边界框格式坐标转YOLO格式坐标
边界框格式坐标为(x1,y1),(x2,y2),1。其中(x1,y1)表示边界框的左上角坐标,(x2,y2)表示边界框的右下角坐标,a表示目标的类别。需要根据自己的路径对上面两个路径进行替换,其中labels_directory是labels路径,images_directory是labels对应的图片路径。其中c是目标的类别数量,x、y是目标中心相对于图像宽度和高度的坐标,w、h是目标的宽度和高
形如下左图这样的,我们需要将其转换成右图方可用于YOLO。
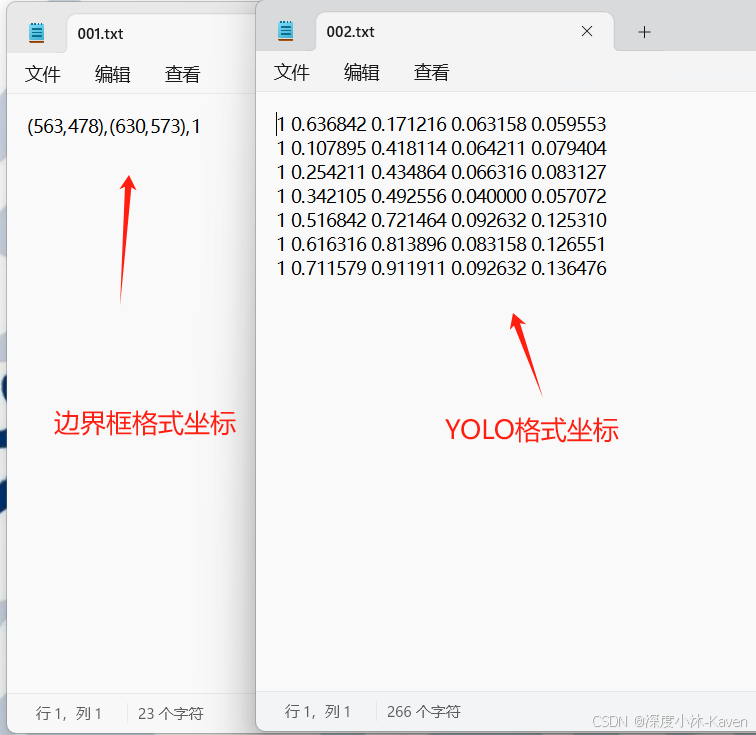
边界框格式坐标解释:
边界框格式坐标为(x1,y1),(x2,y2),1。其中(x1,y1)表示边界框的左上角坐标,(x2,y2)表示边界框的右下角坐标,a表示目标的类别。这种格式直观地给出了边界框在图像中的位置。
YOLO 格式坐标解释
YOLO 格式坐标为c x y w h。其中c是目标的类别数量,x、y是目标中心相对于图像宽度和高度的坐标,w、h是目标的宽度和高度相对于图像宽度和高度的比例。
计算公式如下:设图像的宽度为W,高度为H
中心坐标x:
中心坐标y:
宽度w:
高度h:
接下来上干货直接上代码:
首先需要确保安装了 Pillow 库来读取图像的宽高,如果没有安装,可以使用以下命令:
pip install Pillow
安装完后复制粘贴下面代码:
import os
from PIL import Image
def convert_to_yolo_format(x1, y1, x2, y2, img_width, img_height):
# 计算中心坐标和宽高
x_center = (x1 + x2) / 2 / img_width
y_center = (y1 + y2) / 2 / img_height
width = (x2 - x1) / img_width
height = (y2 - y1) / img_height
return x_center, y_center, width, height
def get_image_size(image_path):
with Image.open(image_path) as img:
return img.size # 返回宽度和高度
def process_label_file(file_path, img_width, img_height):
new_lines = []
with open(file_path, 'r') as file:
for line in file:
# 去掉换行符并分割
line = line.strip()
if line: # 确保不处理空行
coords, category = line.rsplit(',', 1)
x1y1, x2y2 = coords.split('),(')
x1y1 = x1y1[1:] # 去掉开头的括号
x2y2 = x2y2[:-1] # 去掉结尾的括号
x1, y1 = map(float, x1y1.split(','))
x2, y2 = map(float, x2y2.split(','))
# 转换为YOLO格式
x_center, y_center, width, height = convert_to_yolo_format(x1, y1, x2, y2, img_width, img_height)
# 创建新的行,以空格分隔
new_line = f"{int(category)} {x_center:.6f} {y_center:.6f} {width:.6f} {height:.6f}"
new_lines.append(new_line)
# 将新内容写回文件
with open(file_path, 'w') as file:
for new_line in new_lines:
file.write(new_line + '\n')
def process_directory(directory, image_directory):
for filename in os.listdir(directory):
if filename.endswith('.txt'):
label_file_path = os.path.join(directory, filename)
# 从新路径拼接图像文件的路径
image_file_path = os.path.join(image_directory, filename.replace('.txt', '.jpg')) # 这里可以调整扩展名
if os.path.exists(image_file_path): # 确保图像文件存在
img_width, img_height = get_image_size(image_file_path) # 获取图像尺寸
process_label_file(label_file_path, img_width, img_height)
else:
print(f"找不到与标签文件 {filename} 对应的图像文件 {image_file_path}")
# 设置标签文件和图像文件所在目录
labels_directory = r'C:\Users\DELL\Desktop\NWPU VHR-10 dataset\labels\train'
images_directory = r'C:\Users\DELL\Desktop\NWPU VHR-10 dataset\images\train'
# 处理目录中的所有标签文件
process_directory(labels_directory, images_directory)
print("标签文件处理完成。")
注意有几个需要修改的地方:
1.# 设置标签文件和图像文件所在目录
labels_directory = r'C:\Users\DELL\Desktop\NWPU VHR-10 dataset\labels\train'
images_directory = r'C:\Users\DELL\Desktop\NWPU VHR-10 dataset\images\train'需要根据自己的路径对上面两个路径进行替换,其中labels_directory是labels路径,images_directory是labels对应的图片路径。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献5条内容
已为社区贡献5条内容







所有评论(0)