sf(四)-VSync校准
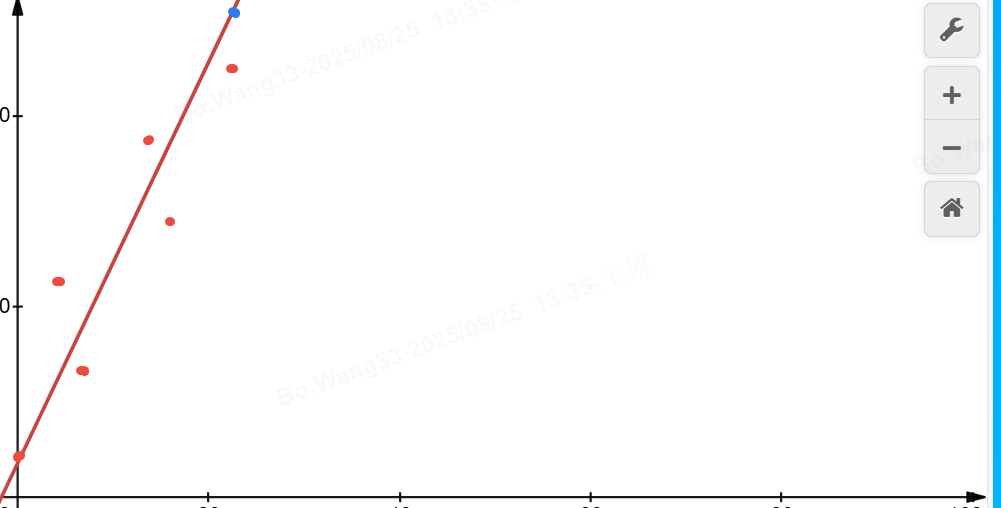
具体实现是HW sync上报最少6个点,然后surfaceflinger通过公式y = ax + b,推导出下一个HW sync的时间点,即下图中的y值。HW vsync信号会上报给surfaceflinger,surfaceflinger会通过公式校准SW vysnc。中,讲了app vsync,大概要经过EventThread的threadMain,
·
1 硬件VSync校准
HW vsync信号会上报给surfaceflinger,surfaceflinger会通过公式校准SW vysnc。
具体实现是HW sync上报最少6个点,然后surfaceflinger通过公式y = ax + b,推导出下一个HW sync的时间点,即下图中的y值。
y = a x + b y = ax + b y=ax+b
- x:第几个HW sync点。
- y:第几个HW sync点的时间。
- a:斜率,可以理解为周期,频率。
- b:截距,可以理解为第一个点的Y值。
即:这条位于xy桌标轴中的斜线,代表了它是距离这6个HW sync最小偏差的斜线,那么当x = 7的时候,对应y轴上的值,就是预测到的偏差最小的HW sync时间,也就是SW Sync的值。
理解上面的内容,看下面的代码,就好理解了。
/frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/Scheduler/VSyncPredictor.cpp
bool VSyncPredictor::addVsyncTimestamp(nsecs_t timestamp) {
std::lock_guard lock(mMutex);
if (!validate(timestamp)) {
// VSR could elect to ignore the incongruent timestamp or resetModel(). If ts is ignored,
// don't insert this ts into mTimestamps ringbuffer. If we are still
// in the learning phase we should just clear all timestamps and start
// over.
if (mTimestamps.size() < kMinimumSamplesForPrediction) {
// Add the timestamp to mTimestamps before clearing it so we could
// update mKnownTimestamp based on the new timestamp.
mTimestamps.push_back(timestamp);
clearTimestamps();
} else if (!mTimestamps.empty()) {
mKnownTimestamp =
std::max(timestamp, *std::max_element(mTimestamps.begin(), mTimestamps.end()));
} else {
mKnownTimestamp = timestamp;
}
return false;
}
if (mTimestamps.size() != kHistorySize) {
mTimestamps.push_back(timestamp);
mLastTimestampIndex = next(mLastTimestampIndex);
} else {
mLastTimestampIndex = next(mLastTimestampIndex);
mTimestamps[mLastTimestampIndex] = timestamp;
}
// kMinimumSamplesForPrediction = 6,这里判断如果小于6个点,return
if (mTimestamps.size() < kMinimumSamplesForPrediction) {
mRateMap[mIdealPeriod] = {mIdealPeriod, 0};
return true;
}
// This is a 'simple linear regression' calculation of Y over X, with Y being the
// vsync timestamps, and X being the ordinal of vsync count.
// The calculated slope is the vsync period.
// Formula for reference:
// Sigma_i: means sum over all timestamps.
// mean(variable): statistical mean of variable.
// X: snapped ordinal of the timestamp
// Y: vsync timestamp
//
// Sigma_i( (X_i - mean(X)) * (Y_i - mean(Y) )
// slope = -------------------------------------------
// Sigma_i ( X_i - mean(X) ) ^ 2
//
// intercept = mean(Y) - slope * mean(X)
//
std::vector<nsecs_t> vsyncTS(mTimestamps.size());
std::vector<nsecs_t> ordinals(mTimestamps.size());
// normalizing to the oldest timestamp cuts down on error in calculating the intercept.
auto const oldest_ts = *std::min_element(mTimestamps.begin(), mTimestamps.end());
auto it = mRateMap.find(mIdealPeriod);
auto const currentPeriod = it->second.slope;
// TODO (b/144707443): its important that there's some precision in the mean of the ordinals
// for the intercept calculation, so scale the ordinals by 1000 to continue
// fixed point calculation. Explore expanding
// scheduler::utils::calculate_mean to have a fixed point fractional part.
static constexpr int64_t kScalingFactor = 1000;
for (auto i = 0u; i < mTimestamps.size(); i++) {
traceInt64If("VSP-ts", mTimestamps[i]);
vsyncTS[i] = mTimestamps[i] - oldest_ts;
ordinals[i] = ((vsyncTS[i] + (currentPeriod / 2)) / currentPeriod) * kScalingFactor;
}
auto meanTS = scheduler::calculate_mean(vsyncTS);
auto meanOrdinal = scheduler::calculate_mean(ordinals);
for (size_t i = 0; i < vsyncTS.size(); i++) {
vsyncTS[i] -= meanTS;
ordinals[i] -= meanOrdinal;
}
auto top = 0ll;
auto bottom = 0ll;
for (size_t i = 0; i < vsyncTS.size(); i++) {
top += vsyncTS[i] * ordinals[i];
bottom += ordinals[i] * ordinals[i];
}
if (CC_UNLIKELY(bottom == 0)) {
it->second = {mIdealPeriod, 0};
clearTimestamps();
return false;
}
// anticipatedPeriod就是上面说的斜率
nsecs_t const anticipatedPeriod = top * kScalingFactor / bottom;
// anticipatedPeriod就是上面说的截距
nsecs_t const intercept = meanTS - (anticipatedPeriod * meanOrdinal / kScalingFactor);
auto const percent = std::abs(anticipatedPeriod - mIdealPeriod) * kMaxPercent / mIdealPeriod;
// 如果误差超过20%,重新硬件校准
if (percent >= kOutlierTolerancePercent) {
it->second = {mIdealPeriod, 0};
clearTimestamps();
return false;
}
traceInt64If("VSP-period", anticipatedPeriod);
traceInt64If("VSP-intercept", intercept);
// 把anticipatedPeriod, intercept保存到mRateMap中的value
// mRateMap的key值一个时间戳,后续分析TODO
it->second = {anticipatedPeriod, intercept};
ALOGV("model update ts: %" PRId64 " slope: %" PRId64 " intercept: %" PRId64, timestamp,
anticipatedPeriod, intercept);
return true;
}
2 获取SW VSync定时
在Vsync(一) app vsync中,讲了app vsync,大概要经过EventThread的threadMain,
VSyncDispatchTimerQueue的schedule,然后定时,时间到再调用callback,那么定时时间是怎么获取的呢,下面说明:
frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/Scheduler/VSyncDispatchTimerQueue.cpp
ScheduleResult VSyncDispatchTimerQueueEntry::schedule(VSyncDispatch::ScheduleTiming timing,
VSyncTracker& tracker, nsecs_t now) {
// 获取下一个nextVsyncTime,传入的参数是当前时间加一个app vsync周期
auto nextVsyncTime = tracker.nextAnticipatedVSyncTimeFrom(
std::max(timing.earliestVsync, now + timing.workDuration + timing.readyDuration));
auto nextWakeupTime = nextVsyncTime - timing.workDuration - timing.readyDuration;
bool const wouldSkipAVsyncTarget =
mArmedInfo && (nextVsyncTime > (mArmedInfo->mActualVsyncTime + mMinVsyncDistance));
bool const wouldSkipAWakeup =
mArmedInfo && ((nextWakeupTime > (mArmedInfo->mActualWakeupTime + mMinVsyncDistance)));
if (wouldSkipAVsyncTarget && wouldSkipAWakeup) {
return getExpectedCallbackTime(nextVsyncTime, timing);
}
bool const alreadyDispatchedForVsync = mLastDispatchTime &&
((*mLastDispatchTime + mMinVsyncDistance) >= nextVsyncTime &&
(*mLastDispatchTime - mMinVsyncDistance) <= nextVsyncTime);
if (alreadyDispatchedForVsync) {
nextVsyncTime =
tracker.nextAnticipatedVSyncTimeFrom(*mLastDispatchTime + mMinVsyncDistance);
nextWakeupTime = nextVsyncTime - timing.workDuration - timing.readyDuration;
}
auto const nextReadyTime = nextVsyncTime - timing.readyDuration;
mScheduleTiming = timing;
mArmedInfo = {nextWakeupTime, nextVsyncTime, nextReadyTime};
return getExpectedCallbackTime(nextVsyncTime, timing);
}
nsecs_t VSyncPredictor::nextAnticipatedVSyncTimeFrom(nsecs_t timePoint) const {
std::lock_guard lock(mMutex);
return nextAnticipatedVSyncTimeFromLocked(timePoint);
}
nsecs_t VSyncPredictor::nextAnticipatedVSyncTimeFromLocked(nsecs_t timePoint) const {
// slope:获取到第一章节中说到的斜率
// intercept:获取到第一章节中说到的截距
auto const [slope, intercept] = getVSyncPredictionModelLocked();
if (mTimestamps.empty()) {
traceInt64If("VSP-mode", 1);
auto const knownTimestamp = mKnownTimestamp ? *mKnownTimestamp : timePoint;
auto const numPeriodsOut = ((timePoint - knownTimestamp) / mIdealPeriod) + 1;
return knownTimestamp + numPeriodsOut * mIdealPeriod;
}
auto const oldest = *std::min_element(mTimestamps.begin(), mTimestamps.end());
// See b/145667109, the ordinal calculation must take into account the intercept.
// zeroPoint : 零点,基准点。
auto const zeroPoint = oldest + intercept;
// timePoint - zeroPoint + slope:当前时间距离基准点的差,再加一个斜率(周期),
// 即:下一个距离基准点的sw sync时间;
// 除以slope,即:ordinalRequest = 下一个sw sync周期的次数
auto const ordinalRequest = (timePoint - zeroPoint + slope) / slope;
// ordinalRequest * slope:下一个周期需要的时间
// 再+ intercept + oldest,即: 下一个sw sync的时间
auto const prediction = (ordinalRequest * slope) + intercept + oldest;
traceInt64If("VSP-mode", 0);
traceInt64If("VSP-timePoint", timePoint);
traceInt64If("VSP-prediction", prediction);
auto const printer = [&, slope = slope, intercept = intercept] {
std::stringstream str;
str << "prediction made from: " << timePoint << "prediction: " << prediction << " (+"
<< prediction - timePoint << ") slope: " << slope << " intercept: " << intercept
<< "oldestTS: " << oldest << " ordinal: " << ordinalRequest;
return str.str();
};
ALOGV("%s", printer().c_str());
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(prediction < timePoint, "VSyncPredictor: model miscalculation: %s",
printer().c_str());
//prediction 就是下一个软件vsync时间
return prediction;
}
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容








所有评论(0)