【ONNX】ONNX的基本使用
ONNX Simplifier 的主要功能是通过分析和优化 ONNX 模型的计算图,移除冗余操作、合并相邻节点、优化常量节点等,从而减小模型的大小和计算量。这不仅可以提高模型的推理速度,还能使模型结构更加清晰,便于理解和部署(若模型结构没问题,其实ONNX Simplifier用处不大)直接使用ONNX搭建计算图的开发效率有些低,通常都是Pytorch转ONNX。类似于链表,注意处理好待删除节点的
·
目录
一、Pytorch导出ONNX
接下来的讲解都使用这个简单的模型
class ImageClassificationModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(ImageClassificationModel, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=6, stride=1, kernel_size=3)
self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=6, out_channels=16, stride=1, kernel_size=3)
self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(2704, 120)
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.linear3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, data):
data = torch.relu(self.conv1(data))
data = self.pool1(data)
data = torch.relu(self.conv2(data))
data = self.pool2(data)
data = data.reshape(data.size(0), -1) # (N, C, H, W) -> (N, -1)
data = torch.relu(self.linear1(data))
data = torch.relu(self.linear2(data))
output = self.linear3(data)
return torch.sigmoid(output)上述代码实现的是一个简单的图像分类模型
def export():
model = ImageClassificationModel()
for name, module in model.named_modules():
print(f"Name: {name}, Type: {type(module).__name__}")
# 执行一次inference, 确保模型搭建正确
# batch_size, channel, height, weight
input = torch.randn([4, 3, 60, 60])
output = model(input)
print(output) # [4, 10] batch_size, class_number
torch.onnx.export(
model, # PyTorch 模型
input, # 模型输入
"image_classification.onnx", # 输出文件路径
export_params=True, # 是否导出模型参数
opset_version=11, # ONNX 算子集版本
do_constant_folding=True, # 是否执行常量折叠优化
input_names=["input"], # 输入节点名称
output_names=["output"], # 输出节点名称
dynamic_axes={"input": {0: "batch_size"}, "output": {0: "batch_size"}} # 动态轴
)可以使用Netorn查看ONNX的结构
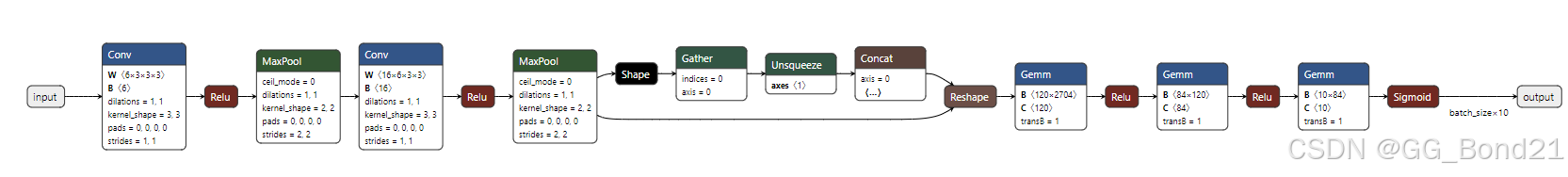
ONNX使用之前可以 check 和简化一下
def simplify_onnx():
model = onnx.load("image_classification.onnx")
onnx.checker.check_model(model)
model_simplified, check = simplify(model)
assert check
onnx.save(model_simplified, 'simplified_model.onnx')ONNX Simplifier 的主要功能是通过分析和优化 ONNX 模型的计算图,移除冗余操作、合并相邻节点、优化常量节点等,从而减小模型的大小和计算量。这不仅可以提高模型的推理速度,还能使模型结构更加清晰,便于理解和部署(若模型结构没问题,其实ONNX Simplifier用处不大)
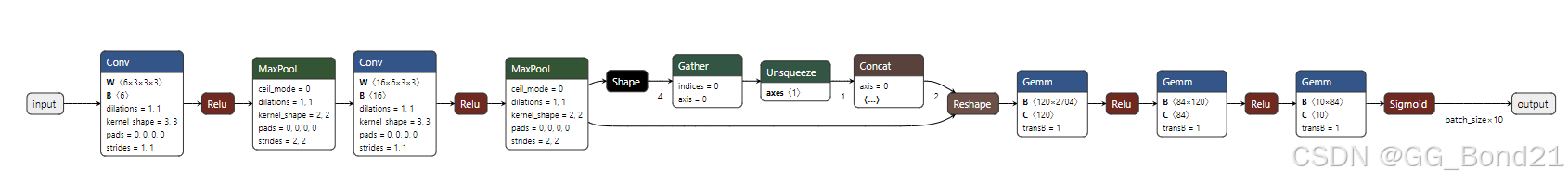
二、新增节点
def add_new_node():
model = onnx.load("simplified_model.onnx")
graph = model.graph
# 定义权重
linear_weight = helper.make_tensor(
name='linear4.weight', # 权重名称
data_type=TensorProto.FLOAT, # 数据类型
dims=[32, 10], # 权重形状
vals=np.random.randn(32, 10).flatten().tolist() # 权重值
)
linear_bias = helper.make_tensor(
name='linear4.bias', # 偏置名称
data_type=TensorProto.FLOAT, # 数据类型
dims=[32], # 偏置形状
vals=np.random.randn(32).tolist() # 偏置值
)
# 将其添加到模型的initializer列表中, 解决节点输入未定义问题
model.graph.initializer.append(linear_weight)
model.graph.initializer.append(linear_bias)
up_stream_node = next(node for node in graph.node if node.name == "/linear3/Gemm")
up_stream_node_index = next(index for index, node in enumerate(model.graph.node) if node.name == "/linear3/Gemm")
down_stream_node = next(node for node in graph.node if node.name == "/Sigmoid")
new_node_input = up_stream_node.output[0]
new_node_output = "/linear4/Gemm_output_0"
# 创建新的 linear 节点
new_node = helper.make_node(
name="/linear4/Gemm", # 节点名称
op_type="Gemm", # 节点操作类型
inputs=[new_node_input, linear_weight.name, linear_bias.name], # 输入张量名称列表
outputs=[new_node_output], # 输出张量名称列表
transB=1 # 矩阵相乘时对第二个矩阵进行转置
)
down_stream_node.input[0] = new_node_output
graph.node.insert(up_stream_node_index + 1, new_node)
onnx.checker.check_model(model)
onnx.save(model, 'add_node_model.onnx')
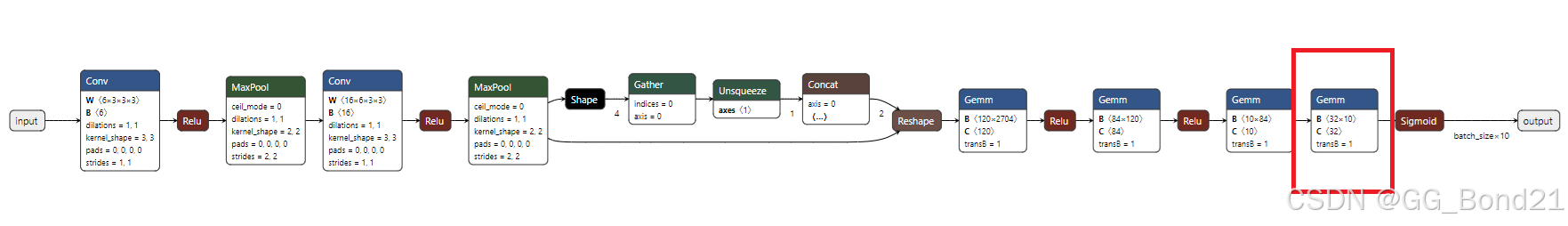
三、删除节点
def del_node():
model = onnx.load("add_node_model.onnx")
graph = model.graph
del_node = next(node for node in graph.node if node.name == "/linear4/Gemm")
up_stream_node = next(node for node in graph.node if node.name == "/linear3/Gemm")
down_stream_node = next(node for node in graph.node if node.name == "/Sigmoid")
model.graph.node.remove(del_node)
down_stream_node.input[0] = up_stream_node.output[0]
onnx.checker.check_model(model)
onnx.save(model, 'del_node_model.onnx')类似于链表,注意处理好待删除节点的上下游节点之间的链接关系
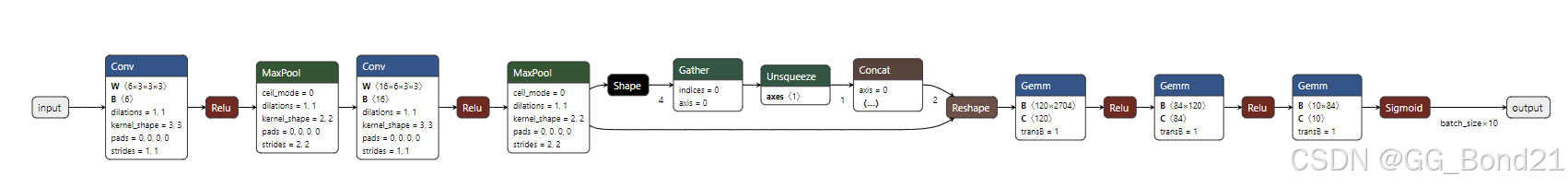
四、构建模型
def make_model():
# 定义输入和输出
input_tensor = helper.make_tensor_value_info("input", onnx.TensorProto.FLOAT, [1, 3, 224, 224])
output_tensor = helper.make_tensor_value_info("output", onnx.TensorProto.FLOAT, [1, 10, 224, 224])
# 创建卷积层的权重和偏置
conv_weight = helper.make_tensor (
"conv_weight",
onnx.TensorProto.FLOAT,
[10, 3, 3, 3], # 输出通道数、输入通道数、卷积核大小
np.random.randn(10, 3, 3, 3).flatten().tolist() # 随机初始化权重
)
conv_bias = helper.make_tensor (
"conv_bias",
onnx.TensorProto.FLOAT,
[10], # 偏置数量
np.random.randn(10).tolist() # 随机初始化偏置
)
# 创建卷积节点
conv_node = helper.make_node (
"Conv",
inputs=["input", "conv_weight", "conv_bias"],
outputs=["conv_output"],
kernel_shape=[3, 3], # 卷积核大小
strides=[1, 1], # 步长
pads=[1, 1, 1, 1], # 填充
dilations=[1, 1], # 膨胀率
group=1 # 分组
)
# 创建ReLU激活函数节点
relu_node = helper.make_node (
"Relu",
inputs=["conv_output"],
outputs=["output"]
)
# 创建图结构
graph = helper.make_graph (
nodes=[conv_node, relu_node],
name="Conv + ReLU Model",
inputs=[input_tensor],
outputs=[output_tensor],
initializer=[conv_weight, conv_bias] # 添加权重和偏置
)
# 创建模型
model = helper.make_model(graph)
model.ir_version = onnx.IR_VERSION
model.producer_name = "ONNX Example"
model.producer_version = "1.0"
model.opset_import.append(helper.make_operatorsetid("ai.onnx", 12))
onnx.checker.check_model(model)
# 保存模型
onnx.save(model, "make_model.onnx")
直接使用ONNX搭建计算图的开发效率有些低,通常都是Pytorch转ONNX。遇到某些不支持的算子或者计算图调整时才使用ONNX
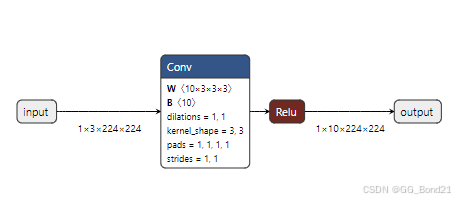
五、增加输出
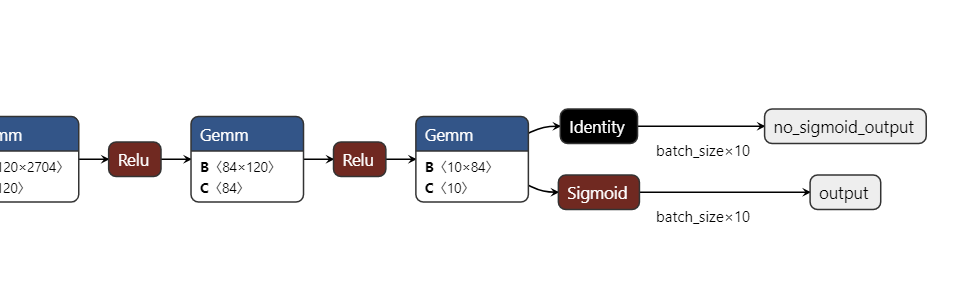
在某些业务情况下,需要提取模型中特殊输出进行特殊处理,这时就需修改ONNX计算图添加输出
原ONNX
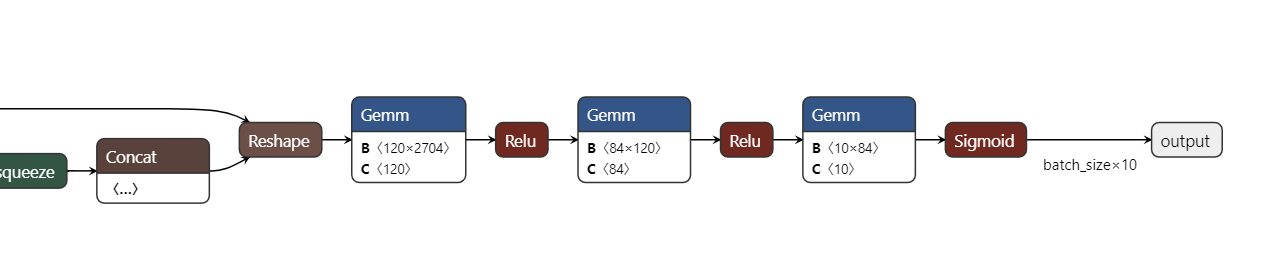
import onnx
import onnx.helper as helper
def add_new_output(onnx_path):
model = onnx.load(onnx_path)
# 找到要获取其输出的节点
target_node = None
for node in model.graph.node:
if node.name == '/linear3/Gemm':
target_node = node
break
print(target_node.output)
new_output = helper.make_tensor_value_info('no_sigmoid_output', onnx.TensorProto.FLOAT, [-1, 10])
dim1 = new_output.type.tensor_type.shape.dim[0]
dim1.dim_param = "batch_size"
model.graph.output.extend([new_output]) # 尾插输出,使用时注意输出顺序
target_node_output = target_node.output[0]
new_output_node = onnx.helper.make_node(
op_type='Identity', # 使用Identity操作作为示例
inputs=[target_node_output],
outputs=['no_sigmoid_output'],
name='no_sigmoid'
)
model.graph.node.append(new_output_node)
onnx.checker.check_model(model)
print("Inputs:")
for input in model.graph.input:
print(f"Name: {input.name}, Type: {input.type}")
print("\nOutputs:")
for output in model.graph.output:
print(f"Name: {output.name}, Type: {output.type}")
onnx.save(model, "model_new.onnx")
if __name__ == "__main__":
onnx_path = "./model.onnx"
add_new_output(onnx_path)
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献9条内容
已为社区贡献9条内容








所有评论(0)