spring切面aspects使用
AOP切面使用
·
java切面aspect 使用
一、项目配置
1. 导入依赖
<!-- aspects切面 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
</dependency>
2. 添加注解配置
给主类添加@EnableAspectJAutoProxy或@SpringBootApplication注解
二、装配AOP
1. 创建需注入的服务类
package com.example.test.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service("AspectService")
public class AspectService {
public void doSome()
{
System.out.println("--doSome--");
}
public String doSome2(String s, int a)
{
System.out.println("--doSome2--" + s + " - " + a);
return s;
}
}
2. 定义aspects类
package com.example.test.aspects;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Date;
@Aspect
@Component
public class MyAspect {
/**
* 定义功能增强方法(方法就是切面)
* 1、方法的必须为public
* 2、方法无返回值
* 3、方法名称自定义
* 4、方法可以有参数,也可以没有参数
* 5、方法的定义上方加入注解,表示切入点的执行时机
*/
@Before("execution(public String com.example.test.service.AspectService.doSome2(..))")
public void doBefore()
{
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println("doSome2 Before 前置通知: " + date);
}
}
三、 创建不同的拦截器类型
1. 前置通知:@Before
这种拦截器先执行拦截代码,再执行目标代码。如果拦截器抛异常,那么目标代码就不执行了
/**
* Before:前置通知,带方法参数的切面
* 切面方法有参数时要求参数是JoinPoint类型,参数名自定义,该参数就代表了连接点方法,即doSome方法
* 使用该参数可以获取切入点表达式、切入点方法签名、目标对象等
*/
@Before(value = "execution(* * ..AspectService.*(..))")
public void doBefore2(JoinPoint joinPoint)
{
System.out.println("方法签名:" + joinPoint.getSignature());
System.out.println("方法签名名称:" + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
System.out.println("方法参数:" + Arrays.toString(args));
Date date = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println("AspectService 前置通知: " + simpleDateFormat.format(date));
}
运行结果: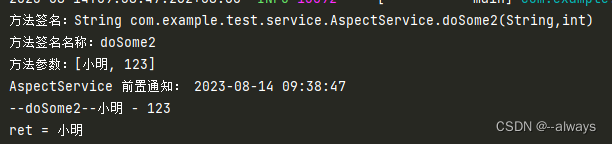
2. 后置通知:@After
这种拦截器先执行目标代码,再执行拦截器代码。无论目标代码是否抛异常,拦截器代码都会执行;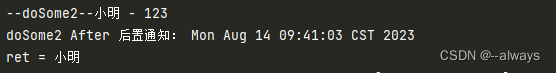
给doSome2方法开头添加一行报错代码int i = 1 / 0;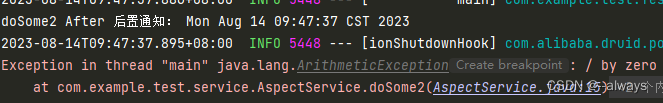
可以看到报错并不会导致拦截代码执行
3. 后置通知:@AfterReturning
@AfterReturning:和@After不同的是,只有当目标代码正常返回时,才执行拦截器代码
/**
* AfterReturning: 后置通知,在连接点方法执行之后执行后置通知方法与前置通知一样,可以有JoinPoint类型参数,该参数表示连接点方法对象;还可以有一个
* Object类型参数,用于接收连接点方法的执行结果,注意该参数的参数名必须与切入点表达式
* 的returning属性的属性值一致,表示将returning属性值赋给Object对象
*/
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(public * com.example.test.service.AspectService.doSome2(String, int))", returning = "obj")
public void AfterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object obj)
{
Date date = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println("doSome2 AfterReturning 后置通知: " + simpleDateFormat.format(date));
// 连接点方法的返回值 obj = 小明
System.out.println("连接点方法的返回值 obj=" + obj);
}
运行结果:
4. 后置通知:@AfterReturning
@AfterThrowing:和@After不同的是,只有当目标代码抛出了异常时,才执行拦截器代码
/**
* AfterThrowing:后置通知
*/
@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(public * com.example.test.service.AspectService.doSome2(String, int))")
public void AfterThrowing()
{
Date date = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println("doSome2 AfterThrowing 后置通知: " + simpleDateFormat.format(date));
}
运行结果: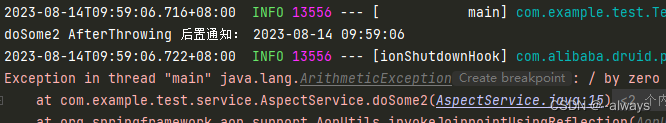
5. 环绕通知:@Around
@Around:能完全控制目标代码是否执行,并可以在执行前后、抛异常后执行任意拦截代码,可以说是包含了上面所有功能
/*
环绕通知:@Around(切入点表达式)
1、环绕通知是最重要的一个通知,他表示在连接点方法的前或者后都可以执行,它的本质就是jdk动态代理的invoke
方法的method参数
2、定义格式
a、public
b、必须有返回值,类型为Object
*/
@Around(value = "execution(public * com.example.test.service.AspectService.doSome2(..))")
public Object Around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("[Around] start " + joinPoint.getSignature());
Object retVal = joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("[Around] done " + joinPoint.getSignature());
// retVal = 小明
System.out.println("[Around] retVal " + retVal);
// 修改接入点doSome2的返回值,小明->小白
retVal = "小白";
return retVal;
}
运行结果: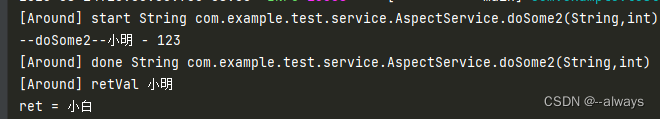
环绕通知可以改变方法返回值
四、使用注释装配AOP
1. 创建注解类
package com.example.test.aspects;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MetricTime {
String value();
}
2. 创建注入类
注意around()方法标注了@Around(“@annotation(metricTime)”),它的意思是,符合条件的目标方法是带有@MetricTime注解的方法,因为around()方法参数类型是MetricTime(注意参数名是metricTime不是MetricTime)
package com.example.test.aspects;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
public class MetricAspect {
@Around("@annotation(metricTime)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, MetricTime metricTime) throws Throwable {
String name = metricTime.value();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("[Metrics] " + name);
try {
return joinPoint.proceed();
} finally {
long t = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
// 写入日志或发送至JMX:
System.out.println("[Metrics] " + name + ": " + t + "ms");
}
}
}
3. 添加注解
给AspectsService 添加新测试方法 doSome3,并添加@MetricTime(“test”)注解
@MetricTime("test")
public void doSome3()
{
System.out.println("run doSome3 ");
}
运行结果: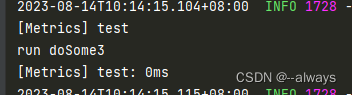
使用注解更加简洁明了,注解使用方式参考的是 java教程
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容






所有评论(0)