【C++ STL】哈希表封装unordered_set和unordered_map
·
文章目录
前言
在该文章中我们将复用哈希中的链地址法的结构。来实现我们对哈希表的封装。
所以这里哈希的数据结构就不再过多描述了!
1. 哈希表分析结构
-
unordered_set:和set类似都是以value作为key值存储在底层结构中。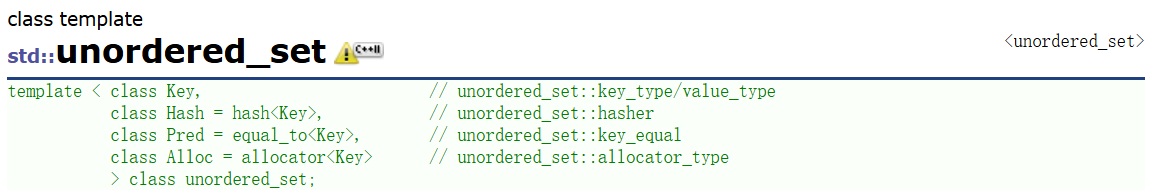
-
unordered_map:和map类似都是key/value的结构以pair键值对的形式存储在底层结构。
Key:键值key的类型。对于unordered_set来说就是value的类型,对于unordered_map来说就是pair键值对的第一个参数的类型。T:映射的数据类型,即value的类型Hash:哈希函数的类型。传入一个可调用对象类型。Pred:用于自定义判断两个key是否相等的规则。(小编为了简化,下面就不再使用这个参数)
下面我们改造一下我们的hash:
template<class T>
struct Node
{
T _data;
Node<T>* _next = nullptr;
Node(const T& data)
:_data(data)
{}
};
// K:key键值类型
// T:节点存储的类型
// KofT:提取T中的key
// HashFunc:哈希函数 —> 交给上层传入
template<class K, class T, class HashFunc, class KOfT>
class HashTable
{
typedef Node<T> Node;
typedef HashTable<K, T, HashFunc, KOfT> self;
public:
HashTable() //默认构造
{
_table.resize(10);
}
~HashTable() //析构函数
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur != nullptr)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_table[i] = nullptr;
}
}
HashTable(const self& ht) //拷贝构造
:_n(ht._n)
{
_table.resize(ht._table.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < ht._table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = ht._table[i];
Node* tail = _table[i];
while (cur != nullptr) //尾插
{
if (_table[i] == tail)
{
_table[i] = tail = new Node(cur->_data);
}
else
{
tail->_next = new Node(cur->_data);
tail = tail->_next;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
}
private:
KOfT _get_key; //获取键值的方法
HashFunc _hf; //哈希函数
private:
vector<Node*> _table; //指针数组
size_t _n = 0; //记录个数
};
KOfT:底层不区分T的类型是什么的,T有可能是Key也有可能是pair。所以需要一个方法能够得到T类型中的key。HashFunc:哈希函数。如何得到哈希值的方法。- 映射算法:我们采用除留余数法。
2. 哈希表迭代器设计
很有意思的是C++命名哈希表作为底层数据结构的集合和映射取名为了unordered_set和unordered_map是因为它们的遍历顺序是无序的(和set&&map区分)因为桶中数据是不确定顺序的!和插入的顺序有关。
而哈希表中的每一个桶中的元素都是以节点的形式存在的,所以其迭代器的设计很有必要的是以节点作为元素的主要。
- 哈希表的迭代器是一个单向迭代器。支持
operator++。
2.1 operator++
-
问题是:现在我们已经得到了某个桶中的每个节点的位置了,如何找到下一个访问的位置呢?
- 在桶(单链表)直接找到下一个节点即可。
- 如果下一个节点为空,就需要前往下一个桶!!!
-
那么如何找到下一个桶呢?
如果我们迭代器中没能指向该迭代器所在哈希表的指针,我们是无法得知它的下一个桶在哪里的,所以我们有必要添加一个指针指向当前迭代器所在哈希表的地址。通过该指针我们就能得知下一个桶的位置了。所以我们很有必要在模板参数上添加上哈希表所需要的参数!
template <class T, class Ptr, class Ref, class K, class HashFunc, class KOfT>
class HTiterator
{
typedef Node<T> Node;
typedef HTiterator<T, Ptr, Ref, K, HashFunc, KOfT> self;
typedef HashTable<K, T, HashFunc, KOfT> HashTable;
typedef HTiterator<T, T*, T&, K, HashFunc, KOfT> Iterator;
public:
HTiterator(const Iterator& iter)
:_ptr(iter._ptr)
,_node(iter._node)
{ }
HTiterator(Node* n, const HashTable* p)
:_ptr(p)
,_node(n)
{ }
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(operator*());
}
self& operator++()
{
KOfT kot;
HashFunc hf;
if (_node->_next != nullptr)
{
_node = _node->_next;
}
else //等于空就找下一个位置
{
//先算当前位置
size_t hashi = hf(kot(_node->_data)) % _ptr->_table.size();
//声明了友元就可以访问private
//
//找下一个位置的桶:
++hashi;
while (hashi < _ptr->_table.size())
{
if (_ptr->_table[hashi] != nullptr)
{
_node = _ptr->_table[hashi];
return *this;
}
++hashi;
}
_node = nullptr;
}
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const self& it)
{
return _node != it._node;
}
public: //方便外界访问
const HashTable* _ptr; //指向迭代器所在的哈希表。
// const属性可以解决两个问题:1、const HashTable* this 2、不用权限的放大
Node* _node; //当前节点
};
哈希表中的迭代器添加:
typedef HTiterator<T, T*, T&, const K, HashFunc, KOfT> iterator;
typedef HTiterator<T, const T*, const T&, const K, HashFunc, KOfT> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
if (cur != nullptr)
{
return iterator(cur, this);
}
}
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
if (cur != nullptr)
{
return const_iterator(cur, this);
}
}
return const_iterator(nullptr, this);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(nullptr, this);
}
3. 哈希表的元素操作
3.1 insert
哈希的元素操作,不管是插入有可能元素插入失败,并且我们需要为其返回正确的迭代器,所以我们应该这样设计:pair<iterator, bool>
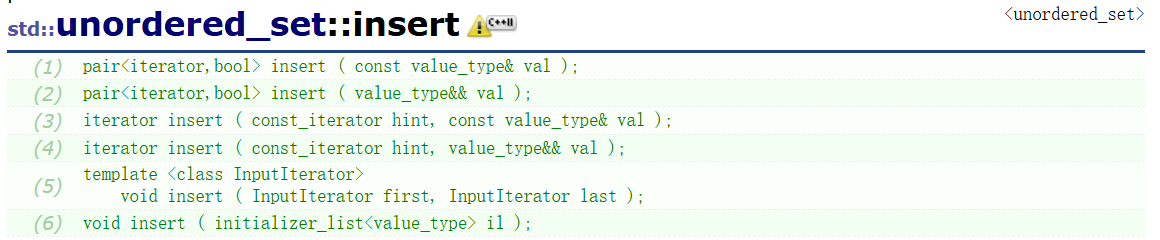
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const T& val)
{
if (_n == _table.size()) //判断是否需要扩容
{
//临时对象交换的思想进行复制
size_t newsize = _table.size() * 2;
vector<Node*> tmp(newsize);
//遍历原哈希表:
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i]; //复制每一个桶
while (cur != nullptr)
{
Node* next = cur->_next; //得到下一个位置
//将cur头插到对应的tmp的映射位置
size_t hashi = _hf(_get_key(cur->_data)) % tmp.size();
cur->_next = tmp[hashi];
tmp[hashi] = cur;
//迭代
cur = next;
}
//将原哈希表位置置空
_table[i] = nullptr;
}
//交换
_table.swap(tmp);
}
//插入新元素
size_t hashi = _hf(_get_key(val)) % _table.size();
Node* cur = _table[hashi];
while (cur != nullptr)
{
if (_hf(_get_key(cur->_data)) == _hf(_get_key(val))) //已经存在了
{
return make_pair(iterator(cur, this), false);
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
//头插链接:
Node* newnode = new Node(val);
newnode->_next = _table[hashi];
_table[hashi] = newnode;
++_n;
return make_pair(iterator(newnode, this), true);
}
3.2 erase
-
我们来看文档:
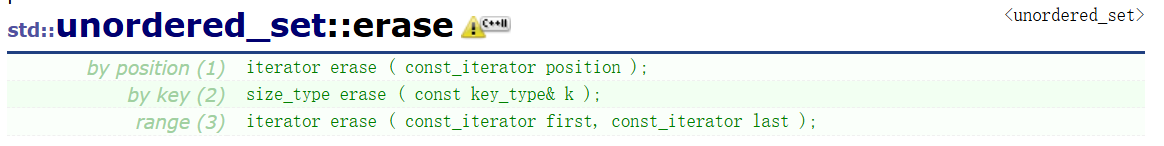
我们尝试写第二个函数接口。返回值,如果删除成功返回1,删除失败返回0。

size_t erase(const K& key)
{
size_t hashi = _hf(key) % _table.size();
Node* cur = _table[hashi];
Node* prev = nullptr;
while (cur != nullptr)
{
if (_hf(_get_key(cur->_data)) == _hf(key))
{
if (prev == nullptr)
{
_table[hashi] = cur->_next;
}
else
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
}
delete cur;
--_n;
return 1;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return 0;
}
4. 封装unordered_set
#pragma once
#include "HashTable.h"
template<class T>
struct DefalutType //转化key的方法
{
size_t operator()(const T& val)
{
return (size_t)val;
}
};
template<>
struct DefalutType<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& val)
{
size_t hashi = 0;
for (auto e : val)
{
hashi *= 131;
hashi += e;
}
return hashi;
}
};
namespace LL
{
template<class K, class HashFunc = DefalutType<K>>
class unordered_set
{
struct KeyOfT_Set
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename HashTable<const K, K, HashFunc, KeyOfT_Set>::const_iterator iterator;
typedef typename HashTable<const K, K, HashFunc, KeyOfT_Set>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin() const
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end() const
{
return _ht.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
pair<typename HashTable<const K, K, HashFunc, KeyOfT_Set>::iterator, bool> tmp = _ht.insert(key);
return pair<iterator, bool>(tmp.first, tmp.second); //匿名对象
}
private:
HashTable<const K, K, HashFunc, KeyOfT_Set> _ht;
};
}
5. 封装unordered_map
#pragma once
#include "HashTable.h"
namespace LL
{
template<class K, class V, class HashFunc = DefalutType<K>>
class unordered_map
{
struct KeyOfT_Map
{
const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename HashTable<const K, pair<const K, V>, HashFunc, KeyOfT_Map>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename HashTable<const K, pair<const K, V>, HashFunc, KeyOfT_Map>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _ht.insert(kv);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _ht.insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
private:
HashTable<const K, pair<const K, V>, HashFunc, KeyOfT_Map> _ht;
};
}
完整哈希表代码
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
template<class T>
struct DefalutType //转化key的方法
{
size_t operator()(const T& val)
{
return (size_t)val;
}
};
template<>
struct DefalutType<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& val)
{
size_t hashi = 0;
for (auto e : val)
{
hashi *= 131;
hashi += e;
}
return hashi;
}
};
template<class T>
struct Node
{
T _data;
Node<T>* _next = nullptr;
Node(const T& data)
:_data(data)
{
}
};
template<class K, class T, class HashFunc, class KOfT>
class HashTable; //前置声明
template <class T, class Ptr, class Ref, class K, class HashFunc, class KOfT>
class HTiterator
{
typedef Node<T> Node;
typedef HTiterator<T, Ptr, Ref, K, HashFunc, KOfT> self;
typedef HashTable<K, T, HashFunc, KOfT> HashTable;
typedef HTiterator<T, T*, T&, K, HashFunc, KOfT> Iterator;
public:
HTiterator(const Iterator& iter)
:_ptr(iter._ptr)
,_node(iter._node)
{ }
HTiterator(Node* n, const HashTable* p)
:_ptr(p)
,_node(n)
{ }
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(operator*());
}
self& operator++()
{
KOfT kot;
HashFunc hf;
if (_node->_next != nullptr)
{
_node = _node->_next;
}
else //等于空就找下一个位置
{
//先算当前位置
size_t hashi = hf(kot(_node->_data)) % _ptr->_table.size();
//声明了友元就可以访问private
//
//找下一个位置的桶:
++hashi;
while (hashi < _ptr->_table.size())
{
if (_ptr->_table[hashi] != nullptr)
{
_node = _ptr->_table[hashi];
return *this;
}
++hashi;
}
_node = nullptr;
}
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const self& it)
{
return _node != it._node;
}
public:
const HashTable* _ptr; //指向迭代器所在的哈希表。
// const属性可以解决两个问题:1、const HashTable* this 2、不用权限的放大
Node* _node; //当前节点
};
// K:key键值类型
// T:节点存储的类型
// KofT:提取T中的key
// HashFunc:哈希函数 —> 交给上层传入
template<class K, class T, class HashFunc, class KOfT>
class HashTable
{
typedef Node<T> Node;
typedef HashTable<K, T, HashFunc, KOfT> self;
public:
HashTable() //默认构造
{
_table.resize(10);
}
~HashTable() //析构函数
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur != nullptr)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_table[i] = nullptr;
}
}
HashTable(const self& ht) //拷贝构造
:_n(ht._n)
{
_table.resize(ht._table.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < ht._table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = ht._table[i];
Node* tail = _table[i];
while (cur != nullptr) //尾插
{
if (_table[i] == tail)
{
_table[i] = tail = new Node(cur->_data);
}
else
{
tail->_next = new Node(cur->_data);
tail = tail->_next;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
}
public:
//为迭代器声明友元
//声明友元,可以在迭代器类中访问私有成员
template <class T, class Ptr, class Ref, class K, class HashFunc, class KOfT>
friend class HTiterator;
typedef HTiterator<T, T*, T&, const K, HashFunc, KOfT> iterator;
typedef HTiterator<T, const T*, const T&, const K, HashFunc, KOfT> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
if (cur != nullptr)
{
return iterator(cur, this);
}
}
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
if (cur != nullptr)
{
return const_iterator(cur, this);
}
}
return const_iterator(nullptr, this);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(nullptr, this);
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const T& val)
{
if (_n == _table.size()) //判断是否需要扩容
{
//临时对象交换的思想进行复制
size_t newsize = _table.size() * 2;
vector<Node*> tmp(newsize);
//遍历原哈希表:
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i]; //复制每一个桶
while (cur != nullptr)
{
Node* next = cur->_next; //得到下一个位置
//将cur头插到对应的tmp的映射位置
size_t hashi = _hf(_get_key(cur->_data)) % tmp.size();
cur->_next = tmp[hashi];
tmp[hashi] = cur;
//迭代
cur = next;
}
//将原哈希表位置置空
_table[i] = nullptr;
}
//交换
_table.swap(tmp);
}
//插入新元素
size_t hashi = _hf(_get_key(val)) % _table.size();
Node* cur = _table[hashi];
while (cur != nullptr)
{
if (_hf(_get_key(cur->_data)) == _hf(_get_key(val))) //已经存在了
{
return make_pair(iterator(cur, this), false);
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
//头插链接:
Node* newnode = new Node(val);
newnode->_next = _table[hashi];
_table[hashi] = newnode;
++_n;
return make_pair(iterator(newnode, this), true);
}
size_t erase(const K& key)
{
size_t hashi = _hf(key) % _table.size();
Node* cur = _table[hashi];
Node* prev = nullptr;
while (cur != nullptr)
{
if (_hf(_get_key(cur->_data)) == _hf(key))
{
if (prev == nullptr)
{
_table[hashi] = cur->_next;
}
else
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
}
delete cur;
--_n;
return 1;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return 0;
}
private:
KOfT _get_key; //获取键值的方法
HashFunc _hf; //哈希函数
private:
vector<Node*> _table; //指针数组
size_t _n = 0; //记录个数
};
- 测试代码
#include "Unordered_map.h"
#include "Unordered_set.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//int main()
//{
// LL::unordered_set<int> s;
// s.insert(1);
// s.insert(2);
// s.insert(3);
// s.insert(4);
// s.insert(5);
// s.insert(6);
// s.insert(11);
// s.insert(12);
//
// for (auto e : s)
// {
// cout << e << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
// return 0;
//}
void test1();
void test2();
int main()
{
test1();
test2();
return 0;
}
void test1()
{
LL::unordered_set<int> s;
s.insert(1);
s.insert(2);
s.insert(3);
s.insert(4);
s.insert(5);
s.insert(6);
s.insert(7);
s.insert(8);
s.insert(9);
s.insert(10);
s.insert(21);
LL::unordered_set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
cout << endl;
}
void test2()
{
LL::unordered_map<string, string> m;
m.insert(make_pair("string", "xx"));
m.insert(make_pair("insert", ""));
m.insert(make_pair("iterator", ""));
m.insert(make_pair("nice", ""));
for (auto& e : m)
{
e.second = "xxx";
cout << e.first << " : " << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl << endl;
m["string"] = "字符串";
m["love"];
m["nice"] = "";
m["I"] = "我";
m["you"] = "不嘻嘻";
LL::unordered_map<string, string>::iterator mit = m.begin();
while (mit != m.end())
{
//mit->first = " ";
cout << mit->first << " : " << mit->second << endl;
++mit;
}
cout << endl;
int a = 0;
}
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献4条内容
已为社区贡献4条内容







所有评论(0)