LangGraph 基础知识教程(一)跟我一起学构建agent,大模型入门到精通,收藏这篇就足够了!
LangGraph 是由LangChain团队开发的开源框架,专为构建状态化、多代理(Multi-Agent)系统而设计。
一、LangGraph:重新定义AI代理开发
LangGraph 是由LangChain团队开发的开源框架,专为构建状态化、多代理(Multi-Agent)系统而设计。它通过图结构(Graph)实现复杂的动态工作流,尤其擅长与大型语言模型(LLMs)结合,支持循环、持久性、人工干预等核心功能,被视为AI代理开发的“终结者”。
核心定位:
- LangChain生态的重要成员:与LangChain无缝集成,但也可独立使用。
- 突破传统DAG限制:传统框架依赖有向无环图(DAG),而LangGraph支持循环图,更贴近真实业务场景的迭代需求。
- 企业级生产工具:提供持久化、错误恢复、人工审核等特性,已被Uber、Klarna等企业用于客服自动化、代码测试生成等场景。
官方教程地址:
https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/concepts/why-langgraph/
二、LangGraph基础知识学习-从零搭建agent
本文介绍0-3个小结的基础教程,完整代码已经上传到github上;文末自取;
0基础环境安装
1构建基本聊天机器人
2添加工具
3添加内存
0基础环境安装
# 创建虚拟环境
conda create -n langgraph python=3.12
# 激活虚拟环境
conda activate langgraph
# 安装uv
pip install uv -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/
# 安装 jupyter
uv pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/ jupyter
# 安装langgraph依赖包
uv pip install -U langgraph langsmith langchain langchain[openai] langchain-tavily langchain-community langchain-text-splitters -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/
1构建基本聊天机器人
参考文档教程:
https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/tutorials/get-started/1-build-basic-chatbot/
from typing import Annotated
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
classState(TypedDict):
# Messages have the type "list". The `add_messages` function
# in the annotation defines how this state key should be updated
# (in this case, it appends messages to the list, rather than overwriting them)
messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)
import os
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
API_KEY = "sk-123"
BASE_URL = "https://api.deepseek.com"
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = API_KEY
os.environ["OPENAI_API_BASE"] = BASE_URL
llm = init_chat_model("openai:deepseek-chat")
defchatbot(state: State):
return {"messages": [llm.invoke(state["messages"])]}
# The first argument is the unique node name
# The second argument is the function or object that will be called whenever
# the node is used.
graph_builder.add_node("chatbot", chatbot)
graph_builder.add_edge(START, "chatbot")
graph = graph_builder.compile()
from IPython.display import Image, display
try:
display(Image(graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))
except Exception:
# This requires some extra dependencies and is optional
pass

defstream_graph_updates(user_input: str):
for event in graph.stream({"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": user_input}]}):
for value in event.values():
print("Assistant:", value["messages"][-1].content)
whileTrue:
try:
user_input = input("User: ")
print("User: " + user_input)
if user_input.lower() in ["quit", "exit", "q"]:
print("Goodbye!")
break
stream_graph_updates(user_input)
except:
# fallback if input() is not available
user_input = "What do you know about LangGraph?"
print("User: " + user_input)
stream_graph_updates(user_input)
break
Assistant: 我是DeepSeek Chat,由深度求索公司(DeepSeek)开发的智能AI助手!🤖✨ 我的使命是帮助你解答各种问题,无论是学习、工作,还是日常生活中的小困惑,我都会尽力提供准确、有用的信息。
你可以问我任何问题,比如:
- **知识科普**:宇宙有多大?
- **学习辅导**:如何提高英语写作?
- **生活建议**:推荐几本好书?
- **技术支持**:Python代码报错怎么解决?
我目前是**免费的**,支持长文本对话(上下文可达128K),还能阅读上传的文档(如PDF、Word、Excel等)来帮你分析内容。不过,我暂时不支持图片识别或多模态功能。
有什么我可以帮你的吗?😊
Goodbye!
2添加工具
参考文档教程:
https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/tutorials/get-started/2-add-tools/
# https://python.langchain.com/docs/integrations/tools/tavily_search/
# 获取密钥的地址: https://app.tavily.com/sign-in
import os
TAVILY_API_KEY="tvly-dev-123"
os.environ["TAVILY_API_KEY"] = TAVILY_API_KEY
from langchain_tavily import TavilySearch
tool = TavilySearch(max_results=5)
tools = [tool]
tool.invoke("What's a 'node' in LangGraph?")
{'query': "What's a 'node' in LangGraph?",
'follow_up_questions': None,
'answer': None,
'images': [],
'results': [{'title': "Introduction to LangGraph: A Beginner's Guide - Medium",
'url': 'https://medium.com/@cplog/introduction-to-langgraph-a-beginners-guide-14f9be027141',
'content': 'Stateful Graph: LangGraph revolves around the concept of a stateful graph, where each node in the graph represents a step in your computation, and the graph maintains a state that is passed around and updated as the computation progresses. LangGraph supports conditional edges, allowing you to dynamically determine the next node to execute based on the current state of the graph. We define nodes for classifying the input, handling greetings, and handling search queries. def classify_input_node(state): LangGraph is a versatile tool for building complex, stateful applications with LLMs. By understanding its core concepts and working through simple examples, beginners can start to leverage its power for their projects. Remember to pay attention to state management, conditional edges, and ensuring there are no dead-end nodes in your graph.',
'score': 0.7065353,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': 'LangGraph Basics: Understanding State, Schema, Nodes, and Edges',
'url': 'https://medium.com/@vivekvjnk/langgraph-basics-understanding-state-schema-nodes-and-edges-77f2fd17cae5',
'content': 'LangGraph Basics: Understanding State, Schema, Nodes, and Edges | by Story_Teller | Medium LangGraph Basics: Understanding State, Schema, Nodes, and Edges LangGraph Basics: Understanding State, Schema, Nodes, and Edges These predefined structures in the messaging app are synonymous with the schema of the state in LangGraph. Just as a messaging app ensures all interactions (messages) follow a consistent format, the schema in LangGraph ensures the state passed along edges is structured and interpretable. This static schema allows nodes to rely on a consistent state format, ensuring seamless communication along edges throughout the graph. In this article, we explored the foundational concepts of graph-based systems, drawing parallels to familiar messaging applications to illustrate how edges, nodes, and state transitions function seamlessly in dynamic workflows.',
'score': 0.6501347,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': 'LangGraph Tutorial: What Is LangGraph and How to Use It?',
'url': 'https://www.datacamp.com/tutorial/langgraph-tutorial',
'content': 'LangGraph is a library within the LangChain ecosystem that provides a framework for defining, coordinating, and executing multiple LLM agents (or chains) in a structured and efficient manner. By managing the flow of data and the sequence of operations, LangGraph allows developers to focus on the high-level logic of their applications rather than the intricacies of agent coordination. Whether you need a chatbot that can handle various types of user requests or a multi-agent system that performs complex tasks, LangGraph provides the tools to build exactly what you need. LangGraph significantly simplifies the development of complex LLM applications by providing a structured framework for managing state and coordinating agent interactions.',
'score': 0.5008063,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': "LangGraph Tutorial: Building Agents with LangChain's Agent Framework",
'url': 'https://www.getzep.com/ai-agents/langgraph-tutorial',
'content': "Finally, we use Zep's long-term memory for egents to create an agent that remembers previous conversations and user facts. Finally, we will create our LangGraph agent that uses long-term memory to respond to user queries: The agent responses will be based on the user facts from Zep's memory. We will define a graph state that stores messages originating from different nodes, user names, and session IDs. Next, we will create the search_facts tool, which uses the Zep clientâ\x80\x99s memory.search_sessions() method to find user facts relevant to the query. Adding external tools enables the agents to retrieve external information, and persisting memory across conversations enables the LangGraph agent to provide contextualized responses.Â",
'score': 0.30464175,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': 'LangGraph - LangChain',
'url': 'https://www.langchain.com/langgraph',
'content': "[LangGraph](https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/tutorials/introduction/)[LangSmith](https://docs.smith.langchain.com/)[LangChain](https://python.langchain.com/docs/introduction/)  [Read a conceptual guide](https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/concepts/agentic_concepts/#human-in-the-loop) .gif) [See different agent architectures](https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/concepts/agentic_concepts/) [Learn about agent memory](https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/concepts/memory/)  [](https://academy.langchain.com/courses/intro-to-langgraph) Design agent-driven user experiences with LangGraph Platform's APIs. Quickly deploy and scale your application with infrastructure built for agents. The next chapter in building complex production-ready features with LLMs is agentic, and with LangGraph and LangSmith, LangChain delivers an out-of-the-box solution to iterate quickly, debug immediately, and scale effortlessly.” The next chapter in building complex production-ready features with LLMs is agentic, and with LangGraph and LangSmith, LangChain delivers an out-of-the-box solution to iterate quickly, debug immediately, and scale effortlessly.” LangGraph Platform is a service for deploying and scaling LangGraph applications, with an opinionated API for building agent UXs, plus an integrated developer studio.",
'score': 0.1965488,
'raw_content': None}],
'response_time': 1.53}
import os
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
API_KEY = "sk-123"
BASE_URL = "https://api.deepseek.com"
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = API_KEY
os.environ["OPENAI_API_BASE"] = BASE_URL
llm = init_chat_model("openai:deepseek-chat")
#我们现在可以将它合并到 :StateGraph
from typing import Annotated
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
classState(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)
# Modification: tell the LLM which tools it can call
# highlight-next-line
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
defchatbot(state: State):
return {"messages": [llm_with_tools.invoke(state["messages"])]}
graph_builder.add_node("chatbot", chatbot)
<langgraph.graph.state.StateGraph at 0x2c7d006b800>
from typing import Annotated
from langchain_tavily import TavilySearch
from langchain_core.messages import BaseMessage
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode, tools_condition
classState(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)
tool = TavilySearch(max_results=2)
tools = [tool]
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
defchatbot(state: State):
return {"messages": [llm_with_tools.invoke(state["messages"])]}
graph_builder.add_node("chatbot", chatbot)
tool_node = ToolNode(tools=[tool])
graph_builder.add_node("tools", tool_node)
graph_builder.add_conditional_edges(
"chatbot",
tools_condition,
)
# Any time a tool is called, we return to the chatbot to decide the next step
graph_builder.add_edge("tools", "chatbot")
graph_builder.add_edge(START, "chatbot")
graph = graph_builder.compile()
from IPython.display import Image, display
try:
display(Image(graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))
except Exception:
# This requires some extra dependencies and is optional
pass

#8. 向机器人提问
defstream_graph_updates(user_input: str):
for event in graph.stream({"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": user_input}]}):
for value in event.values():
print("Assistant:", value["messages"][-1].content)
whileTrue:
try:
user_input = input("User: ")
print("User: " + user_input)
if user_input.lower() in ["quit", "exit", "q"]:
print("Goodbye!")
break
stream_graph_updates(user_input)
except:
# fallback if input() is not available
user_input = "What do you know about LangGraph?"
print("User: " + user_input)
stream_graph_updates(user_input)
break
User: langgraph是什么
Assistant:
Assistant: {"query": "langgraph是什么", "follow_up_questions": null, "answer": null, "images": [], "results": [{"url": "https://www.cnblogs.com/smartloli/p/18276355", "title": "LangGraph实战- 哥不是小萝莉- 博客园", "content": "2.内容 LangGraph是一个功能强大的库,用于构建基于大型语言模型(LLM)的有状态、多参与者应用程序。 它旨在创建代理和多代理工作流,以实现复杂的任务和交", "score": 0.9202254, "raw_content": null}, {"url": "https://blog.csdn.net/musicml/article/details/136441895", "title": "一文搞懂LangChain 新利器:LangGraph 原创 - CSDN博客", "content": "LangGraph 是一个有用于构建有状态和多角色的 Agents 应用,它并不是一个独立于 Langchain 的新框架,而是基于 Langchain 之上构建的一个扩展库,可以与 Langchain 现有的链(Chains)、LangChain Expression Language(LCEL)等无缝协作。LangGraph 能够协调多个 Chain、Agent、Tool 等共同协作来完成输入任务,支持 LLM 调用“循环”和 Agent 过程的更精细化控制。\nLangGraph 的实现方式是把之前基于 AgentExecutor 的黑盒调用过程,用一种新的形式来构建:状态图(StateGraph)。把基于 LLM 的任务(比如:RAG、代码生成等)细节用 Graph 进行精确的定义(定义图的节点与边),最后基于这个图来编译生成应用。在任务运行过程中,维持一个中央状态对象(state),会根据节点的跳转不断更新,状态包含的属性可自行定义。\n我们一起剖析下官方 RAG 应用的 Graph 案例,如下图所示,从而更好理解 LangGraph。 [...] Lan_g_Graph 是一个用于构建有状态和多角色的LLM Apps 的开源库,常用于 创建单代理和多代理的工作流。与其他LLM 框架相比,Lan_g_Graph 具备以下核心优势和特性:• 循环与分支:允许实现循环和条件逻辑,适用于大多数代理架构,区别于以有向无环图(DAG)为基础的解决方案。• 持久化:内置自动状态保存功能,支持在任何时刻暂停和恢复执行,便于错 误恢复、人类参与、时光回溯等复杂工作流。• 人类参与:在执行过程中可以中断,允许人类审核或编辑下一步操作,支持。\nLan_g_Graph:构建多代理动态工作流的开源框架,支持人工干预、循环、持久性等复杂工作流自动化\nCode1994的博客\n01-03 1141 [...] Lan_g_Graph_是_Lan_g_Chai_n的高级库,为大型语言模型(LLM)带来循环计算能力。它超越了_Lan_g_Chai_n的线性工作流,通过循环支持复杂的任务处理。状态:维护计算过程中的上下文,实现基于累积数据的动态决策。节点:代表计算步骤,执行特定任务,可定制以适应不同工作流。边:连接节点,定义计算流程,支持条件逻辑,实现复杂工作流。_Lan_g_Graph_简化了AI开发,自动管理状态,保持上下文,使AI能智能响应变化。它让开发者专注于创_新,而非技术细节,同时确保应用程序的高性能和可靠性。\n使用 Lan_g_Graph 构建生产级 AI Agent\nJAvavvvvv的博客\n12-20 1035", "score": 0.910998, "raw_content": null}], "response_time": 1.36}
Assistant: LangGraph 是一个用于构建基于大型语言模型(LLM)的有状态、多参与者应用程序的开源库。它是 LangChain 的一个扩展库,旨在创建代理(Agent)和多代理工作流,以实现复杂的任务和交互。
### 主要特点:
1. **有状态和多角色**:支持构建有状态和多角色的代理应用,能够协调多个链(Chains)、代理(Agents)和工具(Tools)共同完成任务。
2. **循环与分支**:允许实现循环和条件逻辑,适用于大多数代理架构,区别于传统的有向无环图(DAG)解决方案。
3. **持久化**:内置自动状态保存功能,支持在任何时刻暂停和恢复执行,便于错误恢复、人类参与或回溯工作流。
4. **人类参与**:在执行过程中可以中断,允许人类审核或编辑下一步操作。
### 核心概念:
- **状态图(StateGraph)**:通过定义图的节点与边来精确描述基于 LLM 的任务(如 RAG、代码生成等),并基于此图编译生成应用。
- **中央状态对象**:在任务运行过程中,维持一个中央状态对象,根据节点的跳转不断更新。
### 应用场景:
- 单代理或多代理工作流。
- 需要动态决策和复杂逻辑的任务。
- 需要人工干预或持久化状态的工作流。
LangGraph 简化了 AI 开发,使开发者能够专注于创新,同时确保应用程序的高性能和可靠性。
更多信息可以参考以下链接:
- [LangGraph实战 - 博客园](https://www.cnblogs.com/smartloli/p/18276355)
- [一文搞懂LangGraph - CSDN博客](https://blog.csdn.net/musicml/article/details/136441895)
User: q
Goodbye!
3添加内存
参考文档教程:
https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/tutorials/get-started/3-add-memory/
# https://python.langchain.com/docs/integrations/tools/tavily_search/
# 获取密钥的地址: https://app.tavily.com/sign-in
import os
TAVILY_API_KEY="tvly-dev-123"
os.environ["TAVILY_API_KEY"] = TAVILY_API_KEY
from langchain_tavily import TavilySearch
tool = TavilySearch(max_results=5)
tools = [tool]
tool.invoke("What's a 'node' in LangGraph?")
{'query': "What's a 'node' in LangGraph?",
'follow_up_questions': None,
'answer': None,
'images': [],
'results': [{'title': "Mastering LangGraph: A Beginner's Guide to Building ... - Medium",
'url': 'https://medium.com/@cplog/introduction-to-langgraph-a-beginners-guide-14f9be027141',
'content': 'Stateful Graph: LangGraph revolves around the concept of a stateful graph, where each node in the graph represents a step in your computation, and the graph maintains a state that is passed around and updated as the computation progresses. LangGraph supports conditional edges, allowing you to dynamically determine the next node to execute based on the current state of the graph. We define nodes for classifying the input, handling greetings, and handling search queries. def classify_input_node(state): LangGraph is a versatile tool for building complex, stateful applications with LLMs. By understanding its core concepts and working through simple examples, beginners can start to leverage its power for their projects. Remember to pay attention to state management, conditional edges, and ensuring there are no dead-end nodes in your graph.',
'score': 0.69249696,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': 'LangGraph Basics: Understanding State, Schema, Nodes, and Edges',
'url': 'https://medium.com/@vivekvjnk/langgraph-basics-understanding-state-schema-nodes-and-edges-77f2fd17cae5',
'content': 'LangGraph Basics: Understanding State, Schema, Nodes, and Edges | by Story_Teller | Medium LangGraph Basics: Understanding State, Schema, Nodes, and Edges LangGraph Basics: Understanding State, Schema, Nodes, and Edges These predefined structures in the messaging app are synonymous with the schema of the state in LangGraph. Just as a messaging app ensures all interactions (messages) follow a consistent format, the schema in LangGraph ensures the state passed along edges is structured and interpretable. This static schema allows nodes to rely on a consistent state format, ensuring seamless communication along edges throughout the graph. In this article, we explored the foundational concepts of graph-based systems, drawing parallels to familiar messaging applications to illustrate how edges, nodes, and state transitions function seamlessly in dynamic workflows.',
'score': 0.6501347,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': "An Absolute Beginner's Guide to LangGraph.js",
'url': 'https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/blog/educatordeveloperblog/an-absolute-beginners-guide-to-langgraph-js/4212496',
'content': "We'll add the name and isHuman properties to our State object and update the sayHello and sayBye nodes to use these State object properties. Update the Graph's nodes and edges: We'll build a graph that returns a random fact or joke based on the user's input. Finally, inside src/index.ts, import and execute the Graph with a user input, inside the /joke-or-fact route: In this guide, we've covered the basics of LangGraph.js, building a simple graph that returns a random fact or joke based on user input. We've learned how to define nodes, edges, and state objects and how to add conditional routing to our Graph. LangGraph.js is a powerful tool for building complex workflows and managing State in your applications.",
'score': 0.59457535,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': 'LangGraph Tutorial: What Is LangGraph and How to Use It?',
'url': 'https://www.datacamp.com/tutorial/langgraph-tutorial',
'content': 'LangGraph is a library within the LangChain ecosystem that provides a framework for defining, coordinating, and executing multiple LLM agents (or chains) in a structured and efficient manner. By managing the flow of data and the sequence of operations, LangGraph allows developers to focus on the high-level logic of their applications rather than the intricacies of agent coordination. Whether you need a chatbot that can handle various types of user requests or a multi-agent system that performs complex tasks, LangGraph provides the tools to build exactly what you need. LangGraph significantly simplifies the development of complex LLM applications by providing a structured framework for managing state and coordinating agent interactions.',
'score': 0.5010992,
'raw_content': None},
{'title': 'How to Build AI Agents with LangGraph: A Step-by-Step Guide',
'url': 'https://medium.com/@lorevanoudenhove/how-to-build-ai-agents-with-langgraph-a-step-by-step-guide-5d84d9c7e832',
'content': 'In this step, we’ll define how the AI agent manages its state (the ongoing context of the conversation) and ensure it responds appropriately to the user’s input and tool output. This involves creating a template for the conversation, specifying the tools that the assistant will use, and configuring how the AI agent will respond to user input and trigger different functions (like calculating solar savings). This step ensures that the AI assistant can access and trigger the tools as needed during the conversation, creating a seamless interaction between the user and the assistant. By following these steps, you have successfully created an AI assistant using LangGraph that can calculate solar panel energy savings based on user inputs.',
'score': 0.0924337,
'raw_content': None}],
'response_time': 0.5}
import os
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
API_KEY = "sk-123"
BASE_URL = "https://api.deepseek.com"
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = API_KEY
os.environ["OPENAI_API_BASE"] = BASE_URL
llm = init_chat_model("openai:deepseek-chat")
#我们现在可以将它合并到 :StateGraph
from typing import Annotated
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
classState(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)
# Modification: tell the LLM which tools it can call
# highlight-next-line
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
defchatbot(state: State):
return {"messages": [llm_with_tools.invoke(state["messages"])]}
graph_builder.add_node("chatbot", chatbot)
<langgraph.graph.state.StateGraph at 0x21246095dc0>
from typing import Annotated
from langchain_tavily import TavilySearch
from langchain_core.messages import BaseMessage
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode, tools_condition
classState(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)
tool = TavilySearch(max_results=2)
tools = [tool]
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
defchatbot(state: State):
return {"messages": [llm_with_tools.invoke(state["messages"])]}
graph_builder.add_node("chatbot", chatbot)
tool_node = ToolNode(tools=[tool])
graph_builder.add_node("tools", tool_node)
graph_builder.add_conditional_edges(
"chatbot",
tools_condition,
)
# Any time a tool is called, we return to the chatbot to decide the next step
graph_builder.add_edge("tools", "chatbot")
graph_builder.add_edge(START, "chatbot")
graph = graph_builder.compile()
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import MemorySaver
memory = MemorySaver()
graph = graph_builder.compile(checkpointer=memory)
from IPython.display import Image, display
try:
display(Image(graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))
except Exception:
# This requires some extra dependencies and is optional
pass

#与您的聊天机器人互动
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "1"}}
user_input = "Hi there! My name is Will."
# The config is the **second positional argument** to stream() or invoke()!
events = graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": user_input}]},
config,
stream_mode="values",
)
for event in events:
event["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
================================[1m Human Message [0m=================================
Hi there! My name is Will.
==================================[1m Ai Message [0m==================================
Hi Will! Nice to meet you. How can I assist you today?
user_input = "Remember my name?"
# The config is the **second positional argument** to stream() or invoke()!
events = graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": user_input}]},
config,
stream_mode="values",
)
for event in events:
event["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
================================[1m Human Message [0m=================================
Remember my name?
==================================[1m Ai Message [0m==================================
Of course, Will! I’ll remember your name for the rest of our conversation. How can I help you today?
# The only difference is we change the `thread_id` here to "2" instead of "1"
events = graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": user_input}]},
{"configurable": {"thread_id": "2"}},
stream_mode="values",
)
for event in events:
event["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
================================[1m Human Message [0m=================================
Remember my name?
==================================[1m Ai Message [0m==================================
I don’t have the ability to remember personal information between interactions. However, you can tell me your name, and I’ll happily use it in our current conversation! What should I call you?
# 使用上一个会话的内存,测试,是否支持多轮对话
events = graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": user_input}]},
{"configurable": {"thread_id": "1"}},
stream_mode="values",
)
for event in events:
event["messages"][-1].pretty_print()
================================[1m Human Message [0m=================================
Remember my name?
==================================[1m Ai Message [0m==================================
Got it, Will! I’ll keep your name in mind while we chat. What can I do for you? 😊
# 5. 检查状态
snapshot = graph.get_state(config)
snapshot
StateSnapshot(values={'messages': [HumanMessage(content='Hi there! My name is Will.', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={}, id='daa419e4-9fad-4c1f-bc48-5636cc15c0b6'), AIMessage(content='Hi Will! Nice to meet you. How can I assist you today?', additional_kwargs={'refusal': None}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 15, 'prompt_tokens': 1246, 'total_tokens': 1261, 'completion_tokens_details': None, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'audio_tokens': None, 'cached_tokens': 1216}, 'prompt_cache_hit_tokens': 1216, 'prompt_cache_miss_tokens': 30}, 'model_name': 'deepseek-chat', 'system_fingerprint': 'fp_8802369eaa_prod0425fp8', 'id': '1ff30ffe-4560-4795-8c81-0d91cbafc872', 'service_tier': None, 'finish_reason': 'stop', 'logprobs': None}, id='run--5393b367-8a4c-42dd-9d9b-d07063b7c0fd-0', usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 1246, 'output_tokens': 15, 'total_tokens': 1261, 'input_token_details': {'cache_read': 1216}, 'output_token_details': {}}), HumanMessage(content='Remember my name?', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={}, id='ddb9eacf-bb07-4ec4-98af-cbae1f0a8b62'), AIMessage(content='Of course, Will! I’ll remember your name for the rest of our conversation. How can I help you today?', additional_kwargs={'refusal': None}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 25, 'prompt_tokens': 1268, 'total_tokens': 1293, 'completion_tokens_details': None, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'audio_tokens': None, 'cached_tokens': 1216}, 'prompt_cache_hit_tokens': 1216, 'prompt_cache_miss_tokens': 52}, 'model_name': 'deepseek-chat', 'system_fingerprint': 'fp_8802369eaa_prod0425fp8', 'id': '9f66bdb3-f243-49ec-a707-b2cb8d170ca9', 'service_tier': None, 'finish_reason': 'stop', 'logprobs': None}, id='run--766a711d-5cc1-4351-86a4-573b76633625-0', usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 1268, 'output_tokens': 25, 'total_tokens': 1293, 'input_token_details': {'cache_read': 1216}, 'output_token_details': {}}), HumanMessage(content='Remember my name?', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={}, id='96396e5d-75d2-4ecb-926a-218b8b9938c0'), AIMessage(content='Got it, Will! I’ll keep your name in mind while we chat. What can I do for you? 😊', additional_kwargs={'refusal': None}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 26, 'prompt_tokens': 1300, 'total_tokens': 1326, 'completion_tokens_details': None, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'audio_tokens': None, 'cached_tokens': 1280}, 'prompt_cache_hit_tokens': 1280, 'prompt_cache_miss_tokens': 20}, 'model_name': 'deepseek-chat', 'system_fingerprint': 'fp_8802369eaa_prod0425fp8', 'id': 'c93ae827-4c38-46ca-9dce-b4365680636c', 'service_tier': None, 'finish_reason': 'stop', 'logprobs': None}, id='run--f0a6888f-d66c-4512-bd1b-e7d688c6675c-0', usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 1300, 'output_tokens': 26, 'total_tokens': 1326, 'input_token_details': {'cache_read': 1280}, 'output_token_details': {}})]}, next=(), config={'configurable': {'thread_id': '1', 'checkpoint_ns': '', 'checkpoint_id': '1f03071b-9c33-662e-8007-53b670e8fcc7'}}, metadata={'source': 'loop', 'writes': {'chatbot': {'messages': [AIMessage(content='Got it, Will! I’ll keep your name in mind while we chat. What can I do for you? 😊', additional_kwargs={'refusal': None}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 26, 'prompt_tokens': 1300, 'total_tokens': 1326, 'completion_tokens_details': None, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'audio_tokens': None, 'cached_tokens': 1280}, 'prompt_cache_hit_tokens': 1280, 'prompt_cache_miss_tokens': 20}, 'model_name': 'deepseek-chat', 'system_fingerprint': 'fp_8802369eaa_prod0425fp8', 'id': 'c93ae827-4c38-46ca-9dce-b4365680636c', 'service_tier': None, 'finish_reason': 'stop', 'logprobs': None}, id='run--f0a6888f-d66c-4512-bd1b-e7d688c6675c-0', usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 1300, 'output_tokens': 26, 'total_tokens': 1326, 'input_token_details': {'cache_read': 1280}, 'output_token_details': {}})]}}, 'step': 7, 'parents': {}, 'thread_id': '1'}, created_at='2025-05-14T03:15:45.450142+00:00', parent_config={'configurable': {'thread_id': '1', 'checkpoint_ns': '', 'checkpoint_id': '1f03071b-68d1-6f82-8006-4dddea4a2f2c'}}, tasks=(), interrupts=())
# 完整的demo示例
from typing import Annotated
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langchain_tavily import TavilySearch
from langchain_core.messages import BaseMessage
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import MemorySaver
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode, tools_condition
classState(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)
tool = TavilySearch(max_results=2)
tools = [tool]
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
defchatbot(state: State):
return {"messages": [llm_with_tools.invoke(state["messages"])]}
graph_builder.add_node("chatbot", chatbot)
tool_node = ToolNode(tools=[tool])
graph_builder.add_node("tools", tool_node)
graph_builder.add_conditional_edges(
"chatbot",
tools_condition,
)
graph_builder.add_edge("tools", "chatbot")
graph_builder.set_entry_point("chatbot")
memory = MemorySaver()
graph = graph_builder.compile(checkpointer=memory)
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "1"}}
from IPython.display import Image, display
try:
display(Image(graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))
except Exception:
# This requires some extra dependencies and is optional
pass
#8. 向机器人提问
defstream_graph_updates(user_input: str):
for event in graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": user_input}]},
config
):
for value in event.values():
print("Assistant:", value["messages"][-1].content)
whileTrue:
try:
user_input = input("User: ")
print("User: " + user_input)
if user_input.lower() in ["quit", "exit", "q"]:
print("Goodbye!")
break
stream_graph_updates(user_input)
except:
# fallback if input() is not available
user_input = "What do you know about LangGraph?"
print("User: " + user_input)
stream_graph_updates(user_input)
break

User: 我叫 aixiaoxin
Assistant: 你好,aixiaoxin!有什么可以帮你的吗? 😊
User: 我叫什么
Assistant: 你刚才告诉我你叫 **aixiaoxin**!需要我帮你做什么吗? 😊
User: 你叫什么
Assistant: 我是你的智能助手,你可以叫我 **小助手** 或 **助手**!如果你有其他喜欢的名字,也可以告诉我,我会很乐意接受的! 😊
User: 你会做什么
Assistant: 我可以做很多事情!以下是一些我能帮助你的方面:
### 1. **信息查询**
- 回答各种知识性问题,比如历史、科学、技术、文化等。
- 提供最新的新闻、天气、股票行情等实时信息。
### 2. **学习辅导**
- 解答数学、物理、化学等学科问题。
- 帮助写作、翻译、修改文章或提供写作灵感。
### 3. **日常生活**
- 推荐美食、旅游景点、电影、书籍等。
- 提供健康、健身、心理等方面的建议。
### 4. **技术支持**
- 解释编程问题,帮助调试代码。
- 提供软件、硬件相关的建议或教程。
### 5. **娱乐互动**
- 讲笑话、故事,或者陪你聊天。
- 生成诗歌、歌词、短篇小说等创意内容。
### 6. **工具辅助**
- 单位换算、日期计算、货币转换等。
- 生成待办事项、提醒事项或简单的计划。
### 7. **个性化服务**
- 根据你的喜好推荐内容。
- 记住你的偏好,提供更贴心的服务。
如果你有任何具体的需求,随时告诉我,我会尽力帮你完成! 😊
User: 你会调用哪些工具
Assistant: 目前,我可以调用以下工具来帮助你完成任务:
### 1. **Tavily 搜索引擎**
- **功能**:提供全面的网络搜索功能,适合查找最新的新闻、知识、技术资料等。
- **用途**:
- 回答实时性问题(如新闻、事件)。
- 查找特定领域的资料(如学术论文、产品评测)。
- 支持高级搜索选项(如限定域名、时间范围)。
### 2. **自定义函数**
- 根据你的需求,我还可以通过编程或调用其他 API 来完成特定任务,比如:
- 数据计算与分析。
- 生成图表或报告。
- 与其他平台集成(如社交媒体、数据库等)。
### 3. **文件处理**
- 如果你上传文件(如文本、表格、图片等),我可以:
- 提取和分析内容。
- 帮助编辑或转换格式。
### 4. **其他工具**
- 如果需要,我还可以通过扩展支持更多工具,比如:
- 翻译工具(如 DeepL、Google Translate)。
- 代码执行环境(如运行 Python 代码)。
- 日历或提醒工具。
如果你有具体的需求,告诉我,我会选择最适合的工具来帮你完成! 😊
User: 我叫什么
Assistant: 你之前告诉我你的名字是 **aixiaoxin**!需要我记住这个名字吗?还是你有其他喜欢的称呼? 😊
User: q
Goodbye!
The Kernel crashed while executing code in the current cell or a previous cell.
Please review the code in the cell(s) to identify a possible cause of the failure.
Click <a href='https://aka.ms/vscodeJupyterKernelCrash'>here</a> for more info.
View Jupyter <a href='command:jupyter.viewOutput'>log</a> for further details.
完整教程访问github地址:
https://github.com/aixiaoxin123/langgraph_project
大模型算是目前当之无愧最火的一个方向了,算是新时代的风口!有小伙伴觉得,作为新领域、新方向人才需求必然相当大,与之相应的人才缺乏、人才竞争自然也会更少,那转行去做大模型是不是一个更好的选择呢?是不是更好就业呢?是不是就暂时能抵抗35岁中年危机呢?
答案当然是这样,大模型必然是新风口!
那如何学习大模型 ?
由于新岗位的生产效率,要优于被取代岗位的生产效率,所以实际上整个社会的生产效率是提升的。但是具体到个人,只能说是:
最先掌握AI的人,将会比较晚掌握AI的人有竞争优势。
这句话,放在计算机、互联网、移动互联网的开局时期,都是一样的道理。
但现在很多想入行大模型的人苦于现在网上的大模型老课程老教材,学也不是不学也不是,基于此我用做产品的心态来打磨这份大模型教程,深挖痛点并持续修改了近100余次后,终于把整个AI大模型的学习路线完善出来!

在这个版本当中:
您只需要听我讲,跟着我做即可,为了让学习的道路变得更简单,这份大模型路线+学习教程已经给大家整理并打包分享出来, 😝有需要的小伙伴,可以 扫描下方二维码领取🆓↓↓↓

一、大模型经典书籍(免费分享)
AI大模型已经成为了当今科技领域的一大热点,那以下这些大模型书籍就是非常不错的学习资源。

二、640套大模型报告(免费分享)
这套包含640份报告的合集,涵盖了大模型的理论研究、技术实现、行业应用等多个方面。无论您是科研人员、工程师,还是对AI大模型感兴趣的爱好者,这套报告合集都将为您提供宝贵的信息和启示。(几乎涵盖所有行业)
三、大模型系列视频教程(免费分享)

四、2025最新大模型学习路线(免费分享)
我们把学习路线分成L1到L4四个阶段,一步步带你从入门到进阶,从理论到实战。
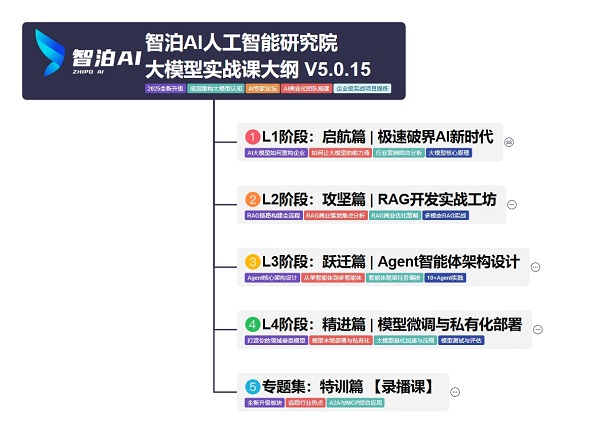
L1阶段:启航篇丨极速破界AI新时代
L1阶段:了解大模型的基础知识,以及大模型在各个行业的应用和分析,学习理解大模型的核心原理、关键技术以及大模型应用场景。
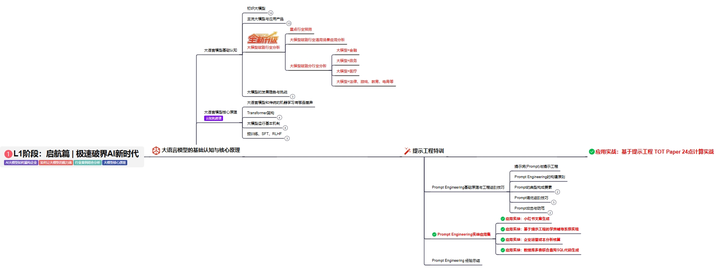
L2阶段:攻坚篇丨RAG开发实战工坊
L2阶段:AI大模型RAG应用开发工程,主要学习RAG检索增强生成:包括Naive RAG、Advanced-RAG以及RAG性能评估,还有GraphRAG在内的多个RAG热门项目的分析。
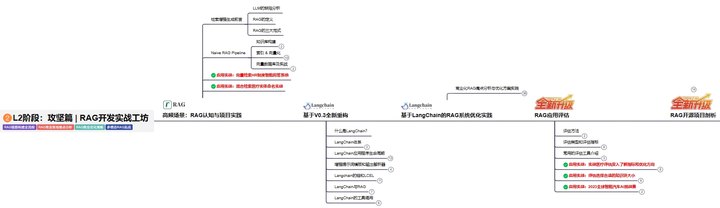
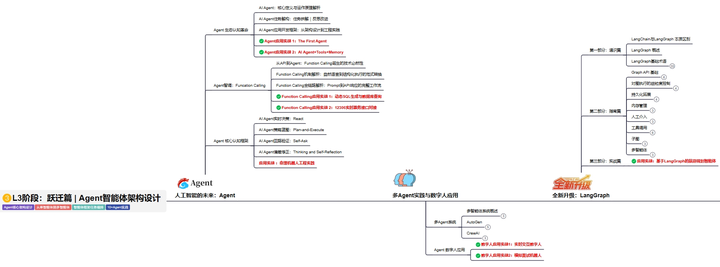
L3阶段:跃迁篇丨Agent智能体架构设计
L3阶段:大模型Agent应用架构进阶实现,主要学习LangChain、 LIamaIndex框架,也会学习到AutoGPT、 MetaGPT等多Agent系统,打造Agent智能体。
L4阶段:精进篇丨模型微调与私有化部署
L4阶段:大模型的微调和私有化部署,更加深入的探讨Transformer架构,学习大模型的微调技术,利用DeepSpeed、Lamam Factory等工具快速进行模型微调,并通过Ollama、vLLM等推理部署框架,实现模型的快速部署。

L5阶段:专题集丨特训篇 【录播课】
全套的AI大模型学习资源已经整理打包,有需要的小伙伴可以微信扫描下方二维码,免费领取

更多推荐
 已为社区贡献228条内容
已为社区贡献228条内容






所有评论(0)