GoogLeNet网络及代码
GoogLeNet是2014年Christian Szegedy提出的一种全新的深度学习结构,inception的提出则从另一种角度来提升训练结果:能更高效的利用计算资源,在相同的计算量下能提取到更多的特征,从而提升训练结果。GoogleNet在2014年由Google团队提出,斩获当年ImageNet竞赛中Classification Task (分类任务)第一名。GoogLeNet亮点(1
GoogLeNet 是 2014 年 Christian Szegedy 提出的一种全新的深度学习结构,inception 的提出则从另一种角度来提升训练结果:能更高效的利用计算资源,在相同的计算量下能提取到更多的特征,从而提升训练结果。GoogleNet 在 2014 年由 Google 团队提出,斩获当年 ImageNet 竞赛中 Classification Task (分类任务)第一名。
GoogLeNet 亮点
(1)引入了 Inception 结构( 融合不同尺度的特征信息)
(2)使用 1*1 的卷积核进行降维以及映射处理
(3)添加两个辅助分类器帮助训练
(4)丢弃全连接层,使用平均池化层(大大减少模型参数)
GoogLeNet 网络结构表格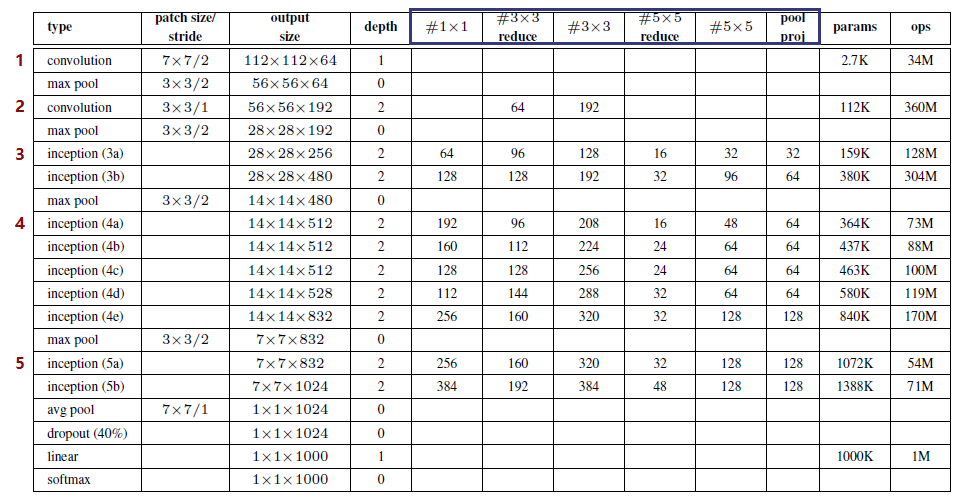
该表清晰记录了各卷积层的卷积核大小、步长、卷积核个数/通道数、输出图像的大小等信息。注:上表中的 “#3x3 reduce”,“#5x5 reduce” 表示在 3x3,5x5 卷积操作之前使用了 1x1 卷积的数量,起到降维的作用。
第一层(卷积层)
使用 7*7 的卷积核,步长 2,64 通道,输出为 112x112x64,卷积后进行 ReLU 操作
经过 3*3 的 max pooling,步长为 2,输出为 56x56x64,再进行 ReLU 操作
第二层(卷积层)
使用 3*3 的卷积核,步长为 1,192 通道,输出为 56x56x192,卷积后进行 ReLU 操作
经过 3*3 的 max pooling,步长为 2,输出为 28x28x192,再进行 ReLU 操作
第三层(Inception 3a层)
分为四个分支,采用不同尺度的卷积核来进行处理
(1)64 个 1*1 的卷积核,然后 ReLU,输出 28x28x64
(2)96 个 1*1 的卷积核,作为 3*3 卷积核之前的降维,变成 28x28x96,然后进行ReLU 计算,再进行 128个3*3 的卷积,输出 28x28x128
(3)16 个 1*1 的卷积核,作为 5*5 卷积核之前的降维,变成 28x28x16,进行 ReLU 计算后,再进行 32 个 5*5 的卷积,输出 28x28x32
(4)pool 层,使用 3*3 的核,输出 28x28x192,然后进行 32 个 1*1 的卷积,输出 28x28x32
将四个结果进行连接,对这四部分输出结果的第三维并联,即 64+128+32+32 = 256,最终输出 28x28x256
按表分析,同理其它层…
第三层(Inception 3b层)
第四层(Inception 4a/b/c/d/e层)
第五层(Inception 5a/b层)
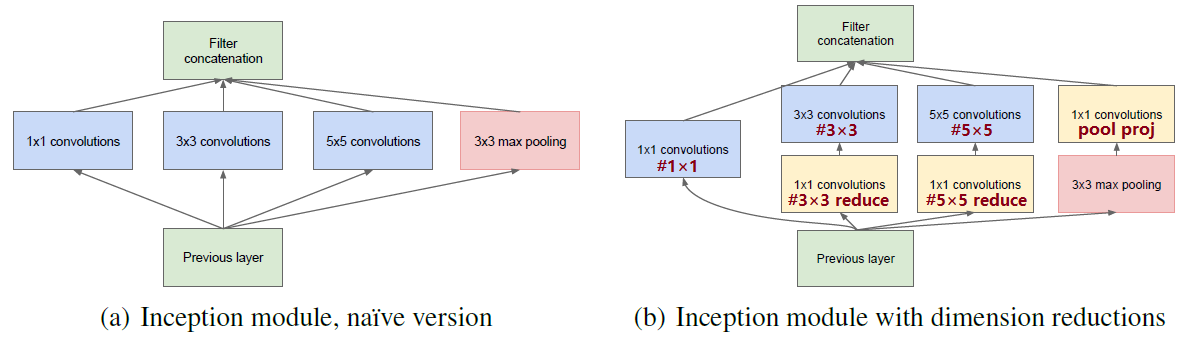
图中右侧淡黄色框即 1*1 卷积核,使用 1*1 卷积核降维。将上表蓝色框起来的列名和上图右侧部分标注的内容进行对应,更好理解 GoogLeNet 网络的 inception 结构。
接下来介绍一下,它到底是如何达到降维的效果的呢?
如果一个 channel 为 512 的图像使用 64 个 5*5 的卷积核进行卷积,需要使用 512*5*5*64 = 819200 个参数;
如果加入 1*1 卷积核,图像先使用 24 个 1*1 卷积核,再使用 64 个 5*5 的卷积核进行卷积,那么参数个数为 512*1*1*24 + 24*5*5*64 = 50688;
由此可见,使用 1*1 卷积核可以达到降维的效果。
GoogLeNet 网络结构图
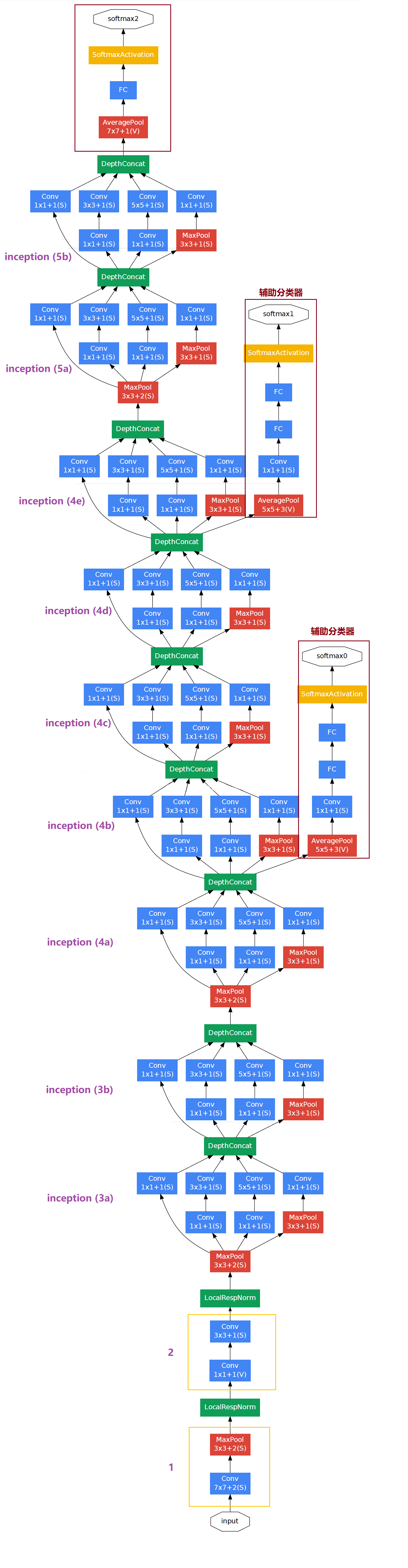 将 GoogLeNet 网络结构表和网络结构图对比起来分析,会使我们更好得理解 GoogLeNet 网络各层的内部结构以及层与层之间的连接。
将 GoogLeNet 网络结构表和网络结构图对比起来分析,会使我们更好得理解 GoogLeNet 网络各层的内部结构以及层与层之间的连接。
代码
这里使用 pytorch 框架构建 GoogLeNet 模型,训练花卉数据集
model.py
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
class GoogLeNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000, aux_logits=True, init_weights=False):
super(GoogLeNet, self).__init__()
self.aux_logits = aux_logits
self.conv1 = BasicConv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3) # BasicConv2d类
self.maxpool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.conv2 = BasicConv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=1)
self.conv3 = BasicConv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.maxpool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.inception3a = Inception(192, 64, 96, 128, 16, 32, 32) # Inception类
self.inception3b = Inception(256, 128, 128, 192, 32, 96, 64)
self.maxpool3 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.inception4a = Inception(480, 192, 96, 208, 16, 48, 64)
self.inception4b = Inception(512, 160, 112, 224, 24, 64, 64)
self.inception4c = Inception(512, 128, 128, 256, 24, 64, 64)
self.inception4d = Inception(512, 112, 144, 288, 32, 64, 64)
self.inception4e = Inception(528, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128)
self.maxpool4 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.inception5a = Inception(832, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128)
self.inception5b = Inception(832, 384, 192, 384, 48, 128, 128)
if self.aux_logits:
self.aux1 = InceptionAux(512, num_classes) # InceptionAux类
self.aux2 = InceptionAux(528, num_classes)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.4)
self.fc = nn.Linear(1024, num_classes)
if init_weights:
self._initialize_weights()
# 正向传播
def forward(self, x):
# N x 3 x 224 x 224
x = self.conv1(x) # N x 64 x 112 x 112
x = self.maxpool1(x) # N x 64 x 56 x 56
x = self.conv2(x) # N x 64 x 56 x 56
x = self.conv3(x) # N x 192 x 56 x 56
x = self.maxpool2(x) # N x 192 x 28 x 28
x = self.inception3a(x) # N x 256 x 28 x 28
x = self.inception3b(x) # N x 480 x 28 x 28
x = self.maxpool3(x) # N x 480 x 14 x 14
x = self.inception4a(x) # N x 512 x 14 x 14
if self.training and self.aux_logits: # eval model不执行该部分
aux1 = self.aux1(x)
x = self.inception4b(x) # N x 512 x 14 x 14
x = self.inception4c(x) # N x 512 x 14 x 14
x = self.inception4d(x) # N x 528 x 14 x 14
if self.training and self.aux_logits: # eval model不执行该部分
aux2 = self.aux2(x)
x = self.inception4e(x) # N x 832 x 14 x 14
x = self.maxpool4(x) # N x 832 x 7 x 7
x = self.inception5a(x) # N x 832 x 7 x 7
x = self.inception5b(x) # N x 1024 x 7 x 7
x = self.avgpool(x) # N x 1024 x 1 x 1
x = torch.flatten(x, 1) # N x 1024
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.fc(x) # N x 1000 (num_classes)
if self.training and self.aux_logits: # eval model不执行该部分
return x, aux2, aux1
return x
# 初始化权重
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
# 类Inception,有四个分支
class Inception(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, ch1x1, ch3x3red, ch3x3, ch5x5red, ch5x5, pool_proj):
super(Inception, self).__init__()
self.branch1 = BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch1x1, kernel_size=1)
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch3x3red, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(ch3x3red, ch3x3, kernel_size=3, padding=1) # 保证输出大小等于输入大小
)
self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch5x5red, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(ch5x5red, ch5x5, kernel_size=5, padding=2) # 保证输出大小等于输入大小
)
self.branch4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
BasicConv2d(in_channels, pool_proj, kernel_size=1)
)
def forward(self, x):
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
branch4 = self.branch4(x)
# 四个分支连接起来
outputs = [branch1, branch2, branch3, branch4]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
# 辅助分类器:类InceptionAux,包括avepool+conv+fc1+fc2
class InceptionAux(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, num_classes):
super(InceptionAux, self).__init__()
self.averagePool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=5, stride=3)
self.conv = BasicConv2d(in_channels, 128, kernel_size=1) # output[batch, 128, 4, 4]
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(2048, 1024)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(1024, num_classes)
def forward(self, x):
# aux1: N x 512 x 14 x 14, aux2: N x 528 x 14 x 14
x = self.averagePool(x) # aux1: N x 512 x 4 x 4, aux2: N x 528 x 4 x 4
x = self.conv(x) # N x 128 x 4 x 4
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = F.dropout(x, 0.5, training=self.training) # N x 2048
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x), inplace=True)
x = F.dropout(x, 0.5, training=self.training) # N x 1024
x = self.fc2(x) # N x num_classes
return x
# 类BasicConv2d,包括conv+relu
class BasicConv2d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs):
super(BasicConv2d, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.relu(x)
return x
train.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
import torchvision
import json
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
import torch.optim as optim
from model import GoogLeNet
# 检测使用 gpu or cpu
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(device)
data_transform = {
"train": transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]),
"val": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])}
image_path = "data_set/flower_data/" # 数据集路径
train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=image_path + "/train",
transform=data_transform["train"])
train_num = len(train_dataset)
# {'daisy':0, 'dandelion':1, 'roses':2, 'sunflower':3, 'tulips':4}
flower_list = train_dataset.class_to_idx
cla_dict = dict((val, key) for key, val in flower_list.items())
# 将字典写入json文件中
json_str = json.dumps(cla_dict, indent=4)
with open('class_indices.json', 'w') as json_file:
json_file.write(json_str)
batch_size = 32
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True,
num_workers=0)
validate_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=image_path + "val",
transform=data_transform["val"])
val_num = len(validate_dataset)
validate_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(validate_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False,
num_workers=0)
# 模型,花数据集5个类别
net = GoogLeNet(num_classes=5, aux_logits=True, init_weights=True)
net.to(device)
loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.0003)
# 开始训练
print('Start training...')
best_acc = 0.0
save_path = './googleNet.pth'
for epoch in range(30):
# train
net.train()
running_loss = 0.0
for step, data in enumerate(train_loader, start=0):
images, labels = data
optimizer.zero_grad() # 清空过往梯度
# 将输入图片载入模型中,得到输出图像,有三个参数:主分类器 + 2个辅助分类器
logits, aux_logits2, aux_logits1 = net(images.to(device))
# 计算三个分类器的损失
loss0 = loss_function(logits, labels.to(device))
loss1 = loss_function(aux_logits1, labels.to(device))
loss2 = loss_function(aux_logits2, labels.to(device))
loss = loss0 + loss1 * 0.3 + loss2 * 0.3 #乘以权重0.3是论文中提出的
loss.backward() # 反向传播,计算当前梯度
optimizer.step() # 根据梯度更新网络参数
running_loss += loss.item() # 累加损失值
# 打印训练过程
rate = (step + 1) / len(train_loader)
a = "*" * int(rate * 50)
b = "." * int((1 - rate) * 50)
print("\rtrain loss: {:^3.0f}%[{}->{}]{:.3f}".format(int(rate * 100), a, b, loss), end="")
print()
# validate
net.eval()
acc = 0.0 # accumulate accurate number / epoch
with torch.no_grad():
for val_data in validate_loader:
val_images, val_labels = val_data
outputs = net(val_images.to(device)) # eval model只需要主分类器的输出
predict_y = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)[1]
acc += (predict_y == val_labels.to(device)).sum().item()
val_accurate = acc / val_num
if val_accurate > best_acc:
best_acc = val_accurate
torch.save(net.state_dict(), save_path)
print('[epoch %d] train_loss: %.3f test_accuracy: %.3f' %
(epoch + 1, running_loss / step, val_accurate))
print('Finished Training')
predict.py
import torch
from model import GoogLeNet
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import json
data_transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])
img = Image.open("data_set/flower_data/predict_flower.jpg") # 载入图像
plt.imshow(img)
img = data_transform(img) # [C, H, W],转换图像为tensor
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0) # [N, C, H, W],增加一个维度N
# 读取类别
try:
json_file = open('./class_indices.json', 'r')
class_indict = json.load(json_file)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
exit(-1)
# 建立模型
model = GoogLeNet(num_classes=5, aux_logits=False)
# 载入保存的权重文件
model_weight_path = "./googleNet.pth"
missing_keys, unexpected_keys = model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_weight_path), strict=False)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
output = torch.squeeze(model(img))
predict = torch.softmax(output, dim=0)
predict_cla = torch.argmax(predict).numpy()
print(class_indict[str(predict_cla)], predict[predict_cla].item())
# 画图
name1 = class_indict[str(predict_cla)]
name2 =predict[predict_cla].numpy()
plt.title("This is %s. The accuracy is %s"%(name1, name2),color='red')
plt.show()
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)