企业级高性能WEB服务器Nginx
目录
2.ngx_http_rewrite_module 模块指令
什么是Nginx
Nginx 的核心功能
-
HTTP 服务器
作为传统的 Web 服务器,Nginx 可以直接处理静态资源(如 HTML、CSS、图片),支持虚拟主机配置(一台服务器托管多个网站),并能通过 URL 重写、缓存控制等功能优化访问体验。 -
反向代理
Nginx 可以作为中间层接收客户端请求,再将请求转发给后端的应用服务器(如 Tomcat、Node.js、Python 服务等),并将后端的响应返回给客户端。- 作用:隐藏后端服务器的真实地址,提高安全性;实现负载均衡(分发请求到多个后端服务器,避免单节点压力过大)。
-
负载均衡
当后端有多台服务器时,Nginx 可通过预设策略(如轮询、权重、IP 哈希等)将请求分配到不同服务器,确保服务的高可用性和稳定性。例如,电商网站的高峰期流量可通过负载均衡分摊到多台应用服务器,避免卡顿或崩溃。 -
缓存服务
Nginx 可缓存后端服务器的响应结果(如静态页面、API 返回数据),当后续有相同请求时直接返回缓存内容,减少后端服务器的处理压力,提高响应速度。 -
SSL/TLS 终端
处理 HTTPS 请求,负责 SSL 证书的解密和加密过程,减轻后端服务器的加密解密负担,同时保障数据传输的安全性。
Nginx 的优势
- 高性能:采用异步非阻塞的事件驱动模型,能高效处理数万并发连接,资源消耗(CPU、内存)极低。
- 稳定性:设计简洁,容错能力强,即使部分请求失败也不影响整体服务运行。
- 灵活可扩展:支持模块化配置,可通过第三方模块扩展功能(如防盗链、限流等)。
- 跨平台:可运行在 Linux、Windows、macOS 等多种操作系统,尤其在 Linux 服务器中应用广泛。
典型应用场景
- 大型网站的静态资源服务(如图片、JS/CSS 文件)。
- 微服务架构中的 API 网关(统一接收请求,转发到不同微服务)。
- 负载均衡器(分发流量到多个应用服务器)。
- 反向代理(隐藏后端服务,实现动静分离:静态资源由 Nginx 处理,动态请求转发给应用服务器)。
总之,Nginx 是一款轻量、高效、多功能的服务器工具,在现代 Web 架构中扮演着关键角色,是构建高可用、高并发服务的核心组件之一。许多知名网站(如淘宝、京东、Netflix 等)都依赖 Nginx 保障服务的稳定运行。
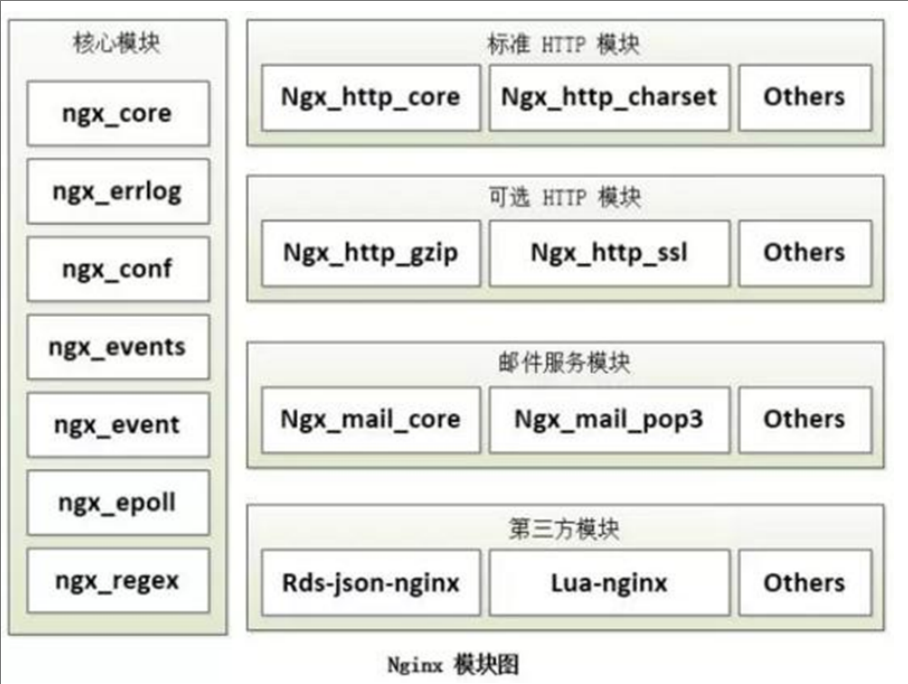
Nginx 模块介绍
Nginx 有多种模块
- 核心模块:是 Nginx 服务器正常运行必不可少的模块,提供错误日志记录 、配置文件解析 、事件 驱动机制 、进程管理等核心功能
- 标准HTTP模块:提供 HTTP 协议解析相关的功能,比如: 端口配置 、 网页编码设置 、 HTTP响应 头设置 等等
- 可选HTTP模块:主要用于扩展标准的 HTTP 功能,让 Nginx 能处理一些特殊的服务,比如: Flash
- 多媒体传输 、解析 GeoIP 请求、 网络传输压缩 、 安全协议 SSL 支持等
- 邮件服务模块:主要用于支持 Nginx 的 邮件服务 ,包括对 POP3 协议、 IMAP 协议和 SMTP协议的 支持
- Stream服务模块: 实现反向代理功能,包括TCP协议代理
- 第三方模块:是为了扩展 Nginx 服务器应用,完成开发者自定义功能,比如: Json 支持、 Lua 支 持等
Nginx安装
1.nginx编译安装
#在nginx官网获取安装包
[root@webserver mnt]# wget https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.24.0.tar.gz
#解压安装包
[root@webserver mnt]# tar zxf nginx-1.24.0.tar.gz
[root@webserver mnt]# cd nginx-1.24.0/
#安装编译nginx需要的环境软件
[root@webserver mnt]# dnf install gcc pcre-devel zlib-devel openssl-devel -y
#创建运行nginx的用户,-M不指定家目录
[root@webserver nginx-1.24.0]# useradd -s /sbin/nologin -M nginx
[root@webserver nginx-1.24.0]# ls
auto CHANGES CHANGES.ru conf configure contrib html LICENSE man README src
#配置编译环境
[root@webserver nginx-1.24.0]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx \ #指定安装路径
--user=nginx \ # 指定nginx运行用户
--group=nginx \ # 指定nginx运行组
--with-http_ssl_module \ # 支持https://
--with-http_v2_module \ # 支持http版本2
--with-http_realip_module \ # 支持ip透传
--with-http_stub_status_module \ # 支持状态页面
--with-http_gzip_static_module \ # 支持压缩
--with-pcre \ # 支持正则
--with-stream \ # 支持tcp反向代理
--with-stream_ssl_module \ # 支持tcp的ssl加密
--with-stream_realip_module # 支持tcp的透传ip
#开始编译
[root@webserver nginx-1.24.0]# make
#安装nginx
[root@webserver nginx-1.24.0]# make install
#完成安装以后,有四个主要的目录
[root@webserver nginx-1.24.0]# ls /usr/local/nginx/
client_body_temp conf fastcgi_temp html logs proxy_temp sbin scgi_temp uwsgi_temp
#conf 保存nginx所有的配置文件目录
#html 保存nginx服务器的web文件
#logs 保存nginx服务器访问日志错误日志等
#sbin 保存nginx二进制启动脚本2.添加nginx到环境变量
[root@webserver nginx-1.24.0]# echo export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/nginx/sbin/ >> ~/.bash_profile
#使新添加的参数生效
[root@webserver nginx-1.24.0]# source ~/.bash_profile
#验证版本及编译参数
[root@webserver nginx-1.24.0]# nginx -V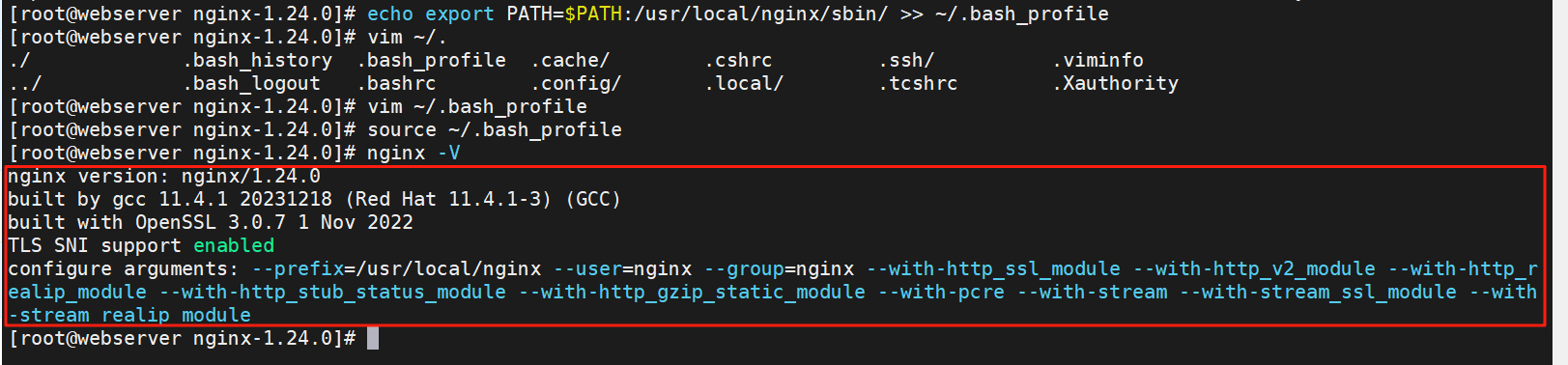
3.平滑升级和回滚
nginx的平滑升级与回滚是在不重启服务的情况下来操作,避免正在访问的服务中断
1.编译要升级版本
#对要升级的版本进行编译
[root@nginx mnt]# tar zxf nginx-1.26.1.tar.gz
[root@nginx mnt]# cd nginx-1.26.1/
[root@nginx nginx-1.26.1]# ls
auto CHANGES CHANGES.ru conf configure contrib html LICENSE man README src
#关闭编译时的显示的调试信息
[root@nginx nginx-1.26.1]# vim auto/cc/gcc
# debug
#CFLAGS="$CFLAGS -g"
#修改HTTP响应头信息的server软件信息
[root@nginx nginx-1.26.1]# vim src/core/nginx.h
#define NGINX_VERSION "6.6.6"
#define NGINX_VER "fjw/" NGINX_VERSION
[root@nginx nginx-1.26.1]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_realip_module
[root@nginx nginx-1.26.1]# make2. 平滑升级
#切换到二进制启动脚本目录,进行平滑升级
[root@nginx ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin/
#对旧版本进行备份
[root@nginx sbin]# cp nginx nginx.old
#把要升级的新版本拷贝过来
[root@nginx sbin]# /bin/cp -f /mnt/nginx-1.26.1/objs/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
[root@nginx sbin]# ll
total 11156
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 5746872 Jul 25 01:08 nginx
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 5671480 Jul 25 01:05 nginx.old
[root@nginx sbin]# ps aux | grep nginx
root 42282 0.0 0.0 9876 2052 ? Ss 01:10 0:00 nginx: master process
nginx 42283 0.0 0.1 14208 4996 ? S 01:10 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 42287 0.0 0.0 221664 2176 pts/0 S+ 01:10 0:00 grep --color=auto
#-USR2对旧nginx进行平滑升级,重载生成新进程
[root@nginx sbin]# kill -USR2 42282 #旧nginx,masterPID
[root@nginx sbin]# ps aux | grep nginx
root 42282 0.0 0.0 9876 2436 ? Ss 01:10 0:00 nginx: master process
nginx 42283 0.0 0.1 14208 4996 ? S 01:10 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 42288 0.0 0.1 9876 6528 ? S 01:13 0:00 nginx: master process
nginx 42289 0.0 0.1 14208 4996 ? S 01:13 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 42291 0.0 0.0 221664 2176 pts/0 S+ 01:13 0:00 grep --color=auto
#-WINCH回收旧nginx也是masterPID
[root@nginx sbin]# kill -WINCH 42283
[root@nginx sbin]# ps aux | grep nginx
root 42282 0.0 0.0 9876 2436 ? Ss 01:10 0:00 nginx: master process
root 42288 0.0 0.1 9876 6528 ? S 01:13 0:00 nginx: master process
nginx 42289 0.0 0.1 14208 4996 ? S 01:13 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 42294 0.0 0.0 221664 2176 pts/0 S+ 01:14 0:00 grep --color=auto
#查看版本,新版本生效
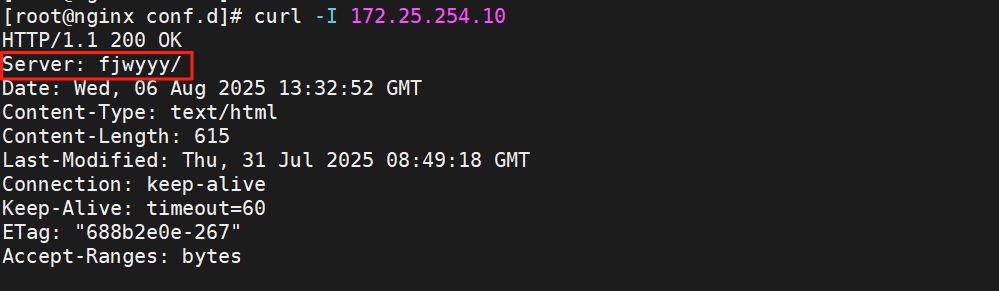
[root@nginx sbin]# nginx -V
nginx version: fjw/6.6.6
......
测试
[root@nginx sbin]# curl -I 172.25.254.11
#如果旧版本的进程没用的话就可以kill -9删除了
[root@nginx sbin]# kill -9 42283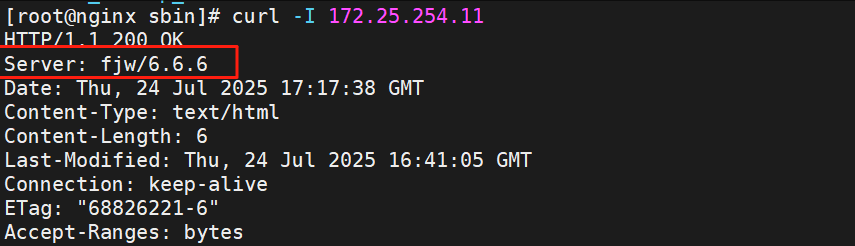
3.版本回滚
#对nginx版本进行回滚
#如果发现升级后新版本有问题,可以重新垃圾旧版本的worker
[root@nginx sbin]# cp nginx nginx.new
[root@nginx sbin]# ls
nginx nginx.new nginx.old
[root@nginx sbin]# mv nginx.old nginx
mv: overwrite 'nginx'? y
[root@nginx sbin]# ls
nginx nginx.new
#重新拉起旧版本nginx的worker
[root@nginx sbin]# kill -HUP 42282 #master
#回收新版本的worker
[root@nginx sbin]# kill -WINCH 42288 #master的pid
[root@nginx sbin]# nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.24.0
测试
[root@nginx sbin]# curl -I 172.25.254.11
#如果新版本的进程没用的话就可以kill -9删除了
[root@nginx sbin]# kill -9 4228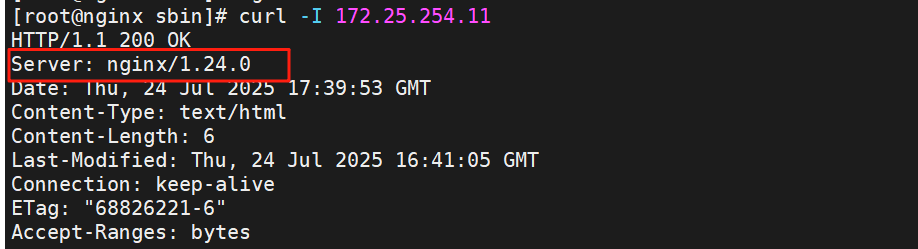
4.nginx生成启动文件systemd
生成systemd可以实现开机自启动
#百度搜索模板
systemd site:nginx.org #搜索内容 site:搜索网址
[root@webserver ~]# cd /lib/systemd/system
[root@webserver system]# vim nginx.service
[Unit]
Description=The NGINX HTTP and reverse proxy server
After=syslog.target network.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid #指定nginx启动的pid
ExecStartPre=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t #指定nginx -t检查配置文件命令
ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx #指定nginx启动命令
ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID
ExecStop=/bin/kill -s QUIT $MAINPID
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
#使编写的配置生效
[root@webserver system]# systemctl daemon-reload
#在启动时要确保nginx已经关闭不然会冲突导致报错
[root@webserver system]# systemctl enable --now nginxNginx核心配置详解
1.nginx主配置文件说明
主配置文件结构:四部分
main block:主配置段,即全局配置段
#事件驱动相关的配置
event {
...
}#http/https 作为web服务器相关配置段
http {
...
}#默认配置文件不包括下面两个部分
#mail 作为邮件服务器相关配置段
mail {
...
}#stream 反向代理相关配置段
stream {
...
}
2.全局配置参数
默认打开全局配置参数

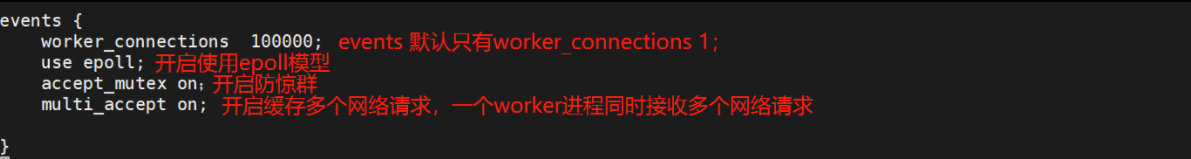
3.events配置参数
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
events {
worker_connections 100000; #单个工作进程最大并发数
use epoll; #使用epoll机制来实现高并发
} #Nginx支持众多的事件驱动,
#比如:select、poll、epoll,只能设置在events模块中设置4.http块配置参数
http块是Nginx服务器配置中的重要部分,缓存、代理和日志格式定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块都可以在这设置,http块可以包含多个server块,而一个server块中又可以包含多个location块。
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
http {
#在响应报文中将指定的文件扩展名映射至MIME对应的类型
include mime.types; #可以识别文本,图像,音频,视频等其他的数据
default_type application/octet-stream; #没有识别的默认类型,例如php,ngxin不识别需要安装php才能渲染呈现
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log logs/access.log main; #使用定义为main的日志格式,存放在根目录的logs/access.log中
sendfile on; #零拷贝功能,sendfile系统调用在两个文件描述符之间直接传递数据(完全在内核中操作)
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65; #长连接超时时间,单位是s
#gzip on; #开启压缩功能
server {
#web服务配置
}
include "/usr/local/nginx/conf.d/*.conf"; #导入其他路径的配置文件,子配置文件
#要放在默认发布文件目录下,不然会覆盖默认
}5.核心配置示例
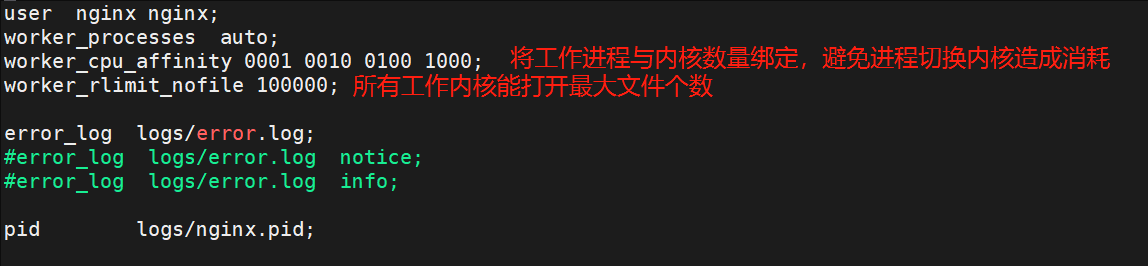
1.nginx的高并发配置
#编辑配置文件设置参数
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
user nginx nginx;
worker_processes auto;
worker_cpu_affinity 0001 0010 0100 1000;
worker_rlimit_nofile 100000; #设置每个工作进程最大能打开的文件个数,此参数要与系统级别的最大打开文件数相同要与ulimit -n的个数相同
error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 100000; #设置单个工作进程最大并发数
use epoll;
}
#设置系统的每个进程打开的最大打开文件数
[root@nginx ~]# vim /etc/security/limits.conf
* - nofile 100000 #打开文件最大个数
* - nproc 100000 #打开程序最大个数
[root@nginx ~]# ulimit -n 100000 #设置当前或者重启shell
[root@nginx ~]# ulimit -n #查看个数
100000
#安装apache工具包中的压力测试工具ab
[root@webserver ~]# dnf install httpd-tools -y
#-n总请求数 -c每次并发数
[root@webserver ~]# ab -n 100000 -c 5000 http://172.25.254.10/index.html2.识别php文件为text/html类型
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/html/index.php
<?php
phpinfo()
?>
[root@nginx ~]# curl -I 172.25.254.10/index.php
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.26.1
Date: Sun, 03 Aug 2025 12:31:48 GMT
Content-Type: application/octet-stream #php不属于mime类型中,所以使用默认
Content-Length: 23
Last-Modified: Sun, 03 Aug 2025 11:17:36 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
ETag: "688f4550-17"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
[root@Nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
default_type text/html;
[root@nginx ~]# curl -I 172.25.254.10/index.php
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.26.1
Date: Sun, 03 Aug 2025 12:35:22 GMT
Content-Type: text/html #将识别类型改为text/html
Content-Length: 23
Last-Modified: Sun, 03 Aug 2025 11:17:36 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
ETag: "688f4550-17"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
[root@Nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
default_type test/php;
[root@nginx ~]# curl -I 172.25.254.10/index.php
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.26.1
Date: Sun, 03 Aug 2025 12:35:22 GMT
Content-Type: test/php #可以自定义将识别不出来的设为想要的类型
Content-Length: 23
Last-Modified: Sun, 03 Aug 2025 11:17:36 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
ETag: "688f4550-17"
Accept-Ranges: bytes3.基于域名的web站点发布
#创建基于域名的发布根目录
[root@nginx ~]# mkdir /web/html -p
#生成发布文件
[root@nginx ~]# echo index.html > /web/html/index.html
#创建子配置目录
[root@nginx ~]# mkdir /usr/local/nginx/conf.d
#创建子配置文件
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
}
#添加本地解析
[root@nginx ~]# vim /etc/hosts
[root@nginx ~]# nginx -t
[root@nginx ~]# nginx -s reload
#测试
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org
index.html4.root和alias
-
root:指定web的家目录,在定义location的时候,文件的绝对路径等于 root+location
-
alias:定义路径别名,会把访问的路径重新定义到其指定的路径,文档映射的另一种机制;仅能用于 location上下文,此指令使用较少

测试
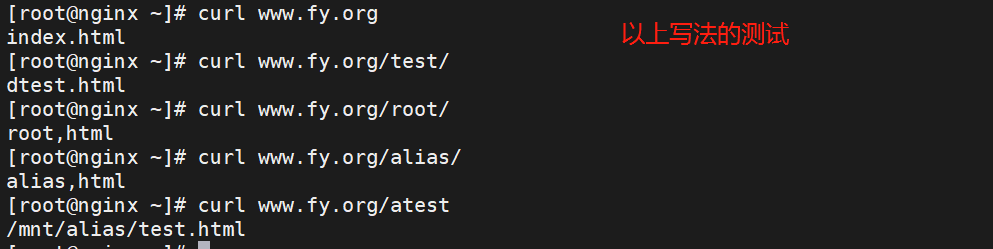
补充
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
location /fjw {
root /mnt;
}
#当location后面/跟的是一个文件时,直接访问的是/mnt/fjw这个文件
测试
[root@nginx ~]# echo 11 > /mnt/fjw
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/fjw
115.location的详细使用
location是用于匹配请求 URI(统一资源标识符)的核心配置指令,它可以根据不同的 URI 路径设置不同的处理规则(如反向代理、静态文件访问、重定向等)。
修饰符与匹配规则
Nginx 的`location`匹配遵循 “优先匹配特定规则,再匹配通用规则”的原则,不同修饰符对应不同的优先级(从高到低排序):
| 修饰符 | 名称 | 匹配规则 | 优先级 |
|---|---|---|---|
= |
精确匹配 | 仅匹配与匹配路径完全一致的 URI。 |
最高 |
^~ |
前缀匹配(优先) | 匹配以匹配路径为前缀的 URI,且一旦匹配成功,不再检查其他正则匹配,区分大小写,也包含正则。 |
次高 |
| 无 | 一般匹配(普通) | 匹配以匹配路径为前缀的 URI,但优先级低于正则匹配,不识别正则表达式。 |
较低 |
~ |
正则匹配(区分大小写) | 按正则表达式匹配 URI,区分大小写。 | 较高 |
~* |
正则匹配(不区分大小写) | 按正则表达式匹配 URI,不区分大小写(如匹配.html和.HTML)。 |
较高 |
#匹配优先级从高到低:
"=" > "^~" > "~/~*",不带符号
1.示例-精准匹配
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
location = /test {
return 200 "punct = \n"; #returun 200.只要访问/test无论是否存在都会返回200存在成功,并输出"punct = \n"
}
}
#测试
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test
punct =
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test1
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/1test
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>404 Not Found</h1></center>2.示例-正则前缀匹配
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
# location = /test {
# return 200 "punct = \n";
# }
location ^~ /test {
return 200 "punct = ^~\n";
}
}
#测试
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test
punct = ^~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test/a/b
punct = ^~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/testc
punct = ^~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/aatestc
\<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>404 Not Found</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.26.1</center>
</body>
</html>
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/TEST #区分大小写
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>404 Not Found</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.26.1</center>
</body>
</html>
3.示例-正则匹配(区分大小写)
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
# location = /test {
# return 200 "punct = \n";
# }
# location ^~ /test {
# return 200 "punct = ^~\n";
# }
location ~ /test {
return 200 "punct = ~\n";
}
}
#测试
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test
punct = ~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/testa
punct = ~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test/a/
punct = ~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/atest
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>404 Not Found</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx/1.26.1</center>
</body>
</html>
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/a/test #匹配的是url要加/
punct = ~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/a/TEST #也区分大小写
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>4.示例-正则匹配(不区分大小写)
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
# location = /test {
# return 200 "punct = \n";
# }
# location ^~ /test {
# return 200 "punct = ^~\n";
# }
# location ~ /test {
# return 200 "punct = ~\n";
# }
location ~* /test {
return 200 "punct = ~*\n";
}
}
#测试
#效果基本与正则匹配一致,只是不区分大小写
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test
punct = ~*
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/TEST
punct = ~*
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/a/TEST
punct = ~*
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/aTEST
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>5.示例-一般匹配
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
# location = /test {
# return 200 "punct = \n";
# }
# location ^~ /test {
# return 200 "punct ^~\n";
# }
# location ~ /test {
# return 200 "punct ~\n";
# }
# location ~* /test {
# return 200 "punct ~*\n";
# }
location /test {
return 200 "punct \'\' \n";
}
}
#测试
#类似前缀匹配^~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test
punct ''
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test/a
punct ''
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/testa
punct ''
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/atest
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/a/test/a
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>
6.示例-"\"的作用
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
# location = /test {
# return 200 "punct = \n";
# }
# location ^~ /test {
# return 200 "punct ^~\n";
# }
# location ~ /test {
# return 200 "punct ~\n";
# }
# location ~* /test {
# return 200 "punct ~*\n";
# }
# location /test {
# return 200 "punct \'\' \n";
# }
location ~* \.(png|JPG|CSS)$ { #命中结尾的文件,且不区分大小写
return 200 "punct ~\n";
}
}
#测试
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/fjw.css
punct ~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/fjw.png
punct ~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/fjw.PNG
punct ~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/fjw
<html>
<head><title>404 Not Found</title></head>7.示例-检测优先级
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
location = /test {
return 200 "=\n";
}
location ^~ /test {
return 200 "^~\n";
}
location ~* /test { #~*与~优先级一致,谁在上面谁优先级就高,区别就是~*区分大小写
return 200 "~*\n";
}
location ~ /test {
return 200 "~\n";
}
}
#测试
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test
=
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/testa
^~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/a/test
~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/a/TEST
~*
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/TEST
~*补充
#^~ 与 无符号 不能同时存在不然会报错只能存在其一
#由于无符号的前缀匹配优先级最低
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
location /test {
return 200 "haha\n"; #优先级最低
}
location = /test {
return 200 "=\n";
}
location ~ /test {
return 200 "~\n";
}
location ~* /test {
return 200 "~*\n";
}
}
#测试
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test
=
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/testa
~
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/Testa
~*
#当把其他location注释后剩下无符号的前缀匹配才能生效
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test
haha6.NginxWeb页面账户认证
#使用不了htpasswd时要下载httpd-tools包
#创建加密信息,-c创建,-m使用md5加密,-b非交互生成
[root@webserver ~]# htpasswd -cmb /usr/local/nginx/.httpasswd admin fjw
#进行创建后,想要添加用户认证信息不用加-c不用会覆盖
[root@webserver ~]# htpasswd -cm /usr/local/nginx/.httpasswd fjw yyy
[root@webserver ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/xixi.conf
[root@webserver ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/.httpasswd
admin:$apr1$ZT2EvYbr$jnH/kOKG/kl7FhROtSsAn1
fjw:$apr1$V0/Pg44B$R63GtnSgfWH.ff0tEoTlf.
#生成测试文件
[root@webserver ~]# mkidr /web/login/index.html
[root@webserver ~]# echo login > /web/login/index.html
[root@webserver ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/xixi.conf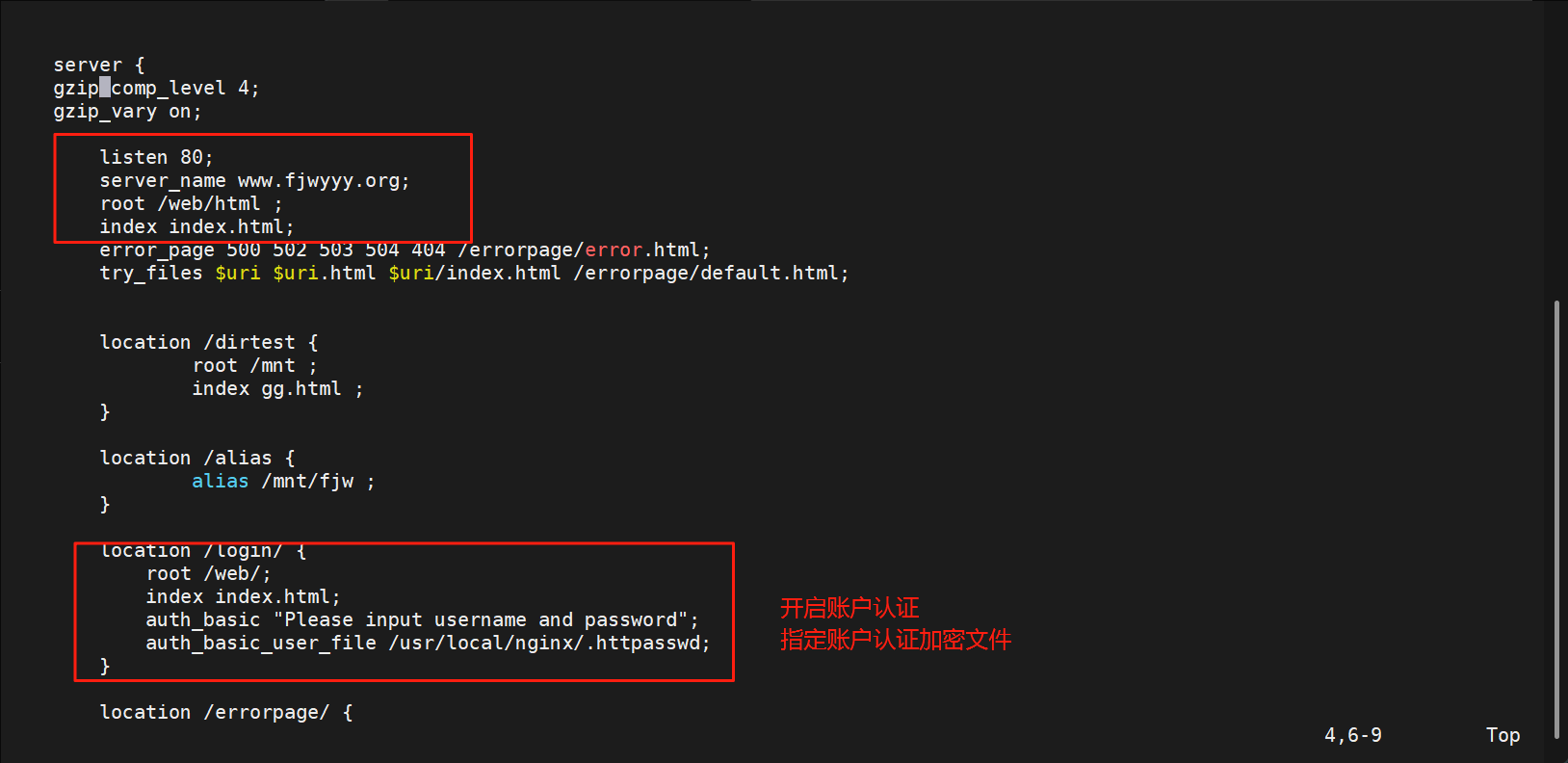
测试
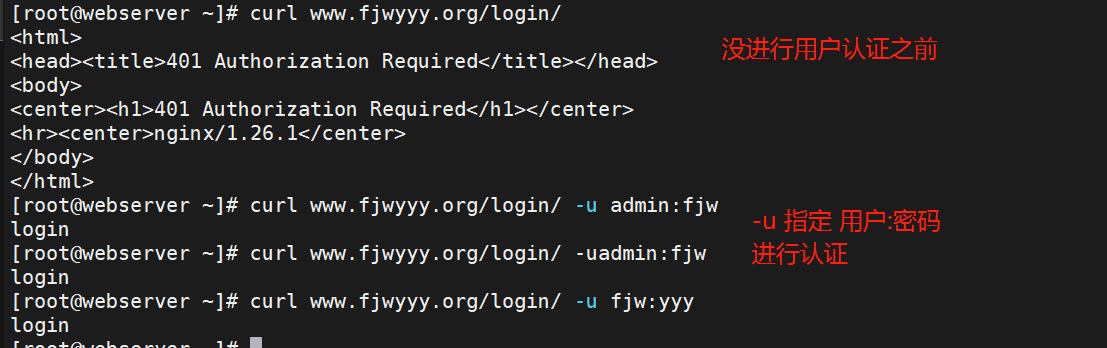
7.自定义错误页面
#生成测试文件
[root@webserver ~]# mkdir /web/errorpage/error.html
[root@webserver ~]# echo errorerror /web/errorpage/error.html
[root@webserver ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/xixi.conf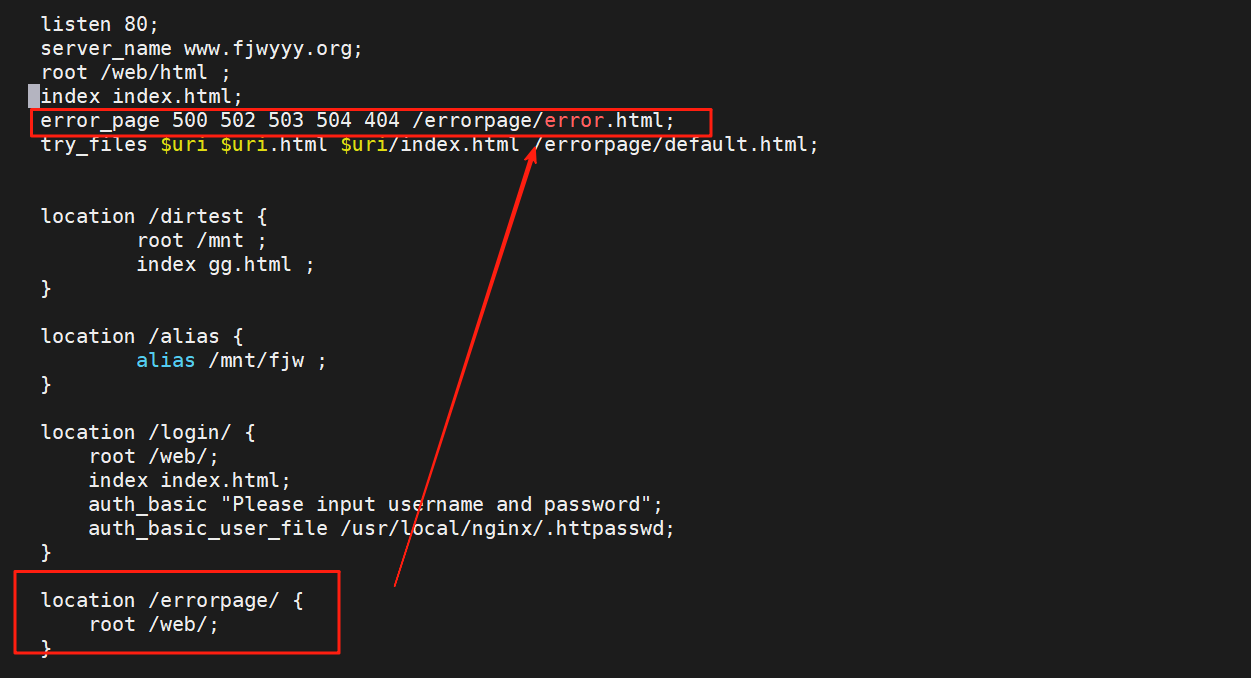
测试

补充
#也可不适用location+root来映射,可以直接使用绝对路径
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
error_page 500 502 503 504 404 /web/errorpage/error.html; #使用绝对路径
error_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/fy.org.err;
access_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/fy.org.access;
try_files $uri $uri.html $uri/index.html /web/errorpage/default.html;
# location /errorpage/ {
# root /web/;
# }
}
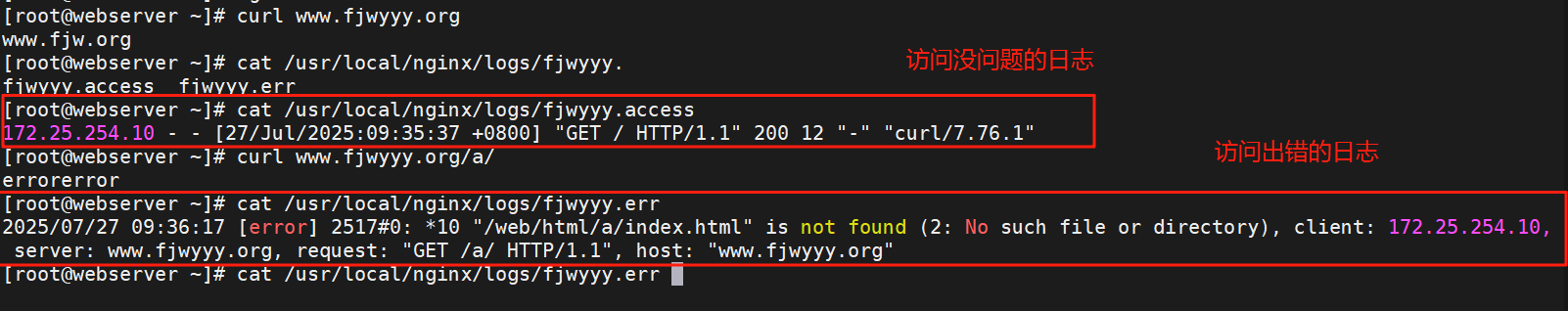
#测试效果一样8.自定义错误日志
#通过自定义错误日志可以把基于域名的虚拟主机的访问日志跟真实主机的日志分开防止过于乱
[root@webserver ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/xixi.conf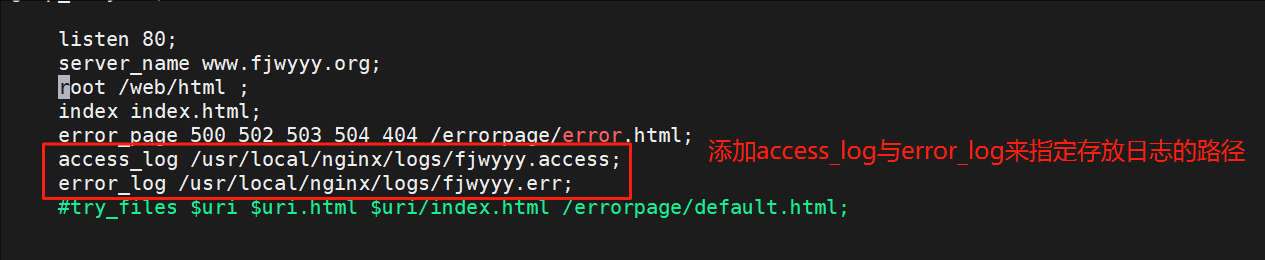
测试
9.检测文件是否存在
-
try_files会按顺序检查文件是否存在,返回第一个找到的文件或文件夹(结尾加斜线表示为文件夹),如 果所有文件或文件夹都找不到,会进行一个内部重定向到最后一个参数。
-
只有最后一个参数可以引起一 个内部重定向,之前的参数只设置内部URI的指向。
-
最后一个参数是回退URI且必须存在,否则会出现内 部500错误。
-
一般为最后一个参数创建一个默认页面
#创建默认页面
[root@nginx ~]# echo default > /web/errorpage/default.html
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
error_page 500 502 503 504 404 /errorpage/error.html;
error_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/fy.org.err;
access_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/fy.org.access;
try_files $uri $uri.html $uri/index.html /errorpage/default.html; #try_files参数
#如果都不存在就看default.html
location /errorpage/ {
root /web/;
}
}
#测试
#访问没有的资源时
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test
default
#创建资源
[root@nginx ~]# echo /web/html/test.html > /web/html/test.html
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/test
/web/html/test.html10.长连接配置
长连接配置一般在主配置文件设置,在http块中设置,设置后子配置文件的全部站点都生效;
#默认配置
http {
#keepalive_timeout 0; #长连接超时次数,在长连接期间发送三次请求就超时断开
keepalive_timeout 65; #长连接超时时间
}
#测试
#设置参数
keepalive_timeout 3;
keepalive_timeout 65 60;
#开启长连接后,返回客户端的会话保持时间为60s,单次长连接累计请求达到指定次数请求或65秒就会被断开,第二个数字60为发送给客户端应答报文头部中显示的超时时间设置为60s:如不设置客户端将不显示超时时间。
#安装测试软件
[root@nginx ~]# dnf install telnet -y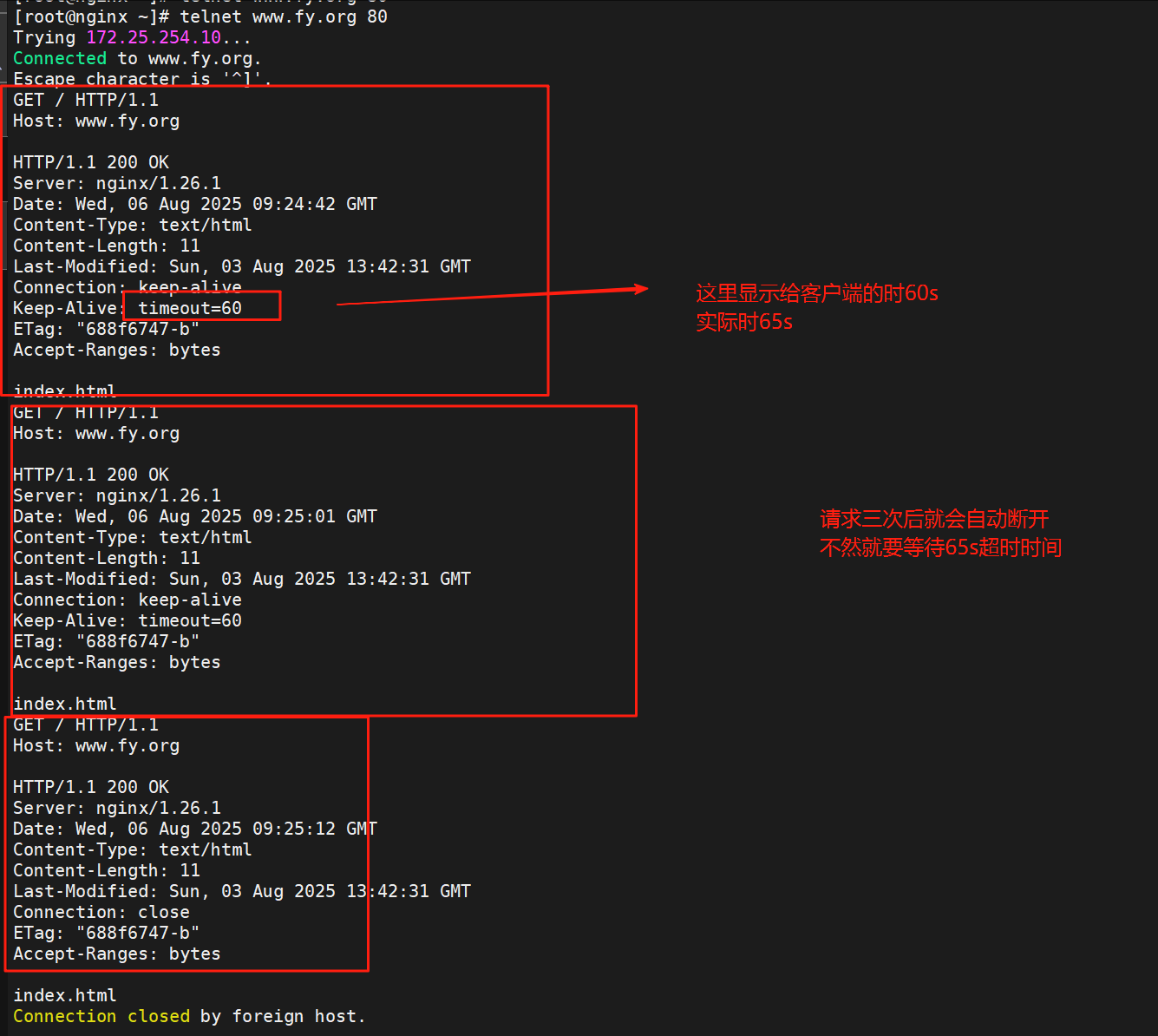
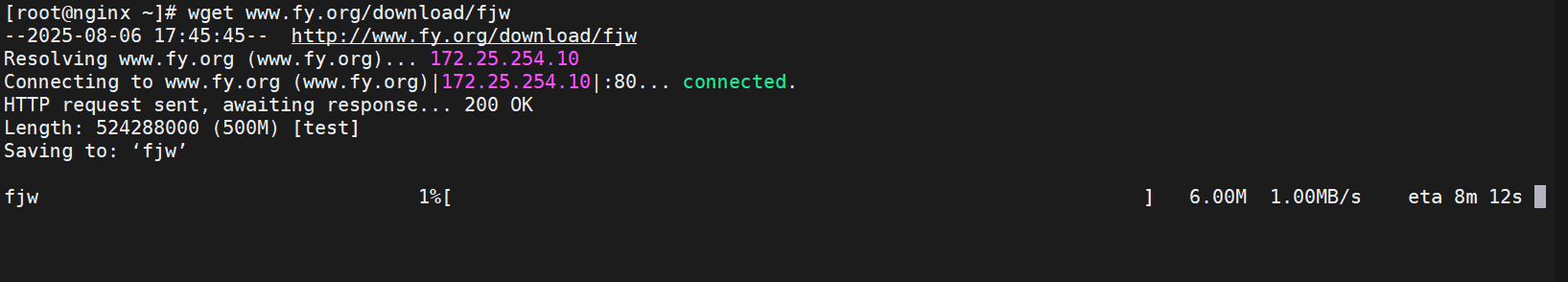
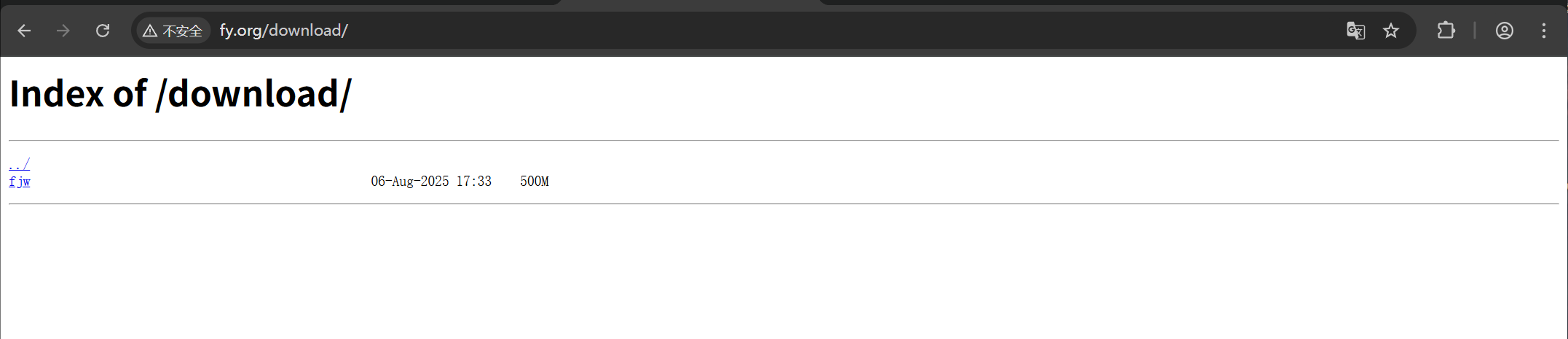
11.配置下载服务器
#创建目录,生成提供下载文件
[root@nginx ~]# mkdir /web/download
[root@nginx ~]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/web/download/fjw bs=1M count=500
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
error_page 500 502 503 504 404 /web/errorpage/error.html;
error_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/fy.org.err;
access_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/fy.org.access;
try_files $uri $uri.html $uri/index.html /web/errorpage/default.html;
[root@nginx ~]# mkdir /web/download
[root@nginx ~]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/web/download/fjw bs=1M count=500
# location /errorpage/ {
# root /web/;
# }
location /download/ {
root /web/;
autoindex on; #开启自动索引功能,由于没默认发布文件,要想作为下载服务器就要自动索引存在的文件
autoindex_exact_size off; #计算文件确切大小,off为显示大概大小(kb,mb,gb)
autoindex_localtime on; #on显示本机时间而不是格林威治时间
autoindex_format html; #设置网页显示格式,默认为html,可以设置xml,json
set $limit_rate 1024k; #限制下载速度/s,默认不限速
}
}测试
访问网页
Nginx高级配置
1.状态页
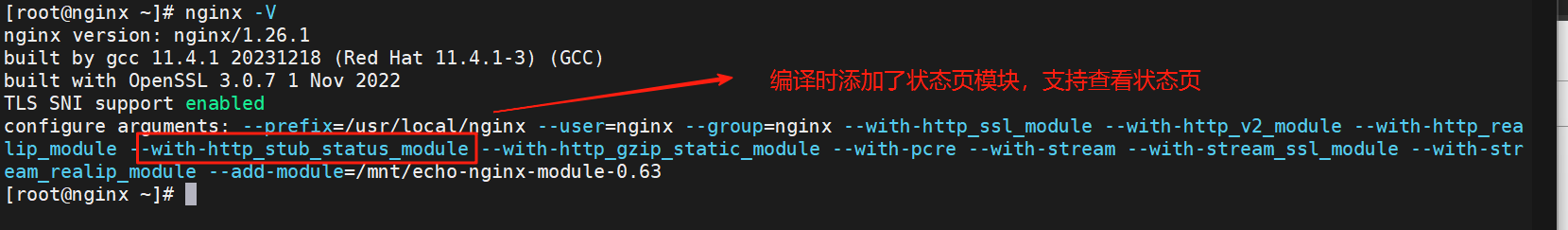
#创建认证用户,一般状态页要认证才能查看不是所有人都能看
[root@nginx ~]# htpasswd -cmb /usr/local/nginx/.htpasswd admin fjw
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
index index.html;
error_page 500 502 503 504 404 /web/errorpage/error.html;
error_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/fy.org.err;
access_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/fy.org.access;
try_files $uri $uri.html $uri/index.html /web/errorpage/default.html;
location /status {
stub_status; #打开状态页功能
auth_basic "status page" #认证提示
auth_basic_user_file "/usr/local/nginx/.htpasswd"; #认证存放文件
}测试
输入认证后查看状态页信息
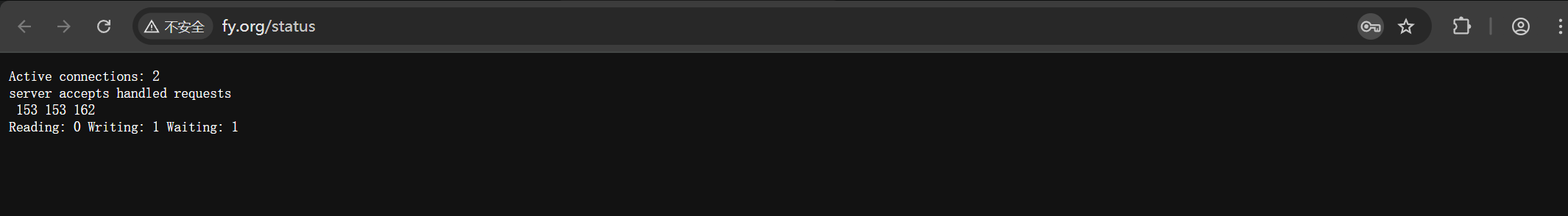
#状态页信息参数
Active connections: #当前处于活动状态的客户端连接数
#包括连接等待空闲连接数=reading+writing+waiting
accepts: #统计总值,Nginx自启动后已经接受的客户端请求连接的总数。
handled: #统计总值,Nginx自启动后已经处理完成的客户端请求连接总数
#通常等于accepts,除非有因worker_connections限制等被拒绝的连接
requests: #统计总值,Nginx自启动后客户端发来的总的请求数
Reading: #当前状态,正在读取客户端请求报文首部的连接的连接数
#数值越大,说明排队现象严重,性能不足
Writing: #当前状态,正在向客户端发送响应报文过程中的连接数,数值越大,说明访问量很大
Waiting: #当前状态,正在等待客户端发出请求的空闲连接数开启 keep-alive的情况下,这个值等于active – (reading+writing)2.压缩功能
Nginx支持对指定类型的文件进行压缩然后再传输给客户端,而且压缩还可以设置压缩比例,压缩后的文 件大小将比源文件显著变小,样有助于降低出口带宽的利用率,降低企业的IT支出,不过会占用相 应的CPU资源。
Nginx对文件的压缩功能是依赖于模块 ngx_http_gzip_module,默认是内置模块。
#配置参数如下
#启用或禁用gzip压缩,默认关闭
gzip on | off;
#压缩比由低到高从1到9,默认为1,值越高压缩后文件越小,但是消耗cpu比较高。基本设定未4或者5
gzip_comp_level 4;
#禁用IE6 gzip功能,早期的IE6之前的版本不支持压缩
gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6]\.";
#gzip压缩的最小文件,小于设置值的文件将不会压缩
gzip_min_length 1k;
#启用压缩功能时,协议的最小版本,默认HTTP/1.1
gzip_http_version 1.0 | 1.1;
#指定Nginx服务需要向服务器申请的缓存空间的个数和大小,平台不同,默认:32 4k或者16 8k;
gzip_buffers number size;
#指明仅对哪些类型的资源执行压缩操作;默认为gzip_types text/html,不用显示指定,否则出错
gzip_types mime-type ...;
#如果启用压缩,是否在响应报文首部插入“Vary: Accept-Encoding”,一般建议打开
gzip_vary on | off;
#预压缩,即直接从磁盘找到对应文件的gz后缀的式的压缩文件返回给用户,无需消耗服务器CPU
#注意: 来自于ngx_http_gzip_static_module模块
gzip_static on | off;#实验配置
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
http {
......
gzip on;
gzip_comp_level 4;
gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6]\.";
gzip_min_length 1024k;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_static on;
......
}
[root@nginx ~]# nginx -t
[root@nginx ~]# nginx -s reload
#生成测试文件
[root@nginx ~]# echo small > /usr/local/nginx/html/small.html
[root@nginx ~]# du -sh /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
4.0K /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
[root@nginx ~]# cp /web/download/fjw /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/big.html
[root@nginx ~]# du -sh /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/big.html
500M /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/big.html
#测试
#--head 仅获取响应头,不下载正文 --compressed告知服务器可接受压缩格式的响应
[root@nginx ~]# curl --head --compressed 172.25.254.10/big.html
HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
Server: nginx/1.26.1
Date: Wed, 06 Aug 2025 13:05:10 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 153
Connection: keep-alive
Keep-Alive: timeout=60
[root@nginx ~]# curl --head --compressed 172.25.254.10/big.html
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.26.1
Date: Wed, 06 Aug 2025 13:06:48 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Last-Modified: Wed, 06 Aug 2025 13:06:33 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
Keep-Alive: timeout=60
Vary: Accept-Encoding
ETag: W/"68935359-1f400000"
Content-Encoding: gzip #显示被压缩3.版本隐藏
[root@nginx nginx-1.26.1]# vim src/core/nginx.h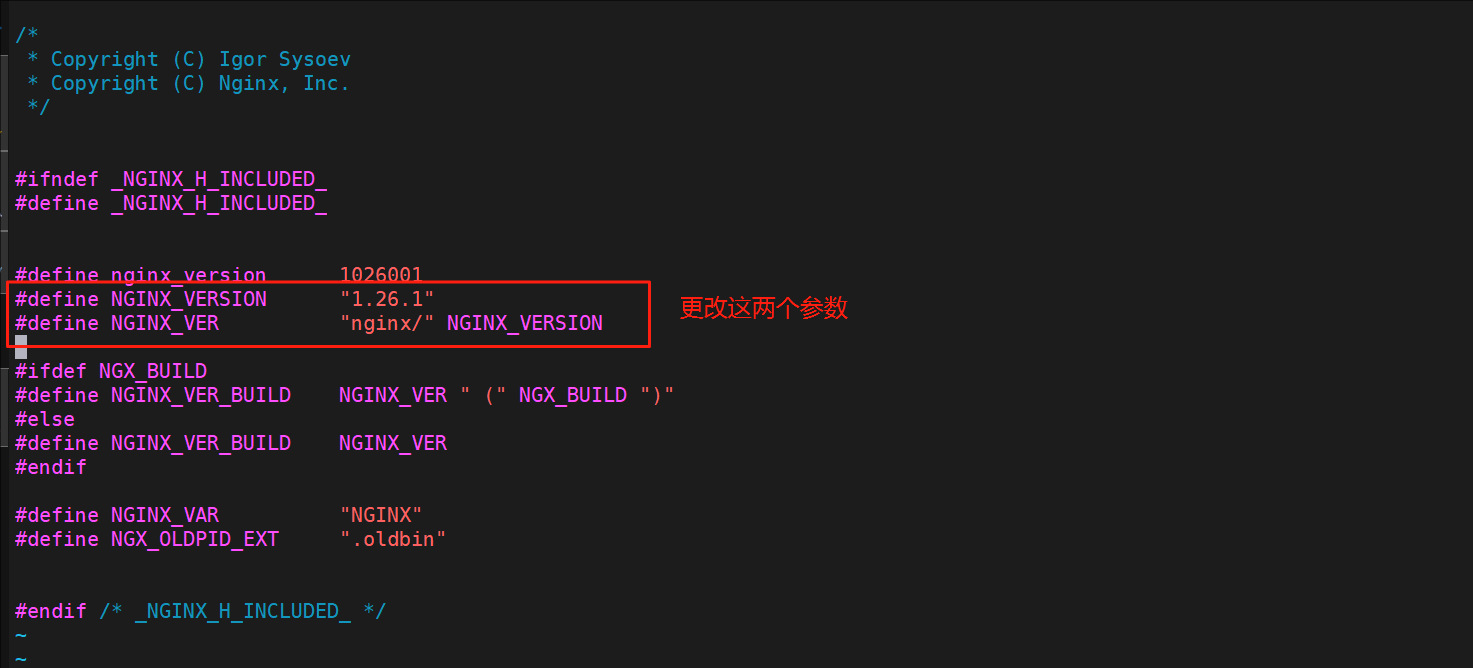
 测试
测试
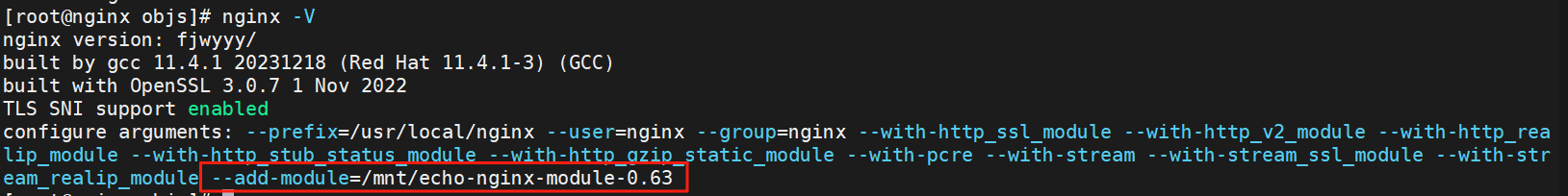
4.变量使用
引用nginx的变量需要添加模块
-
nginx的变量可以在配置文件中引用,作为功能判断或者日志等场景使用
-
变量可以分为内置变量和自定义变量
-
内置变量是由nginx模块自带,通过变量可以获取到众多的与客户端访问相关的值。
内置变量
#以下是常用的内置变量
$remote_addr;
#存放了客户端的地址,注意是客户端的公网IP
$args;
#变量中存放了URL中的所有参数
#例如:https://search.jd.com/Search?keyword=手机&enc=utf-8
#返回结果为: keyword=手机&enc=utf-8
$is_args
#如果有参数为? 否则为空
$document_root;
#保存了针对当前资源的请求的系统根目录,例如:/webdata/nginx/timinglee.org/lee。
$document_uri;
#保存了当前请求中不包含参数的URI,注意是不包含请求的指令
#比如:http://lee.timinglee.org/var?\id=11111会被定义为/var
#返回结果为:/var
$host;
#存放了请求的host名称
limit_rate 10240;
echo $limit_rate;
#如果nginx服务器使用limit_rate配置了显示网络速率,则会显示,如果没有设置, 则显示0
$remote_port;
#客户端请求Nginx服务器时随机打开的端口,这是每个客户端自己的端口
$remote_user;
#已经经过Auth Basic Module验证的用户名
$request_body_file;
#做反向代理时发给后端服务器的本地资源的名称
$request_method;
示例:
#请求资源的方式,GET/PUT/DELETE等
$request_filename;
#当前请求的资源文件的磁盘路径,由root或alias指令与URI请求生成的文件绝对路径,
#如:webdata/nginx/timinglee.org/lee/var/index.html
$request_uri;
#包含请求参数的原始URI,不包含主机名,相当于:$document_uri?$args,
#例如:/main/index.do?id=20190221&partner=search
$scheme;
#请求的协议,例如:http,https,ftp等
$server_protocol;
#保存了客户端请求资源使用的协议的版本,例如:HTTP/1.0,HTTP/1.1,HTTP/2.0等
$server_addr;
#保存了服务器的IP地址
$server_name;
#虚拟主机的主机名
$server_port;
#虚拟主机的端口号
$http_user_agent;
#客户端浏览器的详细信息
$http_cookie;
#客户端的所有cookie信息
$cookie_<name>
#name为任意请求报文首部字部cookie的key名
$http_<name>
#name为任意请求报文首部字段,表示记录请求报文的首部字段,name的对应的首部字段名需要为小写,如果有
横线需要替换为下划线
$http_<name>的示例
echo $http_user_agent;
echo $http_host;
$sent_http_<name>
#name为响应报文的首部字段,name的对应的首部字段名需要为小写,如果有横线需要替换为下划线,此变量有
问题
$arg_<name>
#此变量存放了URL中的指定参数,name为请求url中指定的参数#实验配置
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
location /vars {
default_type text/html;
echo $remote_addr;
echo $args;
echo $is_args;
echo $document_root;
echo $document_uri;
echo $host;
echo $remote_port;
echo $remote_user;
echo $request_method;
echo $request_filename;
echo $request_url;
echo $scheme;
echo $server_protocol;
echo $server_addr;
echo $server_name;
echo $server_port;
echo $server_user_agent;
echo $http_cookie;
echo $cookie_key1;
echo $http_Accept;
echo $arg_name;
}
}
#测试
[root@nginx ~]# curl -A "fjwyyy" -b "fjw=a,key1=2" -ufjw:fjw www.fy.org/vars?name=fjw
172.25.254.10
name=fjw
?
/web/html
/vars
www.fy.org
41430
fjw
GET
/web/html/vars
/vars?name=fjw
http
HTTP/1.1
172.25.254.10
www.fy.org
80
fjwyyy
fjw=a,key1=2
2
*/*
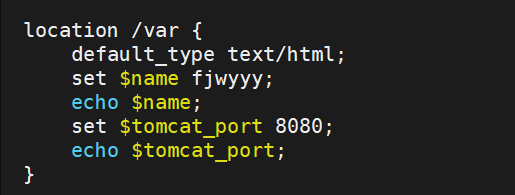
fjw自定义变量
[root@nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.fy.org;
root /web/html;
location /var {
default_type text/html;
set $name fjwyyy;
echo $name;
set $tomcat_port 8080;
echo $tomcat_port;
}
}
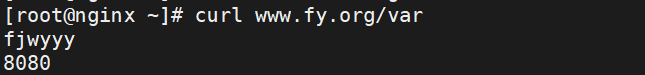
#测试
[root@nginx ~]# curl www.fy.org/var
fjwyyy
8080Nginx Rewrite相关功能
1.什么是rewrite
-
Nginx服务器利用 ngx_http_rewrite_module 模块解析和处理rewrite请求
-
此功能依靠 PCRE(perl compatible regular expression),因此编译之前要安装PCRE库
-
rewrite是nginx服务器的重要功能之一,用于实现URL的重写,URL的重写是非常有用的功能
-
比如它可以在我们改变网站结构之后,不需要客户端修改原来的书签,也无需其他网站修改我们的 链接,就可以设置为访问
-
另外还可以在一定程度上提高网站的安全性。
2.ngx_http_rewrite_module 模块指令
if
用于条件匹配判断,并根据条件判断结果选择不同的Nginx配置,可以配置在server或location块中进行 配置,Nginx的if语法仅能使用if做单次判断,不支持使用if else或者if elif这样的多重判断
使用正则表达式对变量进行匹配,匹配成功时if指令认为条件为true,否则认为false,变量与表达式之间 使用以下符号链接:
= #比较变量和字符串是否相等,相等时if指令认为该条件为true,反之为false
!= #比较变量和字符串是否不相等,不相等时if指令认为条件为true,反之为false
~ #区分大小写字符,可以通过正则表达式匹配,满足匹配条件为真,不满足匹配条件为假
!~ #区分大小写字符,判断是否匹配,不满足匹配条件为真,满足匹配条件为假
~* #不区分大小写字符,可以通过正则表达式匹配,满足匹配条件为真,不满足匹配条件为假
!~* #不区分大小字符,判断是否匹配,满足匹配条件为假,不满足匹配条件为真
-f 和 !-f #判断请求的文件是否存在和是否不存在
-d 和 !-d #判断请求的目录是否存在和是否不存在
-x 和 !-x #判断文件是否可执行和是否不可执行
-e 和 !-e #判断请求的文件或目录是否存在和是否不存在(包括文件,目录,软链接)
#注意:
#如果$变量的值为空字符串或0,则if指令认为该条件为false,其他条件为true用法如下:
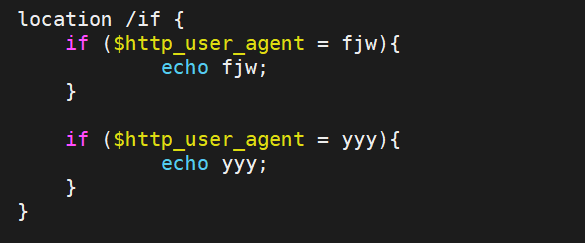
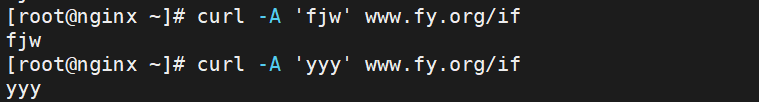
测试
set
指定key并给其定义一个变量,变量可以调用Nginx内置变量赋值给key 另外set定义格式为set $key value,value可以是text, variables和两者的组合,可以用于自定义变量。
用法如下:
测试:
break
-
用于中断当前相同作用域(location)中的其他Nginx配置
-
与该指令处于同一作用域的Nginx配置中,位于它前面的配置生效
-
位于后面的 ngx_http_rewrite_module 模块中指令就不再执行
注意: 如果break指令在location块中后续指令还会继续执行,只是不执行 ngx_http_rewrite_module 模块的指令,其它指令还会执行
用法如下:

测试:
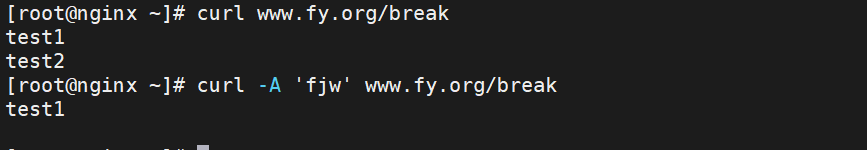
break只会停止 ngx_http_rewrite_module的指令,echo模块是第三方模块插入的,所以输出的值是空的
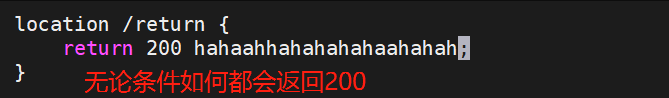
return
return用于完成对请求的处理,并直接向客户端返回响应状态码,比如:可以指定重定向URL(对于特殊重 定向状态码,301/302等) 或者是指定提示文本内容(对于特殊状态码403/500等),处于此指令后的所有配 置都将不被执行。
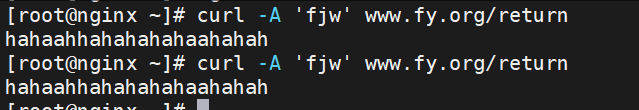
用法如下:
测试:
3.rewrite指令
通过正则表达式的匹配来改变URI,可以同时存在一个或多个指令,按照顺序依次对URI进行匹配, rewrite主要是针对用户请求的URL或者是URI做具体处理
正则表达式格式
. #匹配除换行符以外的任意字符
\w #匹配字母或数字或下划线或汉字
\s #匹配任意的空白符
\d #匹配数字
\b #匹配单词的开始或结束
^ #匹配字付串的开始
$ #匹配字符串的结束
* #匹配重复零次或更多次
+ #匹配重复一次或更多次
? #匹配重复零次或一次
(n) #匹配重复n次
{n,} #匹配重复n次或更多次
{n,m} #匹配重复n到m次
*? #匹配重复任意次,但尽可能少重复
+? #匹配重复1次或更多次,但尽可能少重复
?? #匹配重复0次或1次,但尽可能少重复
{n,m}? #匹配重复n到m次,但尽可能少重复
{n,}? #匹配重复n次以上,但尽可能少重复
\W #匹配任意不是字母,数字,下划线,汉字的字符
\S #匹配任意不是空白符的字符
\D #匹配任意非数字的字符
\B #匹配不是单词开头或结束的位置
[^x] #匹配除了x以外的任意字符
[^fjw] #匹配除了fjw 这几个字母以外的任意字符3.1.rewrite flag介绍
利用nginx的rewrite的指令,可以实现url的重新跳转,rewrite有四种不同的flag,分别是redirect(临时 重定向302)、permanent(永久重定向301)、break和last。其中前两种是跳转型的flag,后两种是代理型
-
跳转型指由客户端浏览器重新对新地址进行请求
-
代理型是在WEB服务器内部实现跳转
flag 说明
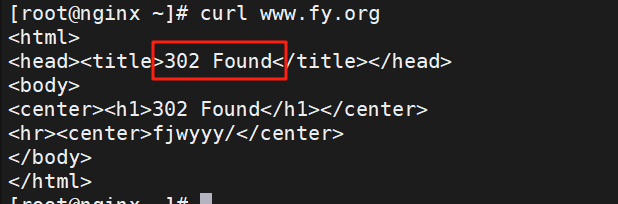
redirect;
#临时重定向,重写完成后以临时重定向方式直接返回重写后生成的新URL给客户端
#由客户端重新发起请求;使用相对路径,或者http://或https://开头,状态码:302
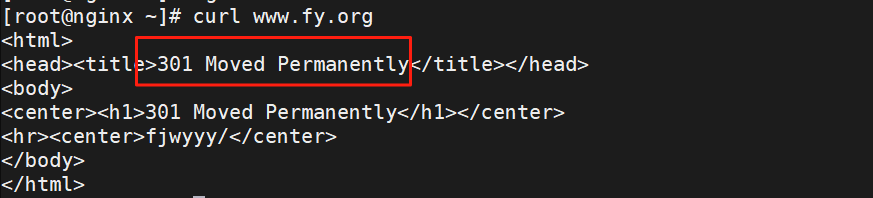
permanent;
#重写完成后以永久重定向方式直接返回重写后生成的新URL给客户端
#由客户端重新发起请求,状态码:301
break;
#重写完成后,停止对当前URL在当前location中后续的其它重写操作
#而后直接跳转至重写规则配置块之后的其它配置,结束循环,建议在location中使用
#适用于一个URL一次重写
last;
#重写完成后,停止对当前URI在当前location中后续的其它重写操作,
#而后对新的URL启动新一轮重写检查,不建议在location中使用
#适用于一个URL多次重写,要注意避免出现超过十次以及URL重写后返回错误的给用户3.2.redirect与permanent
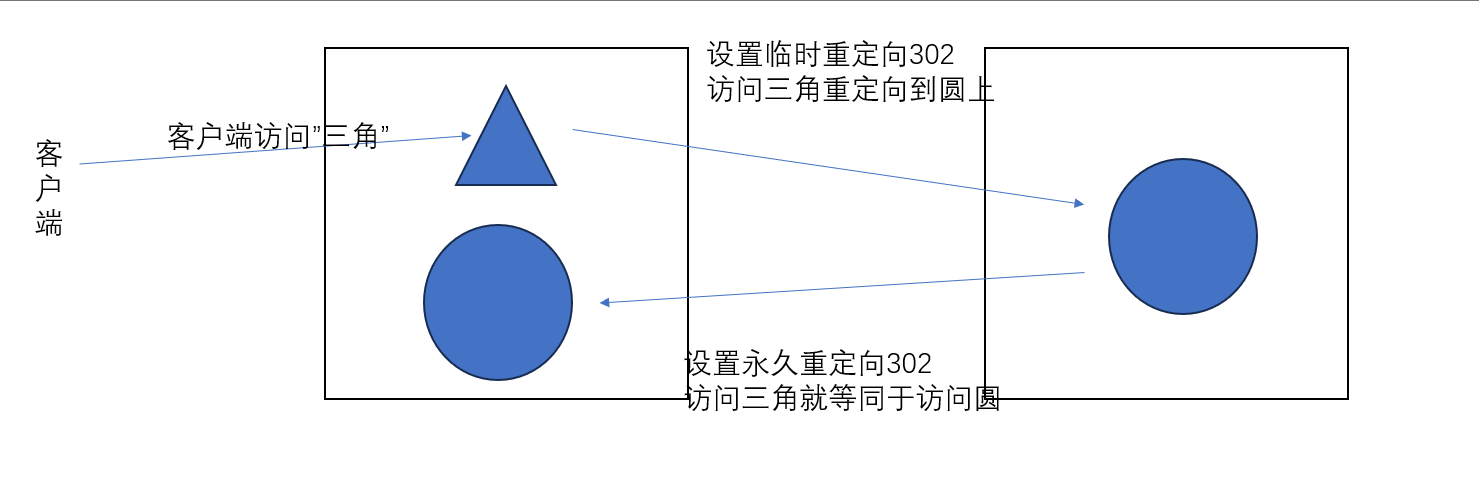
redirect:
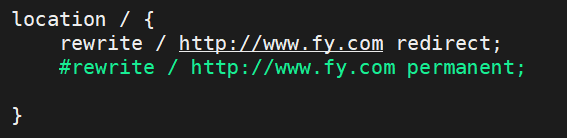
测试
permanent:
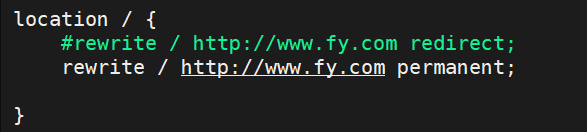
测试
3.3.break与last
#生成测试文件
[root@webserver ~]# mkdir /web/html/{break,last,test1,test2}
[root@webserver ~]# echo break > /web/html/break/index.html
[root@webserver ~]# echo last > /web/html/last/index.html
[root@webserver ~]# echo test1 > /web/html/test1/index.html
[root@webserver ~]# echo test2 > /web/html/test2/index.html
[root@webserver ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/xixi.conf
[root@webserver ~]# nginx -t
[root@webserver ~]# nginx -s reload当没有break与last时访问/break/请求被rewrite至test1,test1会再次被rewrite至fjw;访问last/时会被rewrite至test2,test2会再次被rewrite至yyy
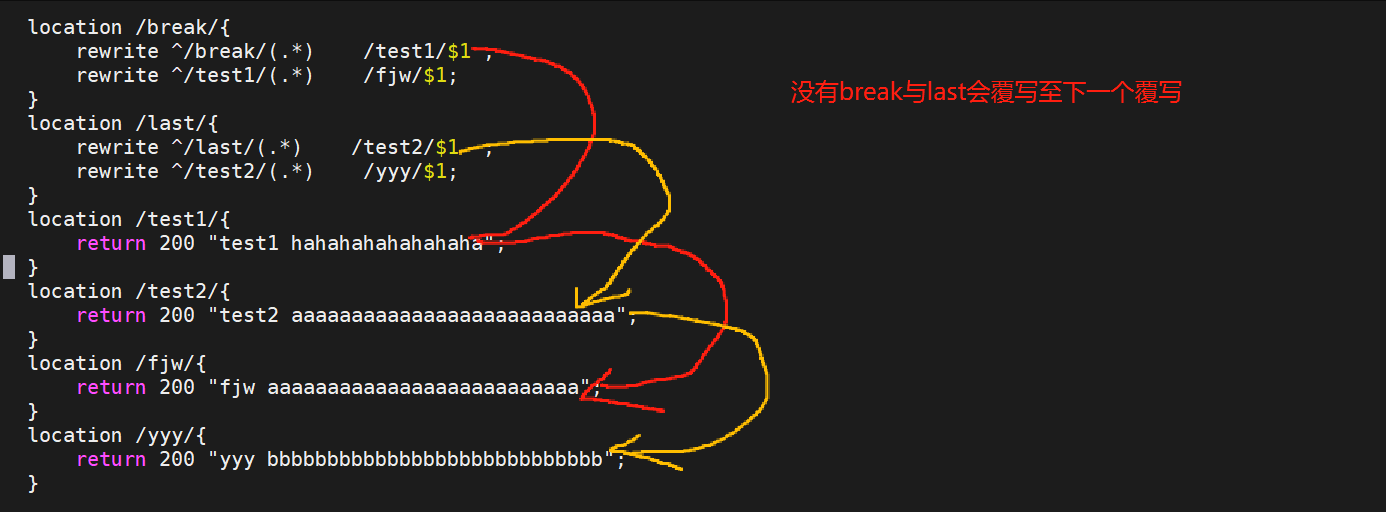
测试

当添加了break与last后
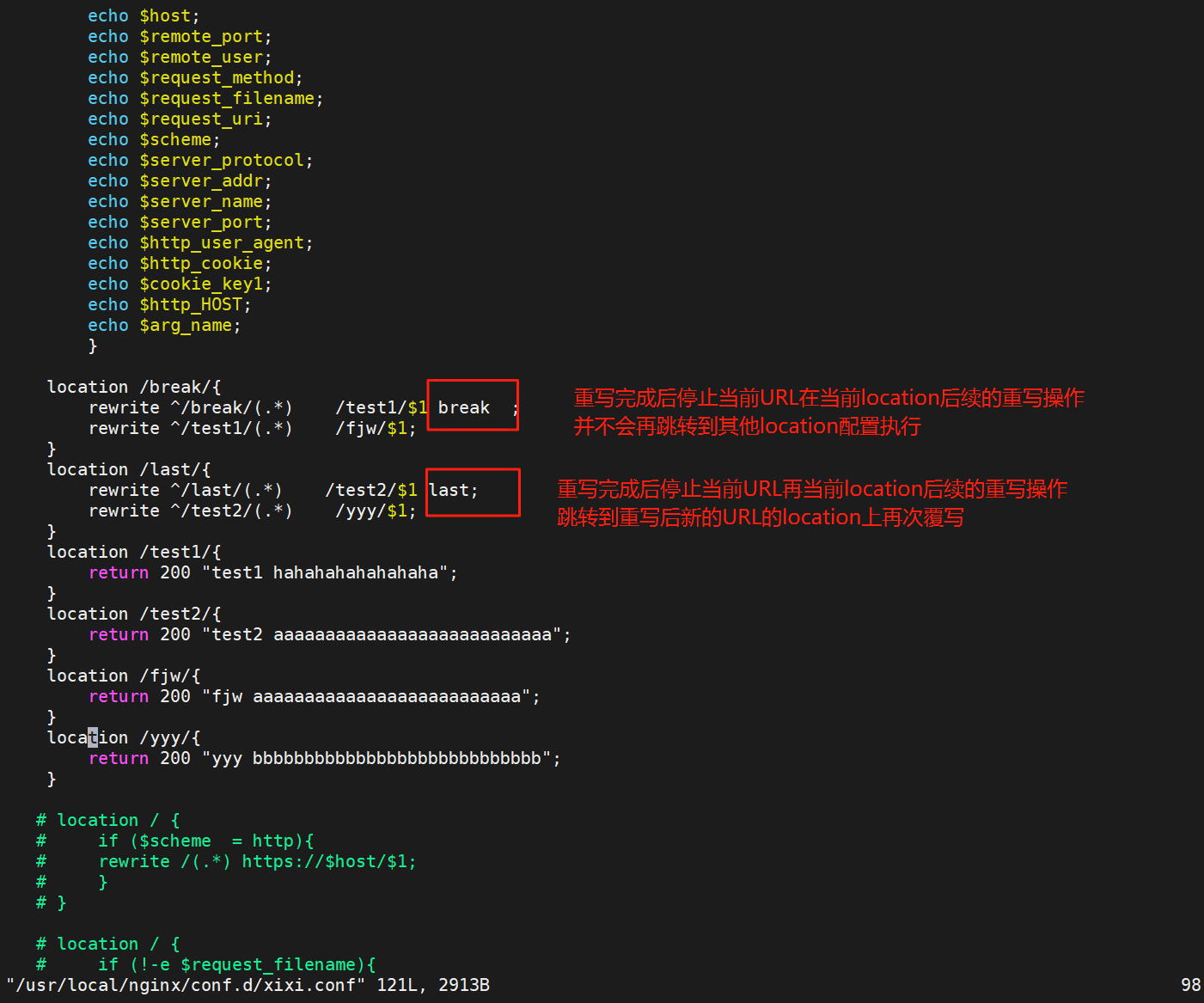
测试

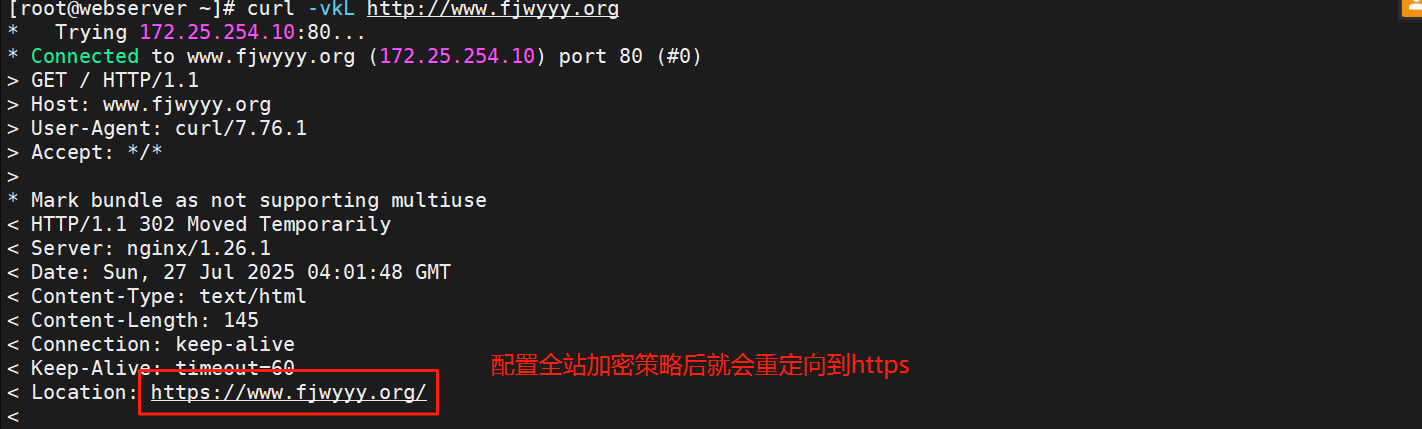
3.4.全站加密策略
[root@webserver ~]# mkdir /usr/local/nginx/certs
[root@webserver ~]# openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 \
> -nodes -sha256 -keyout /usr/local/nginx/certs/fjwyyy.key \
> -x509 -days 365 -out /usr/local/nginx/certs/fjwyyy.crt
[root@webserver ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/xixi.conf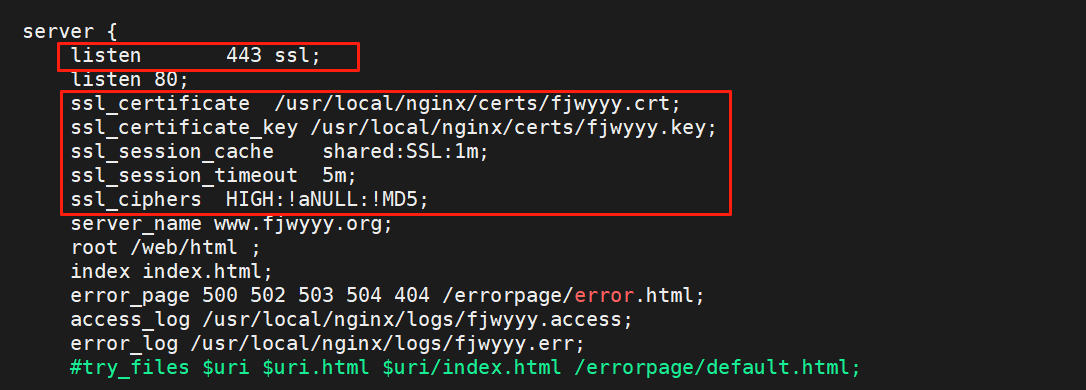
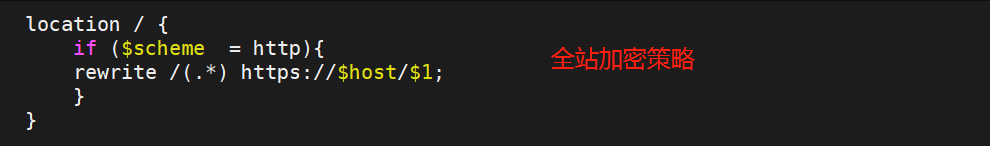
测试
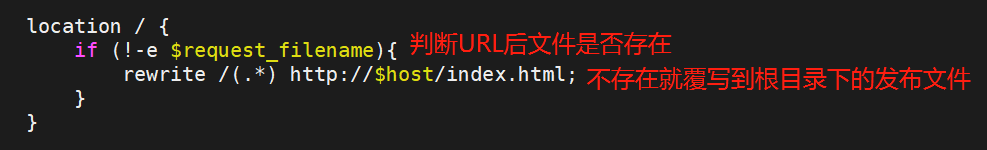
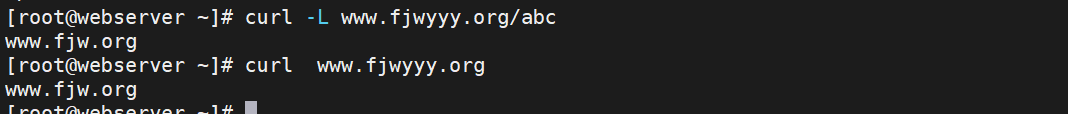
3.5.判断文件是否存在并重定向
测试
3.6.nginx防盗链
什么是盗链?
#生成一个测试主机下载httpd服务,导入一个盗链主页
[root@RS1 ~]# dnf install httpd -y
[root@RS1 ~]# systemctl start httpd
[root@RS1 ~]# vim /var/www/html/index.html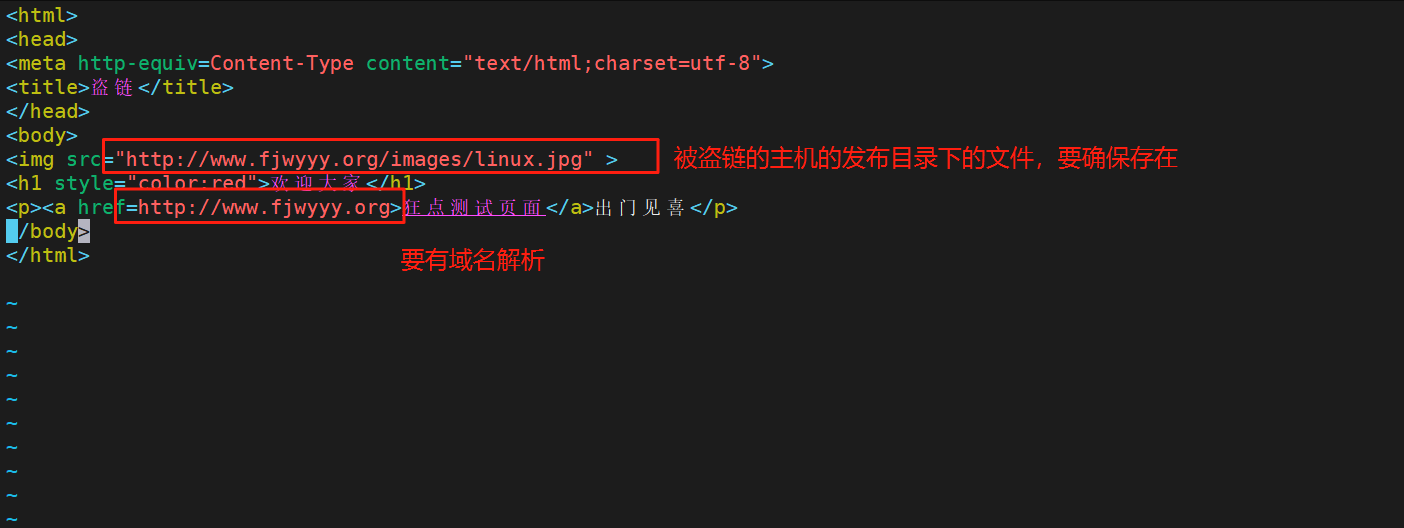
测试
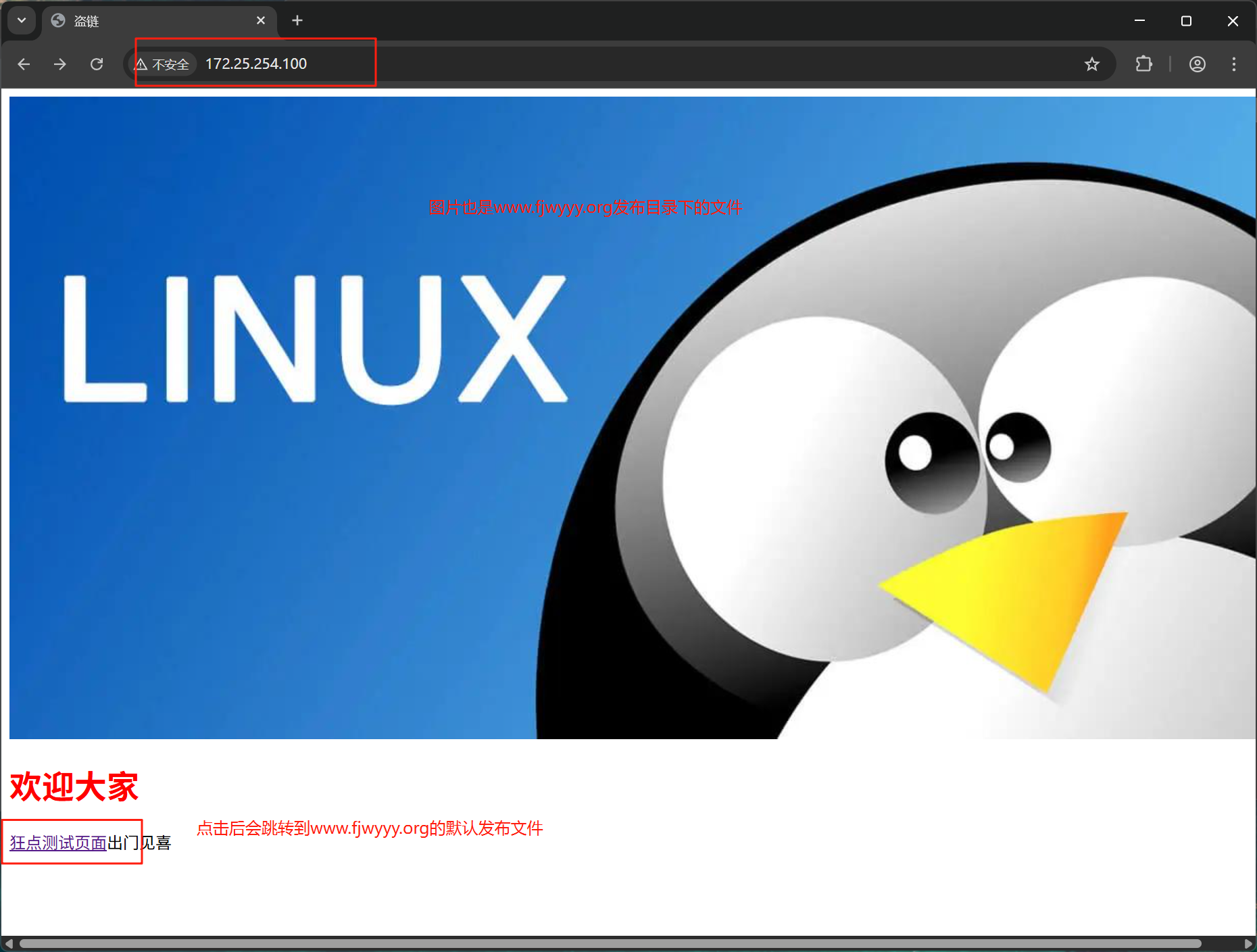
点击后
#查看域名访问的日志,会发现被盗链访问的会有标注referer值就是来源信息
[root@webserver ~]# > /usr/local/nginx/logs/fjwyyy.access
[root@webserver ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/fjwyyy.access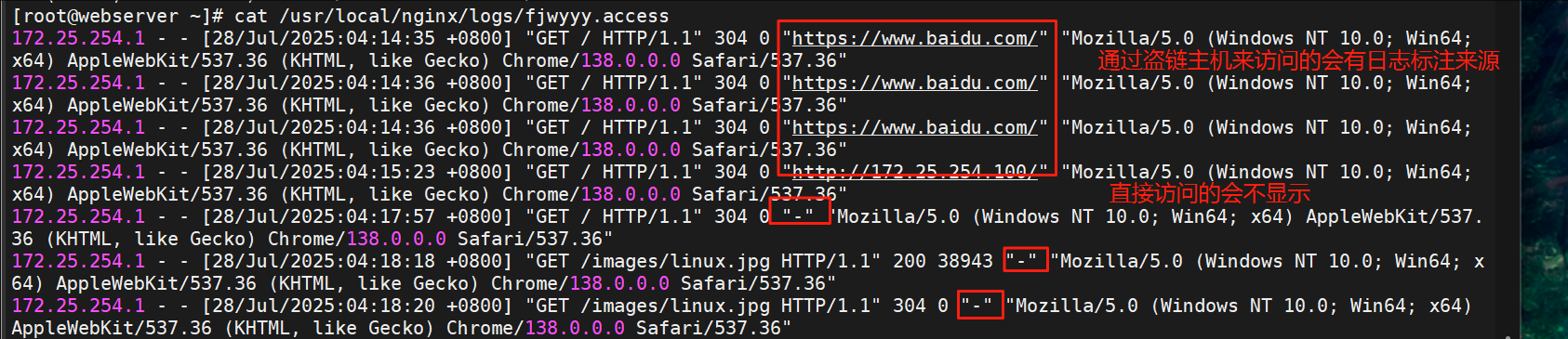
实现防盗链
#部署防盗链,编辑配置文件
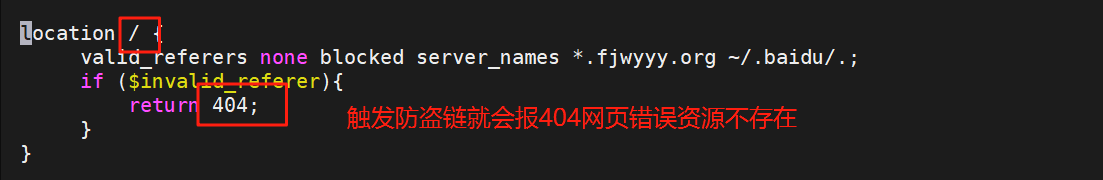
[root@webserver ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/xixi.conf
[root@webserver ~]# nginx -t
[root@webserver ~]# nginx -s reload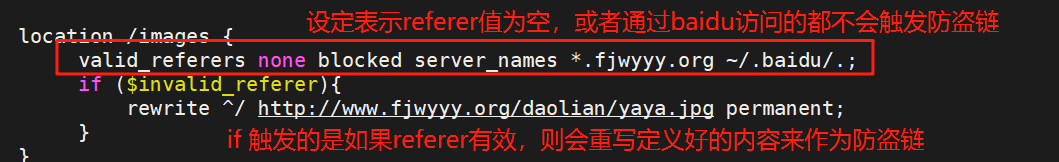
测试

进行全站防盗链
Nginx反向代理功能
1.实现http反向代理
实现网页的动静分离
#在RS1172.25.254.100下安装hhttpd,模拟静态页面
[root@RS1 ~]# dnf install httpd -y
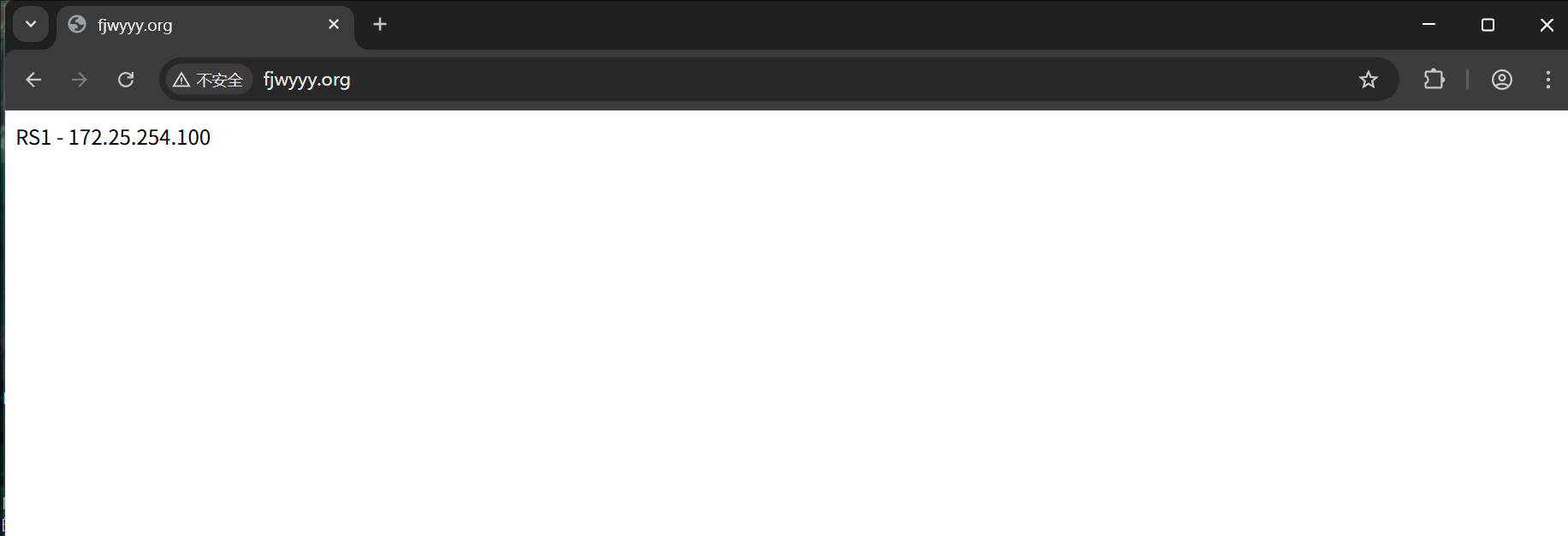
[root@RS1 ~]# echo RS1 - 172.25.254.100 > /var/www/html/index.html
#在RS1172.25.254.100下安装hhttpd与php,模拟动态页面
[root@RS2 ~]# dnf install httpd php -y
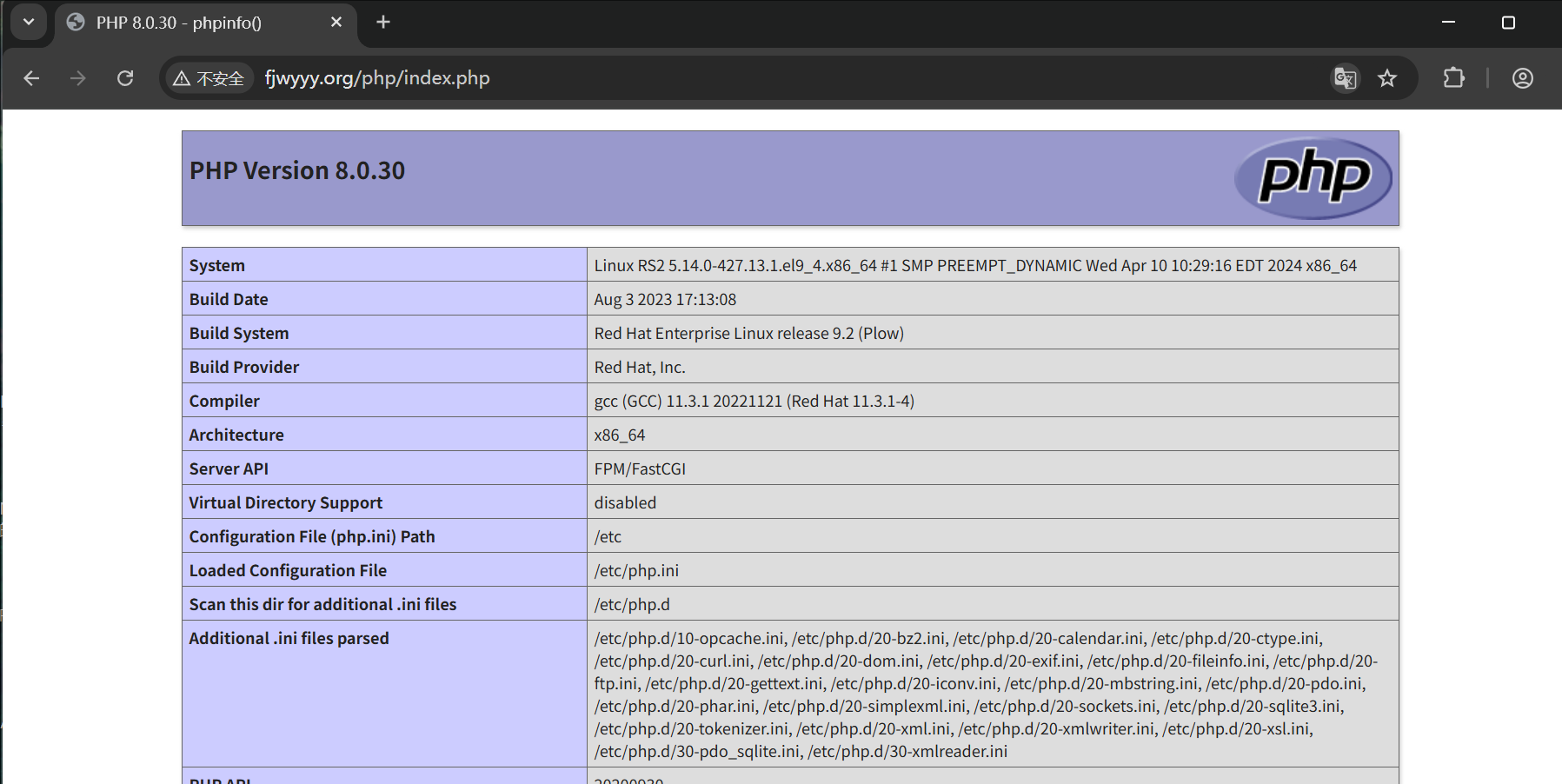
[root@RS2 ~]# vim /var/www/html/php/index.php
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
[root@webserver ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhost.conf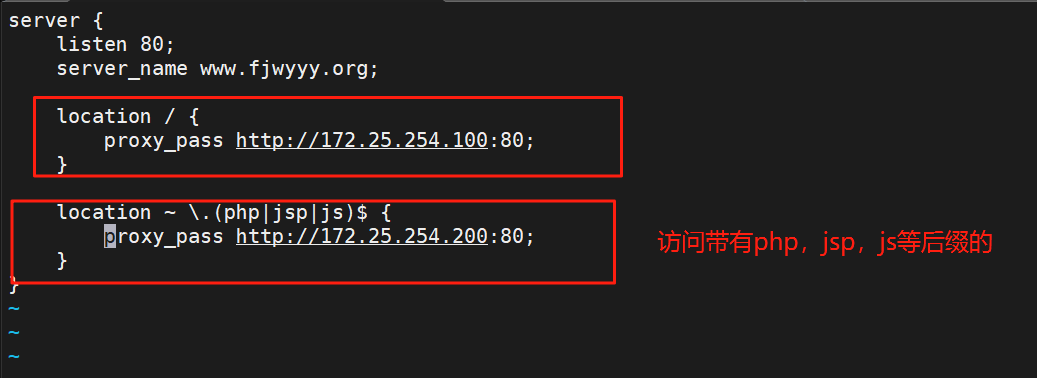
测试
2.nginx四层负载均衡
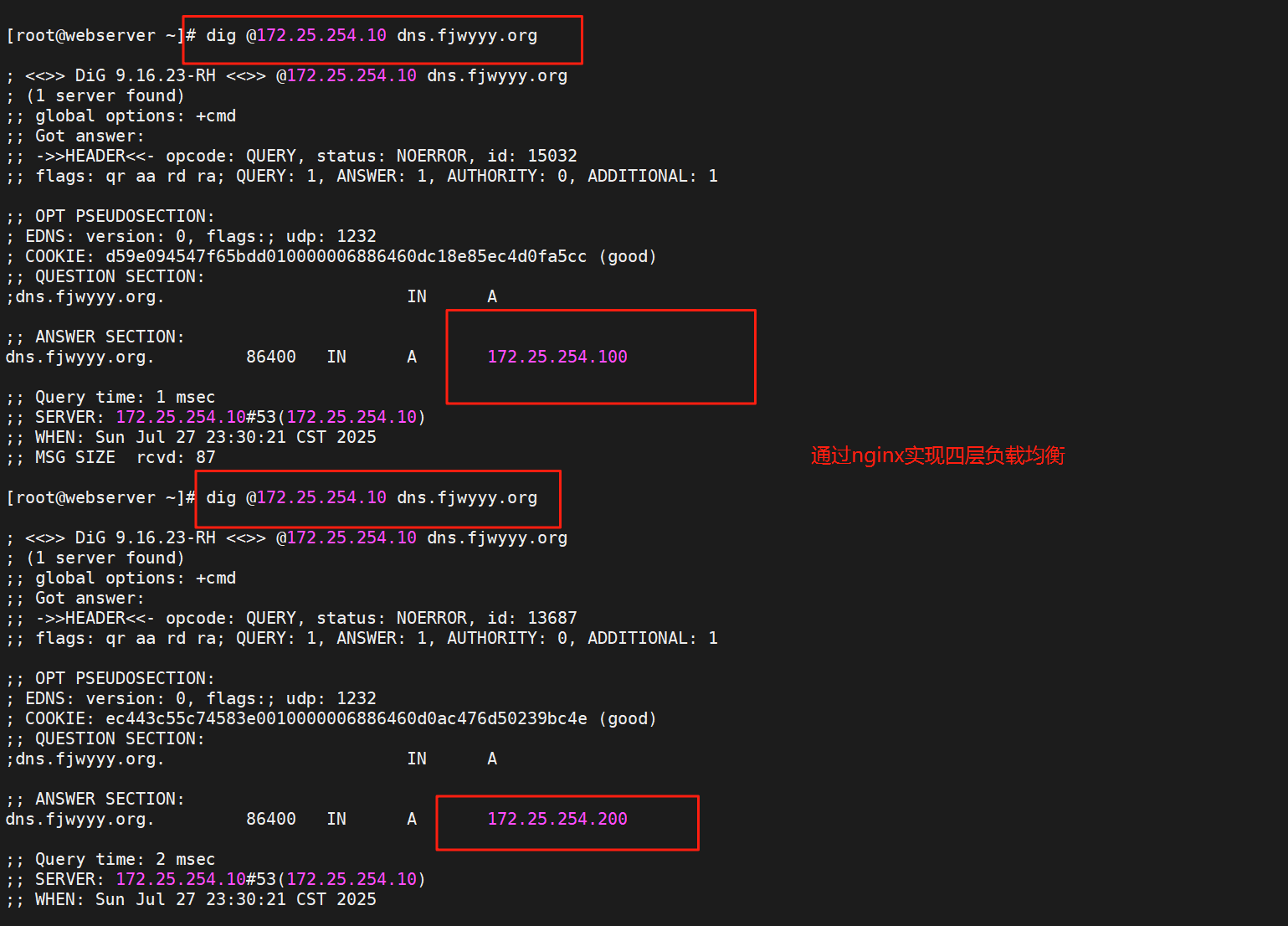
2.1.示例-DNS服务
#RS1,RS2下载DNS服务
[root@RS1 ~]# dnf install bind -y
#RS1,RS2编辑DNS配置文件,编辑A记录,
[root@RS1 ~]# vim /etc/named.conf
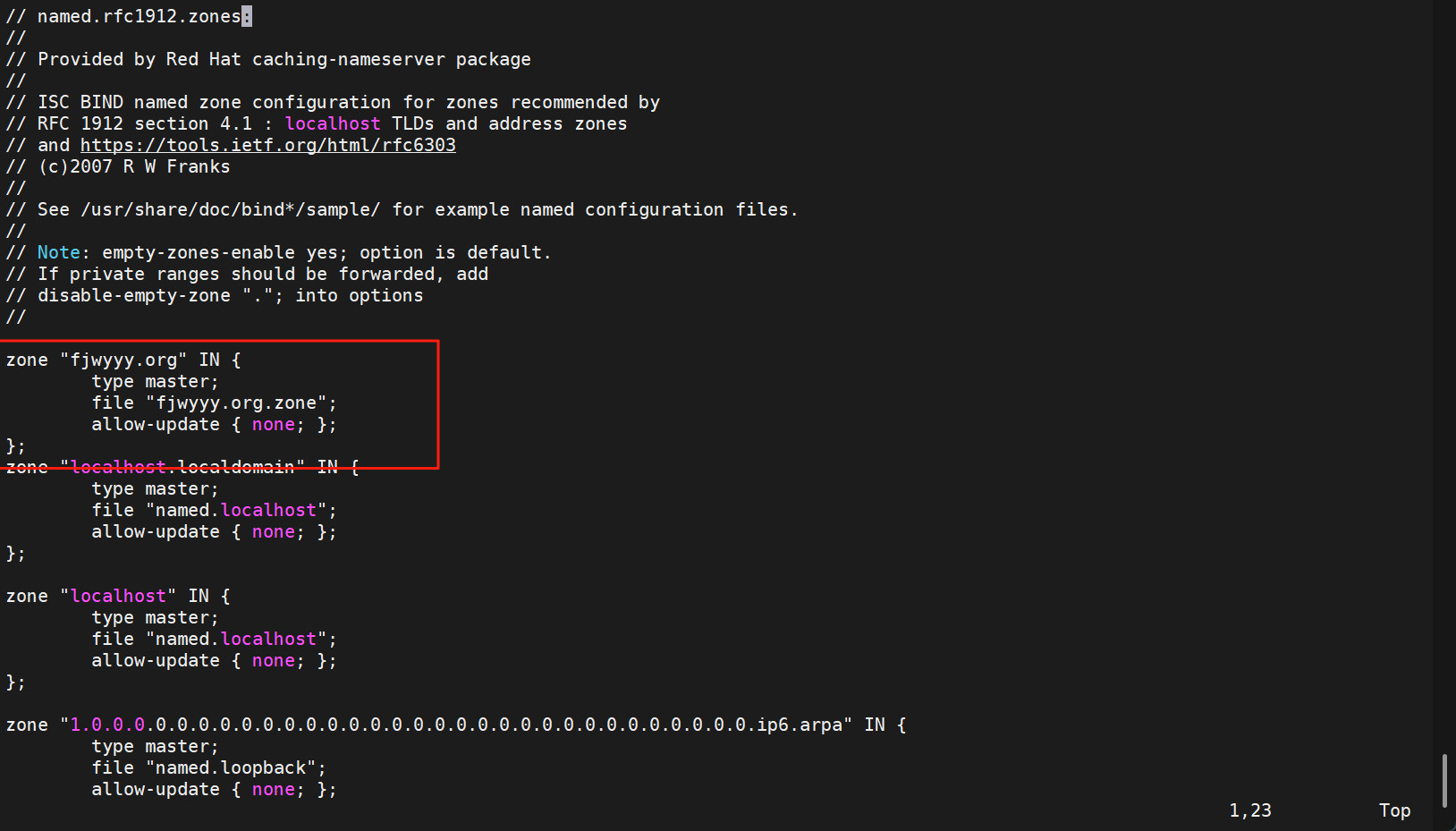
[root@RS1 ~]# vim /etc/named.rfc1912.zones
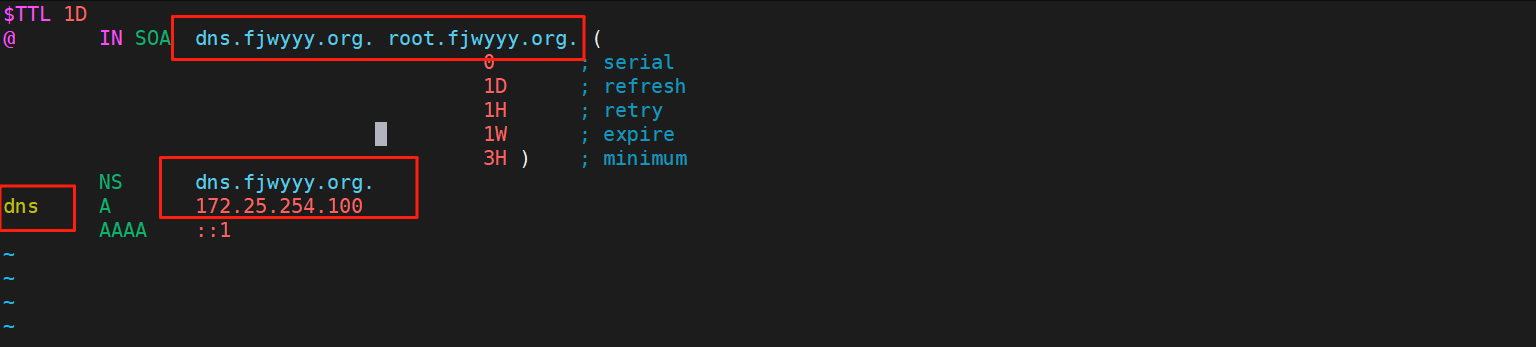
#以named.localhost为模板复制,-p同步权限
[root@RS1 ~]# cp -p /var/named/named.localhost /var/named/fjwyyy.org.zone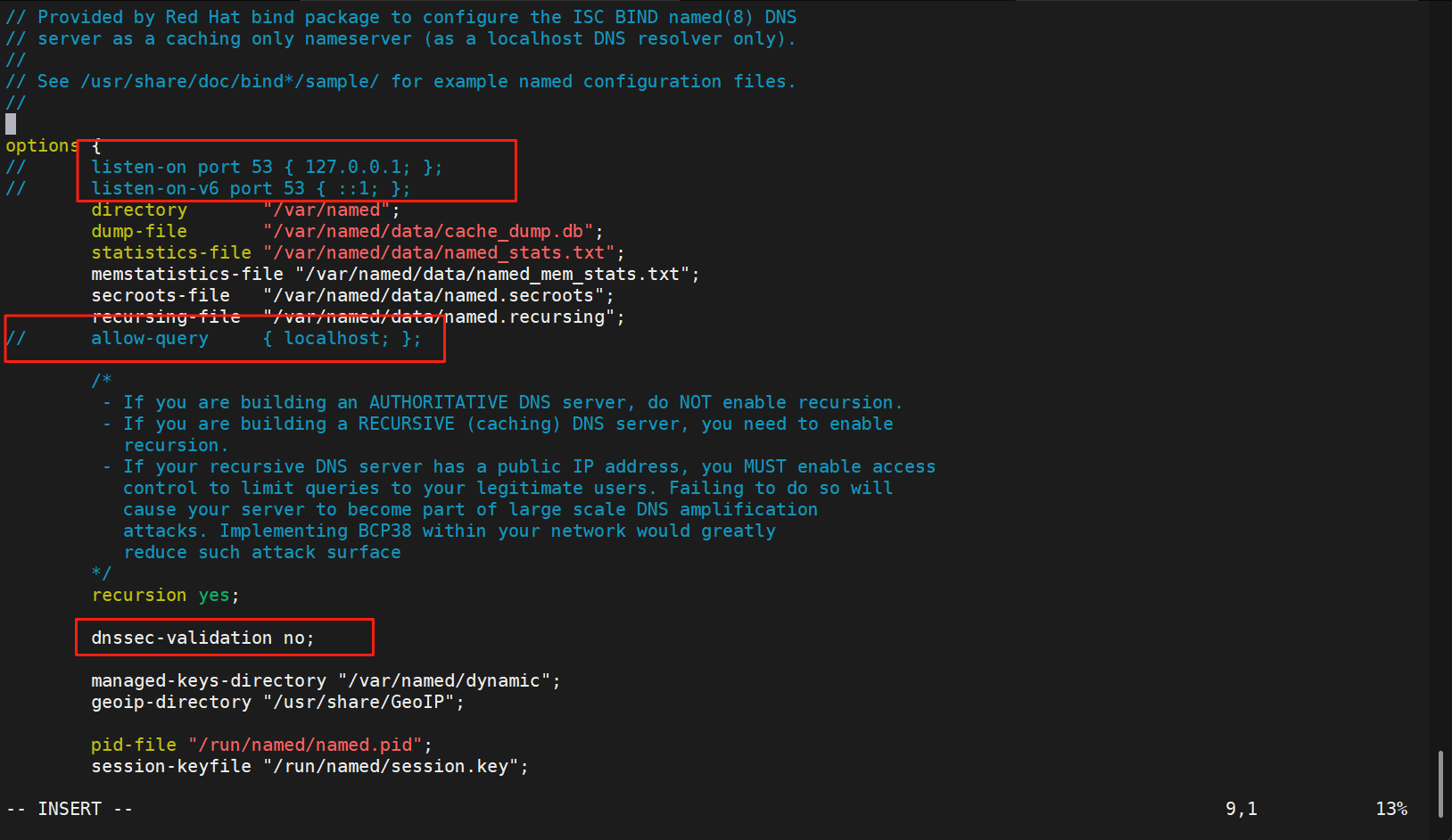
#在http添加子配置目录含于主配置目录,原因是http配置的是七层负载。
[root@webserver ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
include "/usr/local/nginx/tcp.d/*.conf";
http {
......
}
#创建用于管理四层负载的tco文件
[root@webserver ~]# mkdir /usr/local/nginx/tcp.conf
root@webserver ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/tcp.d/tcp.conf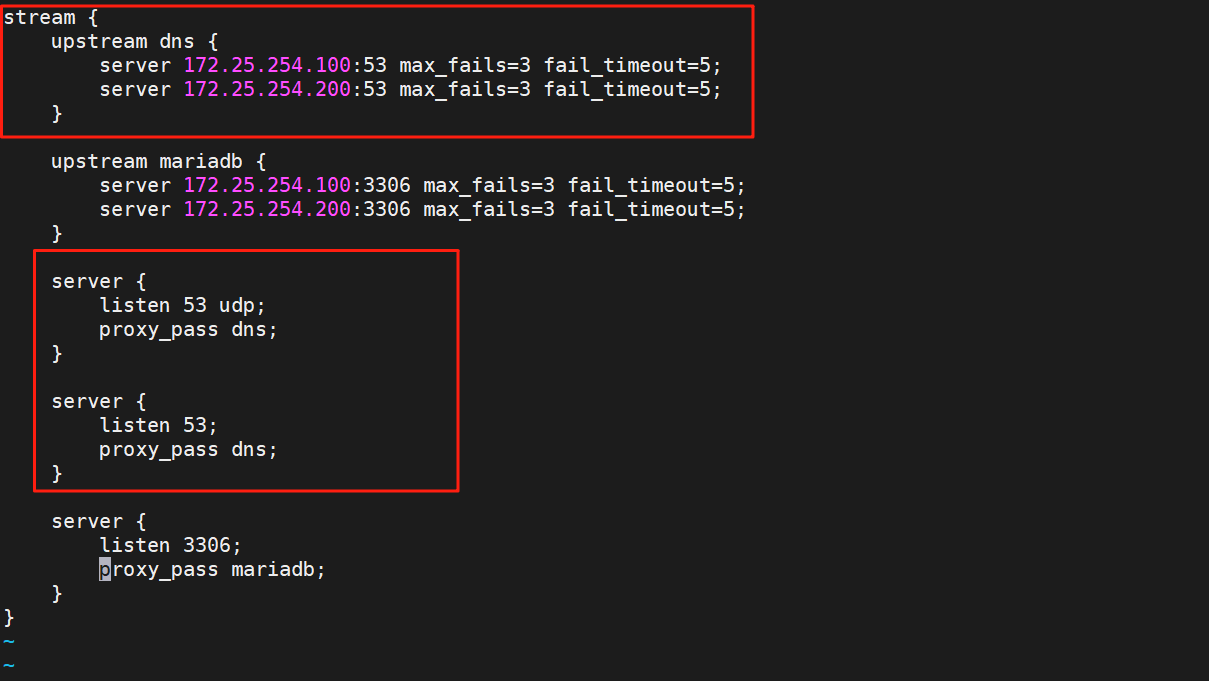
测试
2.2.示例-Mysql服务
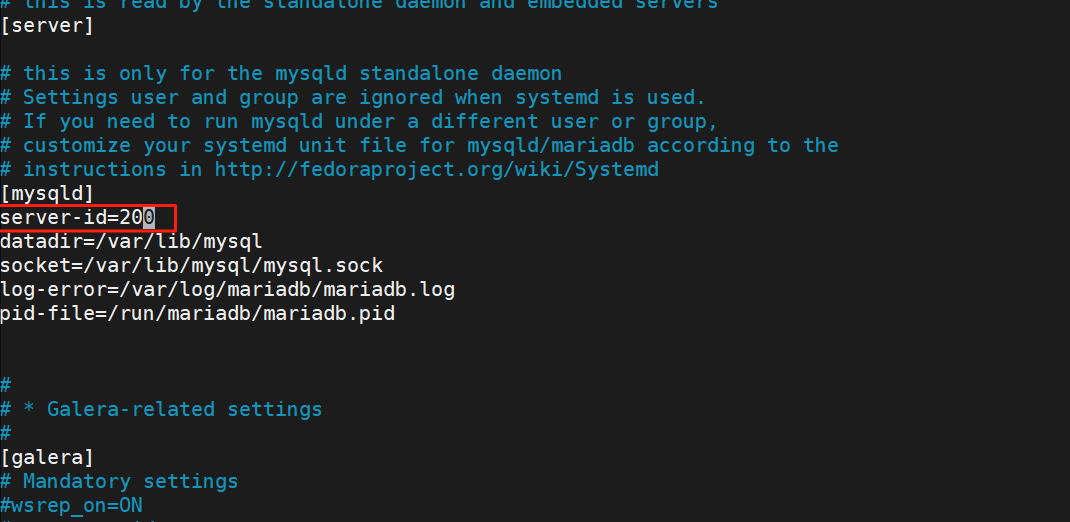
#在RS1,RS2安装maradb-server软件
[root@RS1 ~]# dnf install mariadb-server -y
#编辑配置文件
[root@RS1 ~]# vim /etc/my.cnf.d/mariadb-server.cnf
#在mysql创建用户并授权
[root@RS1 ~]# mysql -e "create user fjw@'%' identified by 'fjw';"
[root@RS1 ~]# mysql -e "grant select on *.* to fjw@'%';"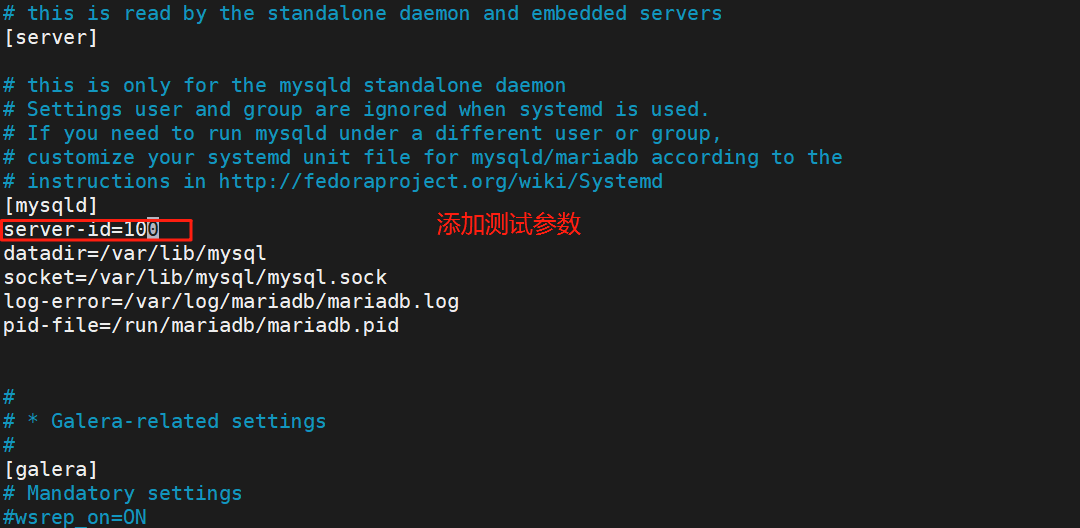
#编辑nginx子配置文件配置四层负载均衡
[root@webserver ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/tcp.d/tcp.conf
测试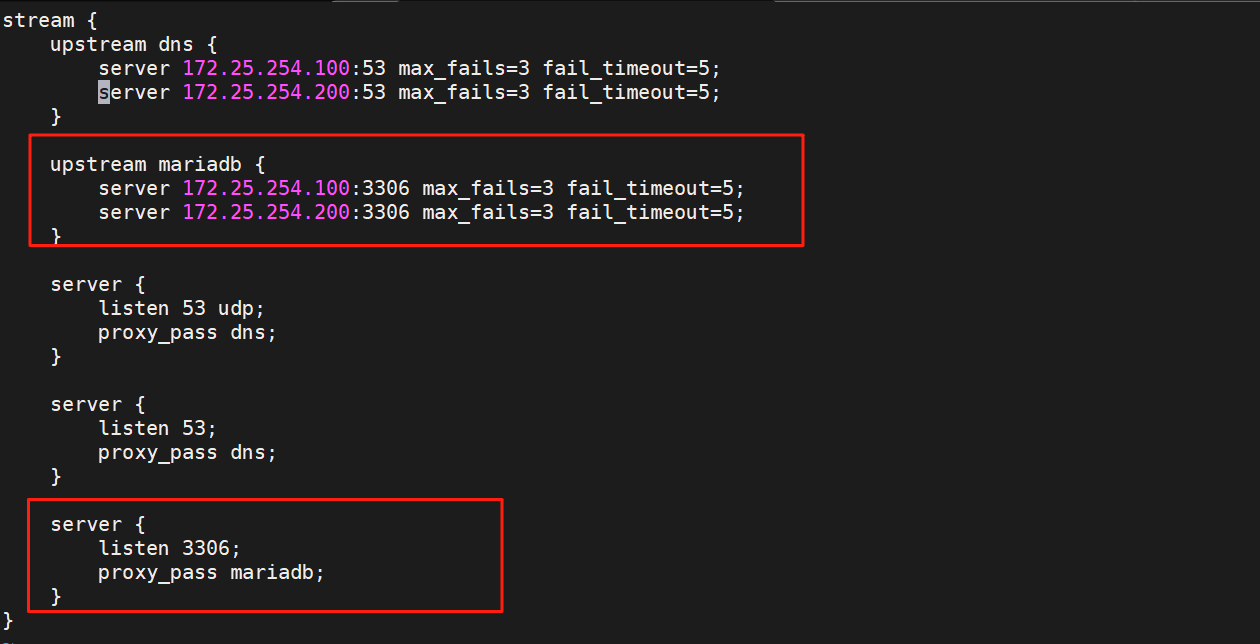
测试
[root@RS1 ~]# mysql -ufjw -pfjw -h172.25.254.10 -e "select @@server_id"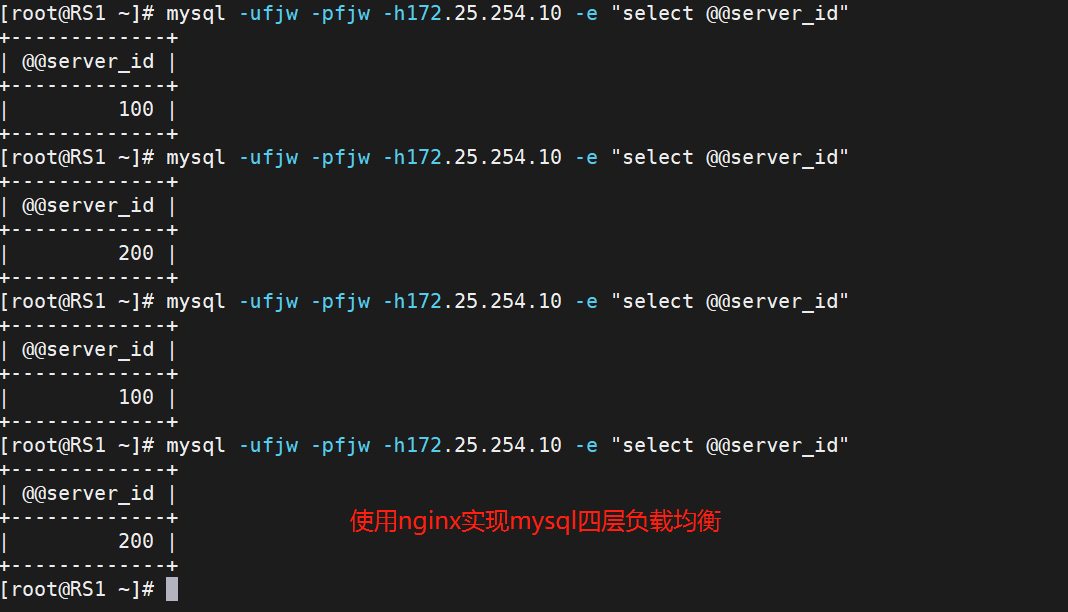
3.实现FastCGI
php动态缓存模块(memcache)
安装memcache模块
#安装memcache插件
[root@webserver mnt]# tar zxf memcache-8.2.tgz
[root@webserver mnt]# cd memcache-8.2
#安装自动编译工具
[root@webserver memcache-8.2]# dnf intall autoconf
#php动态编译
[root@webserver memcache-8.2]# phpize
[root@webserver memcache-8.2]# ./configure && make && make install 配置php加载memcache模块
[root@Nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/php/etc/php.ini
......
;extension=zip
extension=memcache
......
[root@Nginx ~]# systemctl reload php-fpm
[root@Nginx no-debug-non-zts-20230831]# php -m | grep mem
memcache部署memcached
[root@webserver ~]# dnf install memcached -y
[root@webserver ~]# systemctl enable --now memcached.service
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:11211 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 980 158986 163749/memcached
#查看配置文件设置
[root@webserver memcache-8.2]# cat /etc/sysconfig/memcached
PORT="11211" #监听端口
USER="memcached" #运行服务的用户
MAXCONN="1024" #最大并发连接数1024
CACHESIZE="64" #可使用的最大内存缓存大小64M
OPTIONS="-l 0.0.0.0,::1" #默认仅允许本机连接memcached,改为所有主机都能连接memcached访问缓存
#复制测试文件到默认发布目录
[root@webserver ~]# cd /mnt/memcache-8.2/
[root@webserver memcache-8.2]# cp example.php memcache.php /usr/local/nginx/html/
[root@webserver memcache-8.2]# vim /usr/local/nginx/html/memcache.php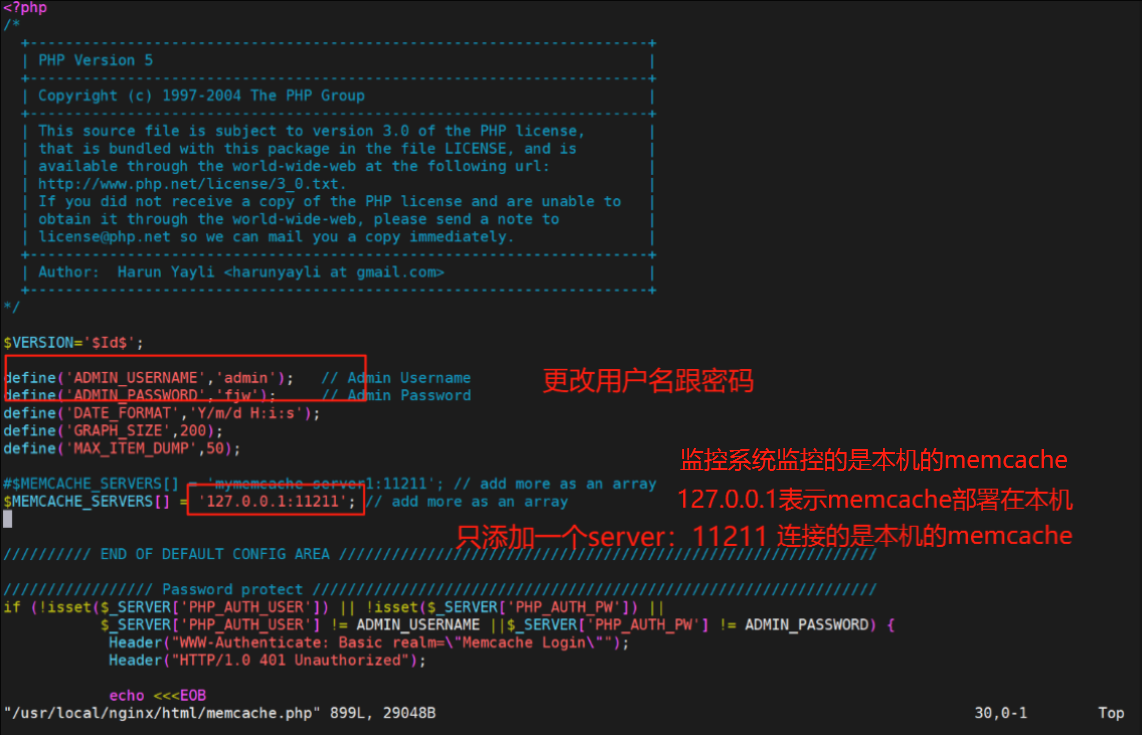
访问memcache.php,查看缓存系统状态监控命中情况
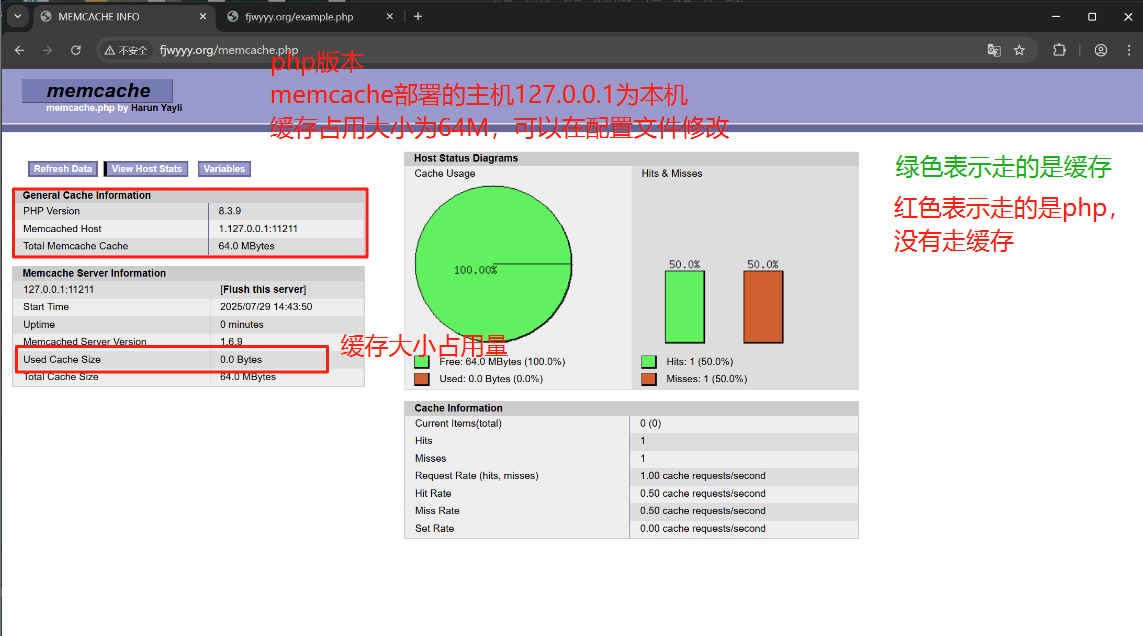
测试
[root@webserver memcache-8.2]# ab -n 1000 -c 500 www.fjwyyy.org/example.php
#于访问的是example.php默认就被缓存在memcache作为测试页面,所以压测全都是走缓存。访问memcache.php,查看缓存系统状态监控命中情况
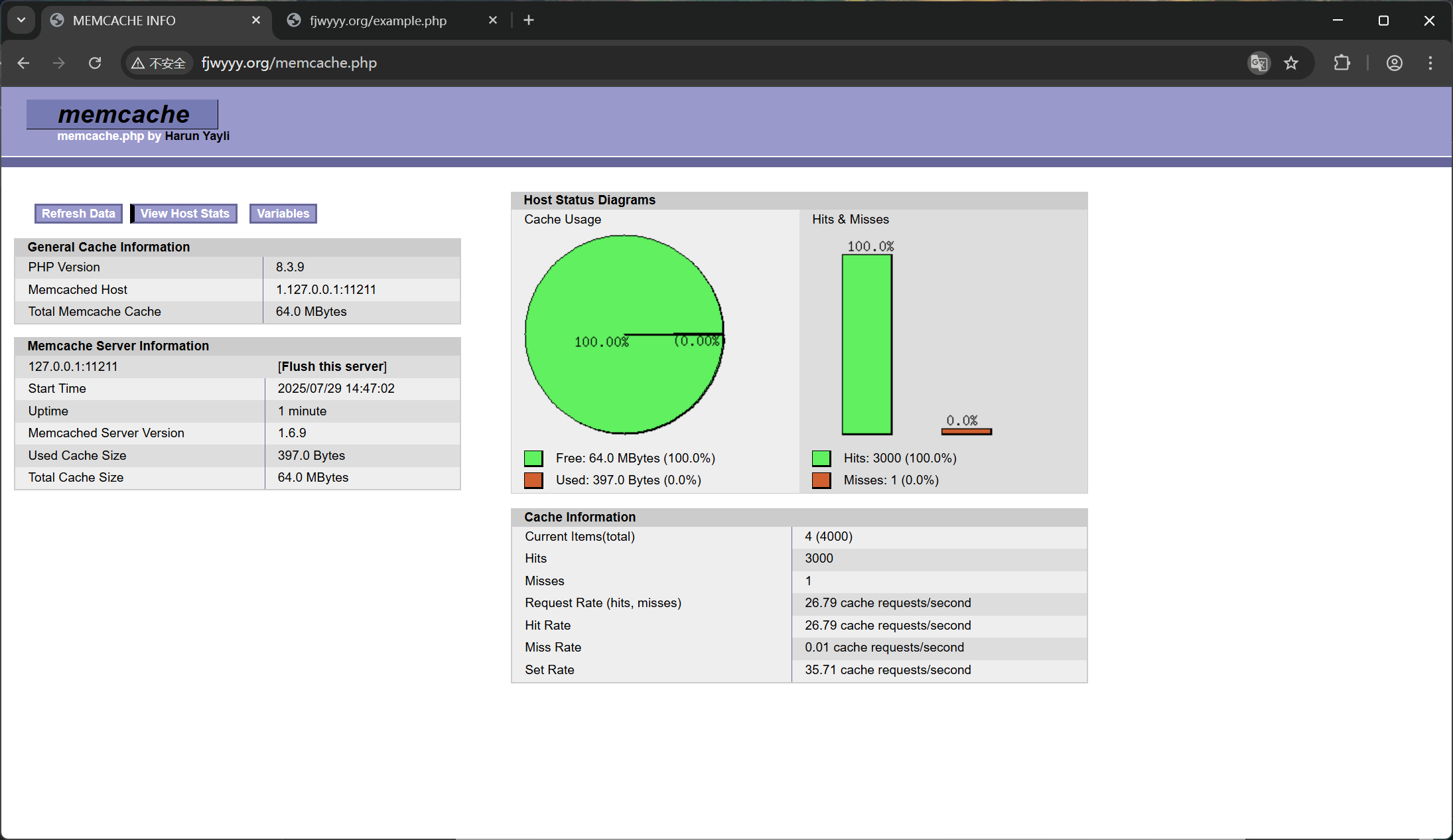
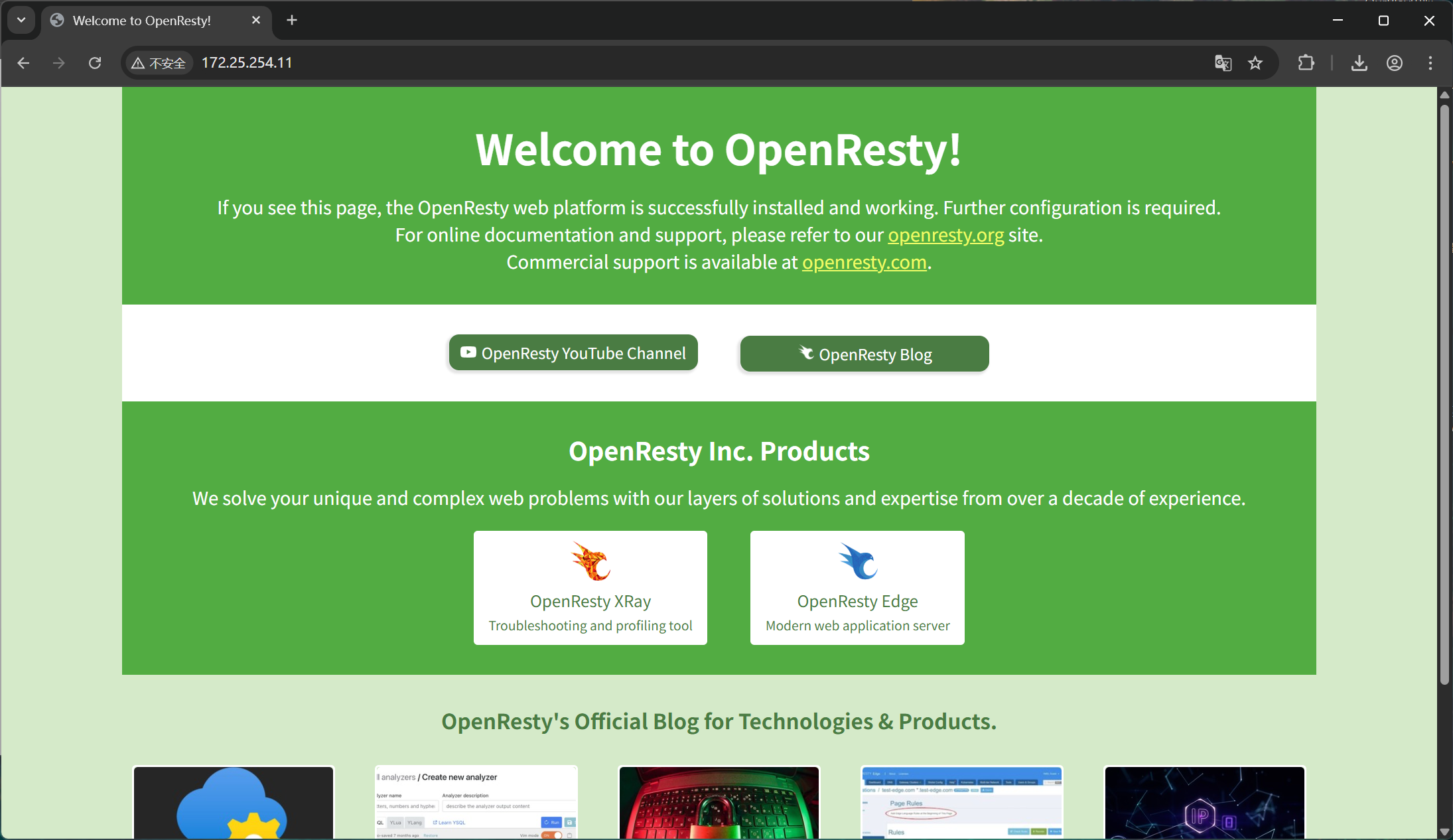
4.nginx二次开发版本
[root@nginx mnt]# tar zxf openresty-1.25.3.1.tar.gz
[root@nginx mnt]# cd openresty-1.25.3.1/
[root@nginx openresty-1.25.3.1]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/openresty --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_realip_module
[root@nginx openresty-1.25.3.1]# gmake && gmake install
[root@nginx openresty-1.25.3.1]# vim ~/.bash_profile
export PATH=/root/.local/bin:/root/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/nginx/sbin/:/usr/local/openresty/bin/
#使新加载的配置生效
[root@webserver nginx-1.25.3.1]# source ~/.bash_profile
[root@webserver nginx-1.25.3.1]# openresty
[root@nginx openresty-1.25.3.1]# ps aux | grep nginx
root 11247 0.0 0.1 12924 2780 ? Ss 17:03 0:00 nginx: master process openresty
nginx 11248 0.0 0.3 16228 6236 ? S 17:03 0:00 nginx: worker process测试
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献4条内容
已为社区贡献4条内容







所有评论(0)