Thread 类的基本用法
代码中Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()查看该线程的中断标志位是否为true,t.interrupt()将该线程的中断标志位设置为true,整体流程就是JVM 启动主线程执行。的方法,将线程设置为阻塞状态,也就是休眠状态,他们在休眠状态下无法自己检查是否到了被唤醒的时间,这个时候就需要一个异常提醒,把阻塞线程唤醒,看自己是不是应该为中断状态,join()的
线程创建的五种方法
方法一:继承Thread类
public class Main {
static class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("线程的继承创建方法");;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new MyThread();
t.start();
}
}方法二:实现Runnable 接口
public class Main {
static class MyThread implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("线程实现Runnable接口的创建方法");;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(new MyThread());
t.start();
}
}方法三:使用匿名类创建 Thread ⼦类对象
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("线程创建");;
}
};
t.start();
}
}方法四:使用匿名内部类创建Runnable⼦类对象
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("线程创建");;
}
});
t.start();
}
}方法五:使用lambda表达式创建
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("线程创建");
});
t.start();
}
}线程的中断
在线程的中断中主要是使用了,isInterrupted()和interrupt()这两个方法,代码中Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()查看该线程的中断标志位是否为true,t.interrupt()将该线程的中断标志位设置为true,整体流程就是JVM 启动主线程执行 main 方法,主线程中创建并启动子线程 t,先让main线程阻塞等待10s,让t线程每个5s打印一次,当main线程等待10s后,将t线程的中断位修改为true,将t线程中断退出循环。
这里面又一次体会到了为什么sleep要抛出异常,因为(sleep,wait,join)的方法,将线程设置为阻塞状态,也就是休眠状态,他们在休眠状态下无法自己检查是否到了被唤醒的时间,这个时候就需要一个异常提醒,把阻塞线程唤醒,看自己是不是应该为中断状态,这里所说的线程中断,并不是把线程直接给中断了而是告诉线程你应该中断了,但线程是否为中断状态这是线程自己的逻辑决定的,就像自己睡着了,但是无法准时的醒来,这时候就需要一个闹铃,闹铃响了提醒你该起床了,但是起不起床还是取决自己。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
while(!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){
System.out.println("线程正在运行");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("线程中断");
Thread.currentThread().isInterrupt();
break;
}
}
System.out.println("线程运行结束");
});
t.start();
Thread.sleep(10000);
t.interrupt();
}
}运行结果:

线程等待
线程的等待是通过join()方法来实现的,核心作用是让当前线程阻塞,直到目标线程执行完毕。简单可以理解就是哪一个线程使用join他就插队插进来,让这个插队线程先执行完。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("进入t线程");
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
try {
System.out.println("第"+i+"s");
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
System.out.println("退出t线程");
});
t.start();
System.out.println("main线程开始等待");
t.join();
System.out.println("main线程等待结束");
}
}运行结果

但是如果有多个线程进行join(),那么就意味着这些线程都插队了,但是这些“插队”线程没有谁优先,他们都是对CPU进行抢占式运行的。还有关键一点必须在 start() 后调用,否则无效。
运行结果:下面是我进行了两次运行结果,可以看出他们的打印没有顺序。但是main线程会等待所有线程运行结束在继续运行。

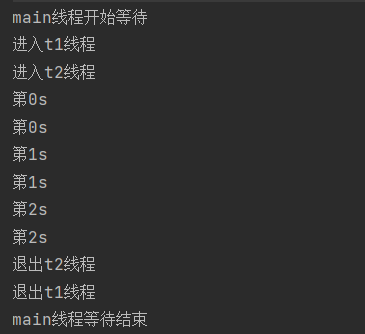
join()带参数的方法
join()的括号里输入时间数,这个时间可以理解为这个插队线程最多能插队多长时间,过了这个时间就该我的main线程运行了。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("进入t1线程");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("退出t1线程");
});
t1.start();
System.out.println("main线程开始等待");
t1.join(2000);//main线程最多等待2s
System.out.println("main线程等待结束");
}
}运行结果:在运行结果可以看出main线程等了2s后继续运行。
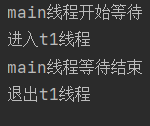
线程的休眠
线程休眠就是使用Thread.sleep()方法,让线程进入阻塞状态,暂停执行指定毫秒数,时间结束后自动唤醒并进入就绪状态等待 CPU 调度。这个里面的时间是ms为单位的。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("进入t1线程");
for(int i=1;i<4;i++){
System.out.println("等待第"+i+"s");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
System.out.println("退出t1线程");
});
t1.start();
System.out.println("main线程:开始等待t1线程执行完毕...");
t1.join();
System.out.println("main线程:等待结束");
System.out.println("main线程:执行结束");
}
}运行结果:
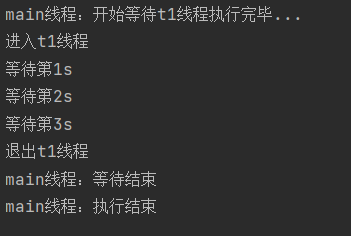
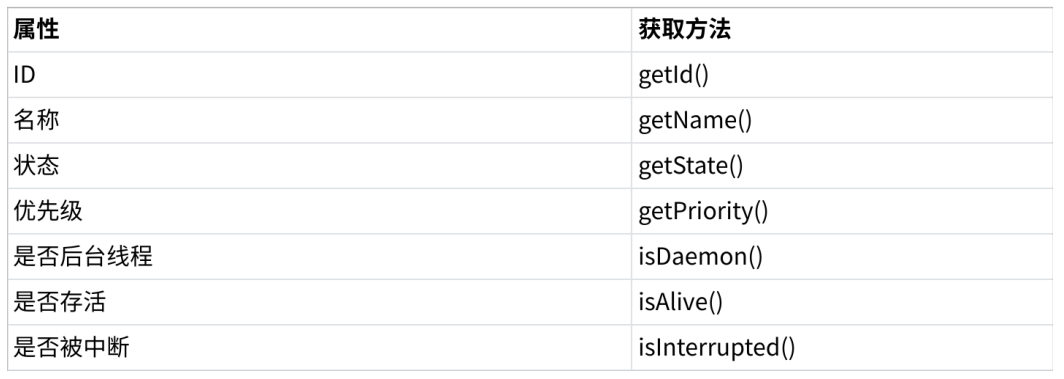
获取线程实例
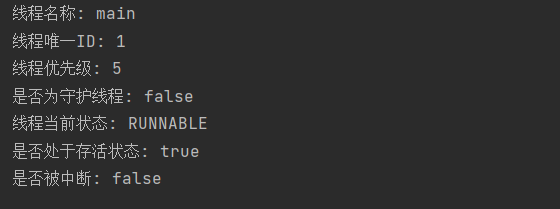
获取线程实例主要通过 Thread.currentThread() 方法,它能返回当前正在执行代码的线程对象。通过这个实例,可以获取线程的各种信息(如名称、状态、优先级等),也能对线程进行操作(如设置名称、中断线程等)。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println("线程名称: " + t1.getName());
System.out.println("线程唯一ID: " + t1.getId());
System.out.println("线程优先级: " + t1.getPriority());
System.out.println("是否为守护线程: " + t1.isDaemon());
System.out.println("线程当前状态: " + t1.getState());
System.out.println("是否处于存活状态: " + t1.isAlive());
System.out.println("是否被中断: " + t1.isInterrupted());
}
}运行结果:
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容






所有评论(0)