机器学习-准备 scikit-learn-Orange安装
一、scikit-learn引导1.1scikit-learn 是什么面向python免费机器学习库建立在Numpy、Scipy、和 scikit-learn 模块之上包含分类、回归、聚类算法 比如:SVM,随机森林,K-mean等包含降维、模型筛选、预处理算法1.2 scikit-learn 安装推荐Anaconda 已经封装了 scikit-lear...
·
一、scikit-learn引导
1.1 scikit-learn 是什么
面向python免费机器学习库 建立在Numpy、Scipy、和 scikit-learn 模块之上 包含分类、回归、聚类算法 比如:SVM,随机森林,K-mean等 包含降维、模型筛选、预处理算法1.2 scikit-learn 安装
推荐Anaconda 已经封装了 scikit-learn Anaconda 查询包信息: conda list|grep matplotlib 通过 pip 安装 由于 scikit-learn 建立在Numpy、Scipy 模块之上,必须先安装这两个 pip install -U numpy scipy scikit-learn1.3 scikit-learn API
1.3.1 sklearn常用数据集一览
类型 获取方式 自带小数据集 sklearn.datasets.load_ 在线下载的数据集 sklearn.datasets.fetch_ 计算机生成的数据集 sklearn.datasets.make_ svmlight/libsvm格式的数据集 sklearn.datasets.load_svmlight_file(…) mldata.org在线下在数据集 sklearn.datasets.fetch_mldata 1.3.2 sklearn自带的小数据集
自带的小数据集
名称 数据包调用方式 适用算法 鸢尾花数据集 load_iris() 分类 乳腺癌数据集 load_bread_cancer() 二分类任务 手写数字数据集 load_digits() 分类 糖尿病数据集 load_diabetes() 回归 波士顿房价数据集 load_boston() 回归 体能训练数据集 load_linnerud() 多变量回归 1.3.2 iris(鸢尾花)数据集的查看
iris包含150个样本,对应数据集的每行数据。每行数据包含每个样本的四个特征和样本的类别信息,所以iris数据集是一个150行5列的二维表。
每个样本包含了花萼长度、花萼宽度、花瓣长度、花瓣宽度四个特征(前4列,单位cm)和品种信息,即目标属性(第5列,也叫target或label)。
from sklearn import datasets import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.datasets import load_iris iris=load_iris() #加载数据集 iris.keys() 输出: dict_keys(['target', 'DESCR', 'data', 'target_names', 'feature_names']) n_samples,n_features=iris.data.shape print("Number of sample:",n_samples) print("Number of feature",n_features) print(iris.data[0]) #第一个样例 print(iris.data.shape) print(iris.target.shape) print(iris.target) 依次输出 : Number of sample: 150 : Number of feature 4 : [ 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2] #第一个样例输出 : (150, 4) : (150,) : [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2]iris=datasets.load_iris() x_index=3 color=['blue','red','green'] for label,color in zip(range(len(iris.target_names)),color): plt.hist(iris.data[iris.target==label,x_index], label=iris.target_names[label], color=color) plt.xlabel(iris.feature_names[x_index]) plt.legend(loc='upper right') plt.show()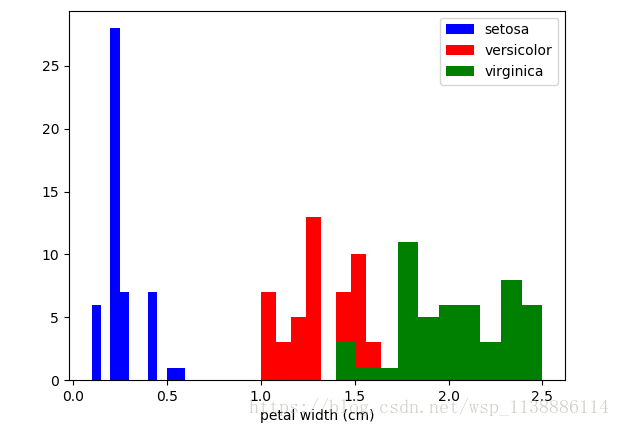
iris=datasets.load_iris() x_index=0 y_index=1 colors=['blue','red','green'] for label,color in zip(range(len(iris.target_names)),colors): plt.scatter(iris.data[iris.target==label,x_index], iris.data[iris.target==label,y_index], label=iris.target_names[label], c=color) plt.xlabel(iris.feature_names[x_index]) plt.ylabel(iris.feature_names[y_index]) plt.legend(loc='upper left') plt.show()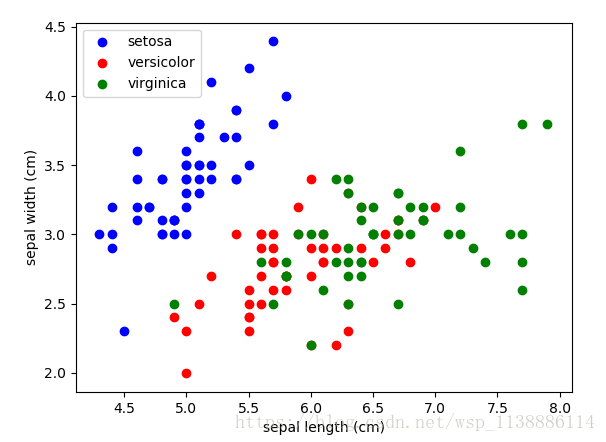
1.4 scikit-learn 三个主要概念
估计器 Estimator :用于分类,聚类,回归 主要函数: fit():训练算法,设置内部参数,接受训练集和内别两个参数 predict(): 预测测试集类别,参数为测试集 大多数 scikit-learn 估计器接收和输出数据格式均为numpy或类似格式 scikit-learn之估计器运行流程 转换器 Transformer:用于数据预处理,数据转换 流水线 Pipeline: 组合数据挖掘,便于再次使用 sklearn.pipeline 包 流水线功能: 跟踪记录各步骤的操作(以便重现实验结果) 对各步骤进行封装 确保代码复杂程度不至于超出掌控范围 基本使用方法 流水线输入 一连串数据挖掘步骤 其中最后一步必须是预估器 前几步是转换器 输入的数据集经过转换器处理后,上一步输出->下一步输入。。。->估计器,对数据进行分类 每一步都有元组('名称','步骤')来表示
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassfier
iris_x = iris.data
iris_y = iris.target
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(iris_x,iris_y,test_size = 0.3)
model = KNeighborsClassfier()
model.fit(x_train,y_train)
print(model.predict(x_test))
print(y_test)二、Orange 与可视化机器学习
2.1 Orange 简介
老司机可作为Python模块2.2 Orange 安装
Orange 已经完全转到python3 项目主页请点击
▶ 安装步骤(
python3.x环境):在 Anaconda Prompt 下执行: conda create --name Py35_Orange3 python=3.5▶ 激活环境:
activate Py35_Orange3 #for windows source activate Py35_Orange3 #for Linux/MacOS▶ 安装 orange3
pip install orange3▶ 验证是否安装成功
>>> import Orange >>> Orange.version.versionOrange扩展包-关联
在 Orange3 中,关联规则算法在 add-on 包中 项目主页:https://pypi.python.org/pypi/Orange3-Associate通过 pip 安装
pip install Orange3-Associate
Orange扩展包-协同过滤
在 Orange3 中,协同过滤算法在 add-on 包中 项目主页:https://github.com/mstrazar/orange通过 pip 安装
pip install Orange3-recommenddation2.3 Orange 使用方式
使用方式 1 –脚本
from orangecontrib.associate.fpgrowth import * #关联 T = [[1,3,4], [2,3,5], [1,2,3,5], [2,5]] itemset = dict(frequent_itemsets(T,2)) itemset rules = [(P,Q,supp,conf) for P,Q,supp,conf in association_rules(itemsets,.8)if len(Q)==1] (rules)使用方式 2 图形界面
source activate python35 orange-canvas&2.4 Orange 功能结构–数据准备与预处理
Data visualize model evaluate
三、Xgboost 简介
Xgboost 是大规模并行boosted tree 工具 安装 Xgboost 的python 版需要Numpy,Scipy等数值计算库, Xgboost 安装--Linux 升级包版本 $ conda updata -all 安装 pip install xgboost 测试 $python Xgboost 安装-windows python3.5及以上版本,基于anaconda http://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/#xgboost 在以上网站找对应版本 安装(install后面为下载保存位置+下载版本) pip install xgboost-0.6-cp35-cp35m-win_amd64.whl
四、 sklearn 主要算法调用及比较
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
#from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split #废弃!!
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons, make_circles, make_classification
from sklearn.neural_network import BernoulliRBM
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.gaussian_process import GaussianProcess
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, AdaBoostClassifier
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis
h = .02 # step size in the mesh
names = ["Nearest Neighbors", "Linear SVM", "RBF SVM",
"Decision Tree", "Random Forest", "AdaBoost",
"Naive Bayes", "QDA", "Gaussian Process","Neural Net", ]
classifiers = [
KNeighborsClassifier(3),
SVC(kernel="linear", C=0.025),
SVC(gamma=2, C=1),
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=5),
RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=5, n_estimators=10, max_features=1),
AdaBoostClassifier(),
GaussianNB(),
QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis(),
#GaussianProcess(),
#BernoulliRBM(),
]
X, y = make_classification(n_features=2, n_redundant=0, n_informative=2,
random_state=1, n_clusters_per_class=1)
rng = np.random.RandomState(2)
X += 2 * rng.uniform(size=X.shape)
linearly_separable = (X, y)
datasets = [make_moons(noise=0.3, random_state=0),
make_circles(noise=0.2, factor=0.5, random_state=1),
linearly_separable
]
figure = plt.figure(figsize=(27, 9))
i = 1
# iterate over datasets
for ds_cnt, ds in enumerate(datasets):
# preprocess dataset, split into training and test part
X, y = ds
X = StandardScaler().fit_transform(X)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = \
train_test_split(X, y, test_size=.4, random_state=42)
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - .5, X[:, 0].max() + .5
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - .5, X[:, 1].max() + .5
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
# just plot the dataset first
cm = plt.cm.RdBu
cm_bright = ListedColormap(['#FF0000', '#0000FF'])
ax = plt.subplot(len(datasets), len(classifiers) + 1, i)
if ds_cnt == 0:
ax.set_title("Input data")
# Plot the training points
ax.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c=y_train, cmap=cm_bright)
# and testing points
ax.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c=y_test, cmap=cm_bright, alpha=0.6)
ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
i += 1
# iterate over classifiers
for name, clf in zip(names, classifiers):
ax = plt.subplot(len(datasets), len(classifiers) + 1, i)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
score = clf.score(X_test, y_test)
# Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each
# point in the mesh [x_min, m_max]x[y_min, y_max].
if hasattr(clf, "decision_function"):
Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
else:
Z = clf.predict_proba(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])[:, 1]
# Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=cm, alpha=.8)
# Plot also the training points
ax.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c=y_train, cmap=cm_bright)
# and testing points
ax.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c=y_test, cmap=cm_bright,
alpha=0.6)
ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
if ds_cnt == 0:
ax.set_title(name)
ax.text(xx.max() - .3, yy.min() + .3, ('%.2f' % score).lstrip('0'),
size=15, horizontalalignment='right')
i += 1
plt.tight_layout()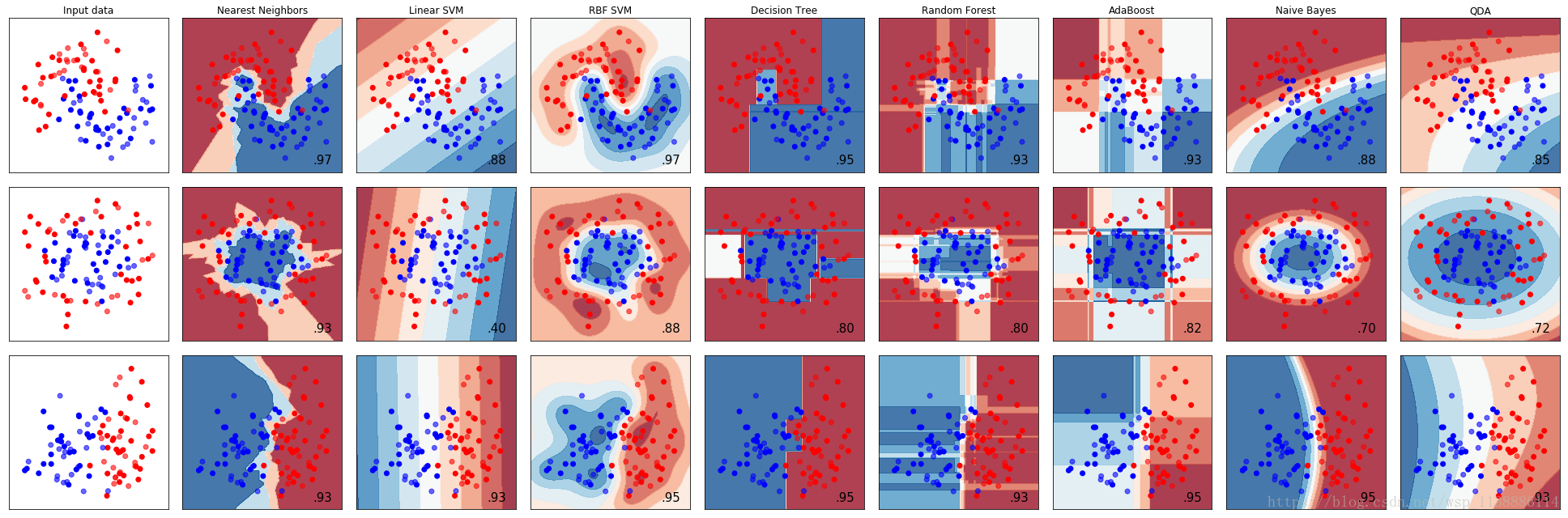
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献70条内容
已为社区贡献70条内容







所有评论(0)