牛客周赛 Round 107(小红打怪/小红砍怪/小红加强打怪/小红走迷宫/小苯的刷怪笼/毒苯)
·
小红打怪
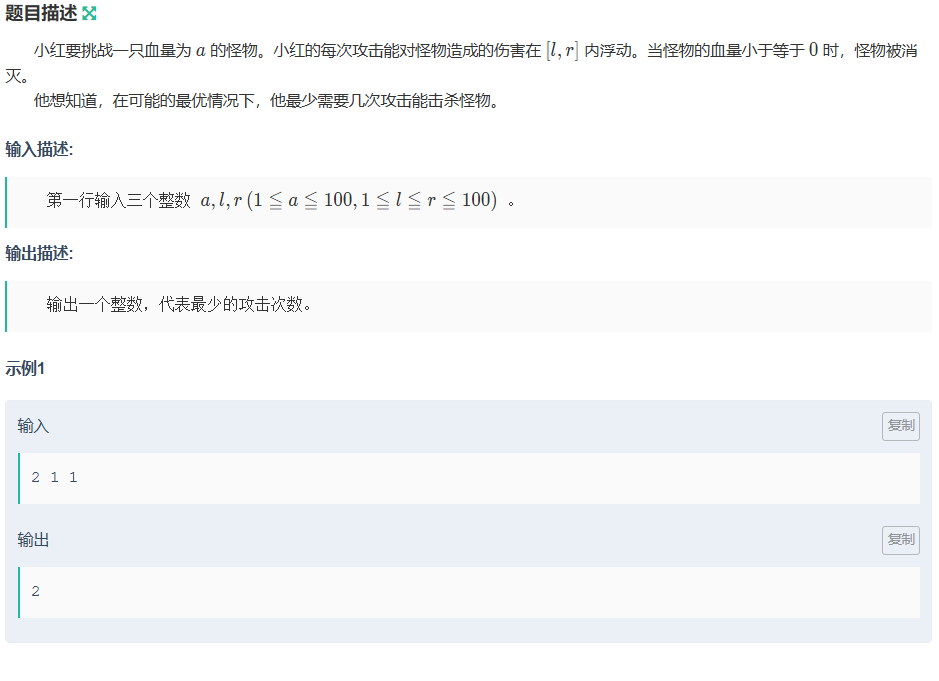
思路:找伤害最高(r)的打
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); // 禁用同步
std::cin.tie(nullptr),std::cout.tie(nullptr); // 解除cin与cout绑定
int n, a, b;
cin >> n >> a >> b;
cout << n / b + (n % b == 0 ? 0 : 1) << endl;
return 0;
}小红砍怪
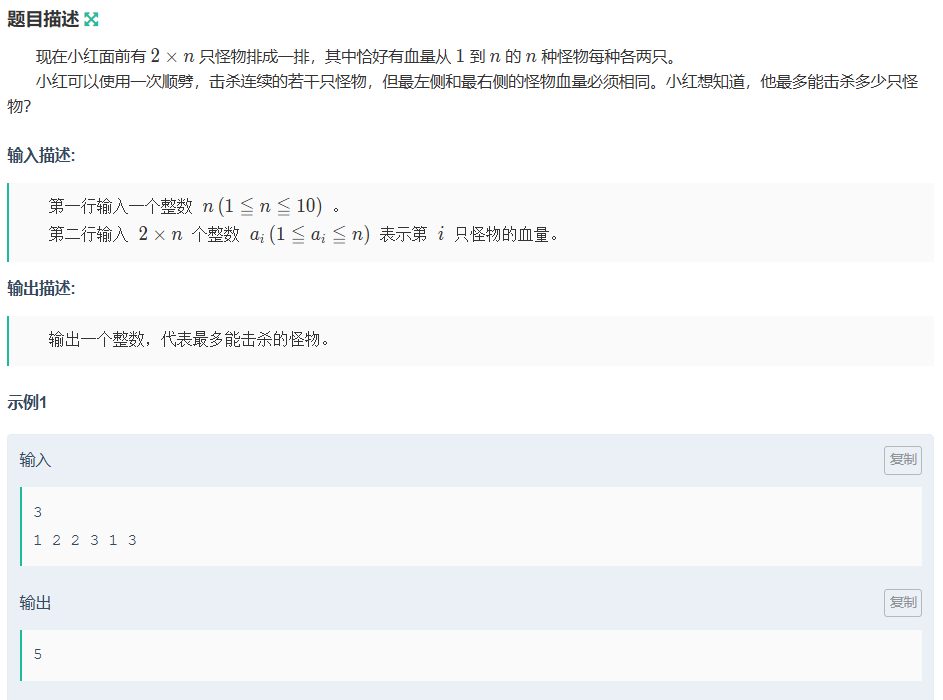
思路:
找到两个相同之间的最短距离,因为啊ai<=n,所以可以像桶一样储存(开a[n][2])
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); // 禁用同步
std::cin.tie(nullptr),std::cout.tie(nullptr); // 解除cin与cout绑定
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<pii> a(n+1,{0,0});
int u = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++) {
cin >> u;
if (a[u].first == 0) {
a[u].first = i;
}
else {
a[u].second = i;
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ans = max(ans, a[i].second - a[i].first + 1);
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}小红加强打怪
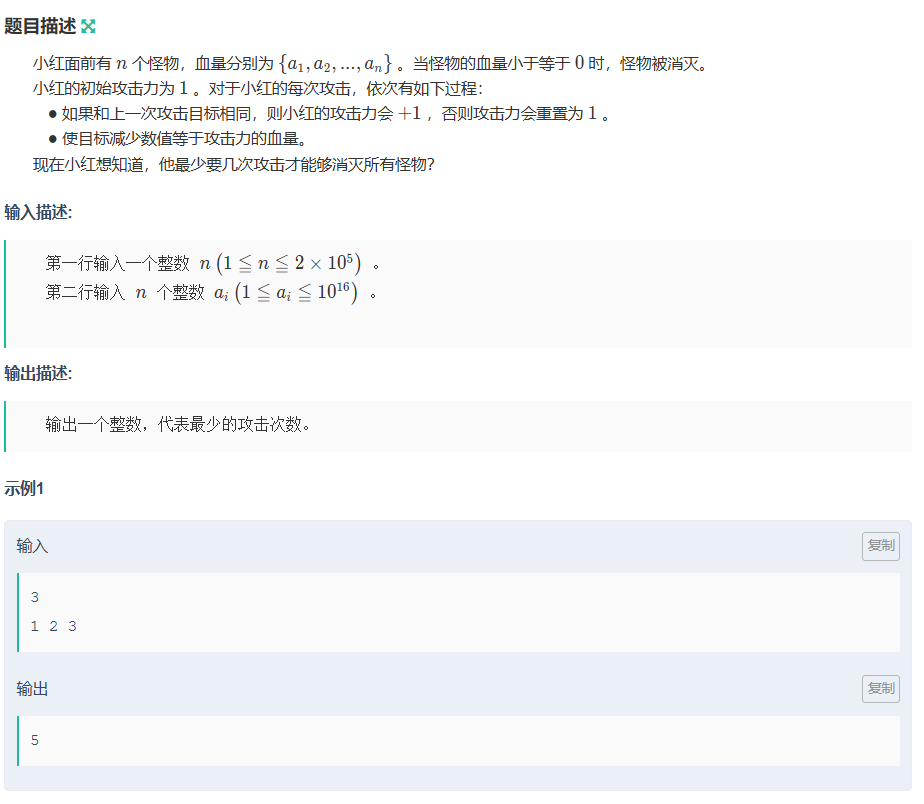
思路:
a[i]要的次数设为x;
x*(x+1)/2>=a[i] 所以用二分答案
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
ll solve(ll x) {
ll l = 1, r = 2 * sqrt(x);
while (l < r) {
ll mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (mid * (mid + 1) / 2 >= x) {
r = mid;
}
else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return l;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); // 禁用同步
std::cin.tie(nullptr),std::cout.tie(nullptr); // 解除cin与cout绑定
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<ll> a(n);
vector<pll>b();
ll ans = 0, sum = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
ans += solve(a[i]);
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}小红走迷宫
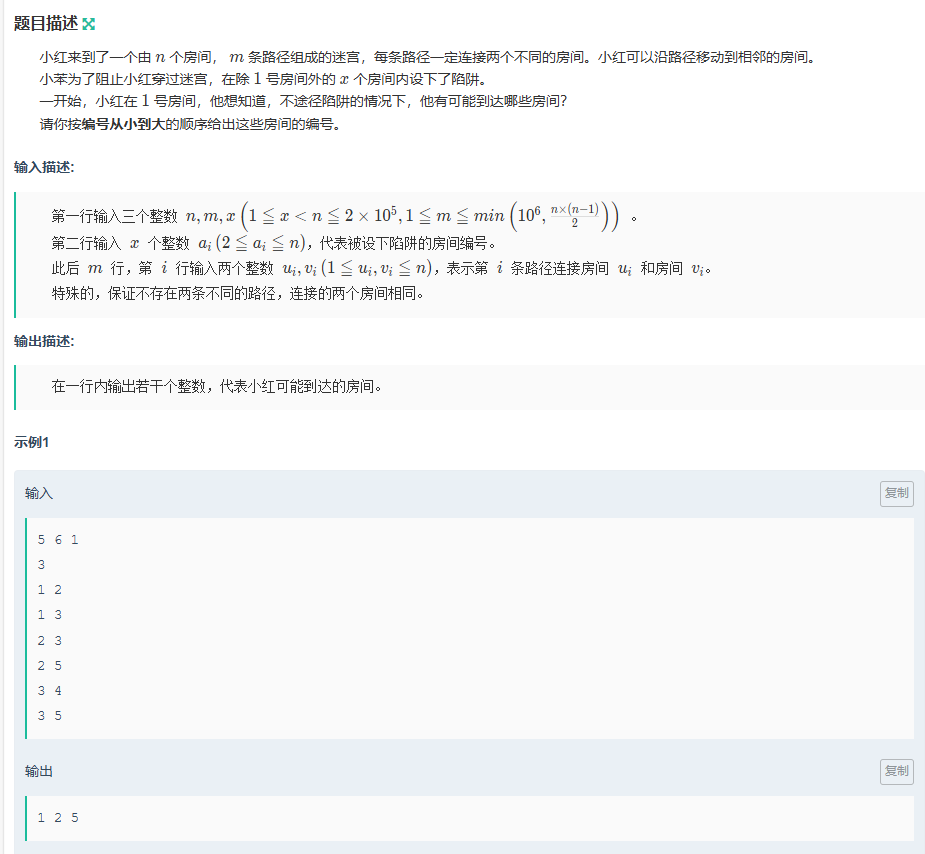
思路:
连通,我是想到并查集的思想,有陷阱的房间就相当于不连通,最后遍历find(1)==find(i)的i;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
int n, m, x;
int a[200005];
bool b[200005];
int find(int i) {
if (i == a[i]) {
return a[i];
}
else {
return a[i] = find(a[i]);
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); // 禁用同步
std::cin.tie(nullptr), std::cout.tie(nullptr); // 解除cin与cout绑定
int n;
cin >> n >> m >> x;
int u = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
cin >> u;
b[u] = true;
}
iota(a,a+ n+1, 0);
int l, r;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cin >> l >> r;
if (b[l] || b[r]) {
continue;
}
else {
int x = find(l), y = find(r);
if (x != y) {
a[x] = a[y];
}
}
}
int ans = find(1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (find(i) == ans) {
cout << i << " ";
}
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}小苯的刷怪笼

思路:
首先要将n==1单独讨论,然后要知道n为奇偶时kmin是不一样的例:(4 5 1),(5,5);
- 最小攻击次数条件:当所有怪物的血量尽可能均匀分配时,攻击次数最小。最小攻击次数为
max(max(h_i), ceil(sum(h_i)/2))。对于均匀分配,最小攻击次数为ceil(a/2)。 - 最大攻击次数条件:当所有怪物血量均为1,除了一个怪物血量为
a - (n-1),此时攻击次数为a - (n-1)。 - 可行条件:
k必须介于最小和最大攻击次数之间,即ceil(a/2) <= k <= a - (n-1)。如果n=1,则k必须等于a。 - 构造方案:
- 如果
n=1,直接输出k。 - 否则,构造一个方案,使得前两个怪物的血量分别为
k - l和a - k + l - (n-2),其余怪物血量为1。其中l是中间变量,用于调整攻击次数。
- 如果
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
int n, a, k;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); // 禁用同步
std::cin.tie(nullptr),std::cout.tie(nullptr); // 解除cin与cout绑定
cin >> n >> a >> k;
int l = (n - 2+1) / 2;
if (n == 1) {
if (k != a) {
cout << -1 << endl;
}
else {
cout << k << endl;
}
}
else if (k > a || (n%2==0&&k < (a - (n - 2) + 1) / 2 + l)||((n % 2 == 1 && k < (a - (n - 2)) / 2 + l)) || k > (a - (n - 2) - 1) + l) {
cout << -1 << endl;
}
else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
cout << k-l << " ";
}
else if (i == 1) {
cout << a - k + l - (n - 2) << " ";
}
else {
cout << 1 << " ";
}
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}毒苯

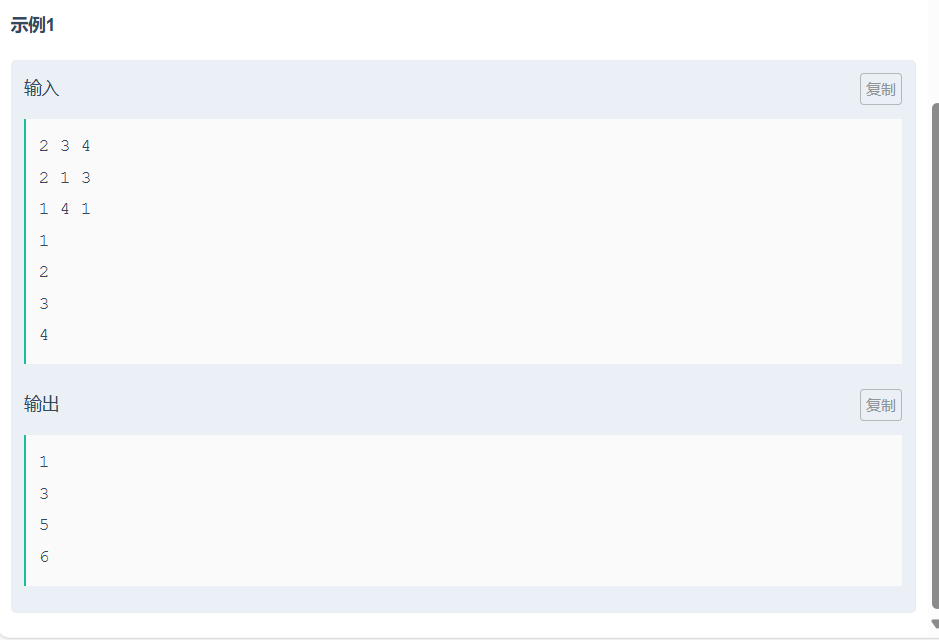
思路:
BFS+优先队列+二分+预处理;
- 预处理阶段:使用优先队列(最小堆)来模拟毒药的传播过程。队列中的元素按照小苯的血量排序,确保每次处理当前血量最小的小苯。这样可以逐步构建一个关于毒药强度x与被消灭小苯数量之间关系的映射表。
- 查询处理:对于每个查询x,使用二分查找在预处理得到的映射表中快速定位x对应的被消灭小苯数量。
复杂度分析
- 预处理阶段:由于每个小苯最多被处理一次,优先队列的操作复杂度为O(nm log(nm)),适用于n和m在500以内的情况。
- 查询处理:每个查询的二分查找复杂度为O(log k),其中k是映射表的大小,总查询处理复杂度为O(q log k),适用于q在2×10^5以内的情况。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
int n, m, qq;
int a[505][505];
vector<pii> c;
int h[4] = { -1,0,0,1 }, f[4] = { 0,1,-1,0 };
struct ComparePii {
bool operator()(const pii& x, const pii& y) const {
return a[x.first][x.second] > a[y.first][y.second];
}
};
void pan(int x) {
int l = 0, r = c.size() - 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
int mid = (r + l+1) / 2;
if (c[mid].first > x) {
r = mid - 1;
}
else {
l = mid;
}
}
cout << c[l].second << endl;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); // 禁用同步
std::cin.tie(nullptr), std::cout.tie(nullptr); // 解除cin与cout绑定
cin >> n >> m >> qq;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
cin >> a[i][j];
}
}
vector<vector<int>>b(n, vector<int>(m, 0));
priority_queue<pii, vector<pii>, ComparePii>q;
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
b[0][j] = 1;
q.push({ 0,j });
}
int ans = 0;
int k = -1;
c.push_back({ 0,0 });
while (!q.empty()) {
pii y = q.top();
if (k == -1) {
k = a[y.first][y.second];
}
q.pop();
if (a[y.first][y.second] > k) {
c.push_back({ k,ans });
k = a[y.first][y.second];
}
ans++;
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
if (y.first + h[j] >= 0 && y.first + h[j] < n && y.second + f[j] >= 0 && y.second + f[j] < m && b[y.first + h[j]][y.second + f[j]] == 0) {
b[y.first + h[j]][y.second + f[j]] = 1;
q.push({ y.first + h[j],y.second + f[j] });
}
}
}
c.push_back({ k,ans });
int x;
sort(c.begin(), c.end());
for (int i = 0; i < qq; i++) {
cin >> x;
pan(x);
}
return 0;
}更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容








所有评论(0)