YOLOv11创新改进: 涨点明显,即插即用!添加动态Tanh(DyT)归一化模块至主干和颈部网络
YOLOv11创新改进: 即插即用!添加动态Tanh(DyT)到主干(backbone)颈部(Neck)网络,用就完了!
·
1. 代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class DyT(nn.Module):
# input x has the shape of[B,T,C]
# B:batch size, T:tokens, C:dimension
def __init__(self, C, init_alpha):
super(DyT, self).__init__()
self.alpha = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(1) * init_alpha)
self.beta = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(C))
self.gamma = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(C))
self.act = nn.Tanh()
def forward(self, x):
b, c, h, w = x.shape
x = x.reshape(b, c, -1).permute(0, 2, 1)
x = self.act(x * self.alpha)
x = self.beta * x + self.gamma
return x.permute(0, 2, 1).reshape(b, c, h, w)
if __name__ == '__main__':
x = torch.randn(1, 100, 512)
model = DyT(512, 0.1)
y = model(x)
print(y.shape)2. yaml配置文件
2.1 添加三层DyT模块
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLO11 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolo11n.yaml' will call yolo11.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.50, 0.25, 1024] # summary: 319 layers, 2624080 parameters, 2624064 gradients, 6.6 GFLOPs
s: [0.50, 0.50, 1024] # summary: 319 layers, 9458752 parameters, 9458736 gradients, 21.7 GFLOPs
m: [0.50, 1.00, 512] # summary: 409 layers, 20114688 parameters, 20114672 gradients, 68.5 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # summary: 631 layers, 25372160 parameters, 25372144 gradients, 87.6 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.50, 512] # summary: 631 layers, 56966176 parameters, 56966160 gradients, 196.0 GFLOPs
# YOLO11n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [256, False, 0.25]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False, 0.25]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
- [-1, 2, C2PSA, [1024]] # 10
# YOLO11n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False]] # 13
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [256, False]] # 16 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, DyT, [64, 0.8]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 13], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False]] # 19 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, DyT, [128, 0.8]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [1024, True]] # 22 (P5/32-large)
- [-1, 1, DyT, [256, 0.8]]
- [[16, 19, 22], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
2.2 改进DyT-C3k2模块
打开 ultralytics\nn\modules\block.py文件,导入DyT类,修改Bottleneck类
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
"""Standard bottleneck."""
def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, k=(3, 3), e=0.5):
"""Initializes a standard bottleneck module with optional shortcut connection and configurable parameters."""
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, k[0], 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, k[1], 1, g=g)
self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2
self.dyt = DyT(c2, 0.85)
def forward(self, x):
"""Applies the YOLO FPN to input data."""
return x + self.dyt(self.cv2(self.cv1(x))) if self.add else self.dyt(self.cv2(self.cv1(x)))3. 如何使用
打开 ultralytics\nn\task.py文件,导入DyT类
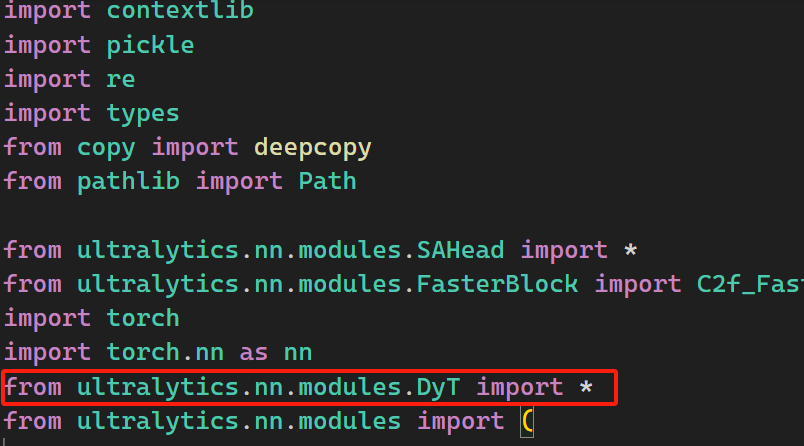
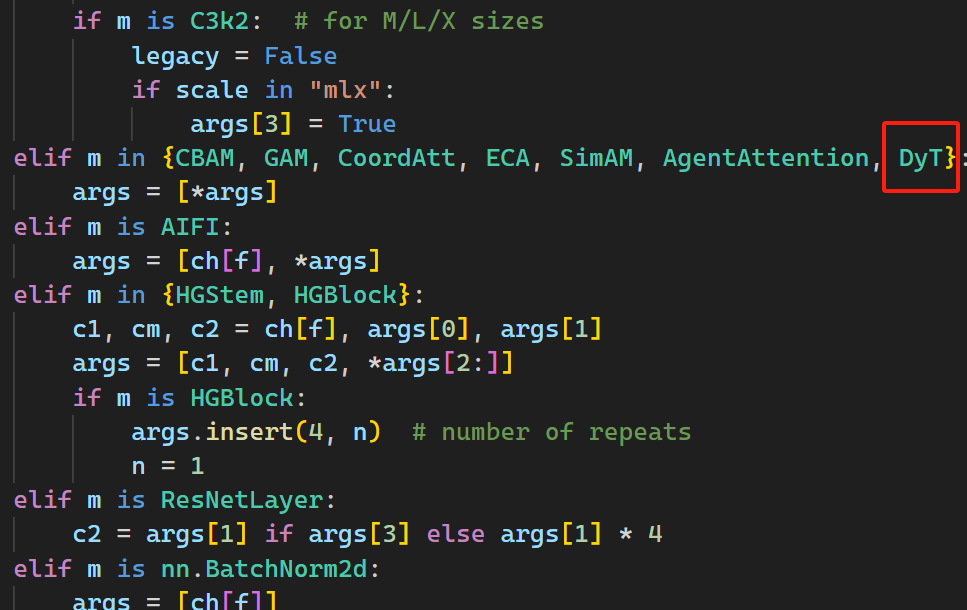
在parse_model函数进行修改。
4.实验结果
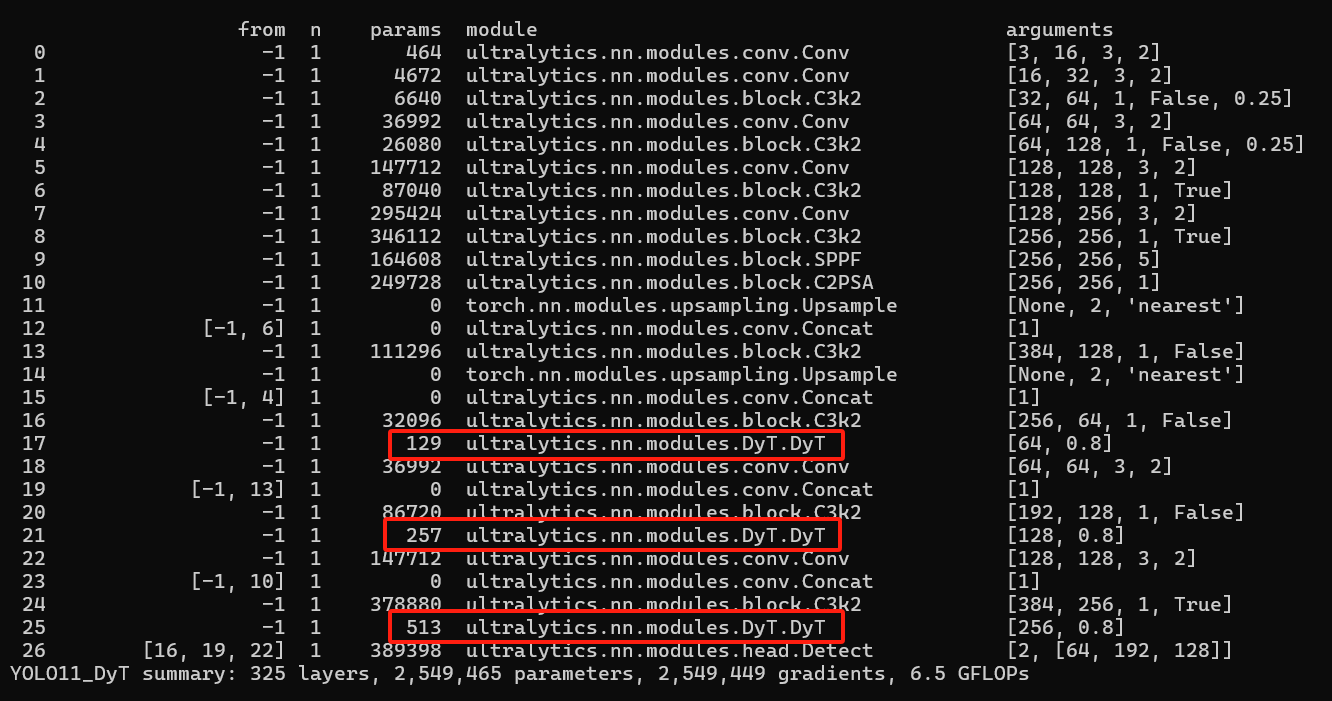
改进前
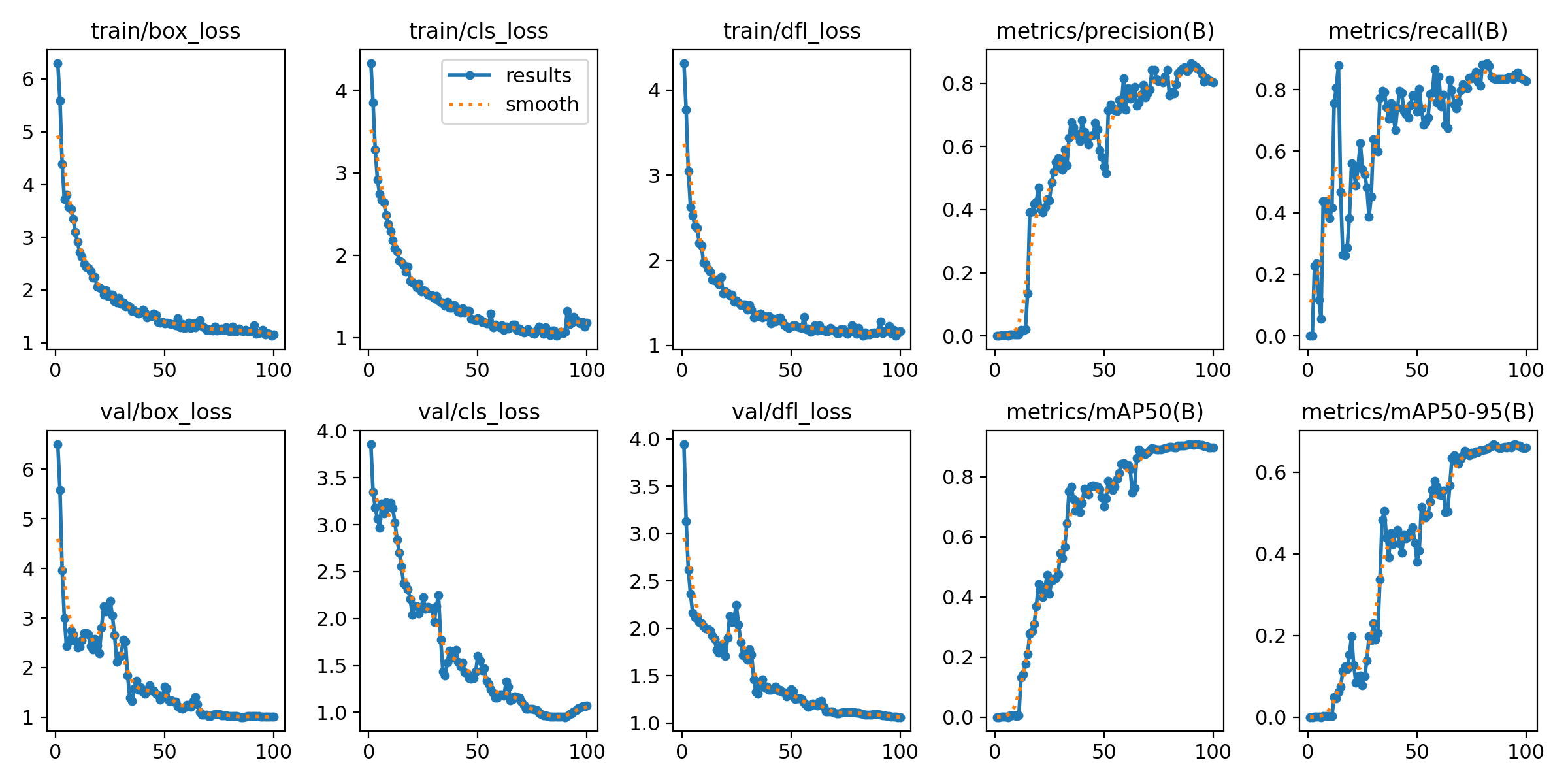
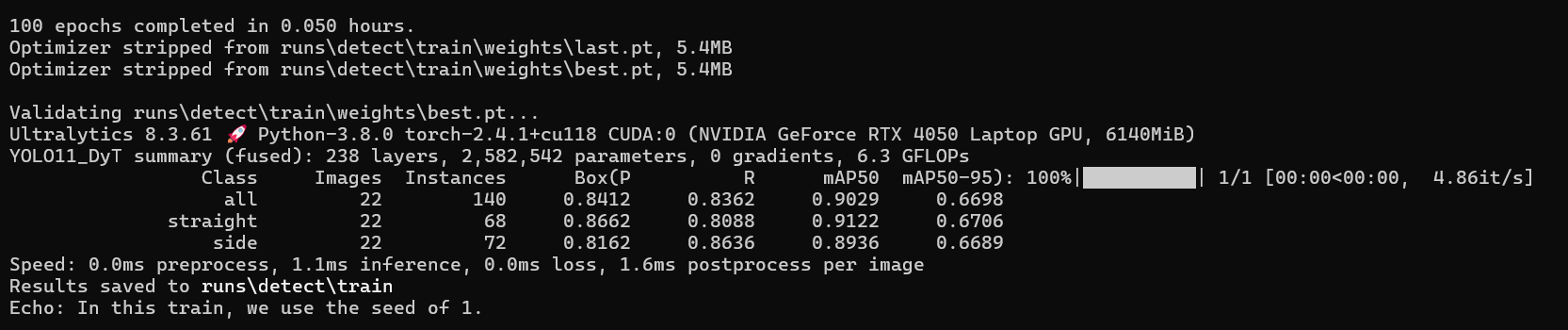
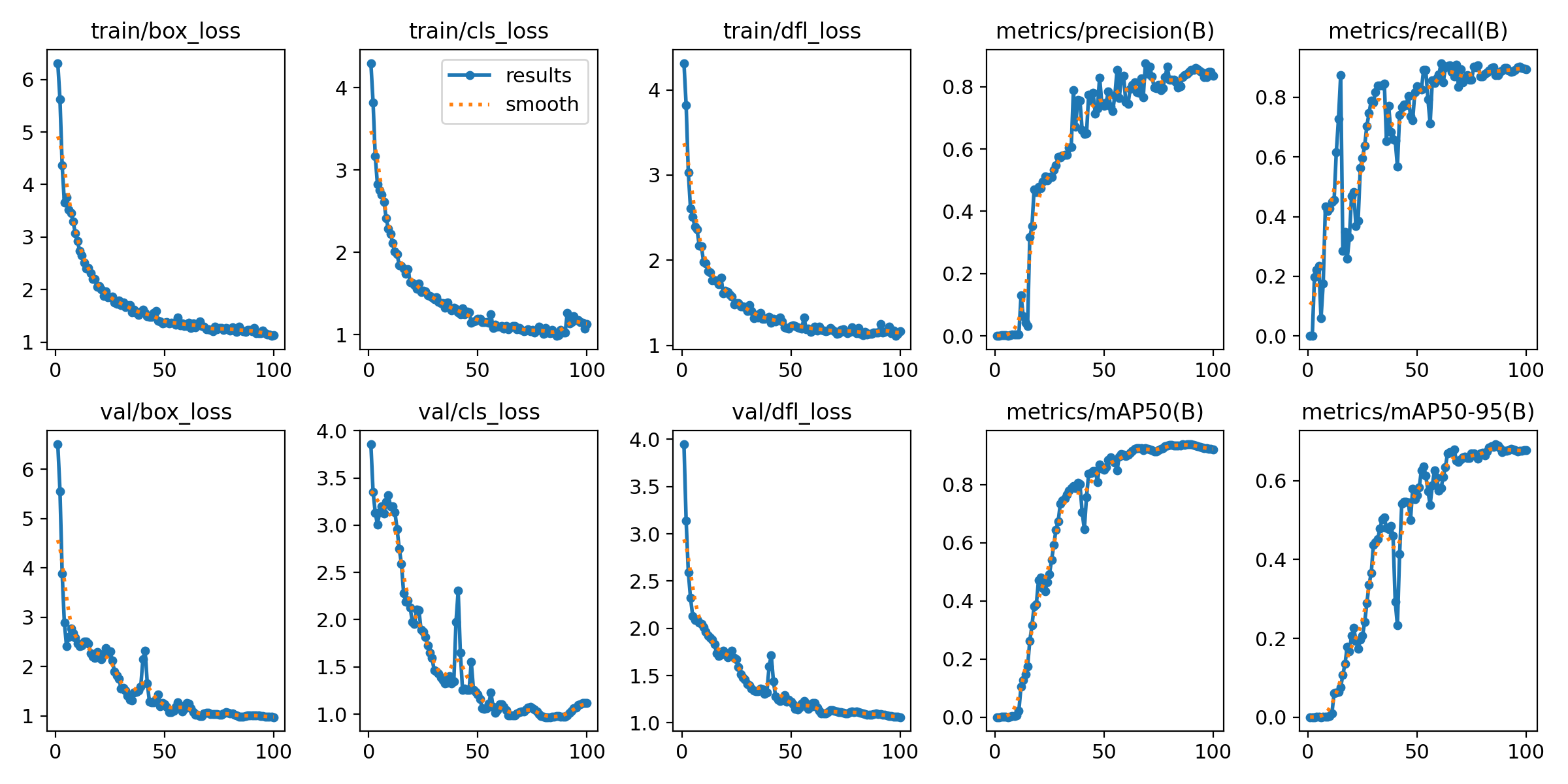
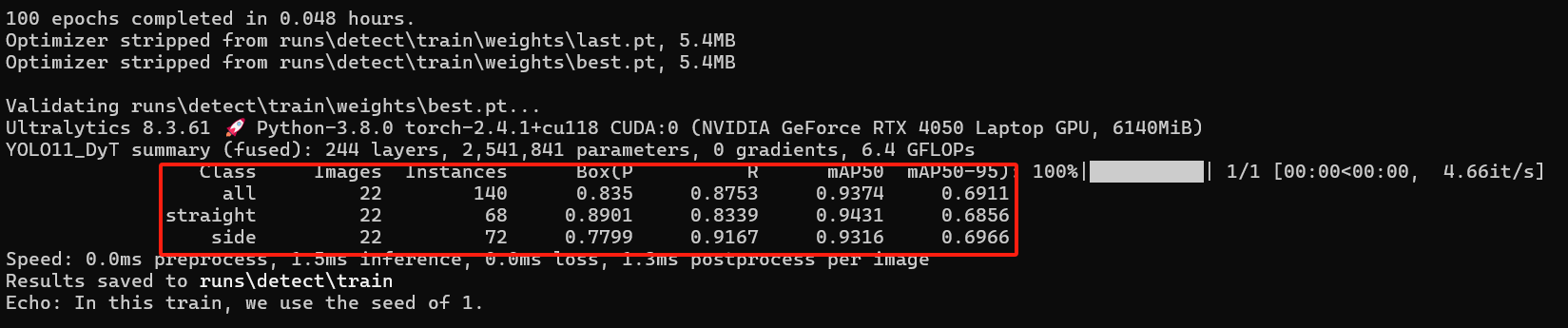
改进后
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容








所有评论(0)