点云与图像融合
貌似没有完全贴合,但是差不多了,那么应该是激光点云不准,跟代码无关。注意相机位姿:相机坐标系到世界坐标系。点云需要世界到相机,因此需要做一个逆。
·
1、点云图融合
注意相机位姿:相机坐标系到世界坐标系
点云需要世界到相机,因此需要做一个逆
import numpy as np
import open3d as o3d
import cv2
# 相机内参
fx = 2146.6838958083667
fy = 2146.6838958083663
cx = 2679.93038561
cy = 2305.20705337
# 相机内参矩阵
K = np.array([[fx, 0, cx],
[0, fy, cy],
[0, 0, 1]])
# 相机外参:旋转矩阵和平移向量(相机到世界)
rotation_matrix = np.array([
[-0.48912398562067366, 0.03004342479447644, -0.8716966899771764],
[0.05569301481387253, -0.9962913778540698, -0.06558794488761173],
[-0.8704343828178484, -0.08062805368020026, 0.4856368006733572]
])
translation_vector = np.array([0.20977785478453875, -0.38812356421196564, 68.19504568766176])
# 逆变换:从世界坐标系转换到相机坐标系
rotation_matrix_inv = rotation_matrix.T
translation_vector_inv = -rotation_matrix_inv @ translation_vector
# 读取点云
full_pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud("/media/kj/2B9747BF3C0EC4D0/Project/hierarchical-3d-gaussians/data/data03/inputs/buildPcd/1.ply")
# 提取点云中的坐标点
points = np.asarray(full_pcd.points)
# 将点云从世界坐标系转换到相机坐标系
points_cam = rotation_matrix_inv @ points.T + translation_vector_inv[:, np.newaxis] # (3xN)
# 使用相机内参将相机坐标系下的点投影到图像平面
points_2d = K @ points_cam # (3xN)
# 归一化,得到像素坐标
points_2d = points_2d[:2, :] / points_2d[2, :] # (2xN)
points_2d = points_2d.T # 转置为 Nx2
# 读取图像
image = cv2.imread("/media/kj/2B9747BF3C0EC4D0/Project/hierarchical-3d-gaussians/data/data03/inputs/buildPcd/1.jpg")
# 将投影的点绘制到图像上
for point in points_2d:
x, y = int(point[0]), int(point[1])
if 0 <= x < image.shape[1] and 0 <= y < image.shape[0]: # 检查点是否在图像边界内
cv2.circle(image, (x, y), 3, (0, 255, 0), -1)
output_path = "/media/kj/2B9747BF3C0EC4D0/Project/hierarchical-3d-gaussians/data/data03/inputs/buildPcd/projected_points.jpg"
cv2.imwrite(output_path, image)
print(f"图像已保存到 {output_path}")
貌似没有完全贴合,但是差不多了,那么应该是激光点云不准,跟代码无关
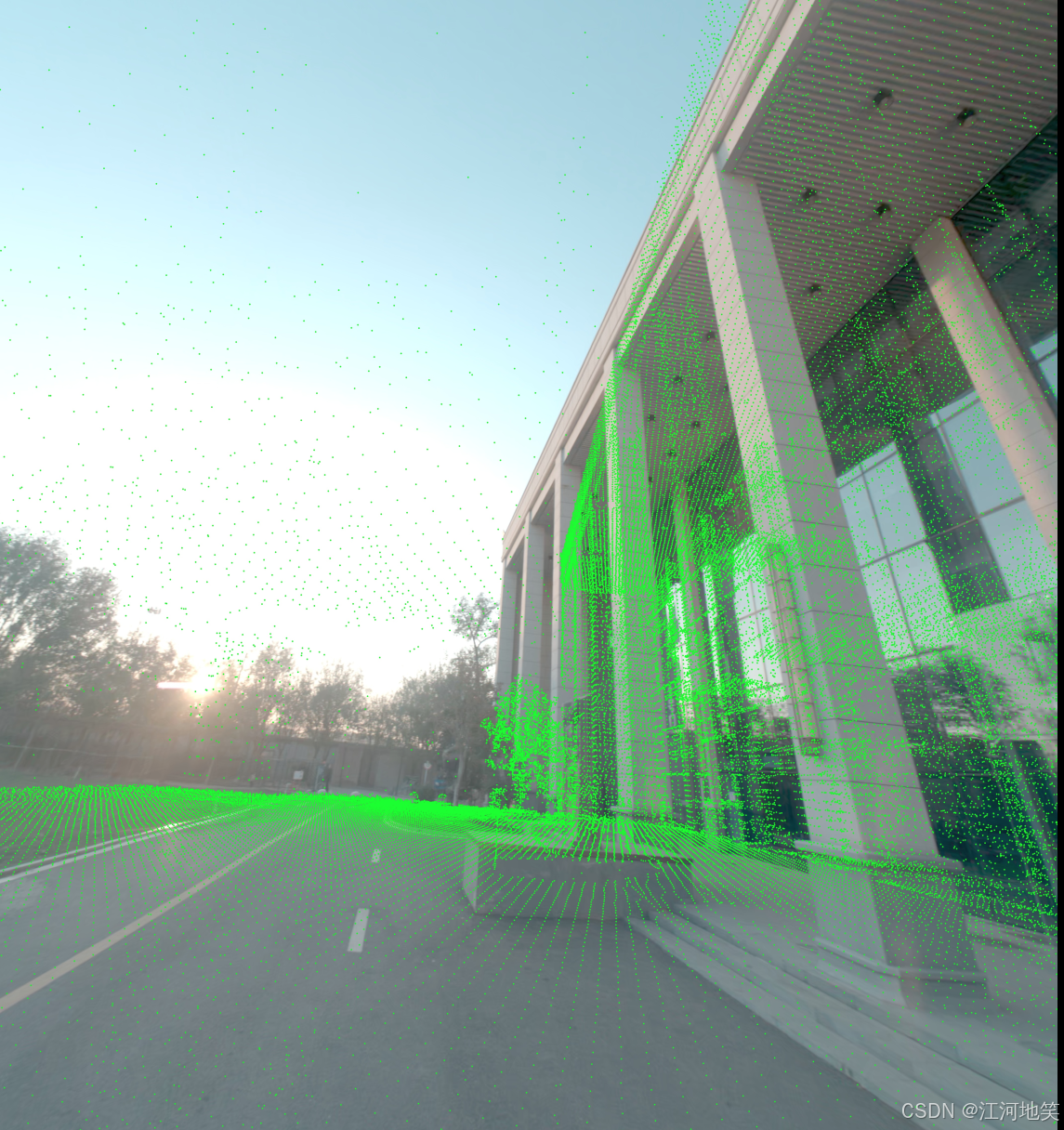

2、生成对应点云
import numpy as np
import open3d as o3d
import cv2
# 相机内参
fx = 2146.6838958083667
fy = 2146.6838958083663
cx = 2679.93038561
cy = 2305.20705337
# 相机内参矩阵
K = np.array([[fx, 0, cx],
[0, fy, cy],
[0, 0, 1]])
# 相机外参:旋转矩阵和平移向量(相机到世界)
rotation_matrix = np.array([
[-0.48912398562067366, 0.03004342479447644, -0.8716966899771764],
[0.05569301481387253, -0.9962913778540698, -0.06558794488761173],
[-0.8704343828178484, -0.08062805368020026, 0.4856368006733572]
])
translation_vector = np.array([0.20977785478453875, -0.38812356421196564, 68.19504568766176])
# 逆变换:从世界坐标系转换到相机坐标系
rotation_matrix_inv = rotation_matrix.T
translation_vector_inv = -rotation_matrix_inv @ translation_vector
# 读取点云
full_pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud("/media/kj/2B9747BF3C0EC4D0/Project/hierarchical-3d-gaussians/data/data03/inputs/buildPcd/1.ply")
# 提取点云中的坐标点
points = np.asarray(full_pcd.points)
# 将点云从世界坐标系转换到相机坐标系
points_cam = rotation_matrix_inv @ points.T + translation_vector_inv[:, np.newaxis] # (3xN)
# 深度截断(例如,0.1到100.0米范围)
depth_min = 0.1
depth_max = 20.0
valid_depth_mask = (points_cam[2, :] > depth_min) & (points_cam[2, :] < depth_max)
# 仅保留符合深度范围的点
points_cam = points_cam[:, valid_depth_mask]
# 使用相机内参将相机坐标系下的点投影到图像平面
points_2d = K @ points_cam # (3xN)
# 归一化,得到像素坐标
points_2d = points_2d[:2, :] / points_2d[2, :] # (2xN)
points_2d = points_2d.T # 转置为 Nx2
# 读取图像
image = cv2.imread("/media/kj/2B9747BF3C0EC4D0/Project/hierarchical-3d-gaussians/data/data03/inputs/buildPcd/1.jpg")
# 将投影的点绘制到图像上
projected_points = []
for point, cam_point in zip(points_2d, points_cam.T):
x, y = int(point[0]), int(point[1])
if 0 <= x < image.shape[1] and 0 <= y < image.shape[0]: # 检查点是否在图像边界内
cv2.circle(image, (x, y), 3, (0, 255, 0), -1)
projected_points.append(cam_point) # 收集投影到图像内的点
# 保存图像
output_image_path = "/media/kj/2B9747BF3C0EC4D0/Project/hierarchical-3d-gaussians/data/data03/inputs/buildPcd/projected_points.jpg"
cv2.imwrite(output_image_path, image)
print(f"图像已保存到 {output_image_path}")
# 将投影后的点保存为PCD文件
projected_points = np.array(projected_points)
projected_pcd = o3d.geometry.PointCloud()
projected_pcd.points = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(projected_points)
output_pcd_path = "/media/kj/2B9747BF3C0EC4D0/Project/hierarchical-3d-gaussians/data/data03/inputs/buildPcd/projected_points.pcd"
o3d.io.write_point_cloud(output_pcd_path, projected_pcd)
print(f"点云已保存到 {output_pcd_path}")
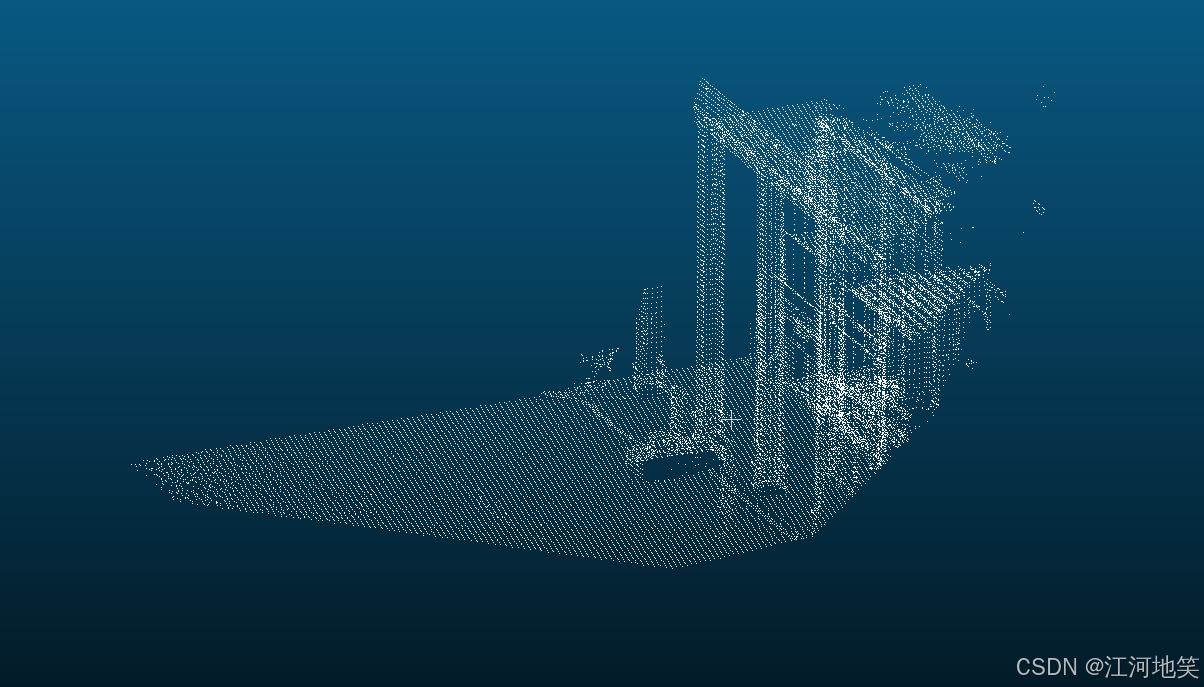
3、生成对应深度图
虽然精度不是很高,但是基本够用
import numpy as np
import open3d as o3d
import cv2
# 相机内参
fx = 2146.6838958083667
fy = 2146.6838958083663
cx = 2679.93038561
cy = 2305.20705337
# 相机内参矩阵
K = np.array([[fx, 0, cx],
[0, fy, cy],
[0, 0, 1]])
# 相机外参:旋转矩阵和平移向量(相机到世界)
rotation_matrix = np.array([
[-0.48912398562067366, 0.03004342479447644, -0.8716966899771764],
[0.05569301481387253, -0.9962913778540698, -0.06558794488761173],
[-0.8704343828178484, -0.08062805368020026, 0.4856368006733572]
])
translation_vector = np.array([0.20977785478453875, -0.38812356421196564, 68.19504568766176])
# 逆变换:从世界坐标系转换到相机坐标系
rotation_matrix_inv = rotation_matrix.T
translation_vector_inv = -rotation_matrix_inv @ translation_vector
# 读取点云
full_pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud("/media/kj/2B9747BF3C0EC4D0/Project/hierarchical-3d-gaussians/data/data03/inputs/buildPcd/1.ply")
# 提取点云中的坐标点
points = np.asarray(full_pcd.points)
# 将点云从世界坐标系转换到相机坐标系
points_cam = rotation_matrix_inv @ points.T + translation_vector_inv[:, np.newaxis] # (3xN)
# 深度截断(例如,0.1到20.0米范围)
depth_min = 0.1
depth_max = 20.0
valid_depth_mask = (points_cam[2, :] > depth_min) & (points_cam[2, :] < depth_max)
# 仅保留符合深度范围的点
points_cam = points_cam[:, valid_depth_mask]
# 使用相机内参将相机坐标系下的点投影到图像平面
points_2d = K @ points_cam # (3xN)
# 归一化,得到像素坐标
points_2d = points_2d[:2, :] / points_2d[2, :] # (2xN)
points_2d = points_2d.T # 转置为 Nx2
# 读取图像
image = cv2.imread("/media/kj/2B9747BF3C0EC4D0/Project/hierarchical-3d-gaussians/data/data03/inputs/buildPcd/1.jpg")
# 初始化深度图
depth_map = np.full((image.shape[0], image.shape[1]), np.inf)
# 将投影的点绘制到图像上,并记录深度
projected_points = []
for point, cam_point in zip(points_2d, points_cam.T):
x, y = int(point[0]), int(point[1])
depth = cam_point[2]
if 0 <= x < image.shape[1] and 0 <= y < image.shape[0]: # 检查点是否在图像边界内
# 如果该像素位置的深度值更小,则更新深度值
if depth < depth_map[y, x]:
depth_map[y, x] = depth
cv2.circle(image, (x, y), 3, (0, 255, 0), -1)
projected_points.append(cam_point) # 收集投影到图像内的点
# 将inf深度值设置为0,以便更好地显示
depth_map[depth_map == np.inf] = 0
# 归一化深度图到0-255范围用于可视化
depth_map_normalized = cv2.normalize(depth_map, None, 0, 255, cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U)
# 保存深度图
output_depth_path = "/media/kj/2B9747BF3C0EC4D0/Project/hierarchical-3d-gaussians/data/data03/inputs/buildPcd/depth_map.png"
cv2.imwrite(output_depth_path, depth_map_normalized)
print(f"深度图已保存到 {output_depth_path}")
# 保存图像
output_image_path = "/media/kj/2B9747BF3C0EC4D0/Project/hierarchical-3d-gaussians/data/data03/inputs/buildPcd/projected_points.jpg"
cv2.imwrite(output_image_path, image)
print(f"图像已保存到 {output_image_path}")
# 将投影后的点保存为PCD文件
projected_points = np.array(projected_points)
projected_pcd = o3d.geometry.PointCloud()
projected_pcd.points = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(projected_points)
output_pcd_path = "/media/kj/2B9747BF3C0EC4D0/Project/hierarchical-3d-gaussians/data/data03/inputs/buildPcd/projected_points.pcd"
o3d.io.write_point_cloud(output_pcd_path, projected_pcd)
print(f"点云已保存到 {output_pcd_path}")
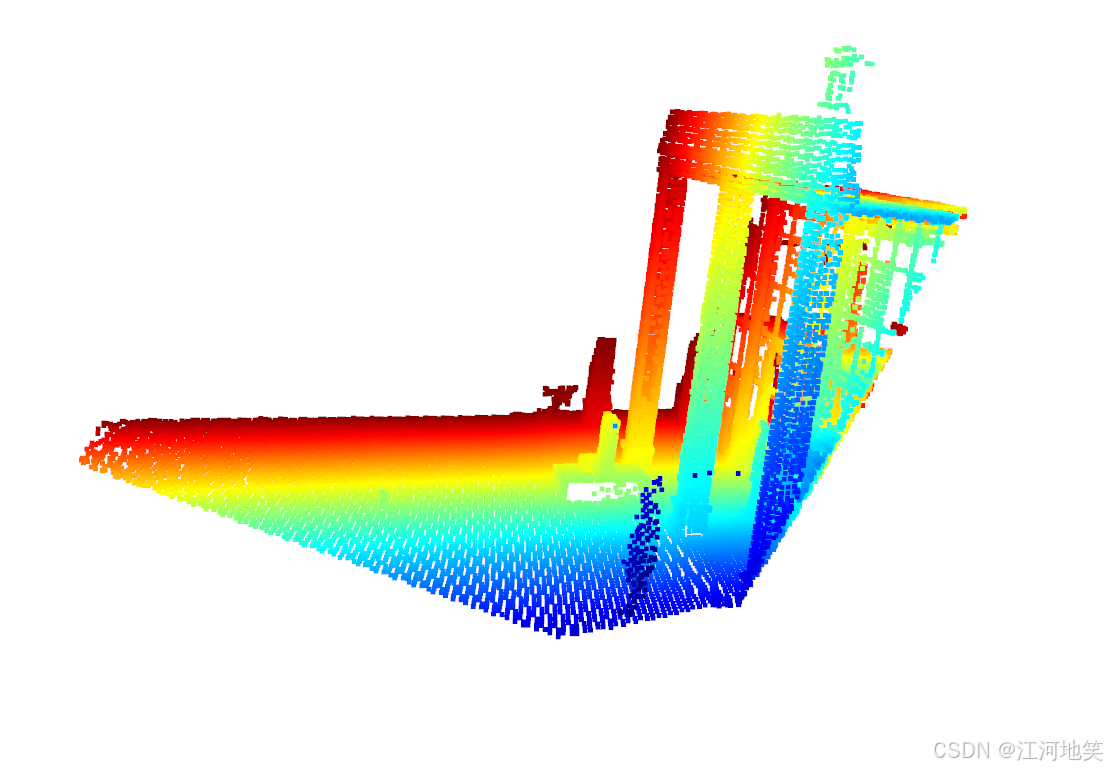
4、生成深度图修改版本
保存真实的深度以及平滑(使用插值技术填补深度图的空洞)
import numpy as np
import open3d as o3d
import cv2
from scipy.interpolate import griddata
# 相机内参
fx = 2146.6838958083667
fy = 2146.6838958083663
cx = 2679.93038561
cy = 2305.20705337
# 相机内参矩阵
K = np.array([[fx, 0, cx],
[0, fy, cy],
[0, 0, 1]])
rotation_matrix = np.array([
[-0.32560901527540903, -0.7302916005356621, -0.6005438762975103],
[0.3695895877154596, -0.6829291298474192, 0.6300883590879641],
[-0.870277143112293, -0.016792313506710427, 0.4922760530265489]
])
translation_vector = np.array([0.9003394723261107, -0.14423862306710328, 68.18943837029964])
# 逆变换:从世界坐标系转换到相机坐标系
rotation_matrix_inv = rotation_matrix.T
translation_vector_inv = -rotation_matrix_inv @ translation_vector
# 读取点云
full_pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud("/media/kj/2B9747BF3C0EC4D0/Project/hierarchical-3d-gaussians/data/data03/inputs/buildRTG/1.ply")
# 提取点云中的坐标点
points = np.asarray(full_pcd.points)
# 将点云从世界坐标系转换到相机坐标系
points_cam = rotation_matrix_inv @ points.T + translation_vector_inv[:, np.newaxis] # (3xN)
# 深度截断(例如,0.1到20.0米范围)
depth_min = 0.3
depth_max = 20.0
valid_depth_mask = (points_cam[2, :] > depth_min) & (points_cam[2, :] < depth_max)
# 仅保留符合深度范围的点
points_cam = points_cam[:, valid_depth_mask]
# 使用相机内参将相机坐标系下的点投影到图像平面
points_2d = K @ points_cam # (3xN)
# 归一化,得到像素坐标
points_2d = points_2d[:2, :] / points_2d[2, :] # (2xN)
points_2d = points_2d.T # 转置为 Nx2
# 读取图像
image = cv2.imread("/media/kj/2B9747BF3C0EC4D0/Project/hierarchical-3d-gaussians/data/data03/inputs/buildRTG/1.jpg")
# 初始化深度图
depth_map = np.full((image.shape[0], image.shape[1]), np.inf)
# 将像素坐标转换为整数索引
indices = np.round(points_2d).astype(int)
# 过滤出在图像边界内的点
valid_indices_mask = (indices[:, 0] >= 0) & (indices[:, 0] < image.shape[1]) & (indices[:, 1] >= 0) & (indices[:, 1] < image.shape[0])
indices = indices[valid_indices_mask]
points_cam = points_cam[:, valid_indices_mask]
# 使用numpy的高级索引并行处理深度图
depth_map[indices[:, 1], indices[:, 0]] = np.minimum(depth_map[indices[:, 1], indices[:, 0]], points_cam[2])
# 将inf深度值设置为0,以便更好地显示
depth_map[depth_map == np.inf] = 0
# 使用插值技术填补深度图中的空洞
# 找到深度图中的非零像素
non_zero_mask = depth_map > 0
coords = np.array(np.nonzero(non_zero_mask)).T
values = depth_map[non_zero_mask]
grid_x, grid_y = np.mgrid[0:image.shape[0], 0:image.shape[1]]
filled_depth_map = griddata(coords, values, (grid_x, grid_y), method='nearest')
# 将深度值从米转换为毫米并保存为16位无符号整数
depth_map_mm = (filled_depth_map * 1000).astype(np.uint16)
# 保存深度图
output_depth_path = "/media/kj/2B9747BF3C0EC4D0/Project/hierarchical-3d-gaussians/data/data03/inputs/buildRTG/depth_map.png"
cv2.imwrite(output_depth_path, depth_map_mm)
print(f"深度图已保存到 {output_depth_path}")
# 保存图像
output_image_path = "/media/kj/2B9747BF3C0EC4D0/Project/hierarchical-3d-gaussians/data/data03/inputs/buildRTG/projected_points.jpg"
cv2.imwrite(output_image_path, image)
print(f"图像已保存到 {output_image_path}")
# 将投影后的点保存为PCD文件
projected_points = points_cam.T # 保持原来的投影点
projected_pcd = o3d.geometry.PointCloud()
projected_pcd.points = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(projected_points)
output_pcd_path = "/media/kj/2B9747BF3C0EC4D0/Project/hierarchical-3d-gaussians/data/data03/inputs/buildRTG/projected_points.pcd"
o3d.io.write_point_cloud(output_pcd_path, projected_pcd)
print(f"点云已保存到 {output_pcd_path}")
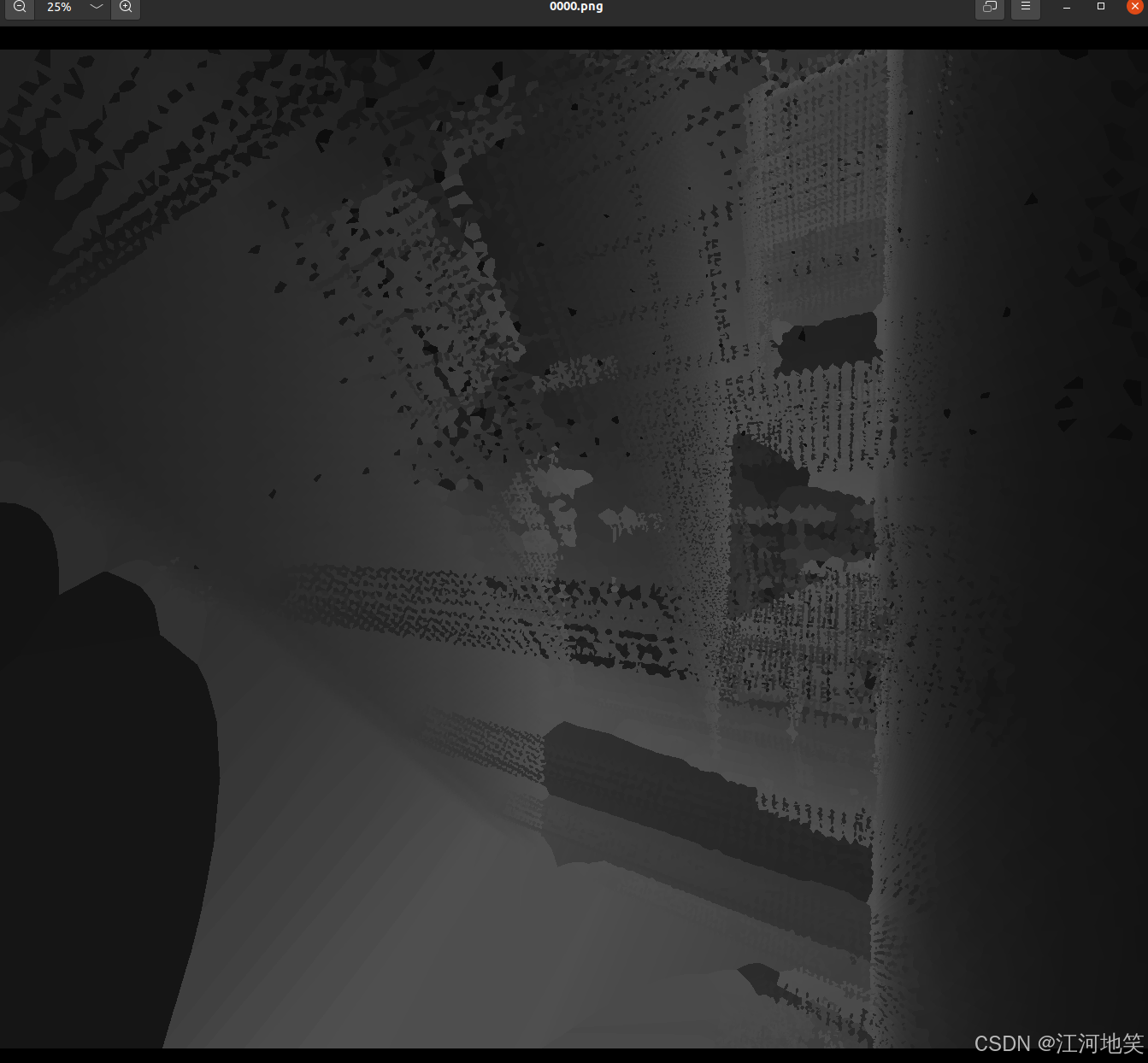
5、批量生成
import numpy as np
import open3d as o3d
import cv2
import json
import os
import shutil
from scipy.ndimage import distance_transform_edt
# 相机内参(固定值)
fx = 2146.6838958083667
fy = 2146.6838958083663
cx = 2679.93038561
cy = 2305.20705337
# 相机内参矩阵
K = np.array([[fx, 0, cx],
[0, fy, cy],
[0, 0, 1]])
floderPath = '/media/kj/2B9747BF3C0EC4D0/Data/buildRTG'
# 固定的点云文件路径
point_cloud_path = os.path.join(floderPath, "1.ply")
# 读取点云
full_pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(point_cloud_path)
# 读取JSON文件
cameras = os.path.join(floderPath, "cameras.json")
with open(cameras, 'r') as f:
data = json.load(f)
# 遍历JSON中的每个条目
for entry in data:
img_name = entry['img_name']
if int(img_name) > 603:
continue
# 检查对应的深度图是否已经存在,如果存在则跳过
depth_dir = os.path.join(floderPath, "depth")
os.makedirs(depth_dir, exist_ok=True)
output_depth_path = os.path.join(depth_dir, f"{img_name}.png")
if os.path.exists(output_depth_path):
print(f"深度图 {output_depth_path} 已存在,跳过处理。")
continue
position = np.array(entry['position'])
rotation_matrix = np.array(entry['rotation'])
# 生成变换矩阵
transformation_matrix = np.eye(4)
transformation_matrix[:3, :3] = rotation_matrix
transformation_matrix[:3, 3] = position
# 保存变换矩阵
pose_dir = os.path.join(floderPath, "pose")
os.makedirs(pose_dir, exist_ok=True)
np.savetxt(os.path.join(pose_dir, f"{img_name}.txt"), transformation_matrix, fmt='%.10f')
# 逆变换:从世界坐标系转换到相机坐标系
rotation_matrix_inv = rotation_matrix.T
translation_vector_inv = -rotation_matrix_inv @ position
# 提取点云中的坐标点
points = np.asarray(full_pcd.points)
# 将点云从世界坐标系转换到相机坐标系
points_cam = rotation_matrix_inv @ points.T + translation_vector_inv[:, np.newaxis]
# 深度截断(例如,0.3到20.0米范围)
depth_min = 0.3
depth_max = 20.0
valid_depth_mask = (points_cam[2, :] > depth_min) & (points_cam[2, :] < depth_max)
# 仅保留符合深度范围的点
points_cam = points_cam[:, valid_depth_mask]
# 使用相机内参将相机坐标系下的点投影到图像平面
points_2d = K @ points_cam
points_2d = points_2d[:2, :] / points_2d[2, :]
points_2d = points_2d.T
# 读取对应的图像
image_path = os.path.join(floderPath, "images", f"{img_name}.jpg")
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
# 检查图像是否成功读取
if image is None:
print(f"无法读取图像 {image_path},跳过处理。")
continue
# 初始化深度图
depth_map = np.full((image.shape[0], image.shape[1]), np.inf)
# 将像素坐标转换为整数索引
indices = np.round(points_2d).astype(int)
# 过滤出在图像边界内的点
valid_indices_mask = (indices[:, 0] >= 0) & (indices[:, 0] < image.shape[1]) & (indices[:, 1] >= 0) & (
indices[:, 1] < image.shape[0])
indices = indices[valid_indices_mask]
points_cam = points_cam[:, valid_indices_mask]
# 使用numpy的高级索引并行处理深度图
depth_map[indices[:, 1], indices[:, 0]] = np.minimum(depth_map[indices[:, 1], indices[:, 0]], points_cam[2])
# 将inf深度值设置为0,以便更好地显示
depth_map[depth_map == np.inf] = 0
# 使用距离变换填充深度图中的空洞
mask = depth_map == 0
indices = distance_transform_edt(mask, return_distances=False, return_indices=True)
filled_depth_map = depth_map.copy()
filled_depth_map[mask] = filled_depth_map[tuple(indices)][mask]
filled_depth_map = np.maximum(filled_depth_map, 0)
# 将深度值从米转换为毫米并保存为16位无符号整数
depth_map_mm = (filled_depth_map * 1000).astype(np.uint16)
# 保存深度图
cv2.imwrite(output_depth_path, depth_map_mm)
print(f"深度图已保存到 {output_depth_path}")
# 拷贝图像到color文件夹
color_dir = os.path.join(floderPath, "color")
os.makedirs(color_dir, exist_ok=True)
shutil.copy(image_path, os.path.join(color_dir, f"{img_name}.jpg"))
print(f"图像已拷贝到 {color_dir}")
6、优化深度图
import shutil
import numpy as np
import open3d as o3d
import cv2
import json
import os
from scipy.ndimage import distance_transform_edt, minimum_filter
# 相机内参(固定值)
fx = 2146.6838958083667
fy = 2146.6838958083663
cx = 2679.93038561
cy = 2305.20705337
# 相机内参矩阵
K = np.array([[fx, 0, cx],
[0, fy, cy],
[0, 0, 1]])
floderPath = '/media/kj/2B9747BF3C0EC4D0/Data/buildRTG'
# 固定的点云文件路径
point_cloud_path = os.path.join(floderPath, "1.ply")
# 读取点云
full_pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(point_cloud_path)
# 读取JSON文件
cameras = os.path.join(floderPath, "one.json")
with open(cameras, 'r') as f:
data = json.load(f)
# 深度扩散半径
diffusion_radius = 100 # 扩散半径,单位:像素
# 遍历JSON中的每个条目
for entry in data:
img_name = entry['img_name']
if int(img_name) > 603:
continue
# 检查对应的深度图是否已经存在,如果存在则跳过
depth_dir = os.path.join(floderPath, "depth")
os.makedirs(depth_dir, exist_ok=True)
output_depth_path = os.path.join(depth_dir, f"{img_name}.png")
position = np.array(entry['position'])
rotation_matrix = np.array(entry['rotation'])
# 生成变换矩阵
transformation_matrix = np.eye(4)
transformation_matrix[:3, :3] = rotation_matrix
transformation_matrix[:3, 3] = position
# 保存变换矩阵
pose_dir = os.path.join(floderPath, "pose")
os.makedirs(pose_dir, exist_ok=True)
np.savetxt(os.path.join(pose_dir, f"{img_name}.txt"), transformation_matrix, fmt='%.10f')
# 逆变换:从世界坐标系转换到相机坐标系
rotation_matrix_inv = rotation_matrix.T
translation_vector_inv = -rotation_matrix_inv @ position
# 提取点云中的坐标点
points = np.asarray(full_pcd.points)
# 将点云从世界坐标系转换到相机坐标系
points_cam = rotation_matrix_inv @ points.T + translation_vector_inv[:, np.newaxis]
# 深度截断(例如,0.1到20.0米范围)
depth_min = 0.1
depth_max = 20.0
valid_depth_mask = (points_cam[2, :] > depth_min) & (points_cam[2, :] < depth_max)
# 仅保留符合深度范围的点
points_cam_filtered = points_cam[:, valid_depth_mask]
# 使用相机内参将相机坐标系下的点投影到图像平面
points_2d = K @ points_cam_filtered
points_2d = points_2d[:2, :] / points_2d[2, :]
points_2d = points_2d.T
# 读取对应的图像
image_path = os.path.join(floderPath, "images", f"{img_name}.jpg")
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
# 初始化深度图
depth_map = np.full((image.shape[0], image.shape[1]), np.inf)
# 将投影的点绘制到图像上
x_indices = points_2d[:, 0].astype(int)
y_indices = points_2d[:, 1].astype(int)
valid_mask = (x_indices >= 0) & (x_indices < image.shape[1]) & (y_indices >= 0) & (y_indices < image.shape[0])
x_indices = x_indices[valid_mask]
y_indices = y_indices[valid_mask]
depths = points_cam_filtered[2, :][valid_mask]
# 将深度值投影到深度图上
depth_map[y_indices, x_indices] = np.minimum(depth_map[y_indices, x_indices], depths)
# 使用最小滤波进行深度扩散
depth_map = minimum_filter(depth_map, size=(2 * diffusion_radius + 1, 2 * diffusion_radius + 1))
# 将inf深度值设置为0,以便更好地显示
depth_map[depth_map == np.inf] = 0
# 将深度值从米转换为毫米并保存为16位无符号整数
depth_map_mm = (depth_map * 1000).astype(np.uint16)
# 保存深度图
cv2.imwrite(output_depth_path, depth_map_mm)
print(f"深度图已保存到 {output_depth_path}")
# # 拷贝图像到color文件夹
color_dir = os.path.join(floderPath, "color")
os.makedirs(color_dir, exist_ok=True)
shutil.copy(image_path, os.path.join(color_dir, f"{img_name}.jpg"))
print(f"图像已拷贝到 {color_dir}")
# 保存带有投影点的图像
projected_image_path = os.path.join(floderPath, "projected_images", f"{img_name}_projected.jpg")
os.makedirs(os.path.join(floderPath, "projected_images"), exist_ok=True)
cv2.imwrite(projected_image_path, image)
print(f"投影点图像已保存到 {projected_image_path}")
# 将投影后的点保存为PCD文件
projected_points = points_cam_filtered.T
projected_pcd = o3d.geometry.PointCloud()
projected_pcd.points = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(projected_points)
output_pcd_path = os.path.join(floderPath, "pcd", f"{img_name}.pcd")
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(output_pcd_path), exist_ok=True)
o3d.io.write_point_cloud(output_pcd_path, projected_pcd)
print(f"点云已保存到 {output_pcd_path}")更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容








所有评论(0)