like Replit, Uber, LinkedIn, and GitLab.
- It provides customizable architectures, long-term memory, and human-in-the-loop features to handle complex tasks reliably.
- You can install it via pip:
```bash
pip install -U langgraph
Explore the GitHub repo: langchain-ai/langgraph
Let me know if you’d like more details or specific aspects of LangGraph!
```plaintext
snapshot = graph.get_state(config)
snapshot.next
()
# replay
to_replay = None
for state in graph.get_state_history(config):
print("Num Messages: ", len(state.values["messages"]), "Next: ", state.next)
print("-" * 80)
if len(state.values["messages"]) == 2: #指定要回放的状态的序号
# We are somewhat arbitrarily selecting a specific state based on the number of chat messages in the state.
to_replay = state
Num Messages: 4 Next: ()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Num Messages: 3 Next: ('chatbot',)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Num Messages: 2 Next: ('tools',)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Num Messages: 1 Next: ('chatbot',)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Num Messages: 0 Next: ('__start__',)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#从检查点恢复
print(to_replay.next)
print(to_replay.config)
('tools',)
{'configurable': {'thread_id': '2', 'checkpoint_ns': '', 'checkpoint_id': '1f036bc4-23b2-6de4-8001-0145d4bbc81e'}}
# 从某个时刻加载状态
# The `checkpoint_id` in the `to_replay.config` corresponds to a state we've persisted to our checkpointer.
for event in graph.stream(None, to_replay.config, stream_mode="values"):
if"messages"in event:
event["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
dict_items([('messages', [HumanMessage(content='Can you look up when LangGraph was released? When you have the answer, use the human_assistance tool for review.', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={}, id='6a9ae8cf-7eb3-4842-a4a4-2d2f8159f5db'), AIMessage(content='', additional_kwargs={'tool_calls': [{'id': 'call_0_fdff2329-f42d-42c8-ba5f-f1bd1ab74c19', 'function': {'arguments': '{"query":"LangGraph release date"}', 'name': 'tavily_search'}, 'type': 'function', 'index': 0}], 'refusal': None}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 23, 'prompt_tokens': 1362, 'total_tokens': 1385, 'completion_tokens_details': None, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'audio_tokens': None, 'cached_tokens': 1344}, 'prompt_cache_hit_tokens': 1344, 'prompt_cache_miss_tokens': 18}, 'model_name': 'deepseek-chat', 'system_fingerprint': 'fp_8802369eaa_prod0425fp8', 'id': '11756e3e-6840-43b0-ad5d-8b9a84c2a344', 'service_tier': None, 'finish_reason': 'tool_calls', 'logprobs': None}, id='run--c0711883-34f8-48ce-a88a-504868074a25-0', tool_calls=[{'name': 'tavily_search', 'args': {'query': 'LangGraph release date'}, 'id': 'call_0_fdff2329-f42d-42c8-ba5f-f1bd1ab74c19', 'type': 'tool_call'}], usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 1362, 'output_tokens': 23, 'total_tokens': 1385, 'input_token_details': {'cache_read': 1344}, 'output_token_details': {}}), ToolMessage(content='{"query": "LangGraph release date", "follow_up_questions": null, "answer": null, "images": [], "results": [{"title": "Releases · langchain-ai/langgraph - GitHub", "url": "https://github.com/langchain-ai/langgraph/releases", "content": "Releases · langchain-ai/langgraph GitHub Copilot Write better code with AI GitHub Advanced Security Find and fix vulnerabilities Code Search Find more, search less * Why GitHub * GitHub Advanced Security Enterprise-grade security features Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests... Releases: langchain-ai/langgraph Releases · langchain-ai/langgraph github-actions github-actions [docs] LangGraph / LangGraph Platform docs updates (#4479) Add clear cache methods github-actions Changes since checkpoint==2.0.25 checkpoint: release 2.0.26 (#4708) docs(reference): filter class methods and add missing docstrings (#4463) github-actions Update python SDK docstrings (#4602) github-actions github-actions feat: CLI: Add main.py (#4637) github-actions github-actions fix for langgraph docstring fixes for libs/langgraph docs: update add_messages API ref (#4495) github-actions Release checkpoint-sqlite (#4509) docstrings for checkpoint-sqlite Add delete_thread method to Checkpointer class (#4328) github-actions", "score": 0.57035583, "raw_content": null}, {"title": "Announcing LangGraph v0.1 & LangGraph Cloud: Running agents at scale ...", "url": "https://blog.langchain.dev/langgraph-cloud/", "content": "Announcing LangGraph v0.1 & LangGraph Cloud: Running agents at scale, reliably Our new infrastructure for running agents at scale, LangGraph Cloud, is available in beta. Separate from the langchain package, LangGraph’s core design philosophy is to help developers add better precision and control into agentic workflows, suitable for the complexity of real-world systems. LangGraph Cloud, currently in closed beta, is infrastructure for deploying your LangGraph agents in a scalable, fault tolerant way. LangGraph Cloud: Scalable agent deployment with integrated monitoring To complement the LangGraph framework, we also have a new runtime, LangGraph Cloud, now available in beta, which provides infrastructure purpose-built for deploying agents at scale. LangGraph Cloud also brings a more integrated experience for collaborating on, deploying, and monitoring your agentic app.", "score": 0.30856565, "raw_content": null}], "response_time": 0.14}', name='tavily_search', id='ec43923b-3f7f-4af8-b429-e8f495fe614a', tool_call_id='call_0_fdff2329-f42d-42c8-ba5f-f1bd1ab74c19'), AIMessage(content='', additional_kwargs={'tool_calls': [{'id': 'call_0_cd7fb545-4808-420d-9599-9b5bd04ea93c', 'function': {'arguments': '{"name":"LangGraph Release Date","birthday":"2023-01-01"}', 'name': 'human_assistance'}, 'type': 'function', 'index': 0}], 'refusal': None}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 32, 'prompt_tokens': 1940, 'total_tokens': 1972, 'completion_tokens_details': None, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'audio_tokens': None, 'cached_tokens': 1920}, 'prompt_cache_hit_tokens': 1920, 'prompt_cache_miss_tokens': 20}, 'model_name': 'deepseek-chat', 'system_fingerprint': 'fp_8802369eaa_prod0425fp8', 'id': '3408c680-e1af-49f9-86ab-3e88ea9a726a', 'service_tier': None, 'finish_reason': 'tool_calls', 'logprobs': None}, id='run--cf4bd759-f570-48e2-81d6-5d5352a4f2d0-0', tool_calls=[{'name': 'human_assistance', 'args': {'name': 'LangGraph Release Date', 'birthday': '2023-01-01'}, 'id': 'call_0_cd7fb545-4808-420d-9599-9b5bd04ea93c', 'type': 'tool_call'}], usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 1940, 'output_tokens': 32, 'total_tokens': 1972, 'input_token_details': {'cache_read': 1920}, 'output_token_details': {}}), ToolMessage(content="Made a correction: {'name': 'LangGraph', 'birthday': 'Jan 17, 2024'}", name='human_assistance', id='4d24e375-fdb4-4e6a-9724-255ce0189309', tool_call_id='call_0_cd7fb545-4808-420d-9599-9b5bd04ea93c'), AIMessage(content="LangGraph was released on January 17, 2024. The information has been reviewed and confirmed. Let me know if you'd like further details!", additional_kwargs={'refusal': None}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 31, 'prompt_tokens': 2004, 'total_tokens': 2035, 'completion_tokens_details': None, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'audio_tokens': None, 'cached_tokens': 1920}, 'prompt_cache_hit_tokens': 1920, 'prompt_cache_miss_tokens': 84}, 'model_name': 'deepseek-chat', 'system_fingerprint': 'fp_8802369eaa_prod0425fp8', 'id': '6d6488c8-0bc1-45a8-a1b5-29087490b223', 'service_tier': None, 'finish_reason': 'stop', 'logprobs': None}, id='run--bb451740-bb5e-4d17-af36-9dbe62a820e5-0', usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 2004, 'output_tokens': 31, 'total_tokens': 2035, 'input_token_details': {'cache_read': 1920}, 'output_token_details': {}})]), ('name', 'LangGraph'), ('birthday', 'Jan 17, 2024')])
{'name': 'LangGraph', 'birthday': 'Jan 17, 2024'}
完整代码访问github地址:
https://github.com/aixiaoxin123/langgraph_project
大模型算是目前当之无愧最火的一个方向了,算是新时代的风口!有小伙伴觉得,作为新领域、新方向人才需求必然相当大,与之相应的人才缺乏、人才竞争自然也会更少,那转行去做大模型是不是一个更好的选择呢?是不是更好就业呢?是不是就暂时能抵抗35岁中年危机呢?
答案当然是这样,大模型必然是新风口!
那如何学习大模型 ?
由于新岗位的生产效率,要优于被取代岗位的生产效率,所以实际上整个社会的生产效率是提升的。但是具体到个人,只能说是:
最先掌握AI的人,将会比较晚掌握AI的人有竞争优势。
这句话,放在计算机、互联网、移动互联网的开局时期,都是一样的道理。
但现在很多想入行大模型的人苦于现在网上的大模型老课程老教材,学也不是不学也不是,基于此我用做产品的心态来打磨这份大模型教程,深挖痛点并持续修改了近100余次后,终于把整个AI大模型的学习路线完善出来!

在这个版本当中:
您只需要听我讲,跟着我做即可,为了让学习的道路变得更简单,这份大模型路线+学习教程已经给大家整理并打包分享出来, 😝有需要的小伙伴,可以 扫描下方二维码领取🆓↓↓↓

一、大模型经典书籍(免费分享)
AI大模型已经成为了当今科技领域的一大热点,那以下这些大模型书籍就是非常不错的学习资源。

二、640套大模型报告(免费分享)
这套包含640份报告的合集,涵盖了大模型的理论研究、技术实现、行业应用等多个方面。无论您是科研人员、工程师,还是对AI大模型感兴趣的爱好者,这套报告合集都将为您提供宝贵的信息和启示。(几乎涵盖所有行业)
三、大模型系列视频教程(免费分享)

四、2025最新大模型学习路线(免费分享)
我们把学习路线分成L1到L4四个阶段,一步步带你从入门到进阶,从理论到实战。
L1阶段:启航篇丨极速破界AI新时代
L1阶段:了解大模型的基础知识,以及大模型在各个行业的应用和分析,学习理解大模型的核心原理、关键技术以及大模型应用场景。
L2阶段:攻坚篇丨RAG开发实战工坊
L2阶段:AI大模型RAG应用开发工程,主要学习RAG检索增强生成:包括Naive RAG、Advanced-RAG以及RAG性能评估,还有GraphRAG在内的多个RAG热门项目的分析。
L3阶段:跃迁篇丨Agent智能体架构设计
L3阶段:大模型Agent应用架构进阶实现,主要学习LangChain、 LIamaIndex框架,也会学习到AutoGPT、 MetaGPT等多Agent系统,打造Agent智能体。
L4阶段:精进篇丨模型微调与私有化部署
L4阶段:大模型的微调和私有化部署,更加深入的探讨Transformer架构,学习大模型的微调技术,利用DeepSpeed、Lamam Factory等工具快速进行模型微调,并通过Ollama、vLLM等推理部署框架,实现模型的快速部署。

L5阶段:专题集丨特训篇 【录播课】
全套的AI大模型学习资源已经整理打包,有需要的小伙伴可以微信扫描下方二维码,免费领取

更多推荐
 已为社区贡献228条内容
已为社区贡献228条内容






所有评论(0)