三角形插值技术
1.最懒的方法——Nearest Neighbor对于三角形内的点,离三个顶点谁最近,就赋值为那个顶点对应的颜色。2.最天真的方法——Distance三角形内一点的值应该来自于三个顶点。计算距离:定义权重:颜色表示为权重的平均:总而言之,我们通过三角形每个顶点到点P的距离来混合定点颜色,从而定义点P的插值颜色。这个方法简单,易于实现,而且相当直观,在一些应用中表现良好...
1.最懒的方法——Nearest Neighbor
对于三角形内的点,离三个顶点谁最近,就赋值为那个顶点对应的颜色。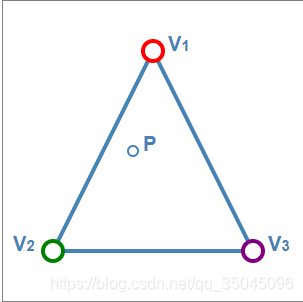
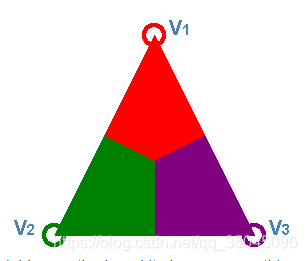
2.最天真的方法——Distance
三角形内一点的值应该来自于三个顶点。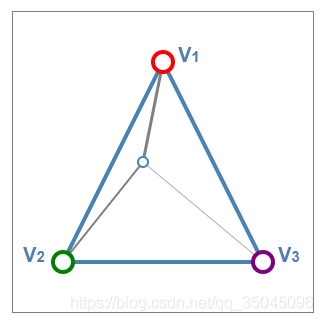
计算距离: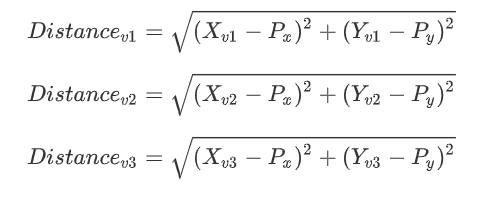
定义权重: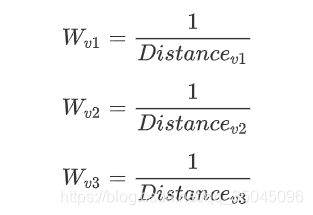
颜色表示为权重的平均: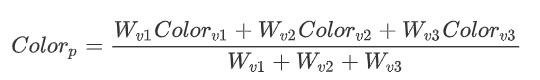
总而言之,我们通过三角形每个顶点到点P的距离来混合定点颜色,从而定义点P的插值颜色。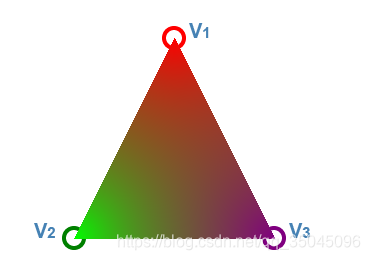
这个方法简单,易于实现,而且相当直观,在一些应用中表现良好。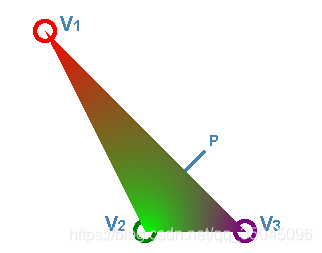
看到上面的例子,我们原本想要用V1和V3的颜色来表示点P的颜色,但是用这种天真的方法,由于V2距离点P最近,所以点P 大部分的颜色值来自于点P,这是我们不想看到的,这就是该方法的一大缺陷。
3.重心坐标
重心坐标的技巧就是寻找顶点V1,V2,V3的权重,来平衡下面的式子: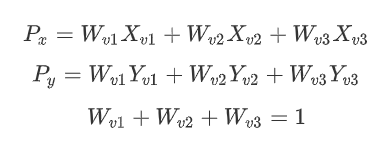
转化成表示权重的式子: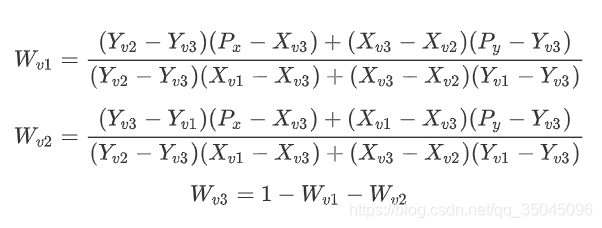
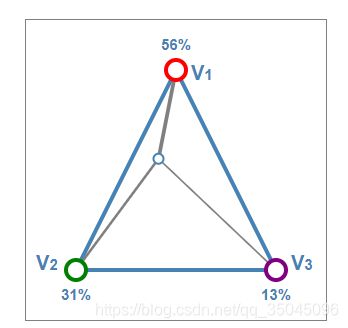
值得注意的是,当点P在三角形外部时,w1,w2,w3中至少有一个值是负数。
实际上,一个常见的三角形绘制算法是查看三角形周围包围框中的每个像素。然后,对于每个像素,计算重心坐标(无论如何,插值深度缓冲区、纹理坐标等都需要重心坐标)。如果其中一个权重是负数,那么该像素将被跳过。这种算法的一个优点是,显卡可以简单地并行化边界框中的每个像素。这使得绘制三角形非常快。
插值效果如下: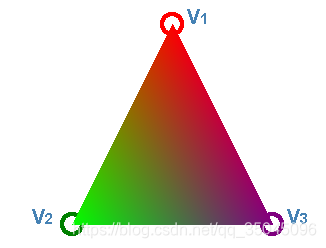
3.1源码
计算重心坐标的优化方法:
bool rayTriangleIntersect(
const Vec3f &orig, const Vec3f &dir,
const Vec3f &v0, const Vec3f &v1, const Vec3f &v2,
float &t, float &u, float &v)
{
// compute plane's normal
Vec3f v0v1 = v1 - v0;
Vec3f v0v2 = v2 - v0;
// no need to normalize
Vec3f N = v0v1.crossProduct(v0v2); // N
float denom = N.dotProduct(N);
// Step 1: finding P
// check if ray and plane are parallel ?
float NdotRayDirection = N.dotProduct(dir);
if (fabs(NdotRayDirection) < kEpsilon) // almost 0
return false; // they are parallel so they don't intersect !
// compute d parameter using equation 2
float d = N.dotProduct(v0);
// compute t (equation 3)
t = (N.dotProduct(orig) + d) / NdotRayDirection;
// check if the triangle is in behind the ray
if (t < 0) return false; // the triangle is behind
// compute the intersection point using equation 1
Vec3f P = orig + t * dir;
// Step 2: inside-outside test
Vec3f C; // vector perpendicular to triangle's plane
// edge 0
Vec3f edge0 = v1 - v0;
Vec3f vp0 = P - v0;
C = edge0.crossProduct(vp0);
if (N.dotProduct(C) < 0) return false; // P is on the right side
// edge 1
Vec3f edge1 = v2 - v1;
Vec3f vp1 = P - v1;
C = edge1.crossProduct(vp1);
if ((u = N.dotProduct(C)) < 0) return false; // P is on the right side
// edge 2
Vec3f edge2 = v0 - v2;
Vec3f vp2 = P - v2;
C = edge2.crossProduct(vp2);
if ((v = N.dotProduct(C)) < 0) return false; // P is on the right side;
u /= denom;
v /= denom;
return true; // this ray hits the triangle
}
参考
Ray Tracing: Rendering a Triangle
Interpolating in a Triangle
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容






所有评论(0)