基于PCL的三维重建——点云配准(一)ICP算法实现
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33933704/article/details/78652633在逆向工程,计算机视觉,文物数字化等领域中,由于点云的不完整,旋转错位,平移错位等,使得要得到的完整的点云就需要对局部点云进行配准,为了得到被测物体的完整数据模型,需要确定一个合适的坐标系,将从各个视角得到的点集合并到统一的坐标系下形成一个完整的点云,然后就可以方便进行可视化的操..
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33933704/article/details/78652633
在逆向工程,计算机视觉,文物数字化等领域中,由于点云的不完整,旋转错位,平移错位等,使得要得到的完整的点云就需要对局部点云进行配准,为了得到被测物体的完整数据模型,需要确定一个合适的坐标系,将从各个视角得到的点集合并到统一的坐标系下形成一个完整的点云,然后就可以方便进行可视化的操作,这就是点云数据的配准。点云的配准有手动配准依赖仪器的配准,和自动配准,点云的自动配准技术是通过一定的算法或者统计学规律利用计算机计算两块点云之间错位,从而达到两块点云自动配准的效果,其实质就是把不同的坐标系中测得到的数据点云进行坐标系的变换,以得到整体的数据模型,问题的关键是如何让得到坐标变换的参数R(旋转矩阵)和T(平移向量),使得两视角下测得的三维数据经坐标变换后的距离最小,,目前配准算法按照过程可以分为整体配准和局部配准,。PCL中有单独的配准模块,实现了配准相关的基础数据结构,和经典的配准算法如ICP。
ICP算法对待拼接的2片点云,首先根据一定的准则确立对应点集P与Q,其中对应点对的个数,然后通过最小乘法迭代计算最优的坐标变换,即旋转矩阵R和平移矢量t,使得误差函数最小,ICP处理流程分为四个主要的步骤:
1. 对原始点云数据进行采样
2.确定初始对应点集
3.去除错误对应点对
4.坐标变换求解
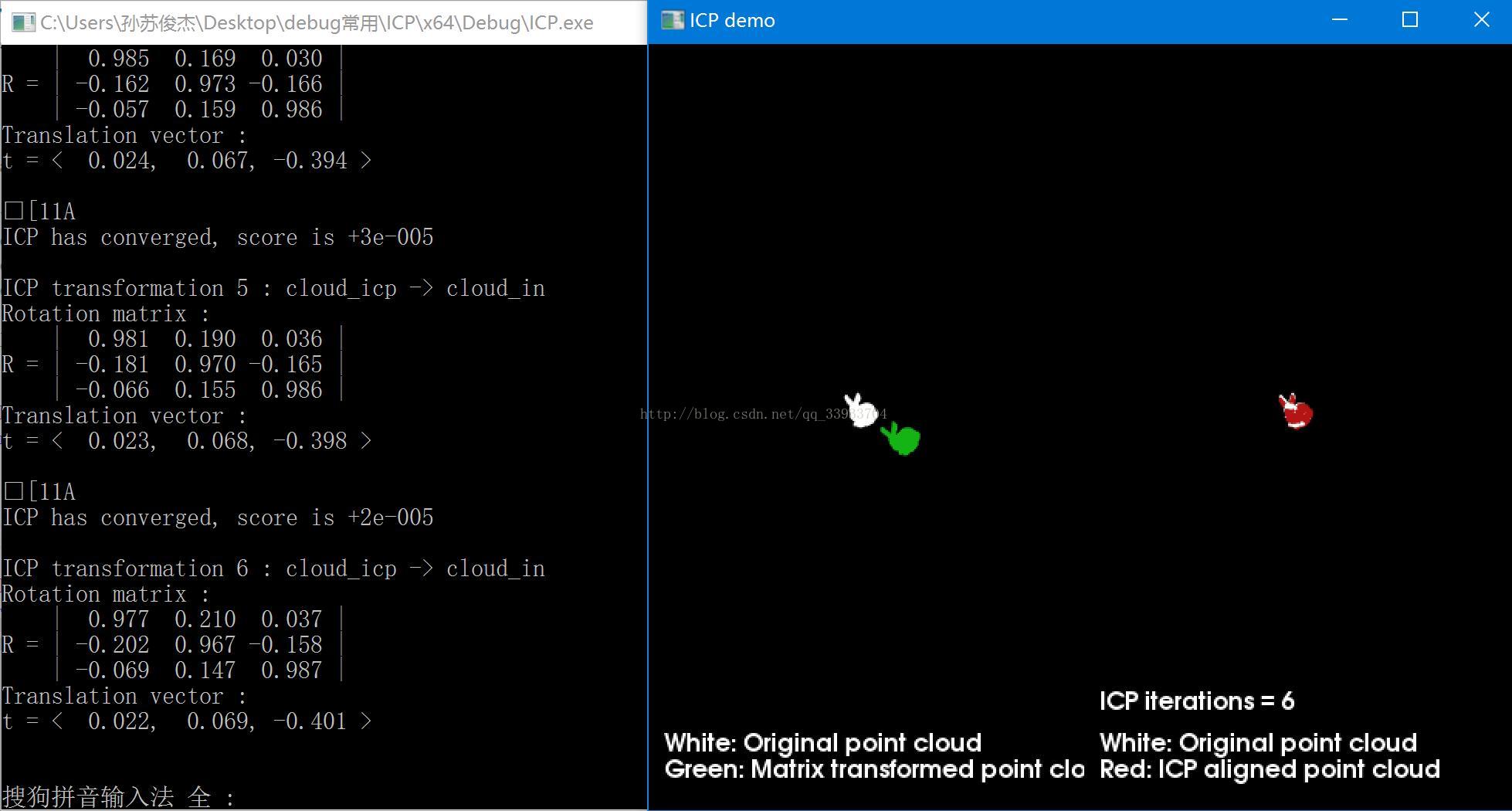
以下代码读取两个pcd点云配准,用空格控制迭代次数,并用visualization可视化出来,其中白色用来显示原始点云数据,经过一定旋转平移的点云显示为绿色,红色用来显示icp匹配后的点云数据。每次迭代都会打出此时的选择矩阵和平移向量。
-
#include<iostream> -
#include<pcl/io/pcd_io.h> -
#include<pcl/point_types.h> -
#include<pcl/registration/icp.h> -
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>//可视化头文件 -
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT; -
typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointT> PointCloudT; -
bool next_iteration = false; -
void print4x4Matrix(const Eigen::Matrix4d & matrix) //打印旋转矩阵和平移矩阵 -
{ -
printf("Rotation matrix :\n"); -
printf(" | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", matrix(0, 0), matrix(0, 1), matrix(0, 2)); -
printf("R = | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", matrix(1, 0), matrix(1, 1), matrix(1, 2)); -
printf(" | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", matrix(2, 0), matrix(2, 1), matrix(2, 2)); -
printf("Translation vector :\n"); -
printf("t = < %6.3f, %6.3f, %6.3f >\n\n", matrix(0, 3), matrix(1, 3), matrix(2, 3)); -
} -
void KeyboardEventOccurred(const pcl::visualization::KeyboardEvent& event,void* nothing) -
{ //使用空格键来增加迭代次数,并更新显示 -
if (event.getKeySym() == "space" && event.keyDown()) -
next_iteration = true; -
} -
int main(int argc, char** argv) -
{ -
// 创建点云指针 -
PointCloudT::Ptr cloud_in(new PointCloudT); // 原始点云 -
PointCloudT::Ptr cloud_tr(new PointCloudT); // 转换后的点云 -
PointCloudT::Ptr cloud_icp(new PointCloudT); // ICP 输出点云 -
//读取pcd文件 -
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile<pcl::PointXYZ>("you.pcd", *cloud_in) == -1) -
{ -
PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read file1 \n"); -
return (-1); -
} -
std::cout << "Loaded " << cloud_in->size() << " data points from file1" << std::endl; -
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile<pcl::PointXYZ>("zuo.pcd", *cloud_icp) == -1) -
{ -
PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read file2 \n"); -
return (-1); -
} -
std::cout << "Loaded " << cloud_icp->size() << " data points from file2" << std::endl; -
int iterations = 1; // 默认的ICP迭代次数 -
//定义旋转矩阵和平移向量Matrix4d是为4*4的矩阵 -
Eigen::Matrix4d transformation_matrix = Eigen::Matrix4d::Identity(); -
//初始化 -
double theta = M_PI / 8; // 旋转的角度用弧度的表示方法 -
transformation_matrix(0, 0) = cos(theta); -
transformation_matrix(0, 1) = -sin(theta); -
transformation_matrix(1, 0) = sin(theta); -
transformation_matrix(1, 1) = cos(theta); -
// Z轴的平移向量 (0.4 meters) -
transformation_matrix(2, 3) = 0.4; -
//打印转换矩阵 -
std::cout << "Applying this rigid transformation to: cloud_in -> cloud_icp" << std::endl; -
print4x4Matrix(transformation_matrix); -
// 执行点云转换 -
pcl::transformPointCloud(*cloud_in, *cloud_icp, transformation_matrix); -
*cloud_tr = *cloud_icp; // 备份cloud_icp赋值给cloud_tr为后期使用 -
//icp配准 -
pcl::IterativeClosestPoint<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::PointXYZ> icp; //创建ICP对象,用于ICP配准 -
icp.setMaximumIterations(iterations); //设置最大迭代次数iterations=true -
icp.setInputCloud(cloud_icp); //设置输入点云 -
icp.setInputTarget(cloud_in); //设置目标点云(输入点云进行仿射变换,得到目标点云) -
icp.align(*cloud_icp); //匹配后源点云 -
icp.setMaximumIterations(1); // 设置为1以便下次调用 -
std::cout << "Applied " << iterations << " ICP iteration(s)"<< std::endl; -
if (icp.hasConverged())//icp.hasConverged ()=1(true)输出变换矩阵的适合性评估 -
{ -
std::cout << "\nICP has converged, score is " << icp.getFitnessScore() << std::endl; -
std::cout << "\nICP transformation " << iterations << " : cloud_icp -> cloud_in" << std::endl; -
transformation_matrix = icp.getFinalTransformation().cast<double>(); -
print4x4Matrix(transformation_matrix); -
} -
else -
{ -
PCL_ERROR("\nICP has not converged.\n"); -
return (-1); -
} -
//可视化 -
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("ICP demo"); -
// 创建两个观察视点 -
int v1(0); -
int v2(1); -
viewer.createViewPort(0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 1.0, v1); -
viewer.createViewPort(0.5, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, v2); -
// 定义显示的颜色信息 -
float bckgr_gray_level = 0.0; // Black -
float txt_gray_lvl = 1.0 - bckgr_gray_level; -
// 原始的点云设置为白色的 -
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> cloud_in_color_h(cloud_in, (int)255 * txt_gray_lvl, (int)255 * txt_gray_lvl, -
(int)255 * txt_gray_lvl); -
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_in, cloud_in_color_h, "cloud_in_v1", v1);//设置原始的点云都是显示为白色 -
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_in, cloud_in_color_h, "cloud_in_v2", v2); -
// 转换后的点云显示为绿色 -
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> cloud_tr_color_h(cloud_tr, 20, 180, 20); -
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_tr, cloud_tr_color_h, "cloud_tr_v1", v1); -
// ICP配准后的点云为红色 -
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> cloud_icp_color_h(cloud_icp, 180, 20, 20); -
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_icp, cloud_icp_color_h, "cloud_icp_v2", v2); -
// 加入文本的描述在各自的视口界面 -
//在指定视口viewport=v1添加字符串“white 。。。”其中"icp_info_1"是添加字符串的ID标志,(10,15)为坐标16为字符大小 后面分别是RGB值 -
viewer.addText("White: Original point cloud\nGreen: Matrix transformed point cloud", 10, 15, 16, txt_gray_lvl, txt_gray_lvl, txt_gray_lvl, "icp_info_1", v1); -
viewer.addText("White: Original point cloud\nRed: ICP aligned point cloud", 10, 15, 16, txt_gray_lvl, txt_gray_lvl, txt_gray_lvl, "icp_info_2", v2); -
std::stringstream ss; -
ss << iterations; //输入的迭代的次数 -
std::string iterations_cnt = "ICP iterations = " + ss.str(); -
viewer.addText(iterations_cnt, 10, 60, 16, txt_gray_lvl, txt_gray_lvl, txt_gray_lvl, "iterations_cnt", v2); -
// 设置背景颜色 -
viewer.setBackgroundColor(bckgr_gray_level, bckgr_gray_level, bckgr_gray_level, v1); -
viewer.setBackgroundColor(bckgr_gray_level, bckgr_gray_level, bckgr_gray_level, v2); -
// 设置相机的坐标和方向 -
viewer.setCameraPosition(-3.68332, 2.94092, 5.71266, 0.289847, 0.921947, -0.256907, 0); -
viewer.setSize(1280, 1024); // 可视化窗口的大小 -
// 注册按键回调函数 -
viewer.registerKeyboardCallback(&KeyboardEventOccurred, (void*)NULL); -
//显示 -
while (!viewer.wasStopped()) -
{ -
viewer.spinOnce(); -
//按下空格键的函数 -
if (next_iteration) -
{ -
// 最近点迭代算法 -
icp.align(*cloud_icp); -
if (icp.hasConverged()) -
{ -
printf("\033[11A"); // Go up 11 lines in terminal output. -
printf("\nICP has converged, score is %+.0e\n", icp.getFitnessScore()); -
std::cout << "\nICP transformation " << ++iterations << " : cloud_icp -> cloud_in" << std::endl; -
transformation_matrix *= icp.getFinalTransformation().cast<double>(); // WARNING /!\ This is not accurate! -
print4x4Matrix(transformation_matrix); // 打印矩阵变换 -
ss.str(""); -
ss << iterations; -
std::string iterations_cnt = "ICP iterations = " + ss.str(); -
viewer.updateText(iterations_cnt, 10, 60, 16, txt_gray_lvl, txt_gray_lvl, txt_gray_lvl, "iterations_cnt"); -
viewer.updatePointCloud(cloud_icp, cloud_icp_color_h, "cloud_icp_v2"); -
} -
else -
{ -
PCL_ERROR("\nICP has not converged.\n"); -
return (-1); -
} -
} -
next_iteration = false; -
} -
return 0; -
}
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献11条内容
已为社区贡献11条内容







所有评论(0)