XGBoost使用总结
一、前言最近用到了XGBoost模型,总结一下。二、原理参考朋友的博客,个人感觉总结的很到位:http://reset.pub/2017/04/01/xgboost/三、参数解读参考:https://xgboost.readthedocs.io/en/latest/parameter.html3.1 常规参数boostergbtree 树模型做为基分类器(默认)...
一、前言
最近用到了XGBoost模型,总结一下。
二、原理
参考朋友的博客,个人感觉总结的很到位:
http://reset.pub/2017/04/01/xgboost/
三、参数解读
参考:https://xgboost.readthedocs.io/en/latest/parameter.html
3.1 常规参数
-
booster
- gbtree 树模型做为基分类器(默认)
- gbliner 线性模型做为基分类器,效果不如前者好,比较少用 silent
- silent=0时,不输出中间过程(默认)
- silent=1时,输出中间过程 nthread
- nthread=-1时,使用全部CPU进行并行运算(默认)
- nthread=1时,使用1个CPU进行运算 scale_pos_weight
- 正样本的权重,在二分类任务中,当正负样本比例失衡时,设置正样本的权重,模型效果更好。例如,当正负样本比例为1:10时,scale_pos_weight=10。
3.2 模型参数
-
n_estimatores
- 含义:总共迭代的次数,即决策树的个数 early_stopping_rounds
- 含义:在验证集上,当连续n次迭代,分数没有提高后,提前终止训练。
- 调参:防止overfitting max_depth
-
含义:树的深度,默认值为6,典型值3-10
调参:值越大,越容易过拟合;值越小,越容易欠拟合 min_child_weight
-
含义:默认值为1,孩子节点中最小的样本权重和。如果一个叶子节点的样本权重和小于min_child_weight则拆分过程结束。在现行回归模型中,这个参数是指建立每个模型所需要的最小样本数。该成熟越大算法越conservative。
调参:值越大,越容易欠拟合;值越小,越容易过拟合(值较大时,避免模型学习到局部的特殊样本) subsample
-
含义:训练每棵树时,使用的数据占全部训练集的比例。如果设置为0.5则意味着XGBoost将随机的冲整个样本集合中随机的抽取出50%的子样本建立树模型,这能够防止过拟合。默认值为1,典型值为0.5-1。
调参:防止overfitting colsample_bytree
-
含义:训练每棵树时,使用的特征占全部特征的比例。默认值为1,典型值为0.5-1。
调参:防止overfitting。
3.3 学习任务参数
-
eta
-
含义:学习率,控制每次迭代更新权重时的步长,默认0.3。
调参:值越小,训练越慢。典型值为0.01-0.2。 objective
-
含义:目标函数
回归任务
reg:linear (默认)
reg:logistic
二分类
binary:logistic 概率
binary:logitraw 类别
多分类
multi:softmax num_class=n 返回类别
multi:softprob num_class=n 返回概率
rank:pairwise(相对于任务来说) eval_metric:预测数据的度量方法
- 默认值取决于objective参数的取值,对于回归问题,默认值是rmse,对于分类问题,默认值是error.
-
回归任务(默认rmse)
rmse–均方根误差
mae–平均绝对误差
分类任务(默认error)
auc–roc曲线下面积
error–错误率(二分类)
merror–错误率(多分类)
logloss–负对数似然函数(二分类)
mlogloss–负对数似然函数(多分类) gamma
- 惩罚项系数,指定节点分裂所需的最小损失函数下降值。 alpha
- L1正则化系数,默认为1 lambda
- L2正则化系数,默认为1
四、主要函数:
建立模型:XGBClassifier(), XGBRegressor()根据任务选择分类或回归函数
模型训练:fit()
模型预测:predict()
特征重要性:plot_importance()显示所有特征的F值和P值
五、调参
Scikit-learn中提供了一个函数可以帮助我们很好地进行调参:
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV参数:
estimator:所使用的分类器,如果使用的是XGBoost的话,estimator = XGBRegressor(**other_params)
param_grid:值为字典或者列表,需要最优化的参数的取值。比如:cv_params = {‘n_estimators’: [550, 575, 600]}
scoring :准确度评价标准,默认None;根据所选模型不同,评价准则不同。如果是None,则使用estimator的误差估计函数。常用的评价准则如下: 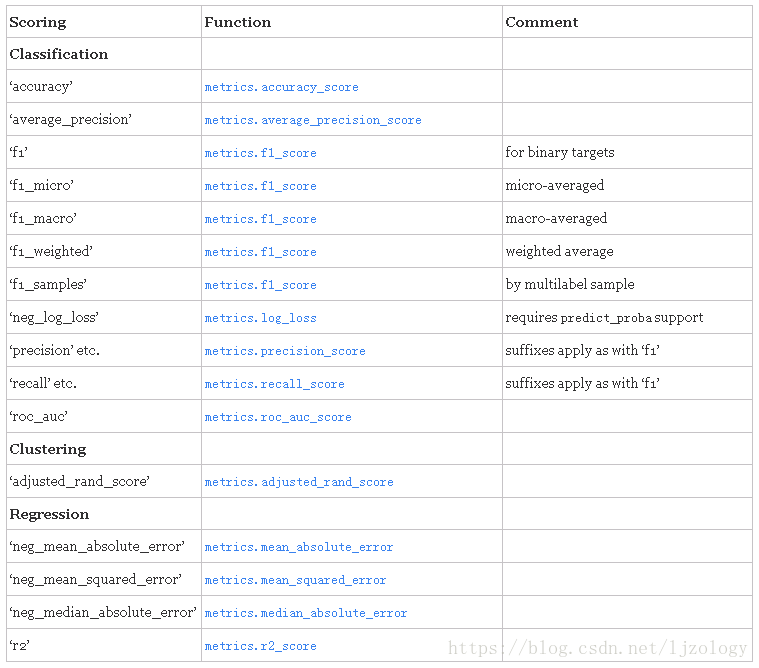
一般,回归模型采用“r2”,分类模型采用“accuracy”
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/xinping-study/p/7116574.html
reg_alpha的调参示例:
cv_params = {'reg_alpha': [0.05, 0.1, 1, 2, 3]}
other_params = {'learning_rate': 0.01, 'n_estimators':1200, 'max_depth': 8, 'min_child_weight': 7, 'seed': 0,
'subsample': 0.2, 'colsample_bytree': 0.9, 'gamma': 0.01, 'reg_alpha': 7, 'reg_lambda': 4}
model = XGBRegressor(**other_params)
reg = GridSearchCV(estimator=model, param_grid=cv_params, scoring='neg_mean_squared_error', cv=5, verbose=1, n_jobs=4)
reg.fit(train, y_train)
evalute_result = reg.grid_scores_
print('每轮迭代运行结果:{0}'.format(evalute_result))
print('参数的最佳取值:{0}'.format(reg.best_params_))
print('最佳模型得分:{0}'.format(reg.best_score_))输出:
[Parallel(n_jobs=4)]: Done 42 tasks | elapsed: 2.0min
[Parallel(n_jobs=4)]: Done 125 out of 125 | elapsed: 5.6min finished
每轮迭代运行结果:[mean: 0.94169, std: 0.00997, params: {'reg_alpha': 0.01, 'reg_lambda': 0.01}, mean: 0.94112, std: 0.01086, params: {'reg_alpha': 0.01, 'reg_lambda': 0.05}, mean: 0.94153, std: 0.01093, params: {'reg_alpha': 0.01, 'reg_lambda': 0.1}, mean: 0.94400, std: 0.01090, params: {'reg_alpha': 0.01, 'reg_lambda': 1}, mean: 0.93820, std: 0.01177, params: {'reg_alpha': 0.01, 'reg_lambda': 100}, mean: 0.94194, std: 0.00936, params: {'reg_alpha': 0.05, 'reg_lambda': 0.01}, mean: 0.94136, std: 0.01122, params: {'reg_alpha': 0.05, 'reg_lambda': 0.05}, mean: 0.94164, std: 0.01120...]
参数的最佳取值:{'reg_alpha': 1, 'reg_lambda': 1}
最佳模型得分:0.9441561344357595六、一个完整的XGBoost例子
来自sofa预测自行车使用量竞赛:http://sofasofa.io/competition.php?id=1
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 引入模块
from xgboost import XGBRegressor
import pandas as pd
# 读取数据
train = pd.read_csv("./data/train.csv")
test = pd.read_csv("./data/test.csv")
submit = pd.read_csv("./data/sample_submit.csv")
# 特征工程
train["t1-t2"] = train.temp_1-train.temp_2
test["t1-t2"] = test.temp_1-test.temp_2
# 离散化
train["temp_1"] = [cut(x) for x in train["temp_1"]]
train["temp_2"] = [cut(x) for x in train["temp_2"]]
test["temp_1"] = [cut(x) for x in test["temp_1"]]
test["temp_2"] = [cut(x) for x in test["temp_2"]]
train["t1-t2-1"] = [cut(x, spots=[-2,2]) for x in train["t1-t2"]]
test["t1-t2-1"] = [cut(x, spots=[-2,2]) for x in test["t1-t2"]]
# 删除id
train.drop('id', axis=1, inplace=True)
test.drop('id', axis=1, inplace=True)
# 取出训练集的y
y_train = train.pop('y')
# 建立一个默认的xgboost回归模型
reg = XGBRegressor(learning_rate = 0.01, n_estimators=1200, max_depth=8, min_child_weight=7, seed=0,
subsample=0.2, colsample_bytree=0.9, gamma=0.01, reg_alpha=7, reg_lambda=4)
reg.fit(train, y_train)
y_pred = reg.predict(test)
# 输出预测结果至my_XGB_prediction.csv
submit['y'] = y_pred
submit.to_csv('my_XGB(t1-t2)1(cut t1-t2)_prediction.csv', index=False)更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容






所有评论(0)