06-netty基础-编码解码
使用其他方式作为结束标志的解码器,比如使用&;等;只需要在发送数据的时候在数据后面加上分隔的符号就行了,只是分隔的符号需要包装成一个ByteBuf// 第三种:分隔符// maxFrameLength :报文的最大长度// stripDelimiter:判断解码的时候是否要把分隔符去掉// failFast:跟maxFrameLength合起来用,如果为true,如果大于消息的长度,直接抛异常,如
netty系列文章:
1 netty实现简易服务端和客户端
1.1 交互流程
- 服务端-实例化boss线程组
- 服务端-实例化work线程组
- 服务端-给两个线程组都配置一些参数
- 服务端-绑定端口,启动服务
- 客户端-启动客户端,实例化一个线程组,客户端不需要boss和work
- 客户端-给线程组配置参数
- 客户端-像服务端发起连接
- 客户端-调用SimpleClientHandle#channelActive
- 服务端-接收客户端传输数据SimpleServerHandler#channelRead, 并向客户端发送数据
- 客户端-接收服务端传输数据SimpleClientHandle#channelRead
1.2 pom依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--常用工具类 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-compress</artifactId>
<version>1.27.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty-all</artifactId>
<version>4.1.63.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.7.21</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.20</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>1.3 服务端代码
package com.bonnie.netty.str.server;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
/**
* netty服务端, 这快用的是String
*/
public class NettyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建Boss线程
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
// 创建work线程
NioEventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
// 实例化serverBootstrap
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
// bossGroup保存AbstractBootStrap的group属性中
// workGroup保存serverBootstrap的childGroup属性中
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workGroup)
// 把NioServerSocketChannel.class保存到ReflectiveChannelFactory工厂对象中,将来要通过实例化把NioServerSocketChannel
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
// Boss线程要处理的业务 LoggingHandler会保存到AbstractBootStrap中的handler中
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
// work线程要处理的业务,把ChannelInitializer保存到ServerBootstrap中的childHandler中
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline()
.addLast(new StringDecoder())
.addLast(new StringEncoder())
.addLast(new SimpleServerHandler());
}
});
try {
// 监听8080端口,并同步返回
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8080).sync();
// 阻止进入finally语句块,只有其他的线程调用 channelFuture.channel().close()的时候,然后进入finally代码块关闭连接池
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
package com.bonnie.netty.str.server;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import java.util.UUID;
/**
* 服务端handle
*/
public class SimpleServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
/**
* 接收客户端数据
* @param ctx
* @param msg
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
String record = (String) msg;
System.out.println("服务端接收消息:" + record);
// 写回数据
ctx.writeAndFlush(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
}
}
1.4 客户端代码
package com.bonnie.netty.str.client;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
/**
* netty客户端
*/
public class NettyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline()
.addLast(new StringDecoder())
.addLast(new StringEncoder())
.addLast(new SimpleClientHandle());
}
});
try {
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
package com.bonnie.netty.str.client;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBufAllocator;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.UUID;
// 客户端接收数据
public class SimpleClientHandle extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private int count;
/**
* 客户端连接成功后,就会调用此方法,然后给服务器去发送数据
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("客户端连接成功");
for (int i=0; i<10; i++) {
ctx.writeAndFlush("客户端消息" + i);
}
super.channelActive(ctx);
}
/**
* 读取服务端发送的数据
* @param ctx
* @param msg
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
String record = (String) msg;
System.out.println("收到服务端消息:" + record);
// 写回数据
ctx.writeAndFlush(UUID.randomUUID());
}
}
1.5 运行结果
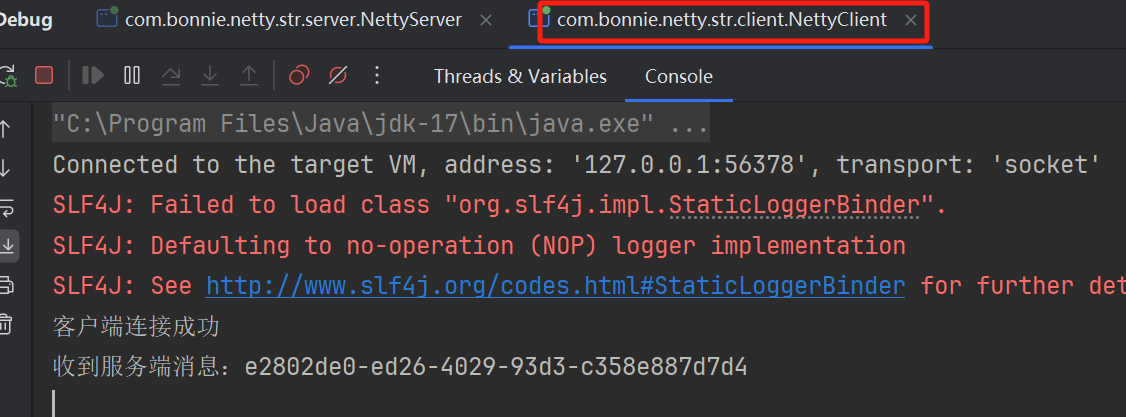
在使用Netty进行数据传输,就会使用到ByteBuf,在传输的过程中我们都会希望把数据先进行编码,也就是 序列化,把对象或者字符串数据转成二进制在网络中进行传输,接收方然后通过解码把二进制又转成对象接 收数据,那么在传输数据的过程中就会出现拆包和粘包的现象,我们来看下粘包和拆包,粘包就是把多个小的 数据包封装成一个打包发送,拆包就是把一个大的数据包拆成多个小数据包发送。
2 拆包和粘包
粘包:数据从客户端发送到服务端,可以把多个小的数据包封装成一个大的数据包发送。
拆包:数据从客户端发送发到服务端,可以一个大的数据包拆分成多个小的数据包发送。
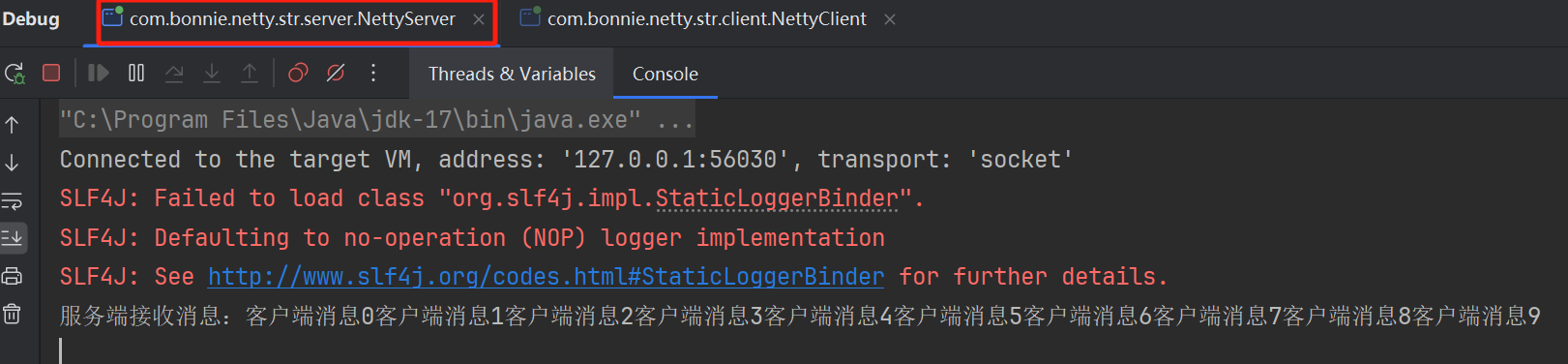
上面的案例中就发生了粘包,多个小的数据包合并成了一个大的数据包
服务端接收消息:客户端消息0客户端消息1客户端消息2客户端消息3客户端消息4客户端消息5客户端消息6客户端消息7客户端消息8客户端消息9
Netty中有4种解码器都是继承了ByteToMessageDecoder类,我们把这个类称之为一次解码器,他的作用是 通过ByteBuf去传递数据,我们把这种把ByteBuf(原始数据流) -> ByteBuf(用户数据) 称之为一次解码器, Netty中对于这个解码器提供了4种
3 netty四种解码器
3.1 FixedLengthFrameDecoder 固定长度解码器
客户端和服务端都是使用,然后设置每次传输数据的长度,所以这种方式就规定我们的数据长度是固定的,所以自然这种解码器不太好用
// 服务端
.addLast(new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(19))
// 客户端
.addLast(new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(37))3.2 LineBasedFrameDecoder 发送消息加上换行符\n
这种是不固定长度,只需要告诉服务端什么时候可以结束即可,我们可以使用换行符表示数据的结束,在发送数据的末尾添加"\n"换行符
//第二种:换行符 我每次\n结束 \n用的不多
.addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024))
// 客户端:换行符
ctx.writeAndFlush("客户端消息" + i + "\n");3.3 DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder 自定义分隔符解码器
使用其他方式作为结束标志的解码器,比如使用& ;等;只需要在发送数据的时候在数据后面加上分隔的符号就行了,只是分隔的符号需要包装成一个ByteBuf
// 第三种:分隔符
// maxFrameLength :报文的最大长度
// stripDelimiter:判断解码的时候是否要把分隔符去掉
// failFast:跟maxFrameLength合起来用,如果为true,如果大于消息的长度,直接抛异常,如果为false,
解码之后抛异常
// Delimiter:分隔符
ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("&".getBytes());
.addLast(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(Integer.MAX_VALUE,true,true,buf))3.4 LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder 长度域解码器
长度域解码器是一种自定义的解码器,可以按照规定的方式去灵活的定义报文,下面会介绍下基本的解码器。
3.4.1 配置代码
/**
* maxFrameLength:防止内存溢出的保护机制,超过此长度的帧会被丢弃
* lengthFieldOffset:长度字段在消息中的起始位置(从 0 开始)
* lengthFieldLength:长度字段本身占用的字节数(1, 2, 3, 4, 8)
* lengthAdjustment: 长度字段的值与实际内容长度的差值(可正可负)
* initialBytesToStrip:解码后需要从帧头部跳过的字节数(通常用于跳过长度字段)
*/
.addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0,4, 0, 4))3.4.2 参数详细解释
maxFrameLength:防止内存溢出的保护机制,超过此长度的帧会被丢弃
含义:允许的最大帧长度(字节数)
作用:防止内存溢出,保护系统安全
行为:当解码出的帧长度超过此值时,会抛出 TooLongFrameException,并关闭连接
建议值:根据业务最大消息大小设置,如 1024*1024(1MB)
lengthFieldOffset:长度字段在消息中的起始位置(从 0 开始)
含义:长度字段在整个消息中的起始偏移量(从 0 开始计数)
作用:定位长度字段的位置
示例:如果消息格式是 [标志位(1字节)][长度(2字节)][内容],则此值为 1
lengthFieldLength:长度字段本身占用的字节数(1, 2, 3, 4, 8)
含义:长度字段本身占用的字节数
允许值:1, 2, 3, 4, 8(分别对应不同范围的数值)
1 字节:0-255
2 字节:0-65535
4 字节:0-4294967295
注意:选择的字节数需能容纳业务最大消息长度
lengthAdjustment:长度字段的值与实际内容长度的差值(可正可负)
含义:长度调整值,用于修正长度字段的值
作用:当长度字段的值不正好等于内容长度时,通过此值进行调整
计算公式:实际内容长度 = 长度字段值 + lengthAdjustment
常见场景:
当长度字段包含自身长度时,使用负值(如 -2 表示减去长度字段自身的 2 字节)
当长度字段后还有其他固定字段时,使用正值(如 +1 表示加 1 字节的版本号字段)
initialBytesToStrip:解码后需要从帧头部跳过的字节数(通常用于跳过长度字段)
含义:解码后从帧的起始位置跳过的字节数
作用:移除不需要的头部信息(通常是长度字段本身)
常见设置:
0:保留所有字节(包括长度字段)
lengthFieldLength:跳过长度字段
其他值:跳过长度字段及前面 / 后面的额外字段
3.4.3 报文格式Length+Content
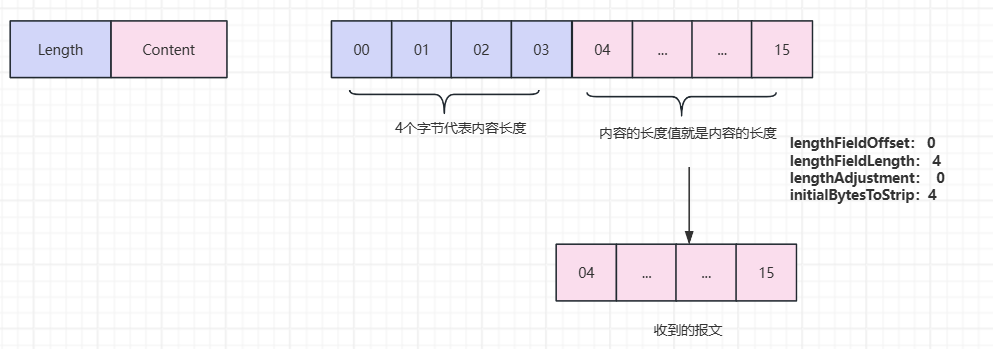
// 服务端,获取数据的时候只获取内容,不过去填充的长度,所以最后一个参数为4
.addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0,4, 0, 4))
.addLast(new LengthFieldPrepender(4, 0, false))
.addLast(new StringDecoder())
.addLast(new StringEncoder())
.addLast(new SimpleServerHandler());
// inbound执行顺序:LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder->StringDecoder->SimpleServerHandler
// outbound执行顺序:StringEncoder->LengthFieldPrepende
// 客户端 服务端,我们获取数据的时候只获取内容,不过去填充的长度,所以最后一个参数为4
.addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0,4, 0, 4))
.addLast(new LengthFieldPrepender(4, 0, false))
.addLast(new StringDecoder())
.addLast(new StringEncoder())
.addLast(new SimpleClientHandle());
// inbound执行顺序:LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder->StringDecoder->SimpleClientHandle
// outbound执行顺序:StringEncoder->LengthFieldPrepende3.4.4 报文格式Type+Length+Content
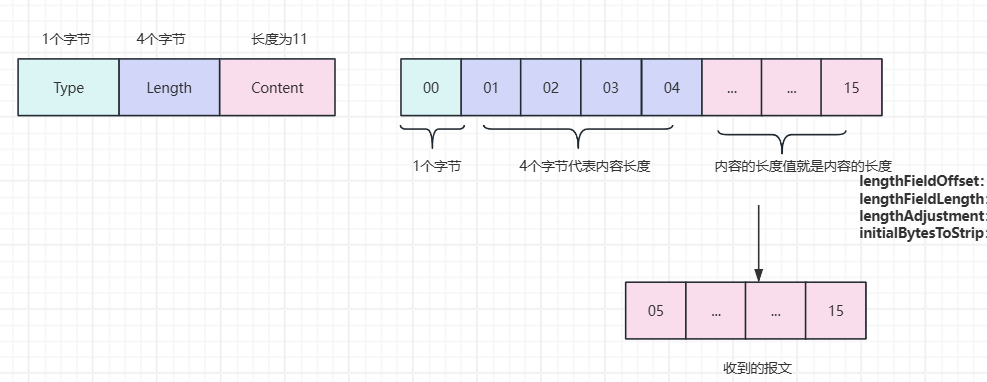
3.4.5 报文格式Length+Type+Content
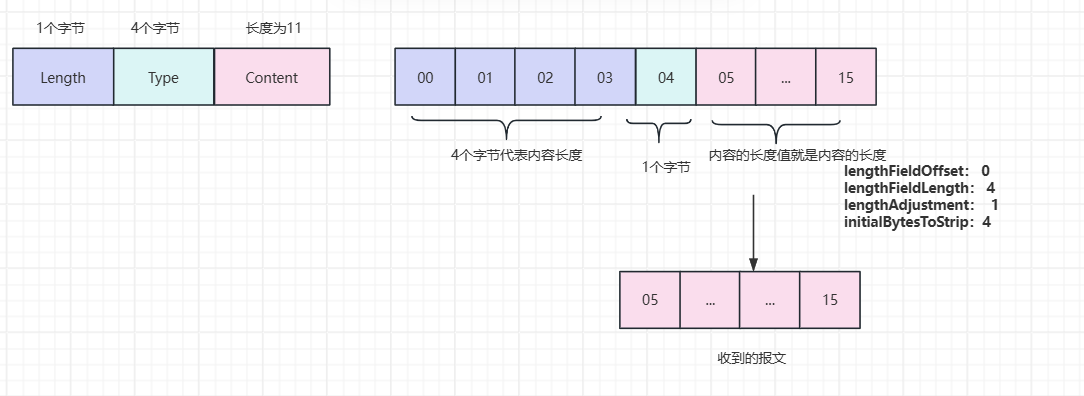
Length从位置0开始,偏移量是4
Length的值为12(Type和Content看成是一个整体1+11),Content的长度和Length的值的差值是1
接收到的实际值从Type+Content,所以是4
3.4.6 报文格式Type1+Length+Type2+Content
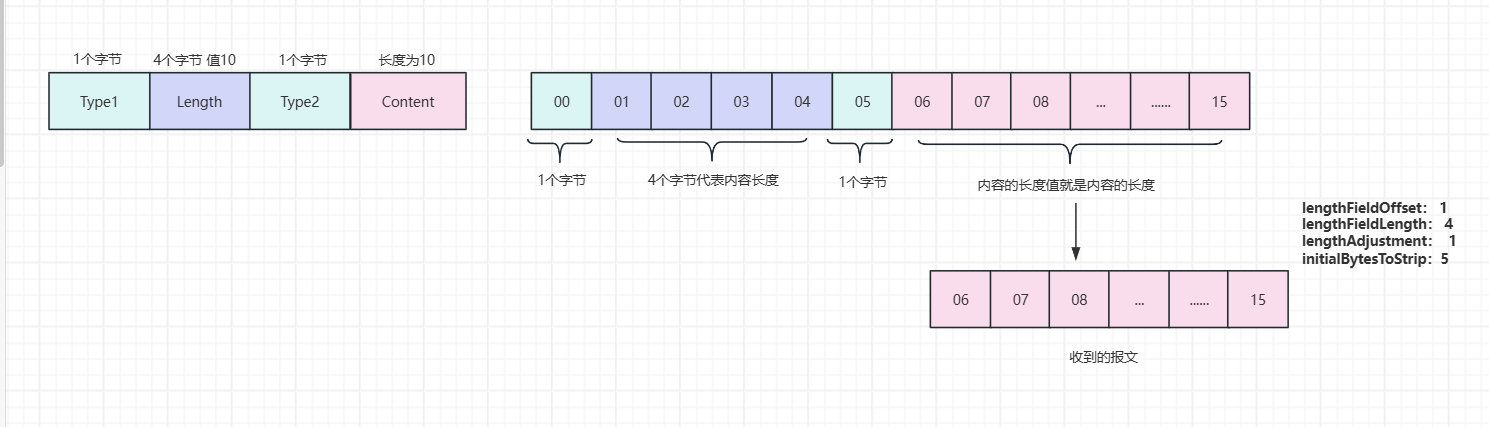
开始的1个字节是长度域,所以需要设置长度域偏移为1 长度域4个字节 我们需要把type2+body当做body处理,所以数据长度需要加1 接收数据不包括type1和长度域,所以需要跳过5个字节。
3.5 LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder长度域的源码简单分析
LengthFieldPrepender构造方法
public LengthFieldPrepender(ByteOrder byteOrder, int lengthFieldLength, int lengthAdjustment, boolean lengthIncludesLengthFieldLength) {
// 长度字段是用字节表示的,只能是1 2 3 4 8
if (lengthFieldLength != 1 && lengthFieldLength != 2 && lengthFieldLength != 3 && lengthFieldLength != 4 && lengthFieldLength != 8) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("lengthFieldLength must be either 1, 2, 3, 4, or 8: " + lengthFieldLength);
} else {
// 传入参数
this.byteOrder = (ByteOrder)ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(byteOrder, "byteOrder");
this.lengthFieldLength = lengthFieldLength;
this.lengthIncludesLengthFieldLength = lengthIncludesLengthFieldLength;
this.lengthAdjustment = lengthAdjustment;
}
}编码方法
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
// 看看是否需要添加长度字段的补偿值
int length = msg.readableBytes() + this.lengthAdjustment;
// 为true时,则length的值 = length的长度+内容的长度
if (this.lengthIncludesLengthFieldLength) {
length += this.lengthFieldLength;
}
ObjectUtil.checkPositiveOrZero(length, "length");
switch (this.lengthFieldLength) {
case 1:
if (length >= 256) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("length does not fit into a byte: " + length);
}
out.add(ctx.alloc().buffer(1).order(this.byteOrder).writeByte((byte)length));
break;
case 2:
if (length >= 65536) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("length does not fit into a short integer: " + length);
}
out.add(ctx.alloc().buffer(2).order(this.byteOrder).writeShort((short)length));
break;
case 3:
if (length >= 16777216) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("length does not fit into a medium integer: " + length);
}
out.add(ctx.alloc().buffer(3).order(this.byteOrder).writeMedium(length));
break;
case 4:
// 首先按照大端序列或者小端序列写入4个字节的长度字段
out.add(ctx.alloc().buffer(4).order(this.byteOrder).writeInt(length));
break;
case 5:
case 6:
case 7:
default:
throw new Error("should not reach here");
case 8:
out.add(ctx.alloc().buffer(8).order(this.byteOrder).writeLong((long)length));
}
// 在Netty中ByteBuf的回收使用的是引用计数器,当你为他增加一个引用时,请使用retain()增加一个引
//用,当引用释放时请调用release()方法减少一个引用,不然在回收的时候将会出问题。
// 把byteBuf保存到list中
out.add(msg.retain());
// 那么此时out的list中就会有两个对象,一个是代表长度的对象,一个是代表内容的对象
// 最后会通过NioSocketChannel去发送数据
}解码:看服务端的长度域解码器是如何解码的
protected final void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
// 解码
Object decoded = this.decode(ctx, in);
if (decoded != null) {
out.add(decoded);
}
}protected Object decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in) throws Exception {
if (this.discardingTooLongFrame) {
this.discardingTooLongFrame(in);
}
if (in.readableBytes() < this.lengthFieldEndOffset) {
return null;
} else {
// lengthFieldOffset表示长度字段需不需要偏移,这里不需要,报文的第一个就是长度字段
int actualLengthFieldOffset = in.readerIndex() + this.lengthFieldOffset;
// 获取到长度字段,并且讲字段表示的内容的值返回
long frameLength = this.getUnadjustedFrameLength(in, actualLengthFieldOffset, this.lengthFieldLength, this.byteOrder);
// 如果内容小于0,直接报错
if (frameLength < 0L) {
failOnNegativeLengthField(in, frameLength, this.lengthFieldEndOffset);
}
// lengthFieldEndOffset = lengthFieldOffset + lengthFieldLength = 0 + 4 = 4
// frameLength = 内容 + 长度,其实这里就是获取整个报文的长度
frameLength += (long)(this.lengthAdjustment + this.lengthFieldEndOffset);
// 如果整个报文的长度比lengthFieldEndOffset还小,就说明没有内容
if (frameLength < (long)this.lengthFieldEndOffset) {
failOnFrameLengthLessThanLengthFieldEndOffset(in, frameLength, this.lengthFieldEndOffset);
}
// 如果整个报文的长度比最大还要大,另行处理
if (frameLength > (long)this.maxFrameLength) {
this.exceededFrameLength(in, frameLength);
return null;
} else {
int frameLengthInt = (int)frameLength;
if (in.readableBytes() < frameLengthInt) {
return null;
} else {
// 跳过长度字节,如果大于最大的内容长度,数据有问题
if (this.initialBytesToStrip > frameLengthInt) {
failOnFrameLengthLessThanInitialBytesToStrip(in, frameLength, this.initialBytesToStrip);
}
// 开始跳过4个字节,直接获取内容
in.skipBytes(this.initialBytesToStrip);
int readerIndex = in.readerIndex();
int actualFrameLength = frameLengthInt - this.initialBytesToStrip;
// 返回内容
ByteBuf frame = this.extractFrame(ctx, in, readerIndex, actualFrameLength);
in.readerIndex(readerIndex + actualFrameLength);
return frame;
}
}
}
}
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容






所有评论(0)