Matlab_Simulink多智能体编队协同规划与控制算法仿真
。Matlab/Simulink多智能体编队协同规划与控制算法仿真具体包括:多智能体一致性控制多智能体事件触发控制多智能体任务分配多智能体协同路径规划多智能体强化学习等
·
Matlab/Simulink多智能体编队协同规划与控制算法仿真
具体包括:
多智能体一致性控制
多智能体事件触发控制
多智能体任务分配
多智能体协同路径规划
多智能体强化学习等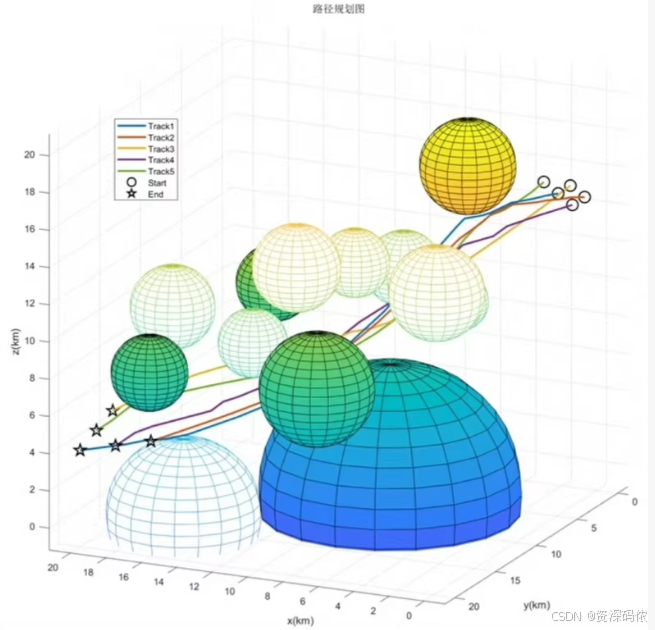
文章目录
在MATLAB/Simulink中实现多智能体系统的仿真,涉及多个方面,如一致性控制、事件触发控制、任务分配、协同路径规划和强化学习等。以下是一个综合示例,展示如何使用MATLAB和Simulink进行这些方面的仿真,并附上相关代码。
1. 多智能体一致性控制
MATLAB代码示例
% 参数设置
numAgents = 5; % 智能体数量
maxIterations = 200; % 最大迭代次数
learningRate = 0.1; % 学习率
initialPositions = rand(numAgents, 2); % 初始位置
% 通信拓扑矩阵(简单环形拓扑)
communicationTopology = eye(numAgents);
for i = 1:numAgents
if i < numAgents
communicationTopology(i, i+1) = 1;
communicationTopology(i+1, i) = 1;
else
communicationTopology(i, 1) = 1;
communicationTopology(1, i) = 1;
end
end
% 归一化通信矩阵
communicationMatrix = communicationTopology / sum(communicationTopology, 2);
% 初始化变量
positions = initialPositions;
% 迭代更新
for iter = 1:maxIterations
% 更新位置
newPosition = zeros(size(positions));
for i = 1:numAgents
neighborSum = sum(bsxfun(@times, communicationMatrix(i, :), positions), 1);
newPosition(i, :) = positions(i, :) + learningRate * (neighborSum - positions(i, :));
end
% 更新位置
positions = newPosition;
% 打印当前状态
fprintf('Iteration %d: Positions = \n', iter);
disp(positions);
end
% 绘制结果
figure;
plot(positions(:, 1), positions(:, 2), 'o');
title('Final Positions of Agents');
xlabel('X Position');
ylabel('Y Position');
grid on;
2. 多智能体事件触发控制
事件触发控制是一种减少通信频率的方法,只在满足某些条件时才进行通信。
MATLAB代码示例
% 参数设置
numAgents = 5; % 智能体数量
maxIterations = 200; % 最大迭代次数
learningRate = 0.1; % 学习率
initialPositions = rand(numAgents, 2); % 初始位置
threshold = 0.1; % 触发阈值
% 通信拓扑矩阵(简单环形拓扑)
communicationTopology = eye(numAgents);
for i = 1:numAgents
if i < numAgents
communicationTopology(i, i+1) = 1;
communicationTopology(i+1, i) = 1;
else
communicationTopology(i, 1) = 1;
communicationTopology(1, i) = 1;
end
end
% 归一化通信矩阵
communicationMatrix = communicationTopology / sum(communicationTopology, 2);
% 初始化变量
positions = initialPositions;
lastUpdate = zeros(numAgents, 1); % 上次更新时间
% 迭代更新
for iter = 1:maxIterations
% 更新位置
newPosition = zeros(size(positions));
for i = 1:numAgents
if iter - lastUpdate(i) >= threshold
neighborSum = sum(bsxfun(@times, communicationMatrix(i, :), positions), 1);
newPosition(i, :) = positions(i, :) + learningRate * (neighborSum - positions(i, :));
lastUpdate(i) = iter;
end
end
% 更新位置
positions = newPosition;
% 打印当前状态
fprintf('Iteration %d: Positions = \n', iter);
disp(positions);
end
% 绘制结果
figure;
plot(positions(:, 1), positions(:, 2), 'o');
title('Final Positions of Agents with Event-Triggered Control');
xlabel('X Position');
ylabel('Y Position');
grid on;
3. 多智能体任务分配
MATLAB代码示例
% 参数设置
numAgents = 5; % 智能体数量
numTasks = 10; % 任务数量
taskLocations = rand(numTasks, 2); % 任务位置
% 初始化变量
assignments = zeros(numAgents, 1); % 每个智能体的任务分配
agentPositions = rand(numAgents, 2); % 智能体初始位置
% 分配任务
for i = 1:numTasks
[~, minIdx] = min(sum(bsxfun(@minus, taskLocations(i, :), agentPositions).^2, 2));
assignments(minIdx) = assignments(minIdx) + 1;
end
% 输出结果
disp('Task Assignments:');
disp(assignments);
% 绘制结果
figure;
hold on;
scatter(agentPositions(:, 1), agentPositions(:, 2), 'filled', 'b');
scatter(taskLocations(:, 1), taskLocations(:, 2), 'filled', 'r');
legend('Agents', 'Tasks');
title('Agent Task Allocation');
xlabel('X Position');
ylabel('Y Position');
grid on;
hold off;
4. 多智能体协同路径规划
MATLAB代码示例
使用A*算法进行路径规划:
function path = multiAgentPathPlanning(startPoints, goalPoints, gridMap)
numAgents = size(startPoints, 1);
paths = cell(1, numAgents);
for i = 1:numAgents
start = startPoints(i, :);
goal = goalPoints(i, :);
path = astar(gridMap, start, goal);
paths{i} = path;
end
path = paths;
end
function path = astar(gridMap, start, goal)
% A*算法实现
openSet = [start];
closedSet = [];
cameFrom = containers.Map();
gScore = inf(size(gridMap));
gScore(start(1), start(2)) = 0;
fScore = inf(size(gridMap));
fScore(start(1), start(2)) = heuristic(start, goal);
while ~isempty(openSet)
current = getLowestFScoreNode(openSet, fScore);
if isequal(current, goal)
path = reconstructPath(cameFrom, current);
return;
end
openSet = setdiff(openSet, current, 'rows');
closedSet = [closedSet; current];
neighbors = getNeighbors(current, gridMap);
for _, neighbor in enumerate(neighbors)
if any(ismember(neighbor, closedSet, 'rows'))
continue;
end
tentativeGScore = gScore(current(1), current(2)) + 1;
if ~any(ismember(neighbor, openSet, 'rows'))
openSet = [openSet; neighbor];
elseif tentativeGScore >= gScore(neighbor(1), neighbor(2))
continue;
end
cameFrom(neighbor) = current;
gScore(neighbor(1), neighbor(2)) = tentativeGScore;
fScore(neighbor(1), neighbor(2)) = gScore(neighbor(1), neighbor(2)) + heuristic(neighbor, goal);
end
end
path = [];
end
function h = heuristic(node, goal)
h = norm(node - goal);
end
function node = getLowestFScoreNode(openSet, fScore)
[~, idx] = min(fScore(openSet(:, 1), openSet(:, 2)));
node = openSet(idx, :);
end
function neighbors = getNeighbors(node, gridMap)
directions = [0 1; 1 0; 0 -1; -1 0];
neighbors = [];
for d = 1:size(directions, 1)
neighbor = node + directions(d, :);
if isValidPosition(neighbor, gridMap)
neighbors = [neighbors; neighbor];
end
end
end
function valid = isValidPosition(pos, gridMap)
valid = pos(1) > 0 && pos(1) <= size(gridMap, 1) && ...
pos(2) > 0 && pos(2) <= size(gridMap, 2) && ...
gridMap(pos(1), pos(2)) == 0;
end
function path = reconstructPath(cameFrom, current)
totalPath = current;
while isKey(cameFrom, current)
current = cameFrom(current);
totalPath = [current; totalPath];
end
path = totalPath;
end
5. 多智能体强化学习
使用Q-learning进行简单的多智能体强化学习:
% 参数设置
numAgents = 5; % 智能体数量
numActions = 4; % 动作数量(上下左右)
numStates = 16; % 状态数量(假设为4x4网格)
learningRate = 0.1; % 学习率
discountFactor = 0.9; % 折扣因子
epsilon = 0.1; % 探索率
maxEpisodes = 1000; % 最大回合数
% 初始化Q表
Q = rand(numAgents, numStates, numActions);
% 模拟环境(简单4x4网格)
environment = zeros(4, 4);
goalState = [3, 3]; % 目标状态
% 模拟训练过程
for episode = 1:maxEpisodes
% 初始化状态
currentState = [randi([1, 4]), randi([1, 4])];
while ~isequal(currentState, goalState)
% 选择动作
if rand < epsilon
action = randi([1, numActions]);
else
[~, action] = max(Q(:, currentState(1), currentState(2)), [], 2);
end
% 执行动作并观察新状态和奖励
nextState = executeAction(currentState, action);
reward = calculateReward(nextState, goalState);
% 更新Q表
bestNextAction = max(Q(:, nextState(1), nextState(2)), [], 2);
Q(:, currentState(1), currentState(2), action) = Q(:, currentState(1), currentState(2), action) + ...
learningRate * (reward + discountFactor * bestNextAction - Q(:, currentState(1), currentState(2), action));
% 更新状态
currentState = nextState;
end
end
% 定义执行动作的函数
function nextState = executeAction(state, action)
switch action
case 1 % 上
nextState = state - [1, 0];
case 2 % 下
nextState = state + [1, 0];
case 3 % 左
nextState = state - [0, 1];
case 4 % 右
nextState = state + [0, 1];
end
% 边界检查
nextState(1) = max(1, min(nextState(1), 4));
nextState(2) = max(1, min(nextState(2), 4));
end
% 定义计算奖励的函数
function reward = calculateReward(state, goalState)
if isequal(state, goalState)
reward = 100;
else
reward = -1;
end
end
总结
上述代码展示了如何在MATLAB中实现多智能体系统的一致性控制、事件触发控制、任务分配、协同路径规划和强化学习。每段代码都针对一个具体的应用场景,可以根据实际需求进一步扩展和优化。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献12条内容
已为社区贡献12条内容








所有评论(0)