CUR矩阵分解
CUR矩阵分解
CUR矩阵分解
1. Intuition
SVD缺点:
- 可解释性差。
- 太过Dense。
SVD: X = U Σ V T X=U\Sigma V^T X=UΣVT,其中 U , V U,V U,V都是Big and Dense, Σ \Sigma Σ是Small But Sparse。
Aims to Get:
CUR: X = C U R X=CUR X=CUR,其中 C , R C,R C,R都是Big but Sparse, U U U是Small and Dense。
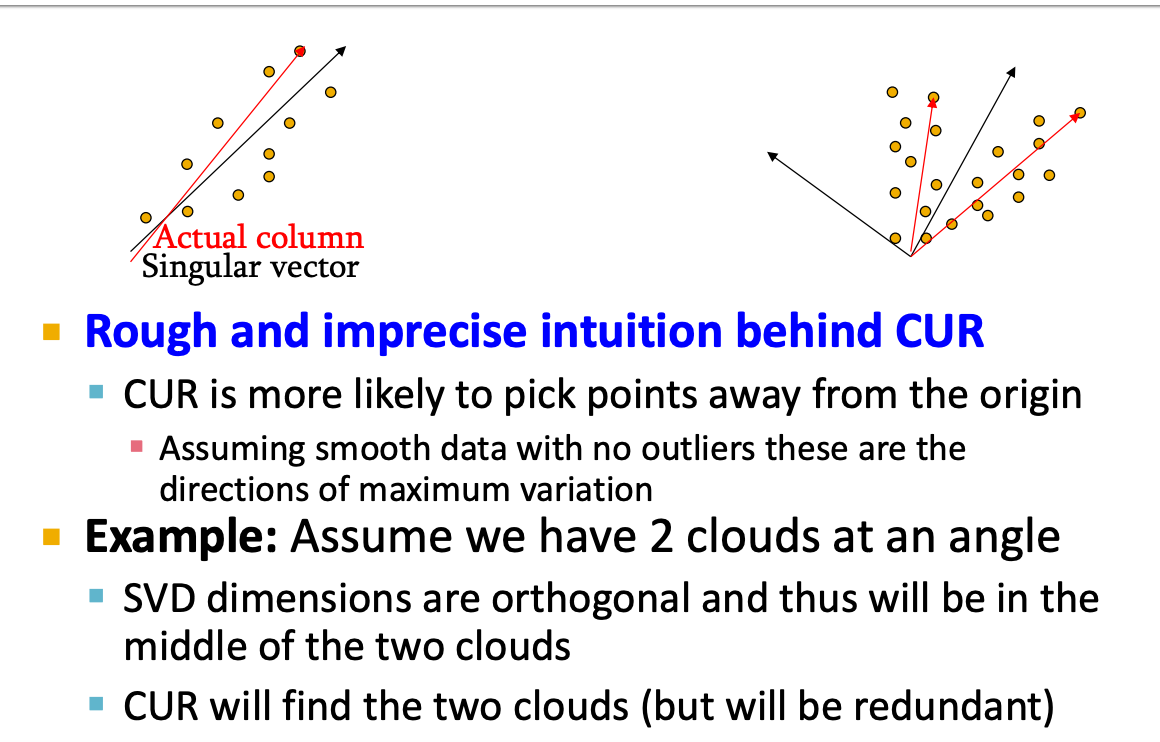
Rough Intuition:
CUR选的点可能是更偏离远点的,同时坐标轴可能是多余的。
2. Proof
TL;DR.
详见CUR理论公式推导。
3. Algo
Given Input Matrix A:
- Randam choose, C columns, R rows.
- C ∩ U C\cap U C∩U intersection point matrix W W W.
- SVD Decomposition W = X Σ Y T W = X\Sigma Y^T W=XΣYT
- Derive Generalized inverse matrix of $\Sigma^{+} $ via Σ \Sigma Σ, i.e. non-zero elements turn to its countdown
- Derive U = Y Σ + X T U=Y\Sigma^{+}X^T U=YΣ+XT
- A = C ⋅ U ⋅ R = C ⋅ Y ⋅ Σ + ⋅ X T ⋅ R A=C\cdot U\cdot R=C\cdot Y\cdot \Sigma^{+}\cdot X^T\cdot R A=C⋅U⋅R=C⋅Y⋅Σ+⋅XT⋅R
4. Remarks
第一步关于如何选择C,R
-
Mahoney等人提出可以里用normalized statistical leverage scores π j = 1 k ∑ η = 1 k = ( v η i ) 2 \pi_j=\frac{1}{k}\sum_{\eta=1}^k=(v_\eta^i)^2 πj=k1∑η=1k=(vηi)2,i.e.该列/行的二范数占所有列数二范数的比例,作为衡量其统计影响力的指标。也即square of its Frobenius norm。
-
可能有读者想问“有代表的q,kq,k要怎么选?”,事实上,大多数情况下都是随机选的,这就留下了一些提升空间,比如可以聚类后选最接近聚类中心的那个,这些就看大家自由发挥了。另外要指出的是,CUR分解本身只是一种近似,它肯定有误差,所以该加速方案主要是为检索场景设计的,检索场景的特点是比较在乎topk的召回率,而不是特别要求top1的精确率,我们可以用CUR分解加速来召回若干个结果后,再用精确的s(q,k)做一次重排序来提高准确度。
第四步关于广义逆矩阵
也有文献表示QR分解更稳定。
Experiments

不放回抽样的CUR效果最好。同时保证了效率和精度。对于large sparse matrix有很不错的效果。
Reference
CUR matrix decompositions for improved data analysis
Sublinear Time Approximation of Text Similarity Matrices
Semantic Representation of Documents Based on Matrix Decomposition
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容






所有评论(0)