M2 Dock V831本地训练与部署的一些坑
V831的开发之旅
前言
最近在云端MaixHub训练,确实很方便,小白式操作,但是缺点是单次训练图片数量是3000张,batch_size和input_size设置也有限制,于是捣鼓一下本地训练的教程,希望各位避坑。
特别鸣谢以下博客以及下文链接引用的经验分享,让我在训练过程少走一些弯路,开始吧!
使用 MaixHub 零 AI 经验零代码快速在线训练和部署模型到设备开发板(V831,K210等硬件AI加速芯片,及STM32,ESP32,Arduino等单片机)
目录
2.遇到一些import包没法导入的,可以尝试按照以下方式导入
这里推荐使用第一个代码,第二个代码有些问题
一、本地训练的环境配置
1.修改训练配置参数
我是华硕天选2笔记本电脑,RTX3060的显卡(6G)+16G内存,安装的是pytorch-gpu-2.0环境,具体操作可以参考以下的一些教程。
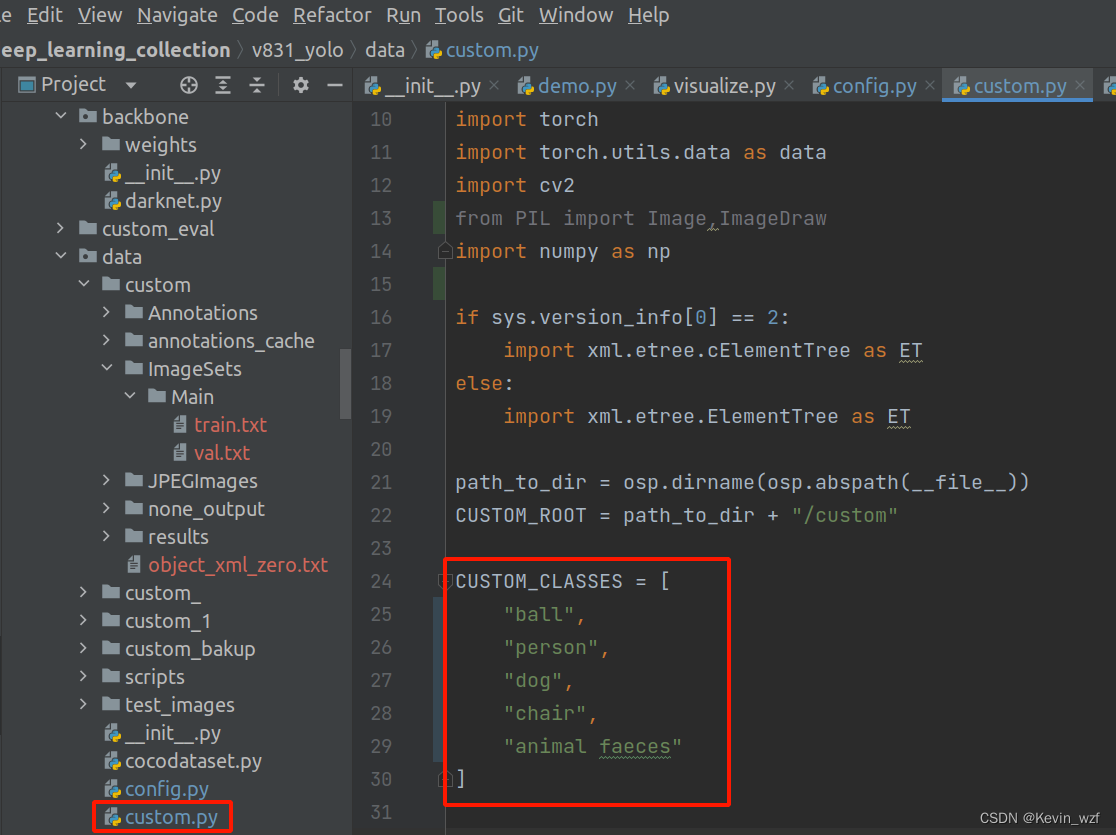
修改 v831_yolo/data/custom.py 的 CUSTOM_CLASSES
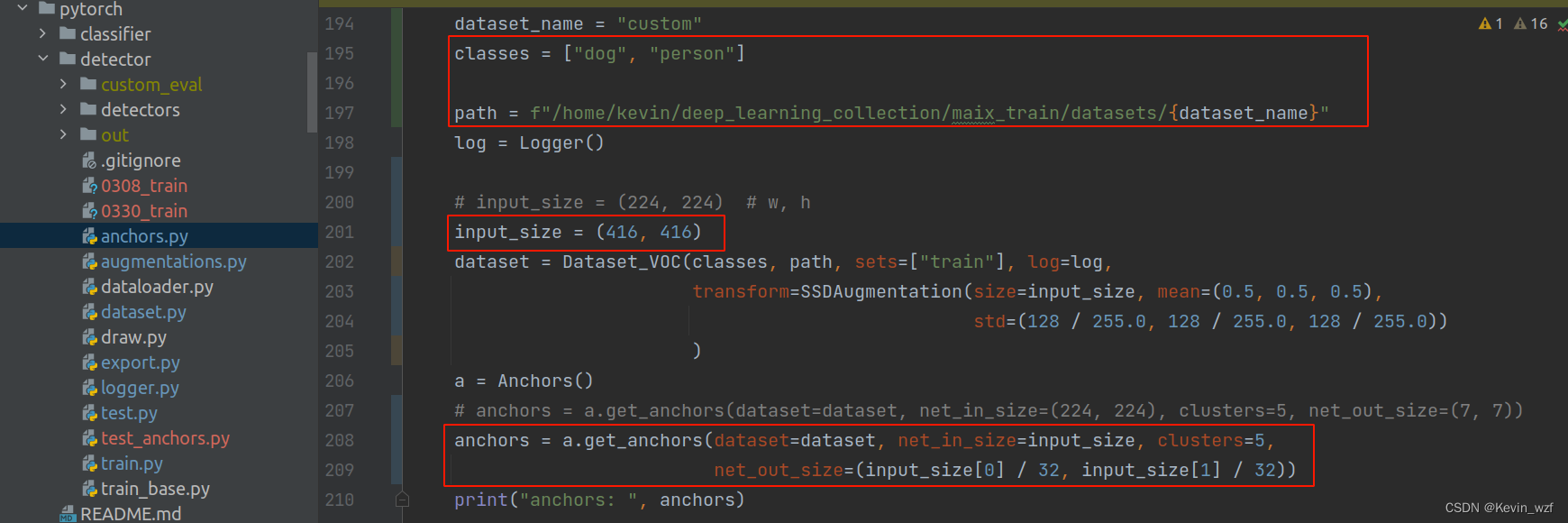
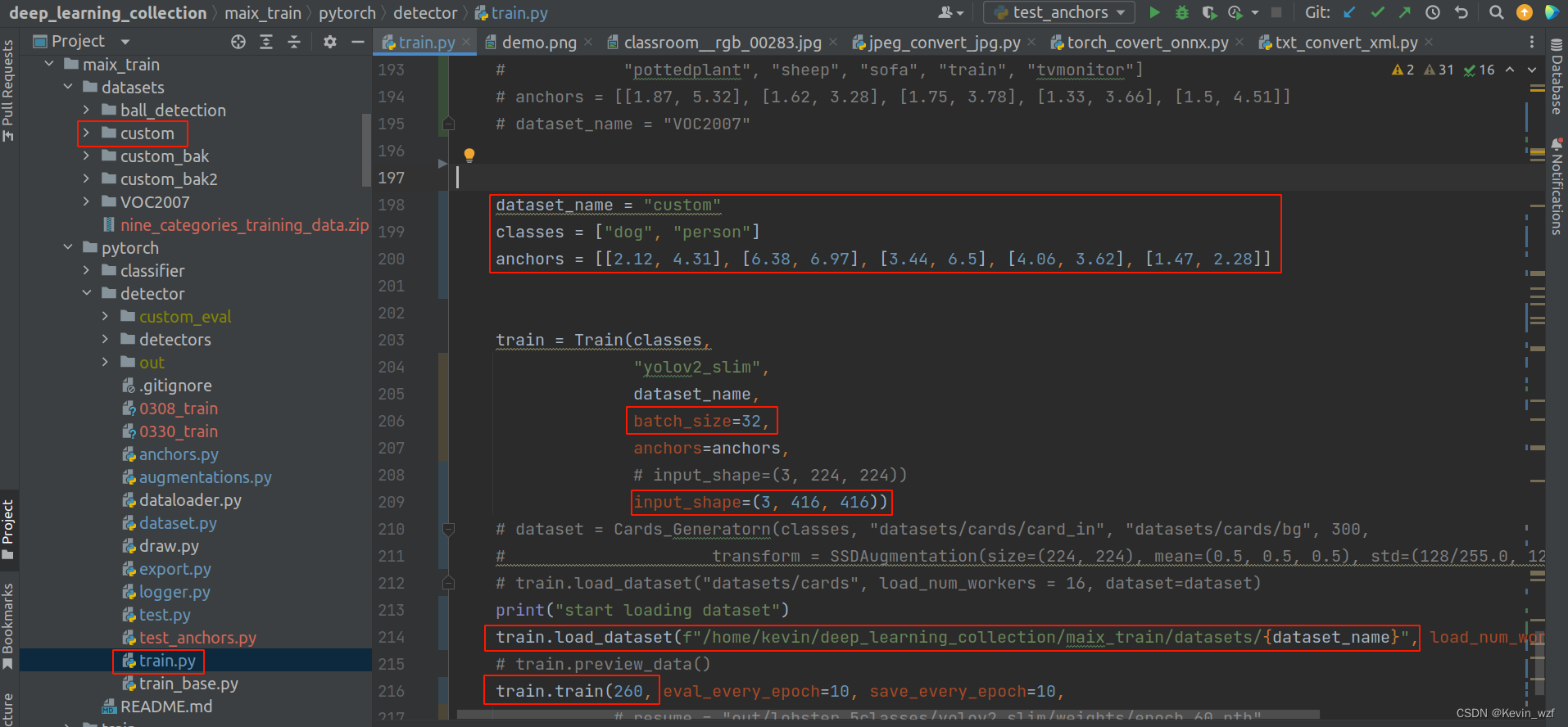
类似地,修改 maix_train/pytorch/detector/train.py 的 classes, dataset_name, anchors, batch_size, input_shape, train_epoch, 自己根据显卡的配置来设置batch_size大小。因为我这里训练集的图片大小都统一resize成 416*416分辨率,所以我的input_shape是(3, 416, 416)。
2.配置anchor参数
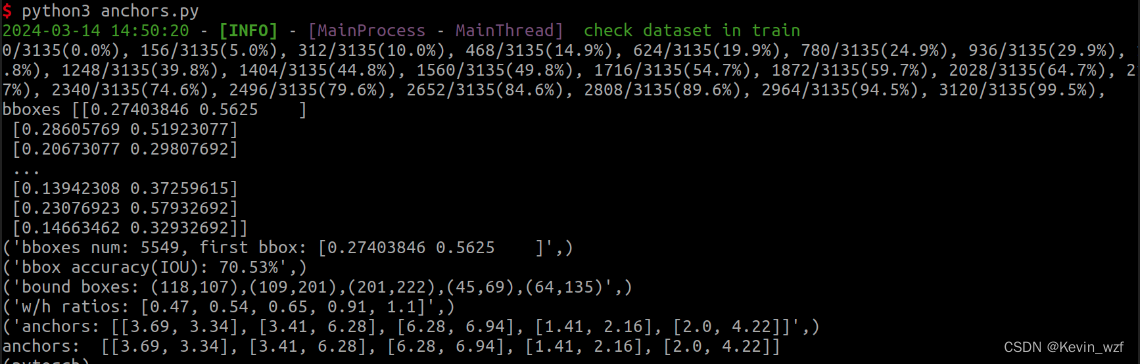
anchor的代码是在maix_train/pytorch/detector/anchors.py,修改对应的classes, path, input_size 和 anchors 里面的 net_out_size=(input_size[0] / 32, input_size[1] / 32)),最好运行该代码3次后再取结果,第一次计算会有些误差。
运行该代码之后会输出一个np.array二维的整数数组
这里要注意是,anchor计算是采用了k-means聚类算法,相关原理可以参考这篇博客5 分钟带你弄懂 k-means 聚类,我设置了一组数据并进行debug调试,加了一些注释,你们可以参考理解一下
import numpy as np
try:
from .logger import Fake_Logger, Logger
from .dataset import Dataset_VOC
from .augmentations import SSDAugmentation
except Exception:
from logger import Fake_Logger, Logger
from dataset import Dataset_VOC
from augmentations import SSDAugmentation
# 假设clusters=np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6], [9, 10],[12, 18]])
# 假设boxes = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6], [7, 8], [9, 10],[12, 18]])
# clusters[:, 0]= [1,3,5,9,12]; clusters[:, 1]= [2,4,6,10,18]; cluster_area=[2,12,30,90,216]
# 则 row box[0] x box[1] y intersection box_area
# 0 1 [1,1,1,1,1] 2 [2,2,2,2,2] [2,2,2,2,2] 2
# 1 3 [1,3,3,3,3] 4 [2,4,4,4,4] [2,12,12,12,12] 12
# 2 5 [1,3,5,5,5] 6 [2,4,6,6,6] [2,12,30,30,30] 30
# 3 7 [1,3,5,7,7] 8 [2,4,6,8,8] [2,12,30,56,56] 56
# 4 9 [1,3,5,9,9] 10 [2,4,6,10,10] [2,12,30,90,90] 90
# 5 12 [1,3,5,9,12] 18 [2,4,6,10,18] [2,12,30,90,216] 216
def iou(box, clusters):
"""
Calculates the Intersection over Union (IoU) between a box and k clusters.
:param box: tuple or array, shifted to the origin (i. e. width and height)
:param clusters: numpy array of shape (k, 2) where k is the number of clusters
:return: numpy array of shape (k, 0) where k is the number of clusters
"""
# clusters[:, 0] 表示选取 clusters 数组的所有行(:)的第 0 列元素
# np.minimum() 是 用于比较两个数组中对应位置的元素,将 clusters 数组的第 0 列元素与 box[0] 进行逐元素比较
# 计算clusters数组中每个聚类框的宽度与box框宽度之间的最小值,并将结果存储在x数组
x = np.minimum(clusters[:, 0], box[0])
# 计算clusters数组中每个聚类框的高度与box框高度之间的最小值,并将结果存储在y数组
y = np.minimum(clusters[:, 1], box[1])
# np.count_nonzero() 是 NumPy 库中的函数,用于计算数组中非零元素的数量
# np.count_nonzero(x == 0) 和 np.count_nonzero(y == 0) 分别计算数组 x 和 y 中等于零的元素的数量
# 检查是否存在x或y中的元素为0,如果存在任何一个为0,则表示框没有面积,抛出ValueError异常
if np.count_nonzero(x == 0) > 0 or np.count_nonzero(y == 0) > 0:
raise ValueError("Box has no area")
# 计算每个聚类框与box框的交集面积
intersection = x * y
# 计算box框的面积,并将结果存储在box_area变量中
box_area = box[0] * box[1]
# 计算每个聚类框的面积,并将结果存储在cluster_area变量中
cluster_area = clusters[:, 0] * clusters[:, 1]
# 计算每个聚类框与box框的交并比(Intersection over Union,IoU),并将结果存储在iou_变量中
iou_ = intersection / (box_area + cluster_area - intersection)
return iou_
# 这个函数可以用于评估聚类算法中聚类中心与边界框之间的相似性程度,平均 IoU 值越高表示聚类效果越好
def avg_iou(boxes, clusters):
"""
Calculates the average Intersection over Union (IoU) between a numpy array of boxes and k clusters.
:param boxes: numpy array of shape (r, 2), where r is the number of rows
:param clusters: numpy array of shape (k, 2) where k is the number of clusters
:return: average IoU as a single float
"""
# np.max 取其与所有聚类中心之间的最大IoU,将所有边界框的最大 IoU 放入一个列表中
# np.mean 计算列表中所有 IoU 的平均值,得到最终的平均 IoU 值
return np.mean([np.max(iou(boxes[i], clusters)) for i in range(boxes.shape[0])])
def translate_boxes(boxes):
"""
Translates all the boxes to the origin.
:param boxes: numpy array of shape (r, 4)
:return: numpy array of shape (r, 2)
"""
new_boxes = boxes.copy()
for row in range(new_boxes.shape[0]):
new_boxes[row][2] = np.abs(new_boxes[row][2] - new_boxes[row][0])
new_boxes[row][3] = np.abs(new_boxes[row][3] - new_boxes[row][1])
return np.delete(new_boxes, [0, 1], axis=1)
def kmeans(boxes, k, dist=np.median):
"""
Calculates k-means clustering with the Intersection over Union (IoU) metric.
:param boxes: numpy array of shape (r, 2), where r is the number of rows;
r 是行数,代表着输入的目标框的数量,每个目标框由两个值组成,通常是左上角和右下角坐标
:param k: number of clusters,聚类的簇的数量
:param dist: distance function,中位数距离
:return: numpy array of shape (k, 2)
有k行,每行表示一个聚类中心,即每个簇的中心点
"""
# boxes 是一个含有检测框的 numpy 数组,通常是一个二维数组,其中每行代表一个检测框,rows就是获取数组的第一个维度的长度,即是行数
# 假设boxes = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6], [7, 8], [9, 10],[12, 18]]),则rows=6
rows = boxes.shape[0]
distances = np.empty((rows, k)) # 创建一个形状为(6, 5)的二维空数组,用于存储每个边界框与聚类中心的距离
last_clusters = np.zeros((rows,)) # 创建一个包含6个元素的全零一维数组,用于存储上一次迭代时的聚类结果
np.random.seed() # 设置随机数种子
# the Forgy method will fail if the whole array contains the same rows
# 从boxes数组中随机选择5个不重复的边界框作为初始聚类中心,假设clusters=np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6], [9, 10],[12, 18]])
clusters = boxes[np.random.choice(rows, k, replace=False)]
# print("clusters", clusters)
while True:
# row的范围是(0,5)
for row in range(rows):
# 计算每个边界框与聚类中心的IoU距离(即1 - IoU),并将结果存储在distances数组中
# 用 1 减去交并比的结果,这是因为距离度量通常是越小越好,而 IOU 衡量的是重叠程度,数值越大表示重叠程度越高
# 通过用 1 减去 IOU,可以将重叠程度转化为距离度量,数值越小表示距离越近
distances[row] = 1 - iou(boxes[row], clusters)
# 用于计算distances数组每行中最小值的索引,即找到每个边界框最近的聚类中心,并将这些索引存储在nearest_clusters数组中
# 参数axis=1指定了要在每行内查找最小值的操作,结果是一个一维数组,其中每个元素表示对应行的最小值的索引
nearest_clusters = np.argmin(distances, axis=1)
# .all()是一个数组方法,用于检查数组中的所有元素是否为True,表示last_clusters和nearest_clusters数组完全相等
if (last_clusters == nearest_clusters).all():
break
for cluster in range(k):
# 在这里k=5,cluster的取值范围是(0,4),假设nearest_clusters=np.array([0, 1, 2, 0, 0])
# 则通过使用布尔索引,当cluster=0,nearest_clusters == cluster就会产生一个bool数组[True, False, False, False, True]
# 则会选取boxes数组的第一和第五个点,赋值给d = np.array([[1, 2], [9, 10]]),依次类推
d = boxes[nearest_clusters == cluster]
# 检查数组d的长度是否为0,如果没有,则继续下一个迭代
if len(d) == 0:
continue
# 这里dist是计算中位数距离,axis=0表示按照列计算距离,按照d = np.array([[1, 2], [9, 10]]),则clusters[0]=np.array([[5, 6]])
clusters[cluster] = dist(d, axis=0)
last_clusters = nearest_clusters
return clusters
class Anchors:
def __init__(self, log=Fake_Logger()):
self.log = log
def get_boxes_by_dataset(self, dataset):
boxes = []
for i in range(len(dataset)):
target = dataset.pull_item(i, test=True)
for bbox in target:
boxes.append((bbox[2] - bbox[0], bbox[3] - bbox[1]))
return boxes
def get_anchors(self, dataset=None, bboxes=None, net_in_size=(224, 224), clusters=5, net_out_size=(7, 7)):
'''
@net_in_size tuple (w, h)
@bboxes_in format: [ [xmin,ymin, xmax, ymax], ]
value range: x [0, w], y [0, h]
@return anchors, format: list, item is rectangle list, [ [w0, h0], [w1, h1], ...]
'''
if not dataset and not bboxes:
raise ValueError("param datasets or bboxes is needed")
w = net_in_size[0]
h = net_in_size[1]
if dataset:
bboxes = self.get_boxes_by_dataset(dataset)
bboxes = np.array(bboxes)
self.log.i(f"bboxes num: {len(bboxes)}, first bbox: {bboxes[0]}")
out = kmeans(bboxes, k=clusters)
iou = avg_iou(bboxes, out) * 100
self.log.i("bbox accuracy(IOU): {:.2f}%".format(iou))
self.log.i(
"bound boxes: {}".format(",".join("({:.0f},{:.0f})".format(item[0] * w, item[1] * h) for item in out)))
for i, wh in enumerate(out):
out[i][0] = wh[0] * net_out_size[0]
out[i][1] = wh[1] * net_out_size[1]
anchors = list(out.flatten())
ratios = np.around(out[:, 0] / out[:, 1], decimals=2).tolist()
self.log.i("w/h ratios: {}".format(sorted(ratios)))
final_anchors = []
for i in range(0, len(anchors) // 2):
final_anchors.append([round(anchors[i * 2], 2), round(anchors[i * 2 + 1], 2)])
self.log.i(f"anchors: {final_anchors}")
return final_anchors
if __name__ == "__main__":
bboxes = np.array([[5, 2], [7, 4], [3, 6], [2, 8], [11, 10], [12, 18]])
out = kmeans(bboxes, 5)
print("out: ", out)
iou = avg_iou(bboxes, out) * 100
print("iou: ", iou)
二、本地训练的一些坑
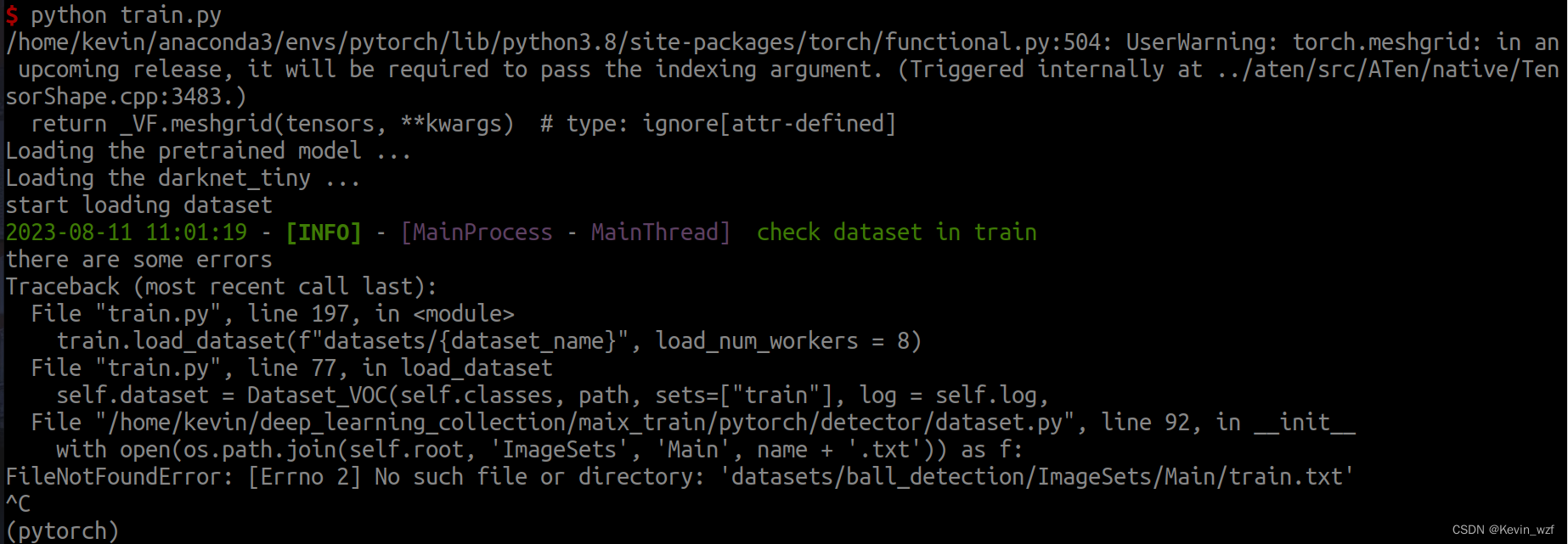
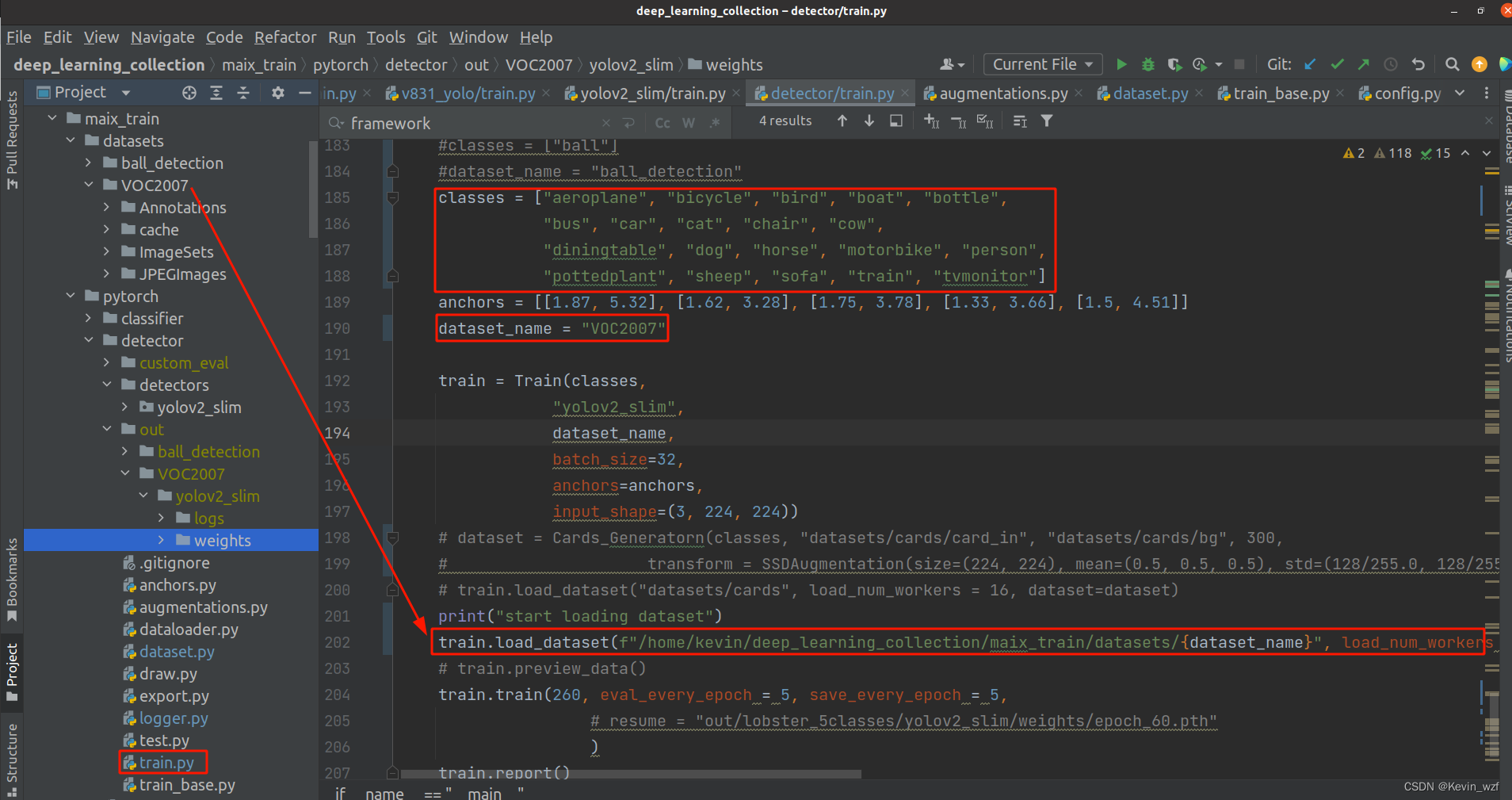
1.训练的文件找不到出错,按照红色框的地方进行修改
记得按照VOC的数据集格式存放就好了,train.txt 和 val.txt是图片文件名(不含.jpg后缀)
2.遇到一些import包没法导入的,可以尝试按照以下方式导入
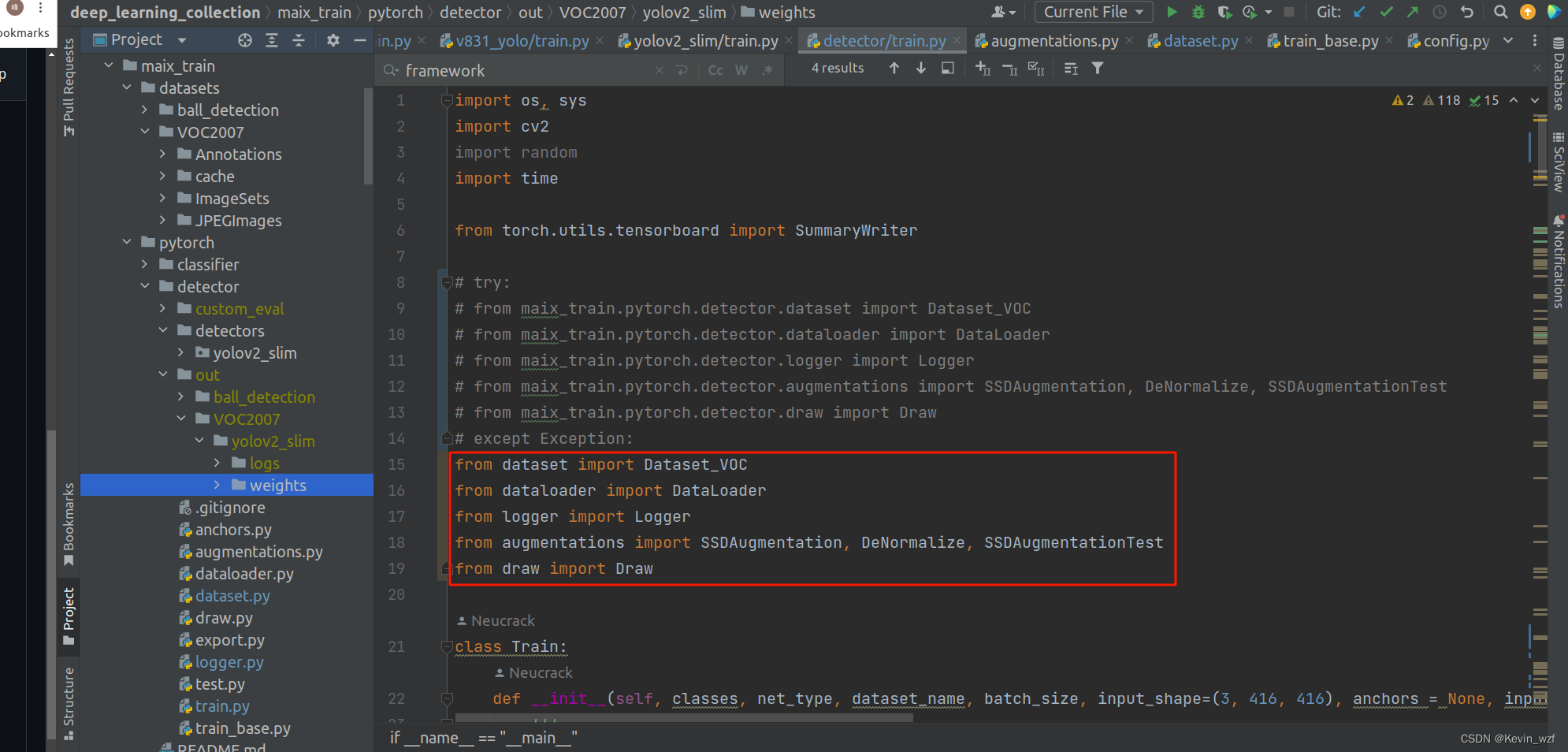
提示缺包的,pip install 相应的包即可
pip install coloredlogs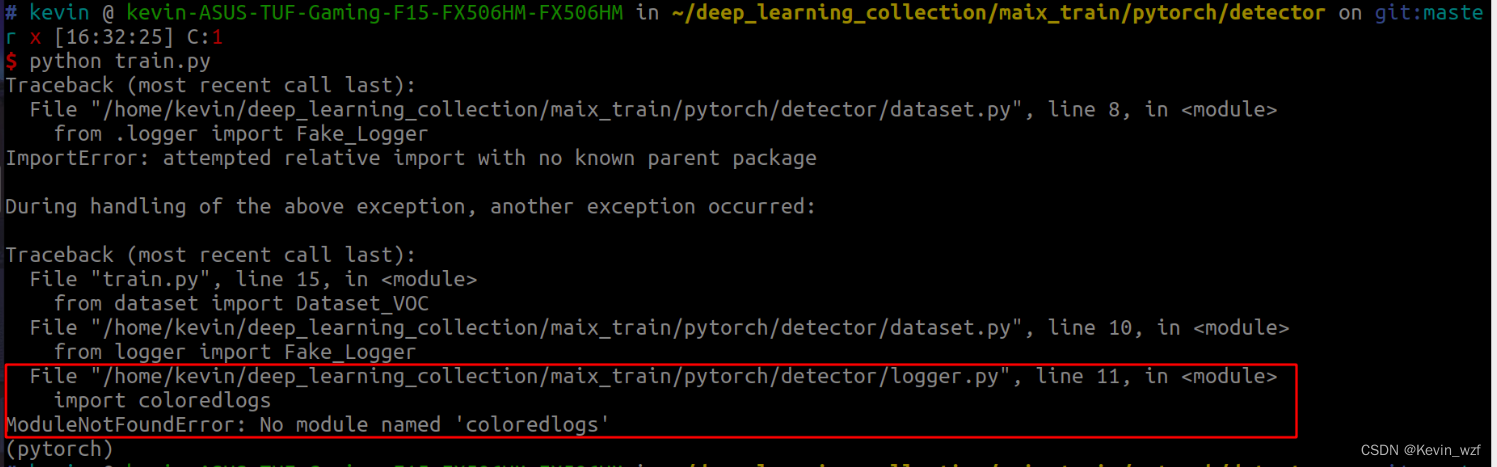
3.numpy版本也许太高级,引起巨大的坑!!
我的是 numpy==1.24.4 版本,后面参考了这个方法,降低版本可以训练了
pip install numpy==1.23.1具体错误是如下,忘记截图了!
AttributeError: Caught AttributeError in DataLoader worker process 0
ValueError: setting an array element with a sequence. The requested array has an inhomogeneous shape after 1 dimensions. The detected shape was (6,) + inhomogeneous part
一开始还以为是自己的数据集或者环境配置有问题,后面换了VOC2007的数据集还是报错!折腾了半天!!!
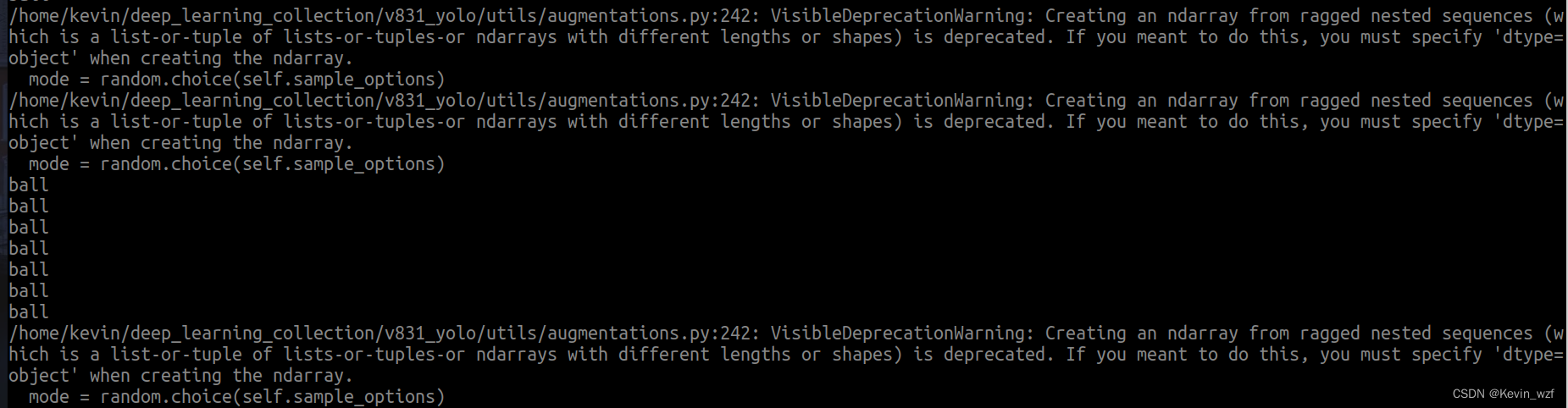
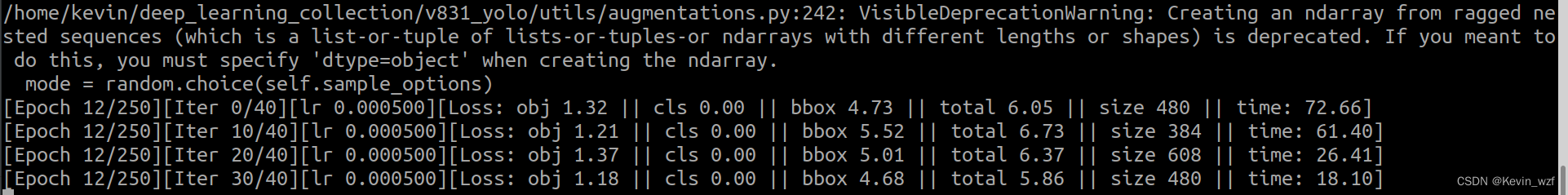
虽然不报错,但是一直有warning: 具体还没找到原因,可以参考这个教程解析,大概率就是说多维列表中子列表中的元素个数不一致

于是我根据警告提示的地方找到对应的代码
【v831_yolo/utils/augmentations.py】
【maix_train/pytorch/detector/augmentations.py】
进行修改,如下
sample_id = np.random.randint(len(self.sample_options))
mode = self.sample_options[sample_id]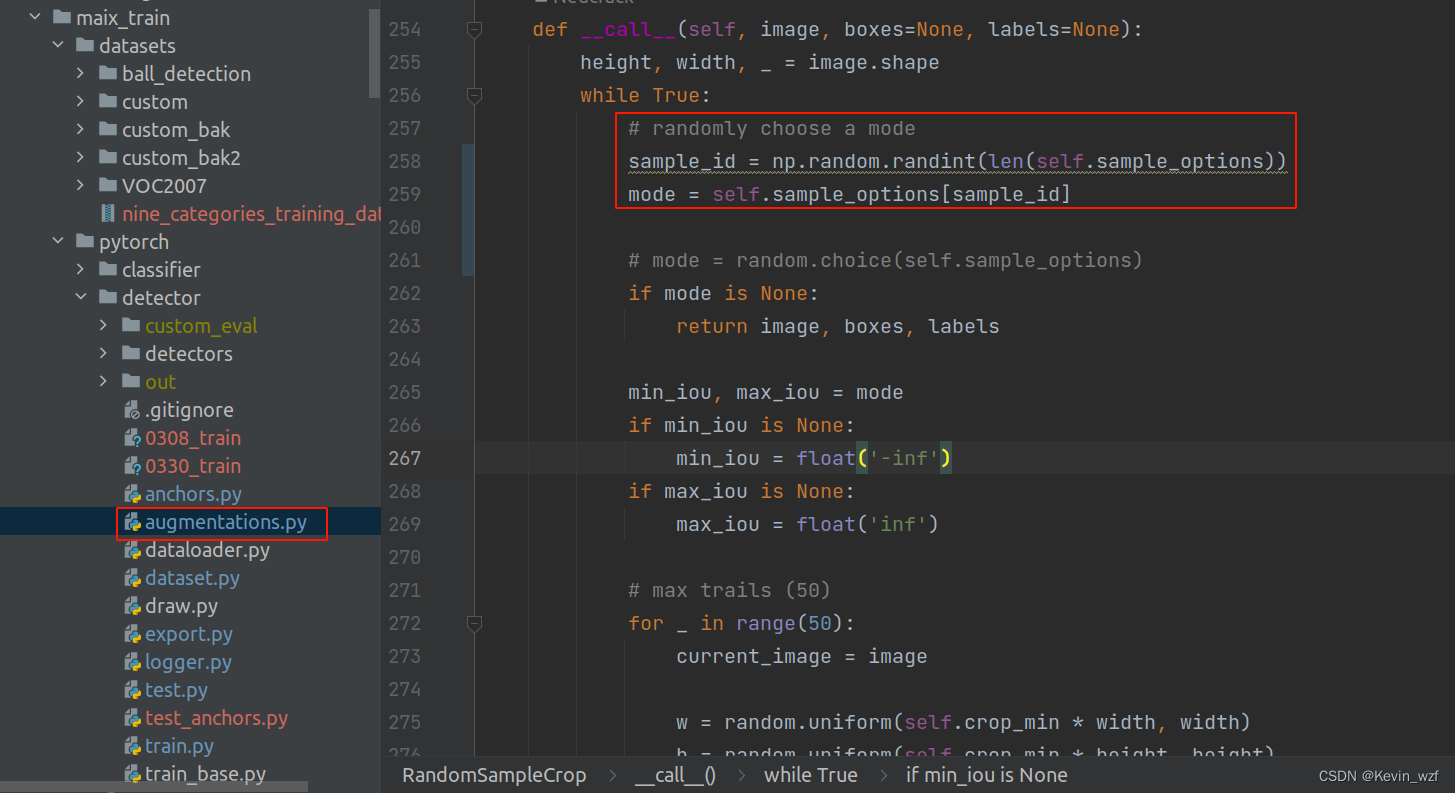
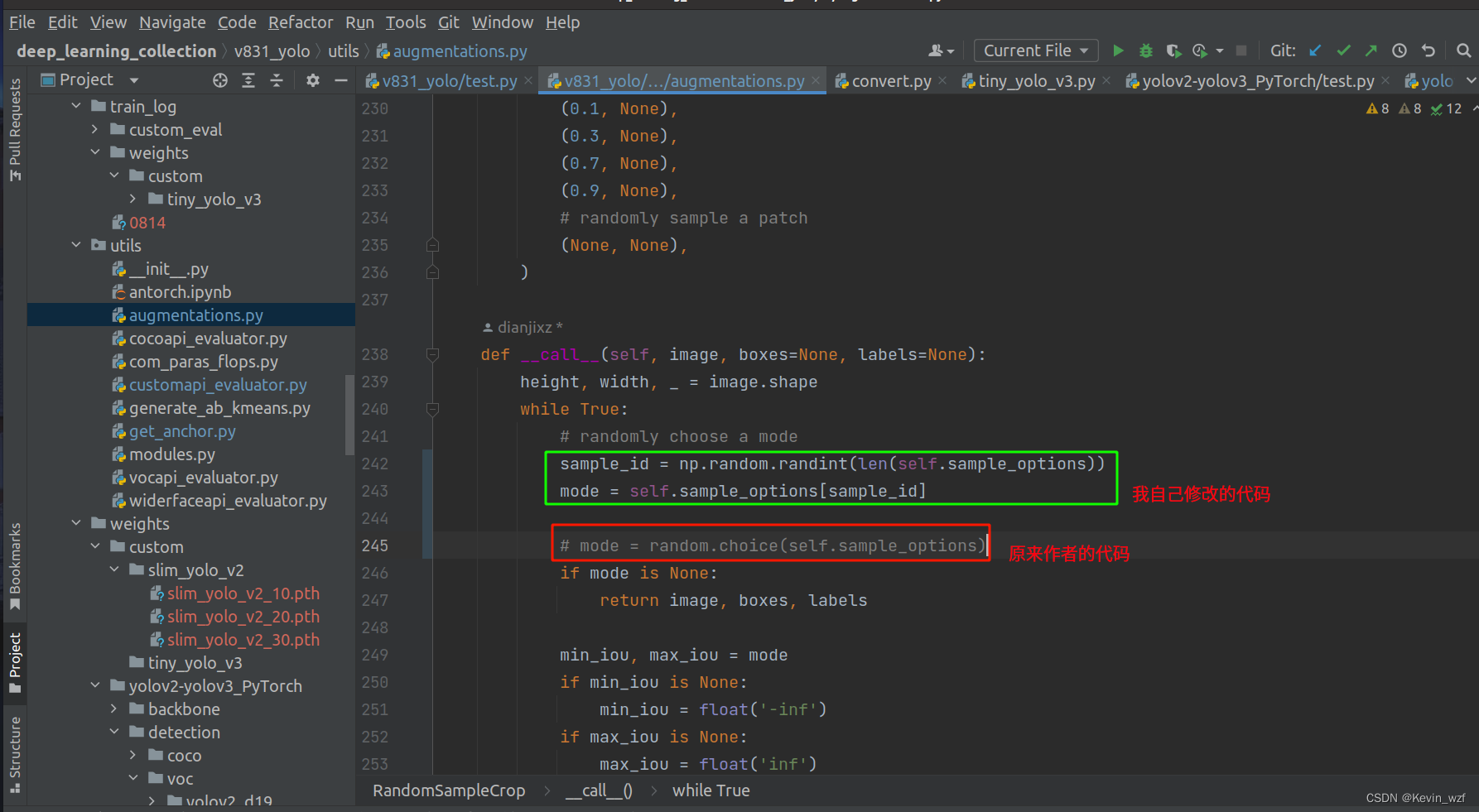
4. 训练过程一直打印标签类别,满屏幕都是,很难受!
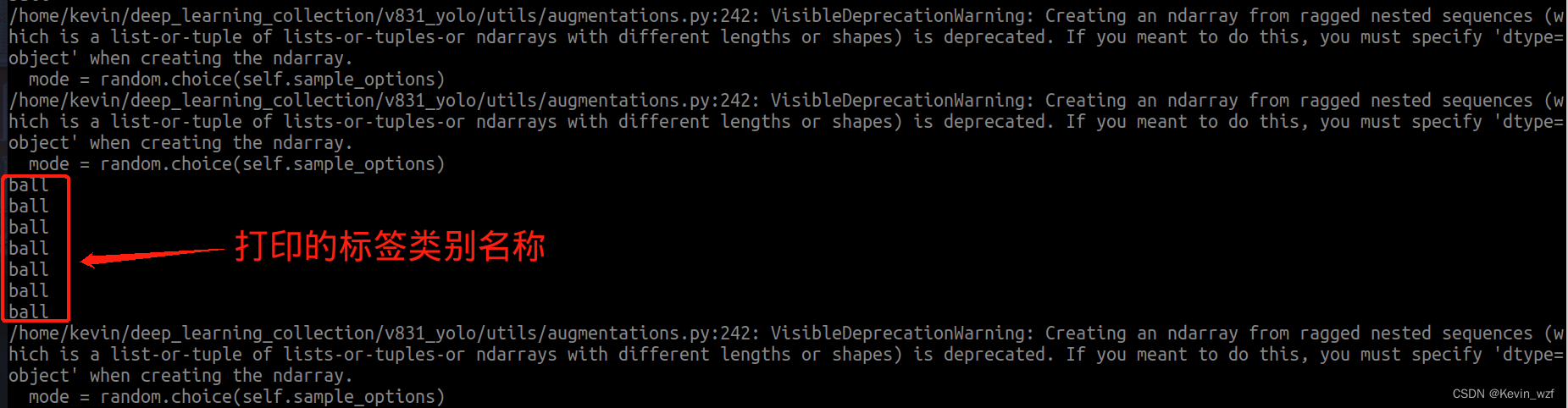
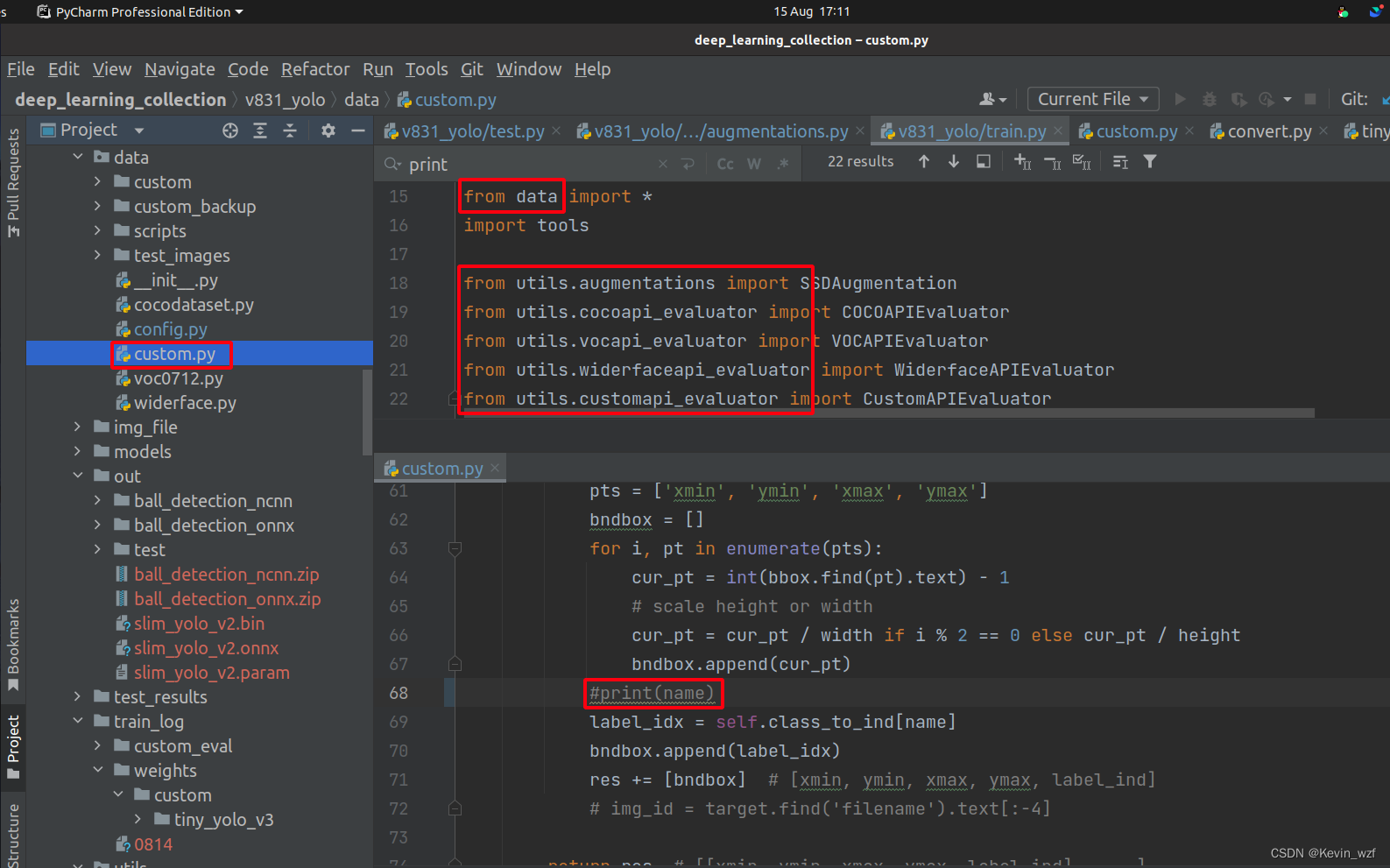
于是在train.py代码中找到导入的相关代码,找到了,哈哈,非常隐蔽!
在原作者代码[v831_yolo/data/custom.py]中屏蔽第68行代码打印
5.训练策略
关于训练策略和网络结构的优化,我还没研究透彻,如果后面有空,我尝试修改网络结构,因为好V831目前只支持的一些算子,算力有限,也可能涉及网络的问题,如果大家有什么好的想法和尝试,也可以评论区分享,具体可以看下文。
目前参考了知乎以下教程《目标检测》-第7章-YOLO轻量化初尝试-SlimYOLOv2 和使用 MaixHub 零 AI 经验零代码快速在线训练和部署模型到设备开发板(V831,K210等硬件AI加速芯片,及STM32,ESP32,Arduino等单片机)

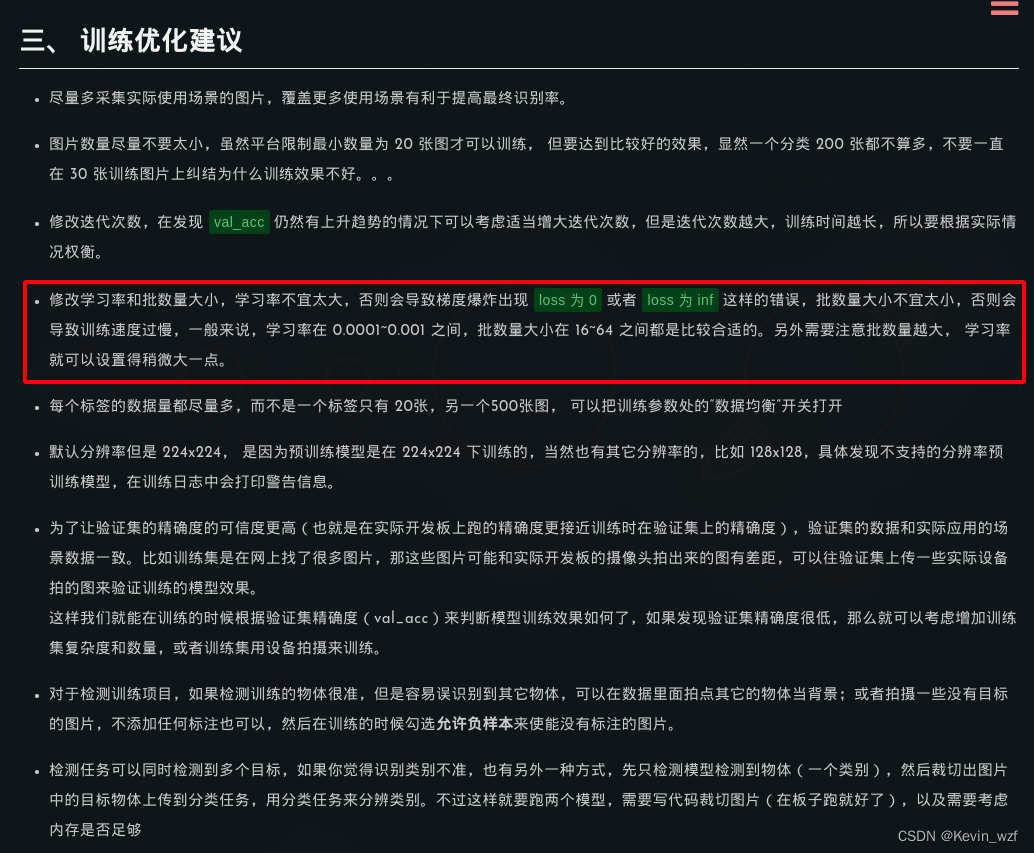
我就改了v831_yolo/data/config.py 和 v831_yolo/train.py以下参数,可以根据自己的显卡配置来修改
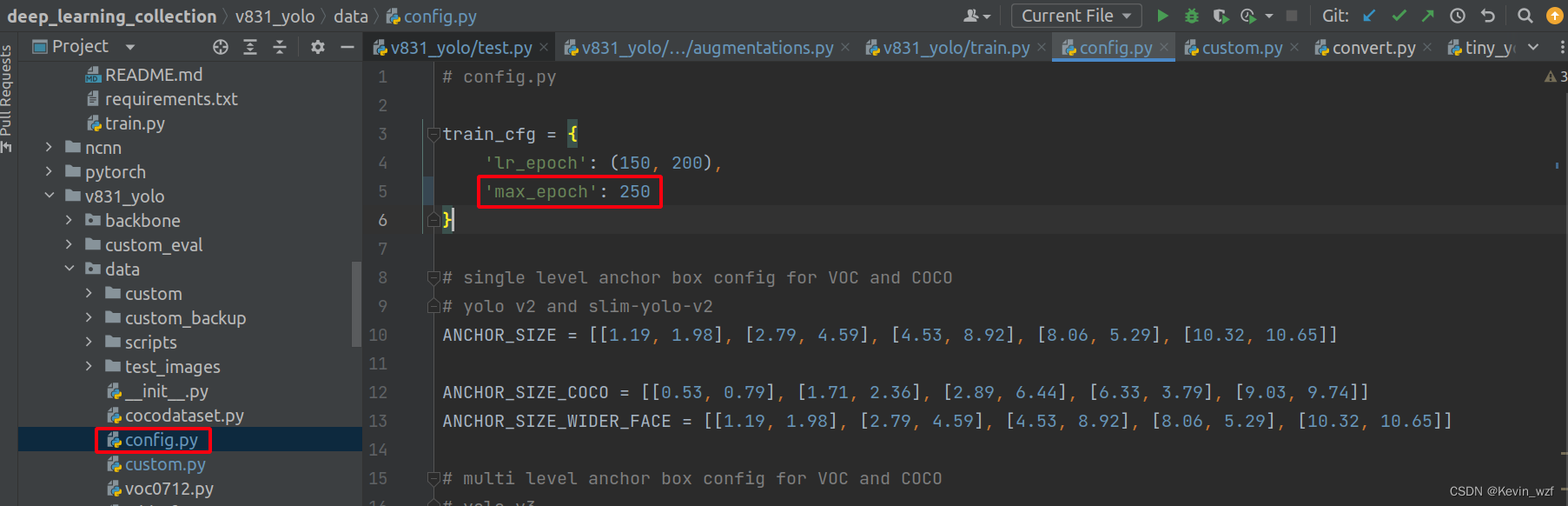
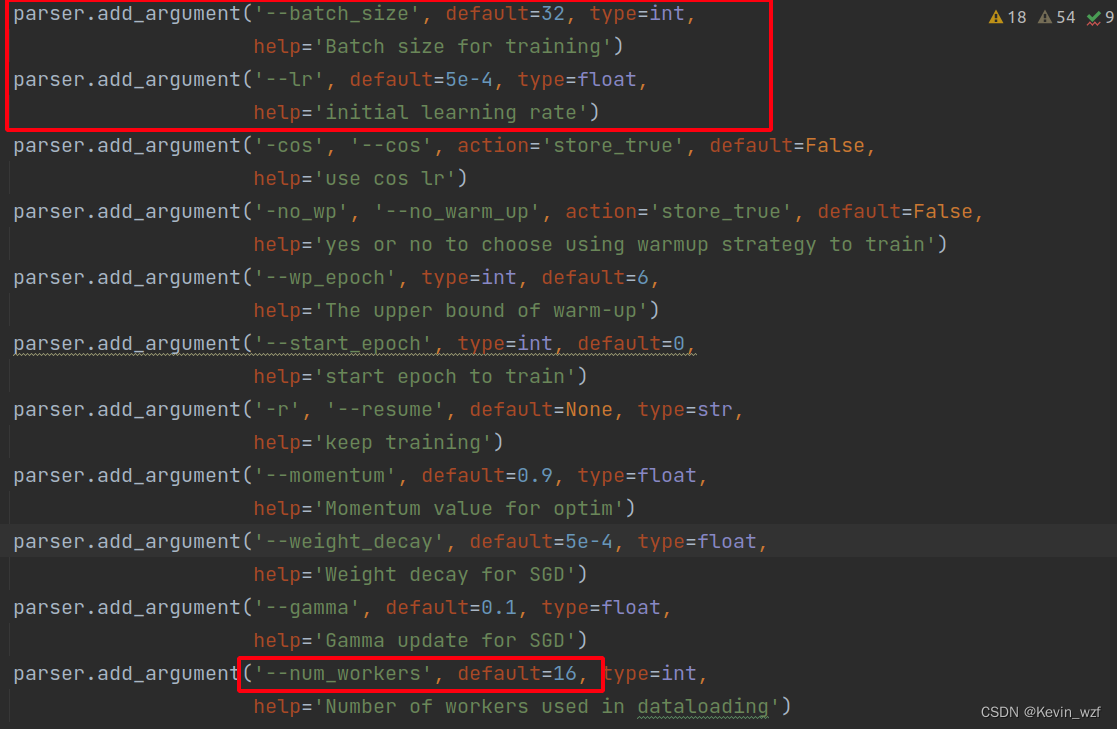
开始愉快地训练!
python train.py -d custom --cuda -v slim_yolo_v2 -hr -ms
python train.py
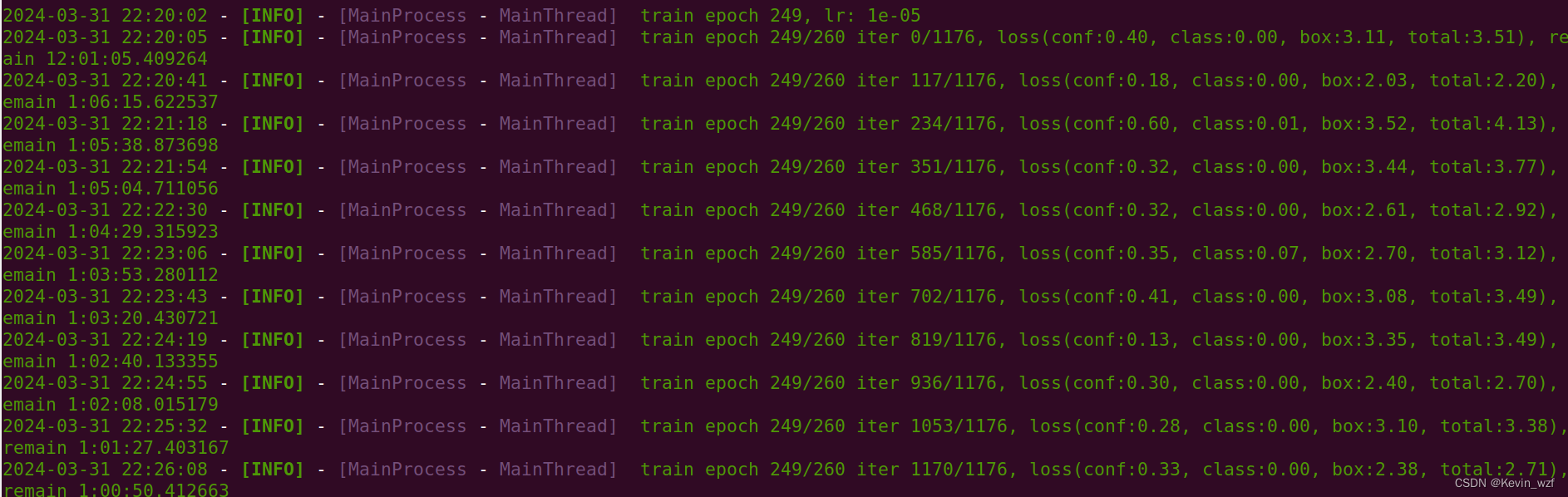
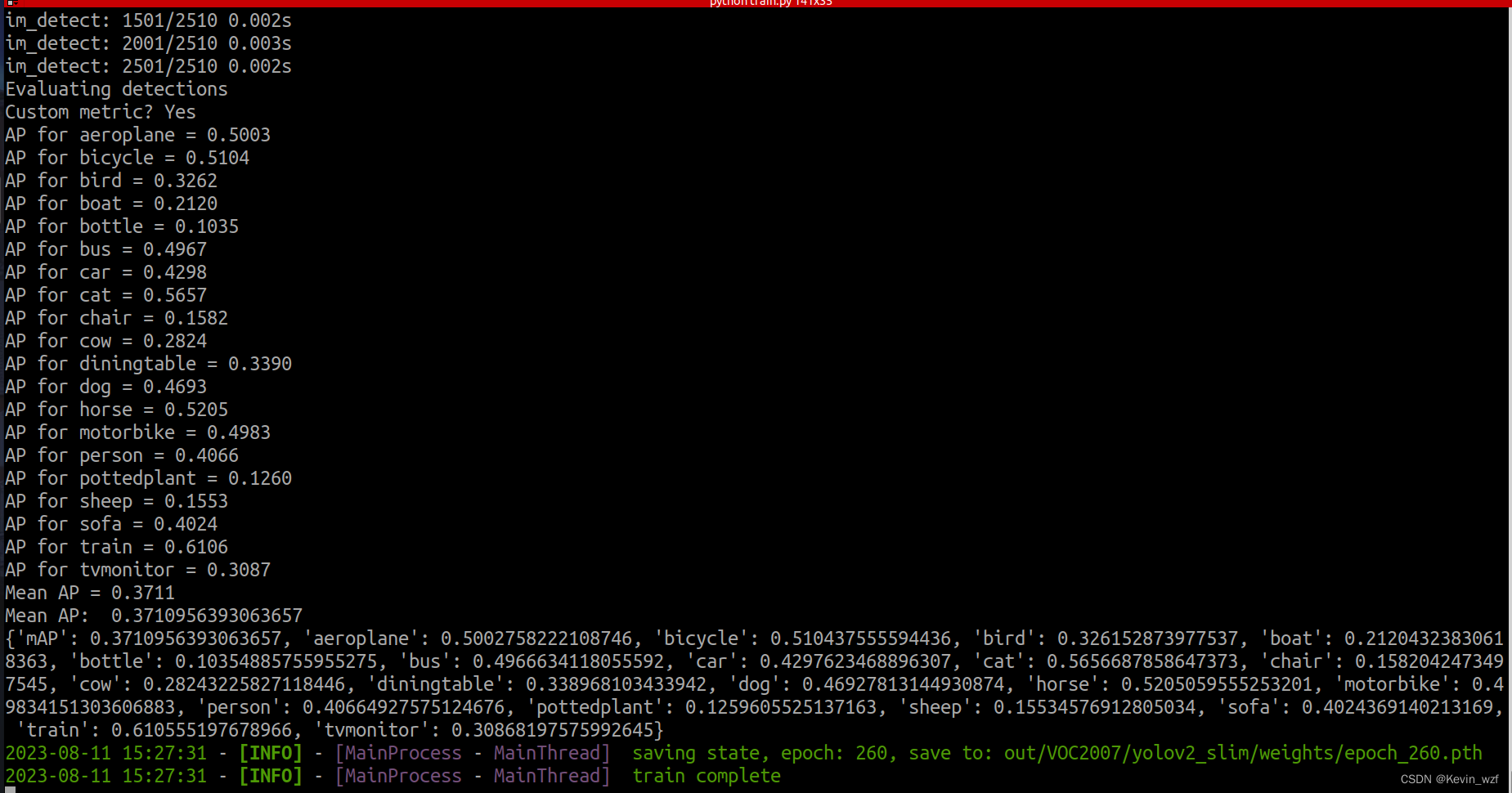
我用了slim_yolo_v2和tiny_yolo_v3训练都训练了,tiny_yolo_v3是用了接近10个小时训练完250个epoch,slim_yolo_v2我当时因为赶着回家,只训练了30 epoch就中止了,当然大家也可以根据执行中断恢复训练,可以试试!
代码是有恢复训练的机制,也可以试试拿别人的预训练权重
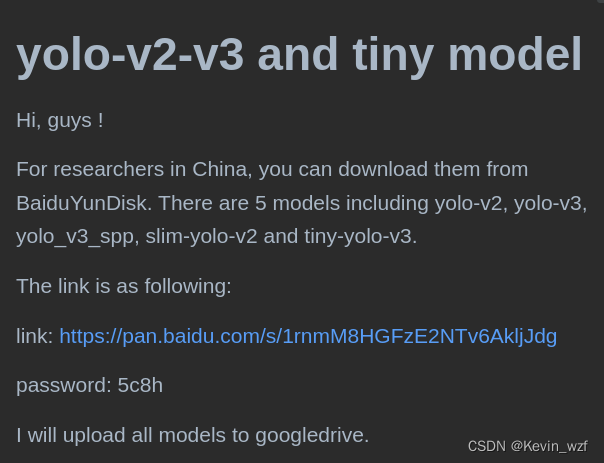

python train.py -r /path/to/pretrained_weights.pth训练结果如下:
maix_train/pytorch/detector/out/custom/yolov2_slim/weights
红色框的代码,没有用上,我屏蔽掉了
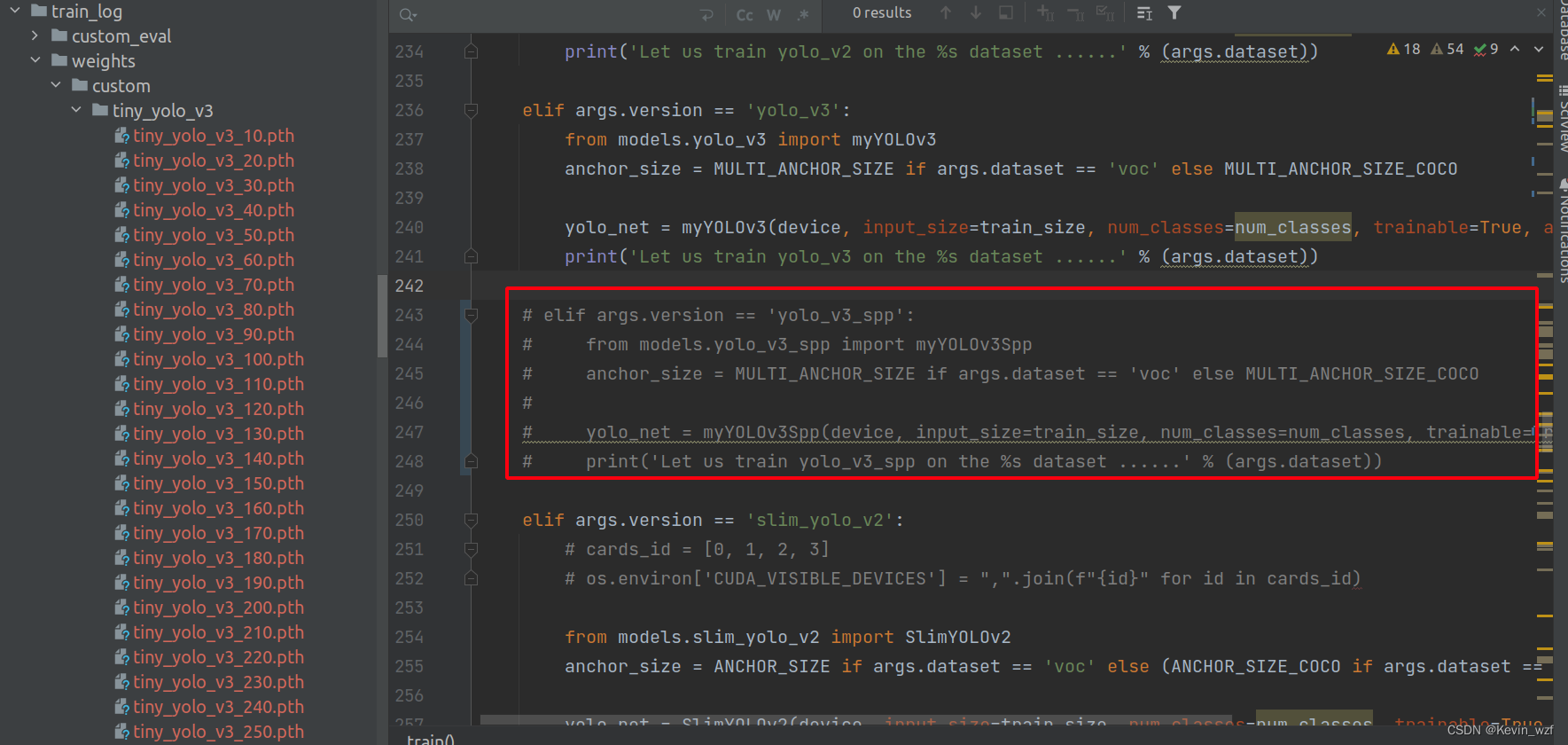
三、模型转换的一些坑
1.安装 onnx2ncnn模型转换工具
具体可以参考这个教程,注意一下最后一步,一定要改成自己安装NCNN的具体路径,不然没法用!!!
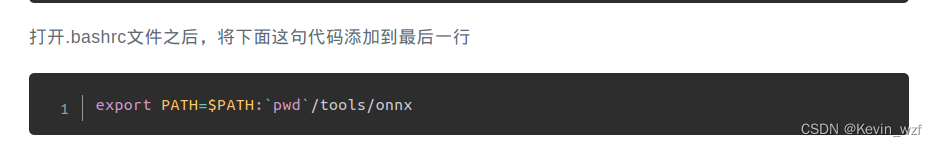
我的是这个路径

如果没有onnx,那就安装ONNX模块
pip install onnx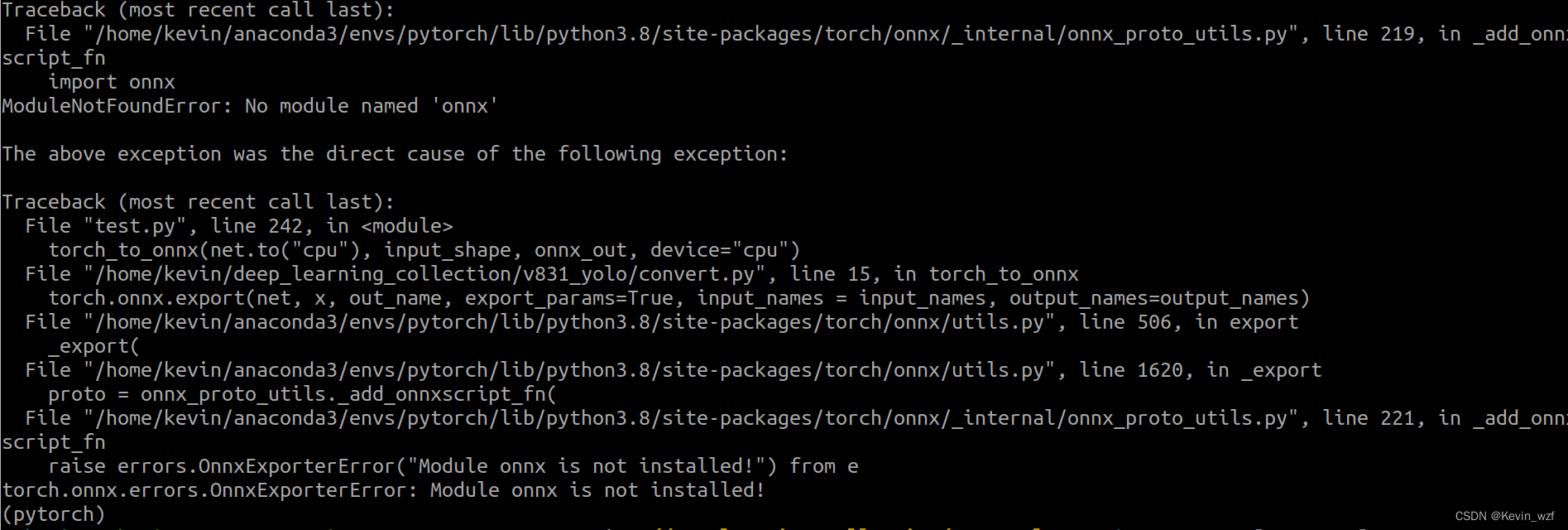
2.模型转换
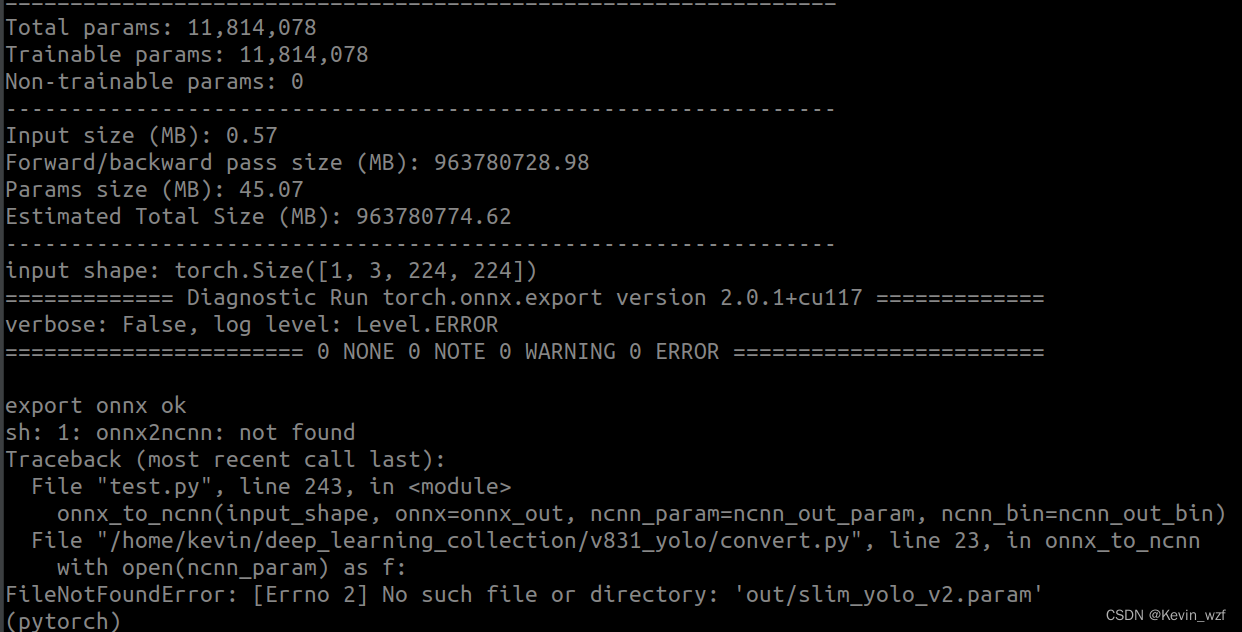
2.1执行test.py,进行转换onnx和ncnn
python3 test.py -d custom -v slim_yolo_v2 --trained_model weights/custom/slim_yolo_v2/slim_yolo_v2_30.pth --visual_threshold 0.3 -size 224 --export
其实代码主要调用了convert.py的两个函数,先从.pth转成.onnx,然后再用.onnx转.ncnn,生成对应的.bin和.param的文件。
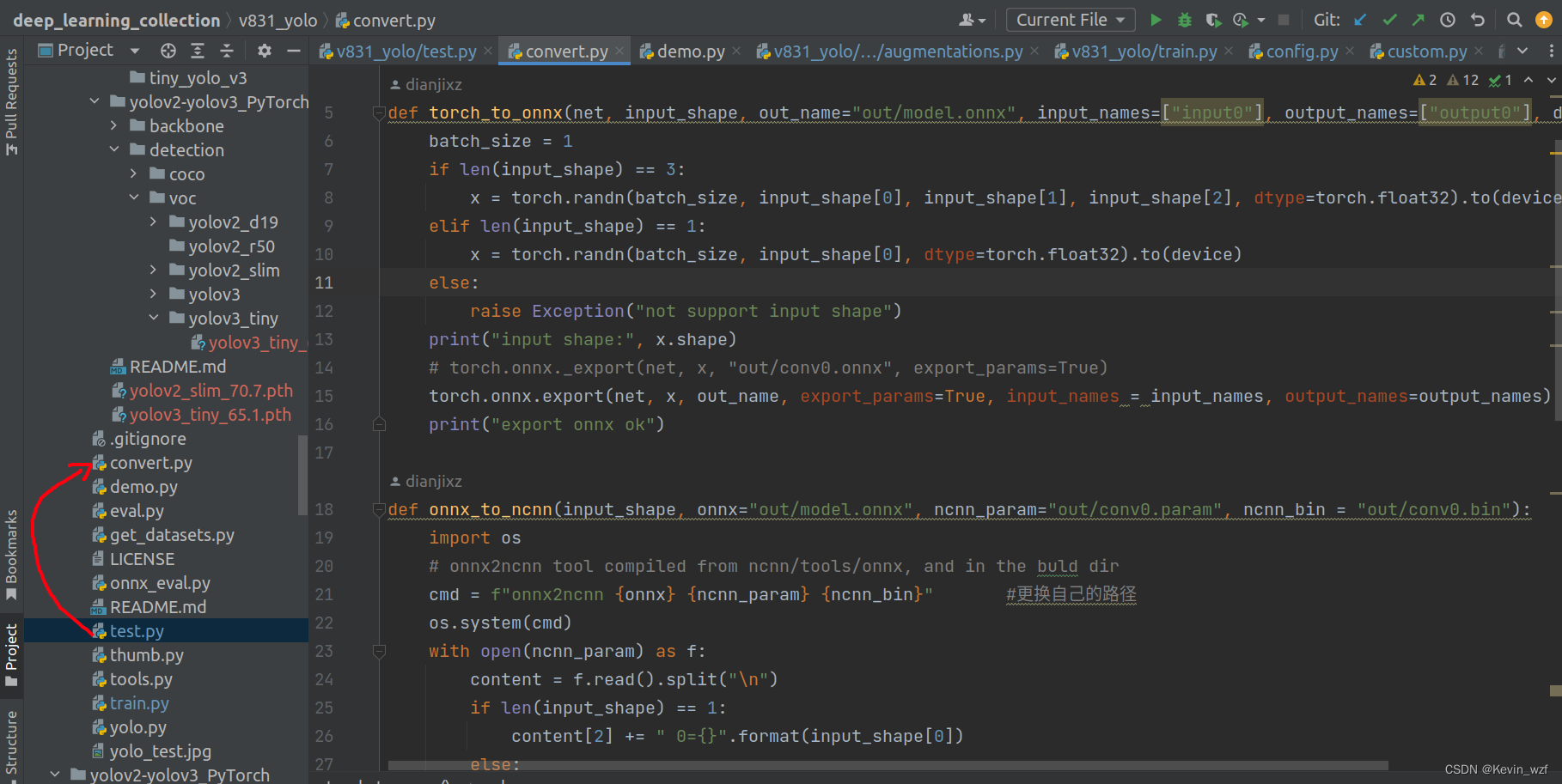 我有些地方是修改了,可以参考一下
我有些地方是修改了,可以参考一下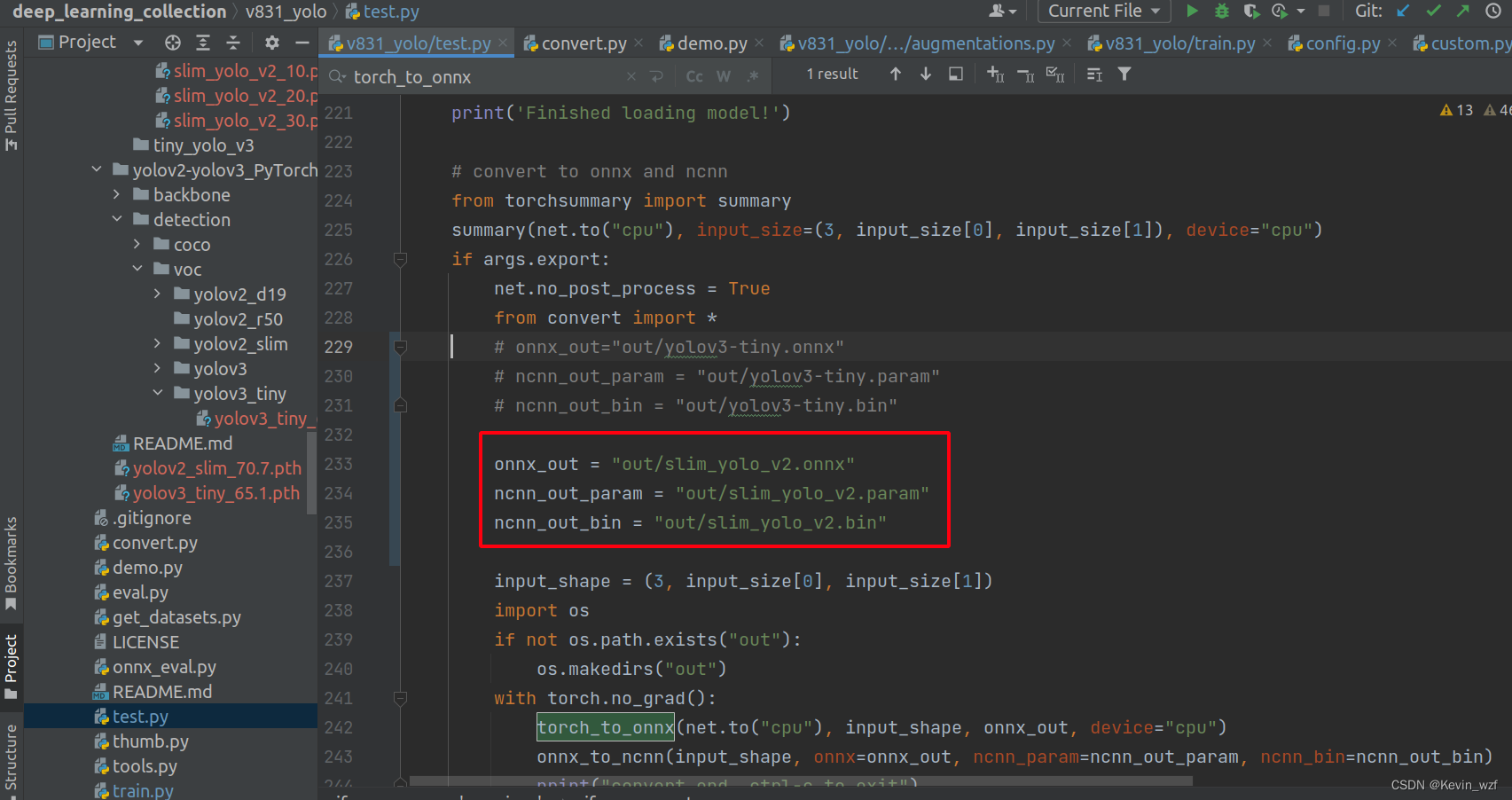
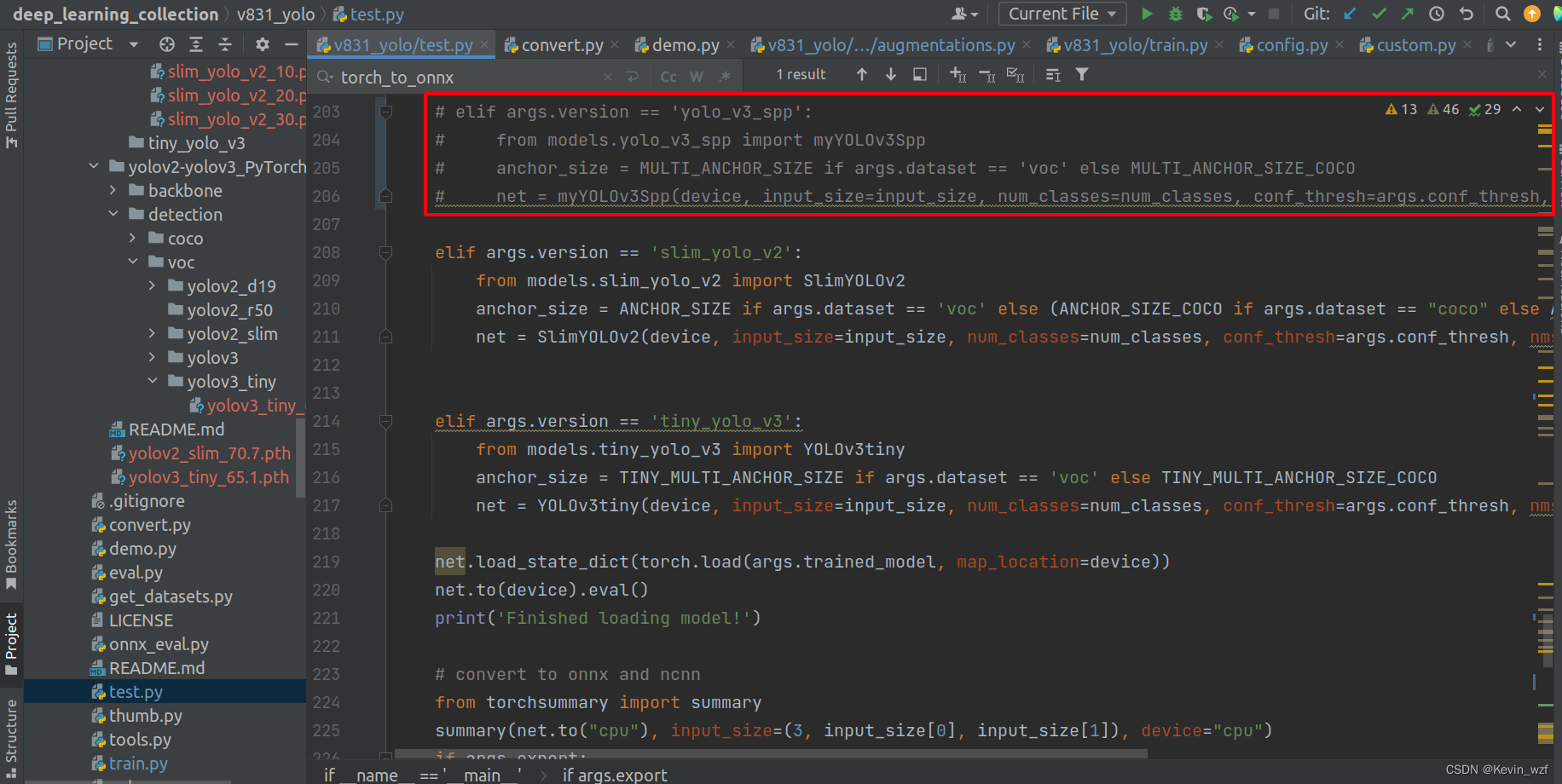
类似地,修改maix_train/pytorch/detector/export.py相应的参数,运行即可
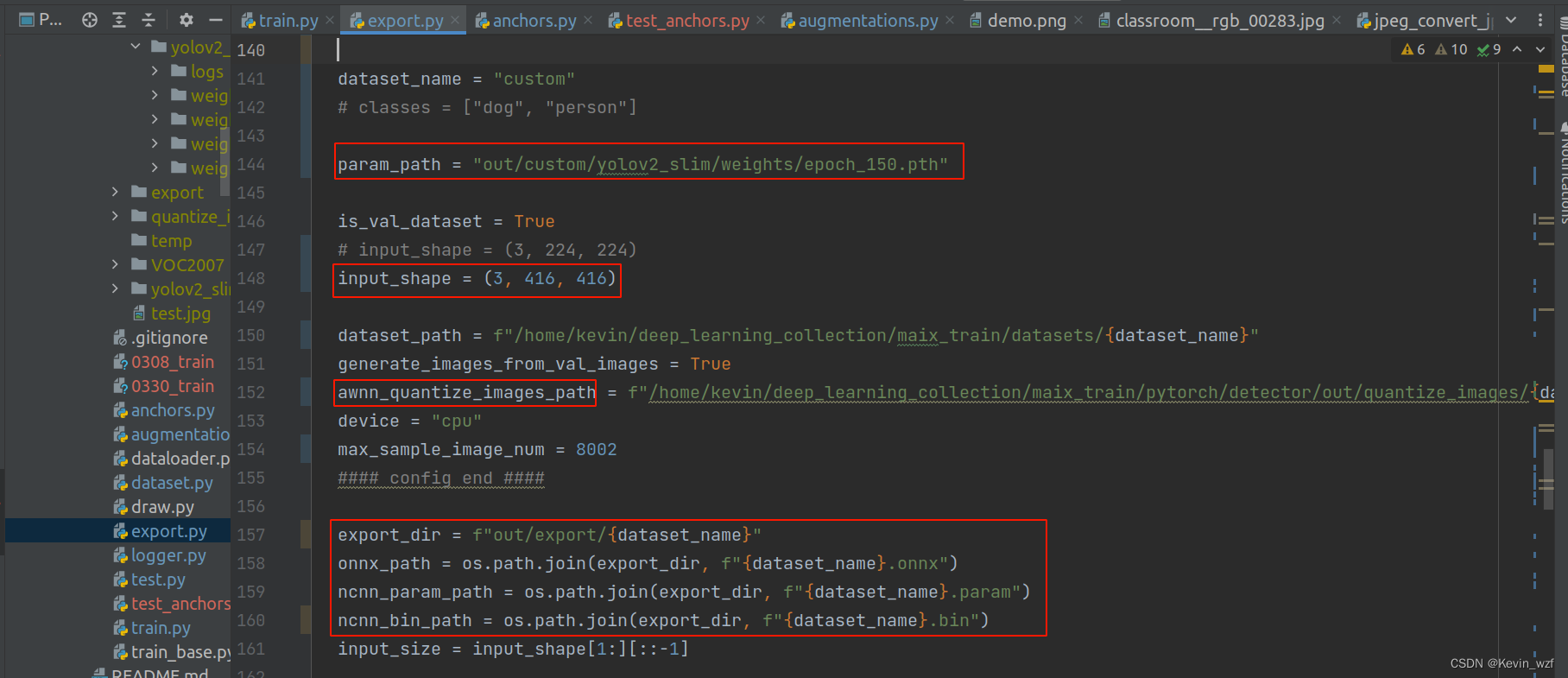
2.2转换awnn模型
后面就是按照以下格式进行打包上传到网页,两种方式都可以
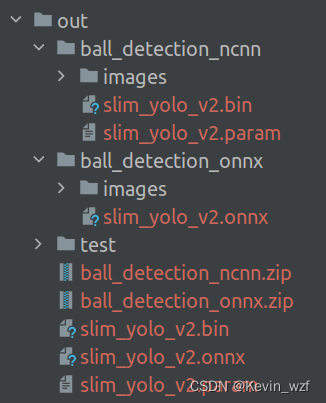
2.3.onnx和ncnn模型
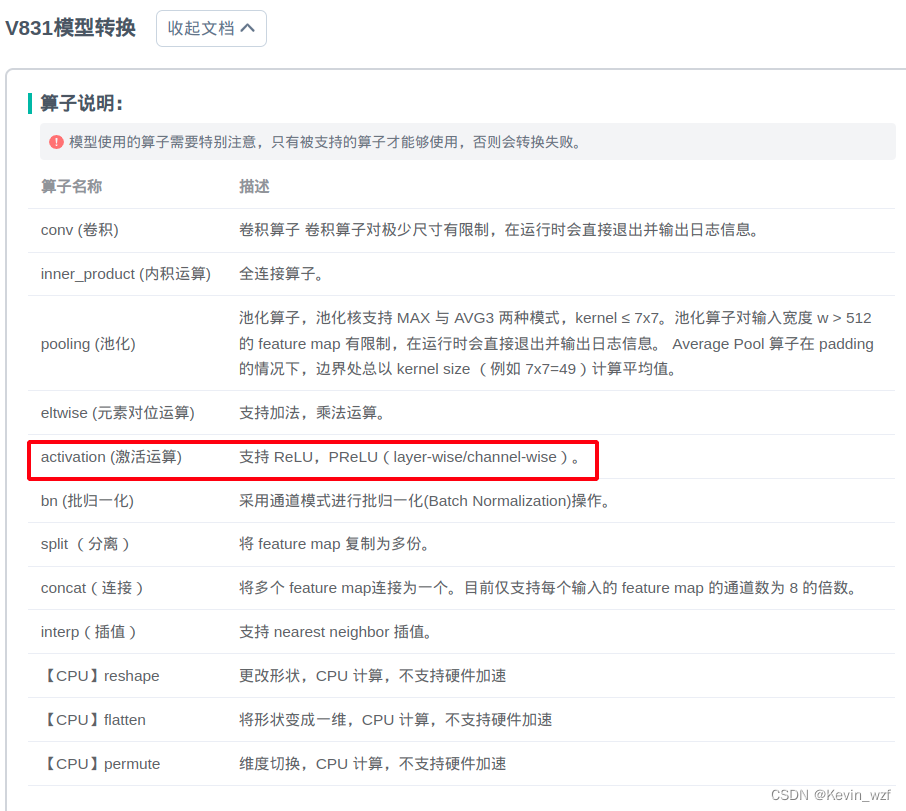
我发现转换出来的onnx模型有一个LeakyRelu的激活算子,我看文档,支持的算子只有 ReLU,PReLU(layer-wise/channel-wise),但是我转成awnn模型正常,说明应该是没问题。
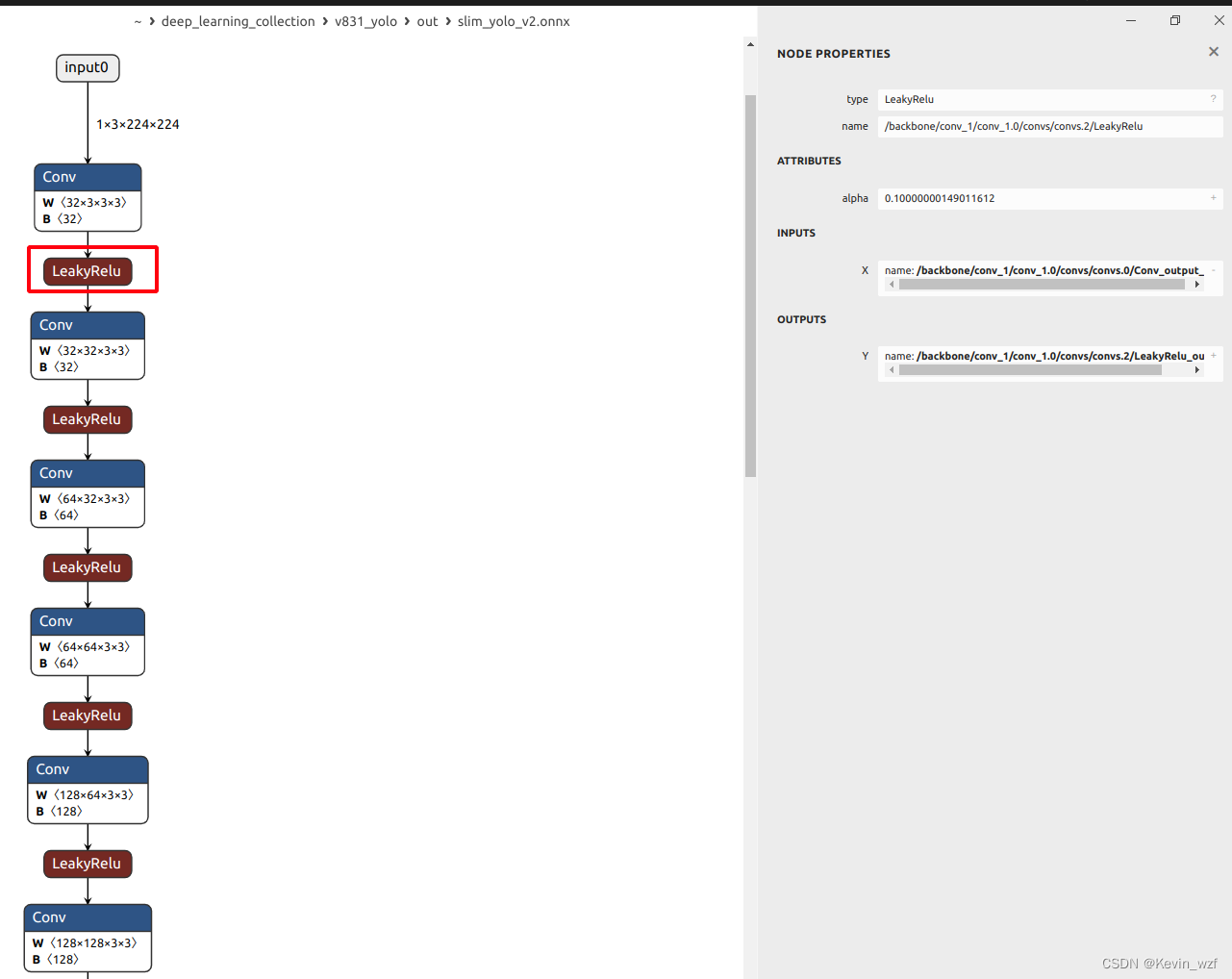
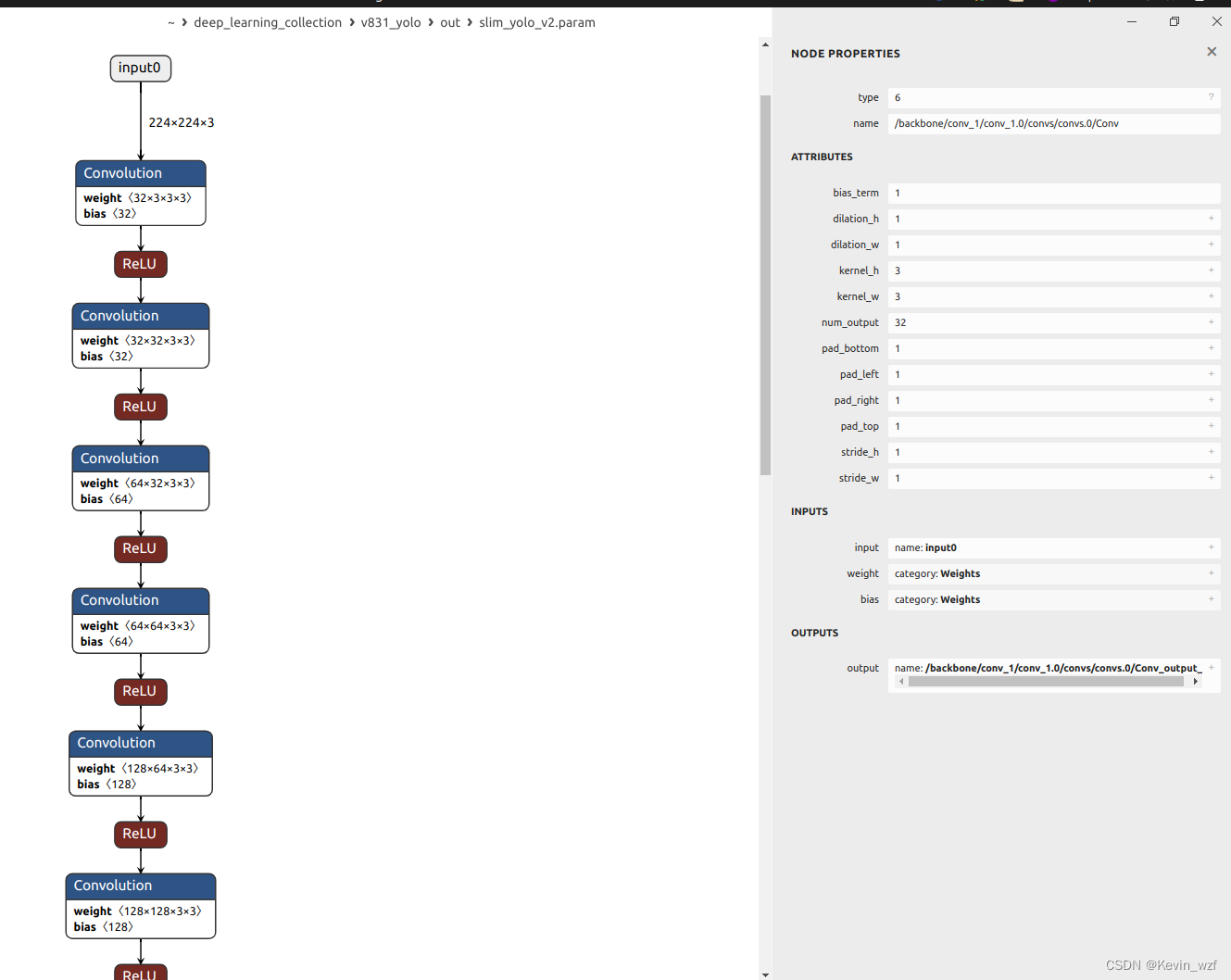
四、说明
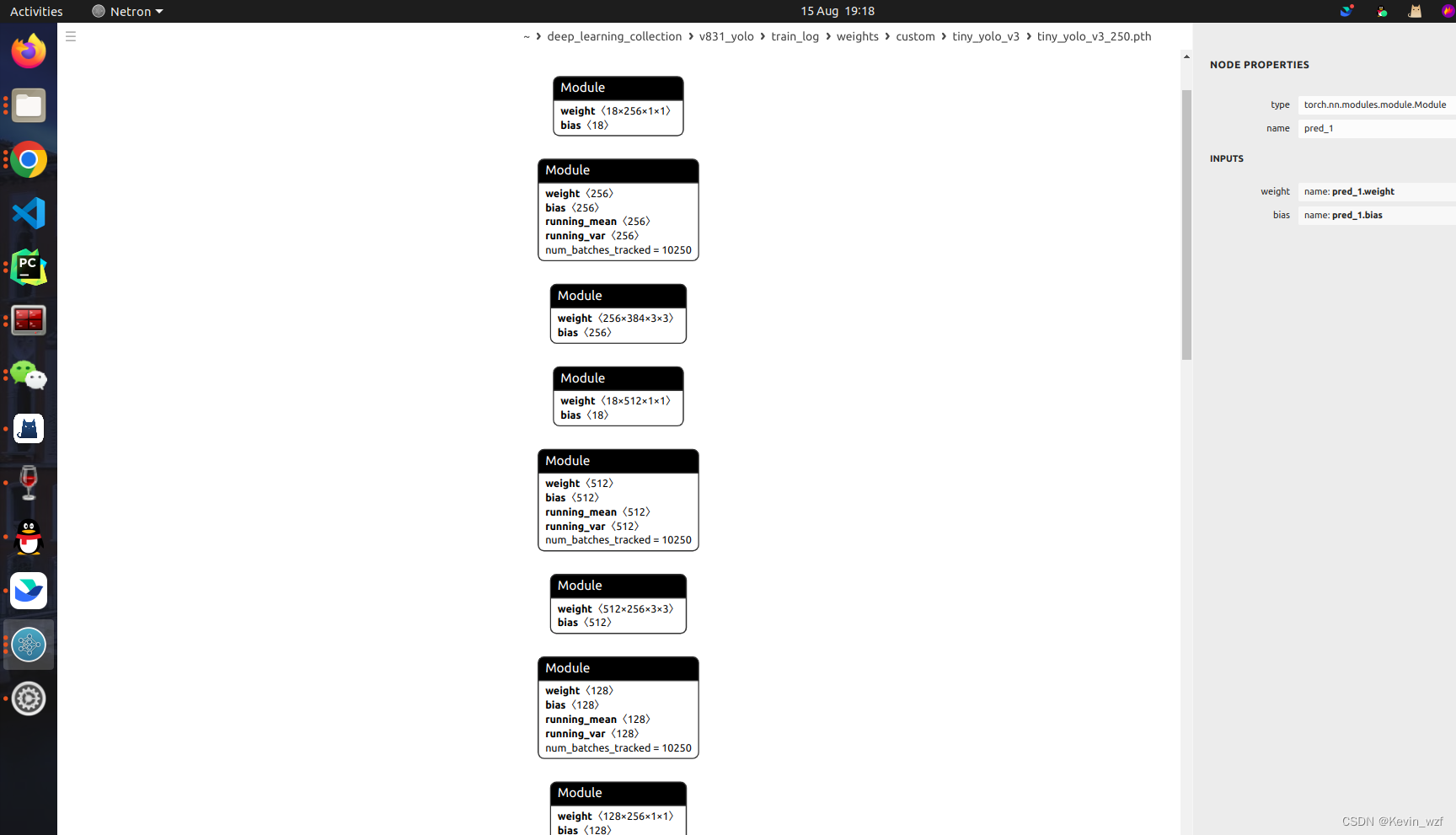
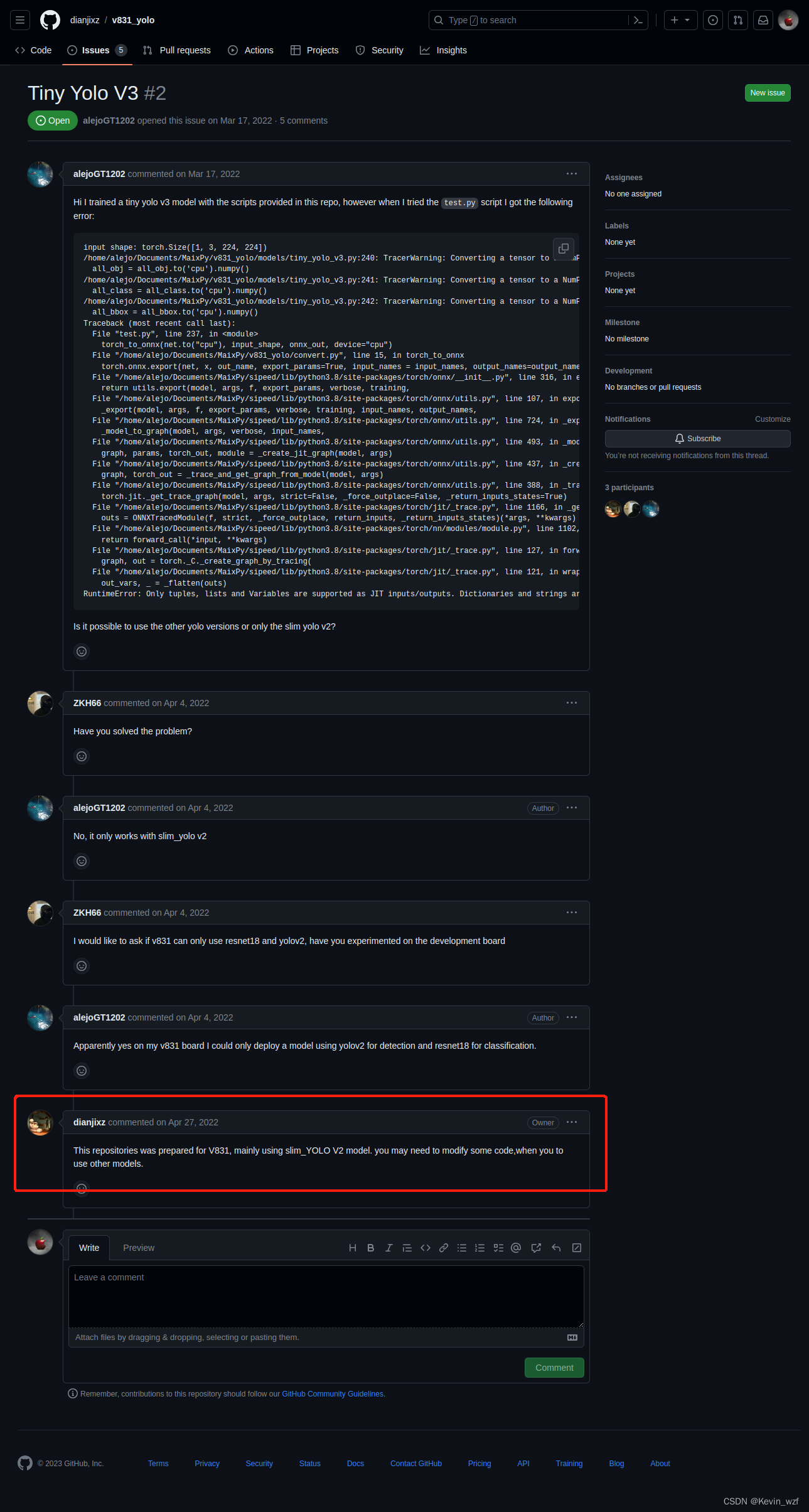
1.关于YOLOV3-tiny模型的转换
我目前还没解决,如果解决了,后面会继续更新文章
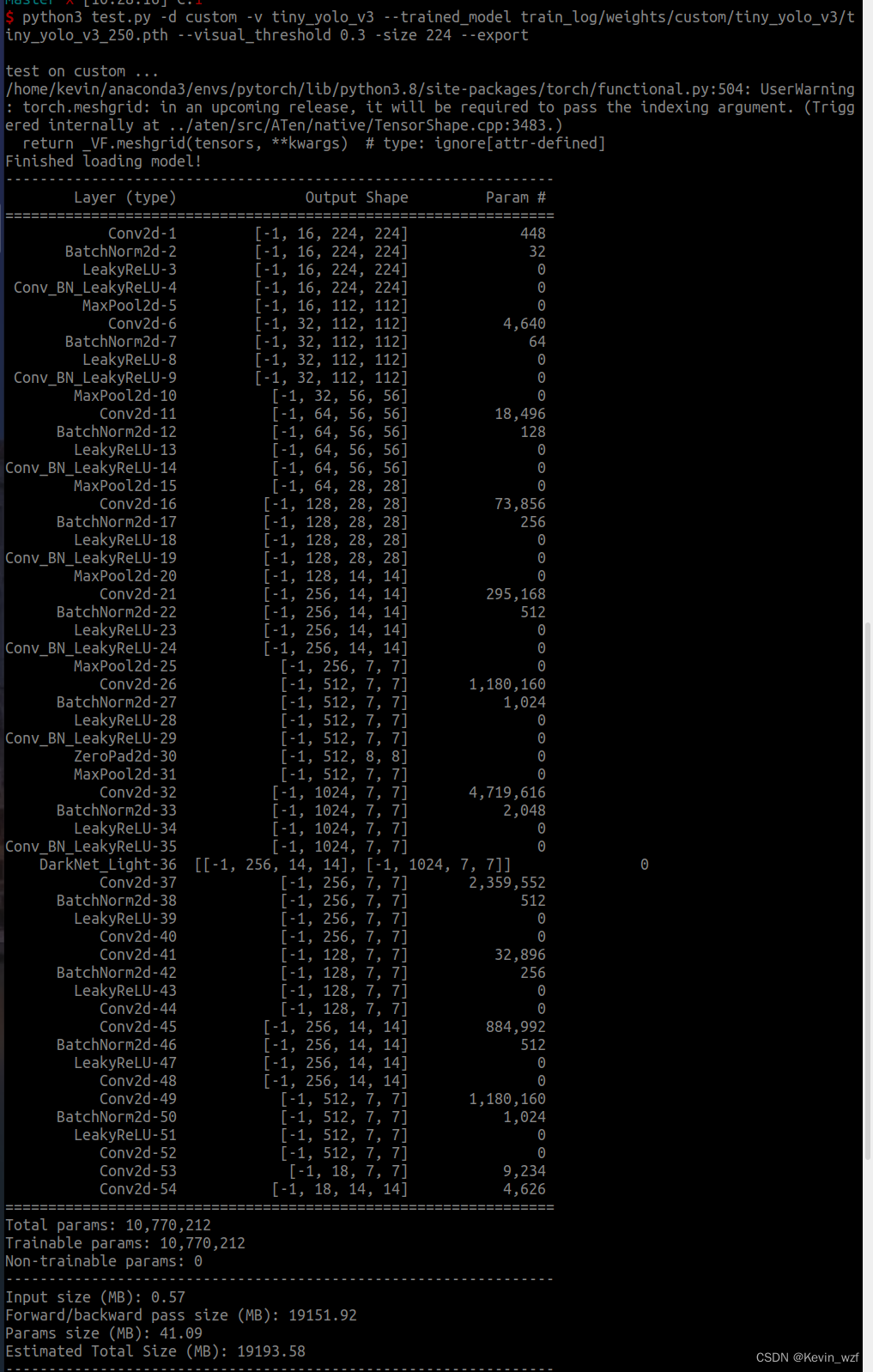
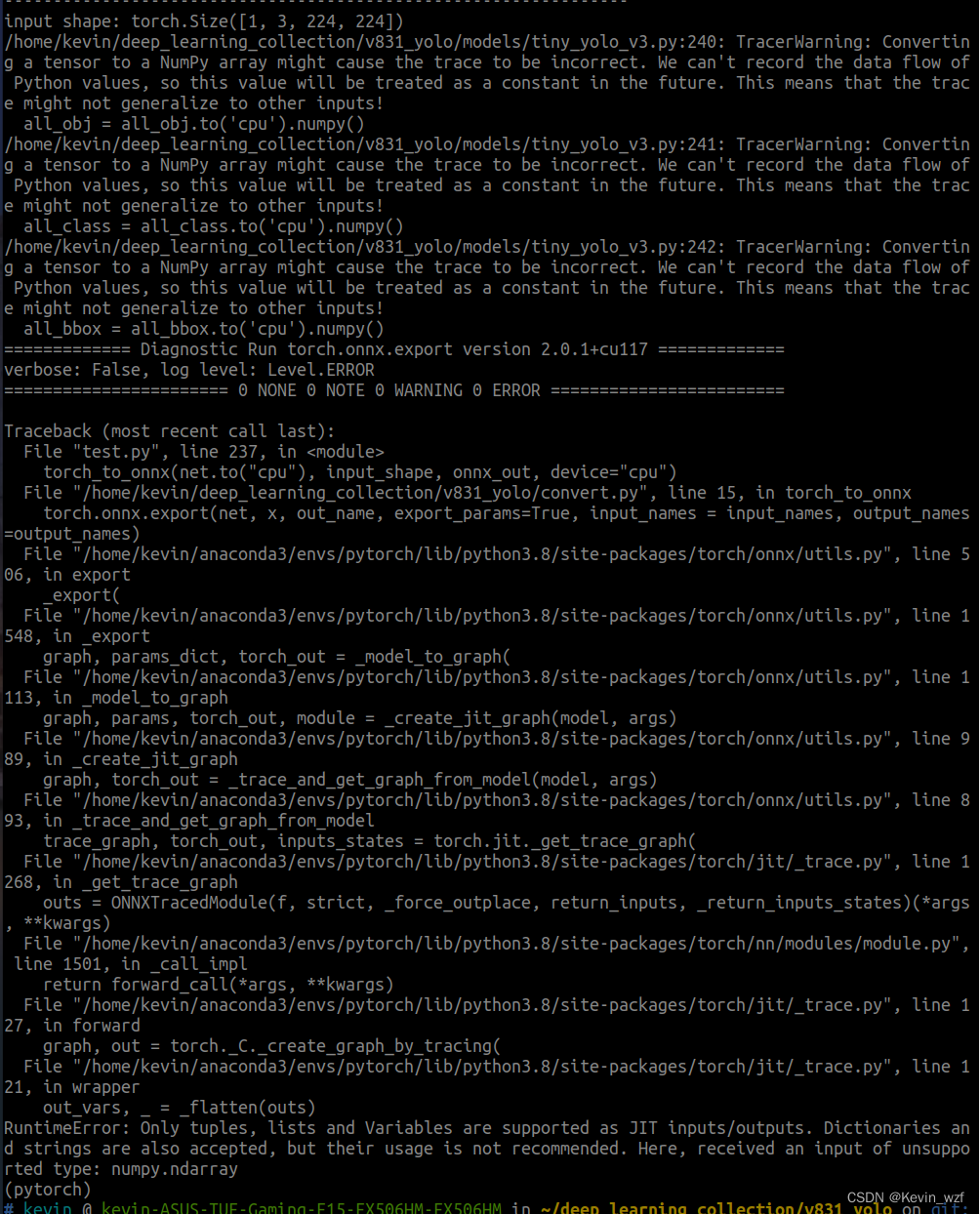
2.特别鸣谢
上述代码,dianjixz 作者是参考了yolov2-yolov3_PyTorch这个代码进行修改,确实有些地方不够完善,但也很感激 dianjixz 和 Jianhua Yang 两位大佬以及 Sipeed的团队成员开源,也特别感谢 neucrack 大佬分享了他写的基于pytorch代码基于pytorch训练的代码,是支持YOLOV2的本地训练,流程差不多。
后来我在issues的评论区,发现之前也有人尝试用YOLOV3-tiny进行转换没有成功,我遇到的错误跟他差不多,目前我还在研究,其实按照全志的SDK进行开发,应该是可以支持,需要一定时间,但因为本人最近赶项目,时间有点匆忙。
最后希望更多开发者能看到这篇文章,少走一些弯路,众人拾柴火焰高,也更希望大家分享一些新的尝试方法,喜欢的点个赞或留言,我看到都会回复。
(未完待续。。。)
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容






所有评论(0)