java请求传参方式的总结
背景:关于请求方式一直没有整理过,今天空闲来整理一篇1.请求路径参数1、@PathVariable获取路径参数。即url/{id}这种形式。GET方式请求路径:http://localhost:8080/test/id=10后端接收代码:@GetMapping("/test/{id}")public String test(@PathVariable(name = "id") String id)
背景:关于请求方式一直没有整理过,今天空闲来整理一篇
第一类,请求路径参数
1、@PathVariable
获取路径参数。即url/{id}这种形式。
GET方式
请求路径:http://localhost:8080/test/id=10
后端接收代码:
@GetMapping("/test/{id}")
public String test(@PathVariable(name = "id") String id){
System.out.println("id:"+id);
return "test:"+id;
}浏览器请求效果如下:
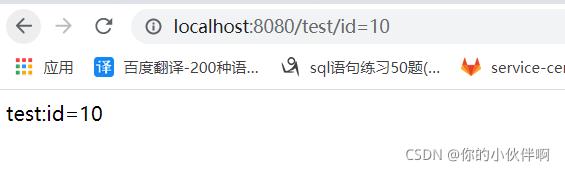
postman请求效果如下:
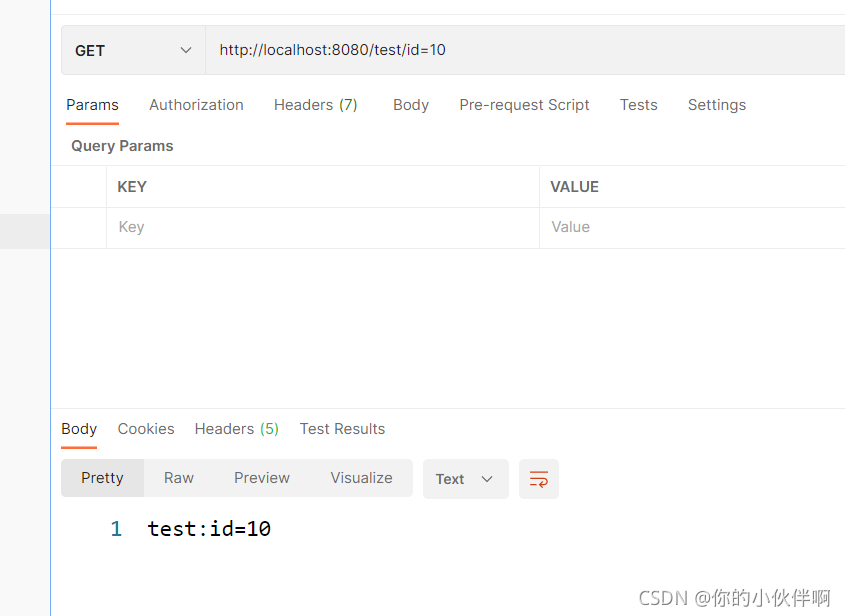
2021/9/13补充,如上,这里实际有点问题 http://localhost:8080/test/id=10这样传参后台接收代码如上,实际接收到的id值并不是10而是id=10这个字符串,如下:
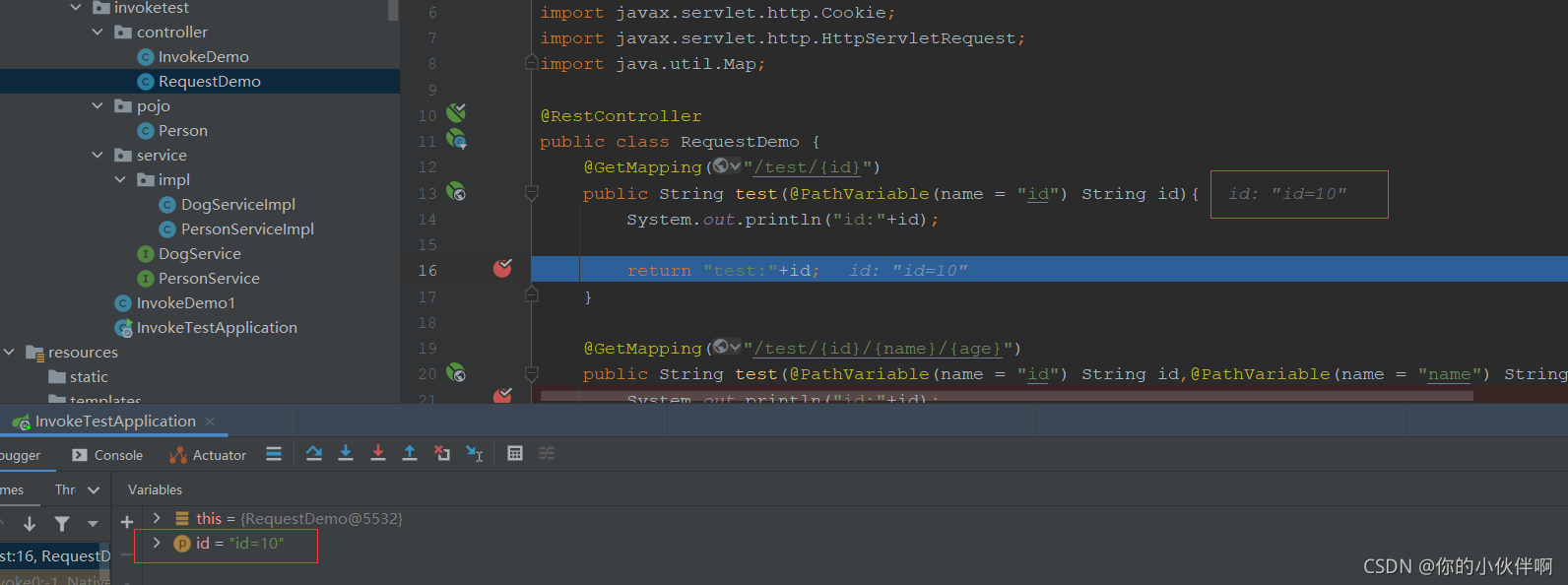
多个参数时:
请求方式:http://localhost:8080/test/10/xhw/20
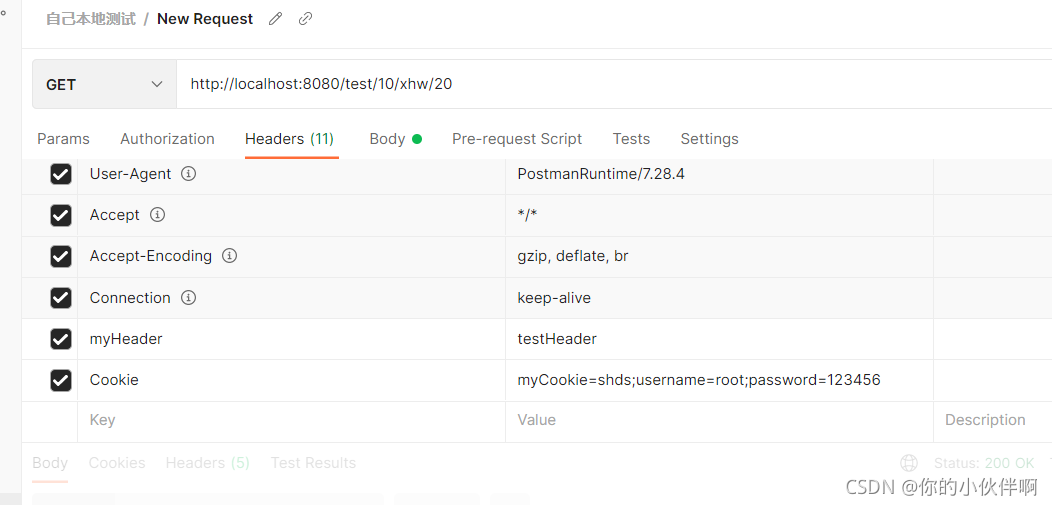
后端接收方式:
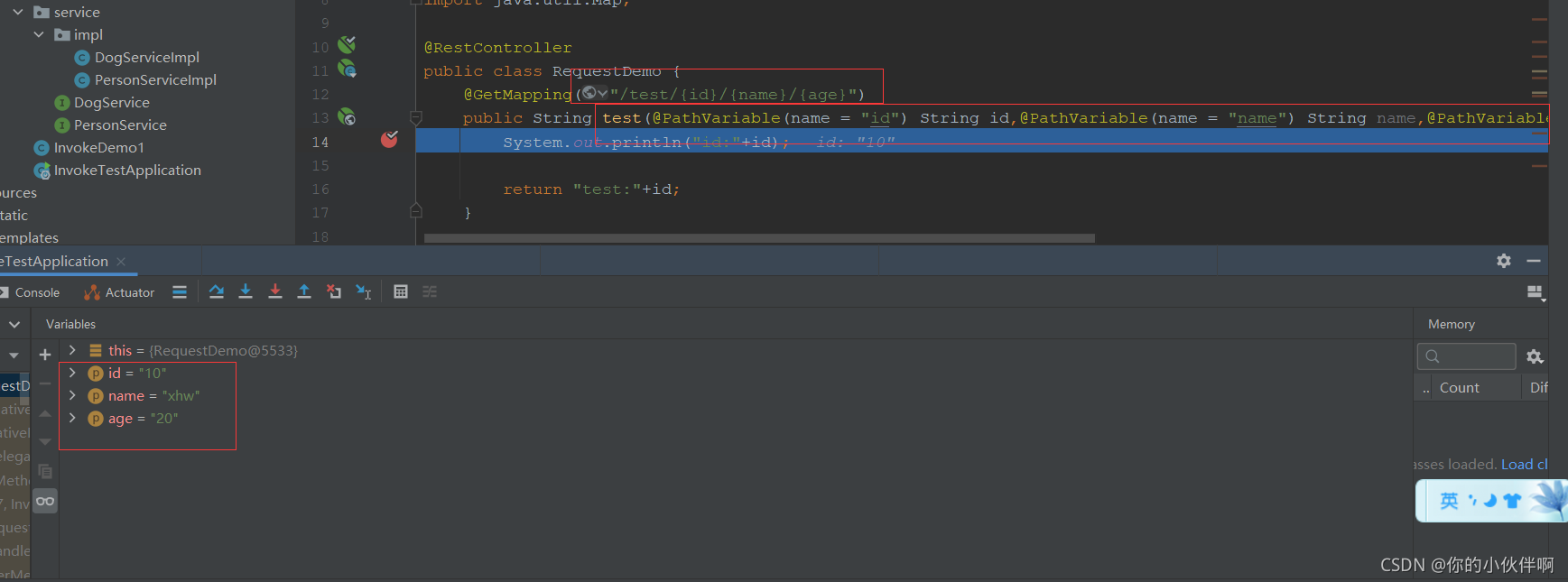
POST方式
请求路径:http://localhost:8080/testForPost/id=10
后端接收代码:
@PostMapping("/testForPost/{id}")
public String testForPost(@PathVariable(name = "id") String id){
System.out.println("id:"+id);
return "test:"+id;
}postman请求效果如下:
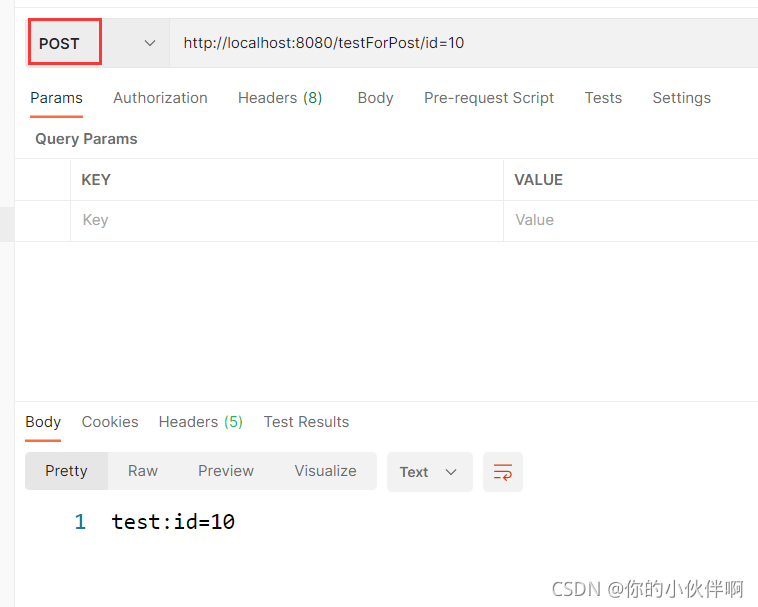
2、@RequestParam
获取查询参数。即url?name=这种形式
GET方式
请求路径:http://localhost:8080/test1?name=xhw
后端接收代码:
@GetMapping("/test1")
public String test1(@RequestParam(name = "name") String name){
System.out.println("name:"+name);
return "test:"+name;
}浏览器访问效果:
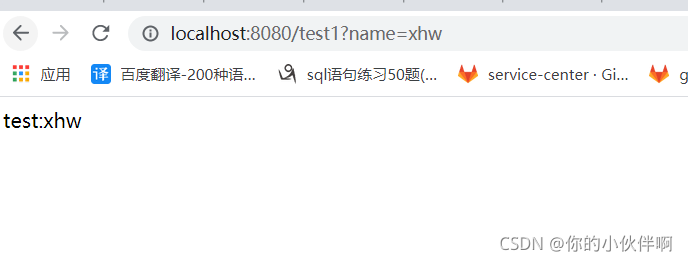
postman访问效果:
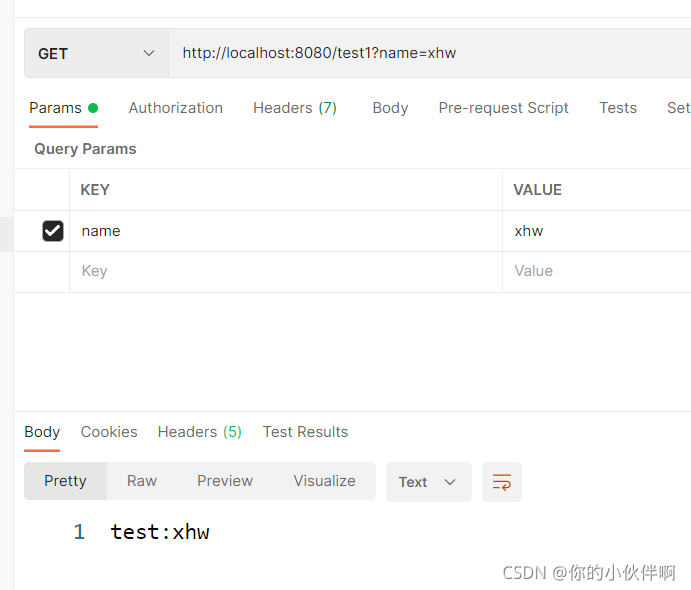
POST方式
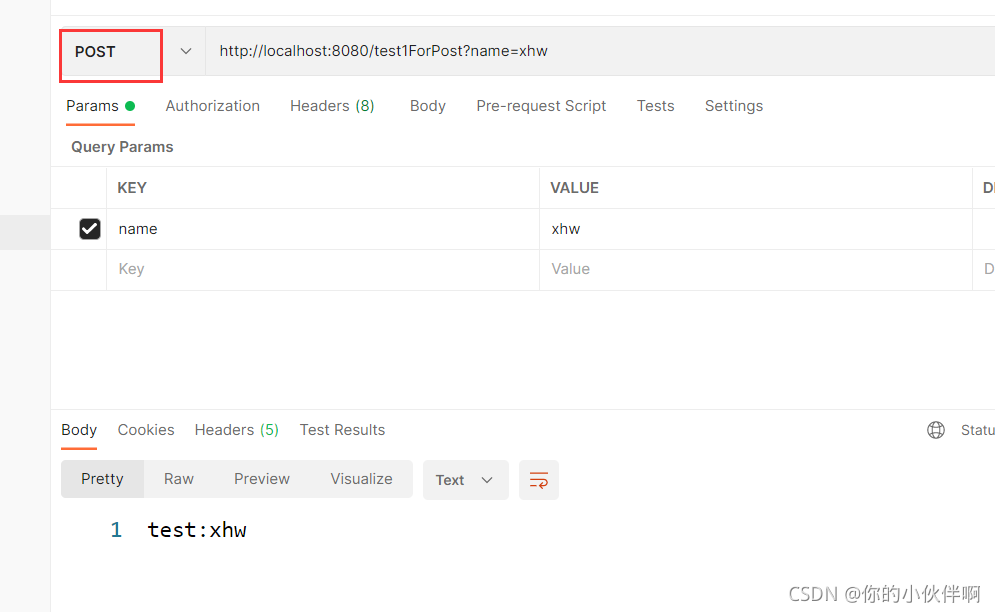
请求路径:http://localhost:8080/test1ForPost?name=xhw
后端接收方式:
@PostMapping("/test1ForPost")
public String test1ForPost(@RequestParam(name = "name") String name){
System.out.println("name:"+name);
return "test:"+name;
}
postman访问效果
第二类,Body参数
1、@RequestBody
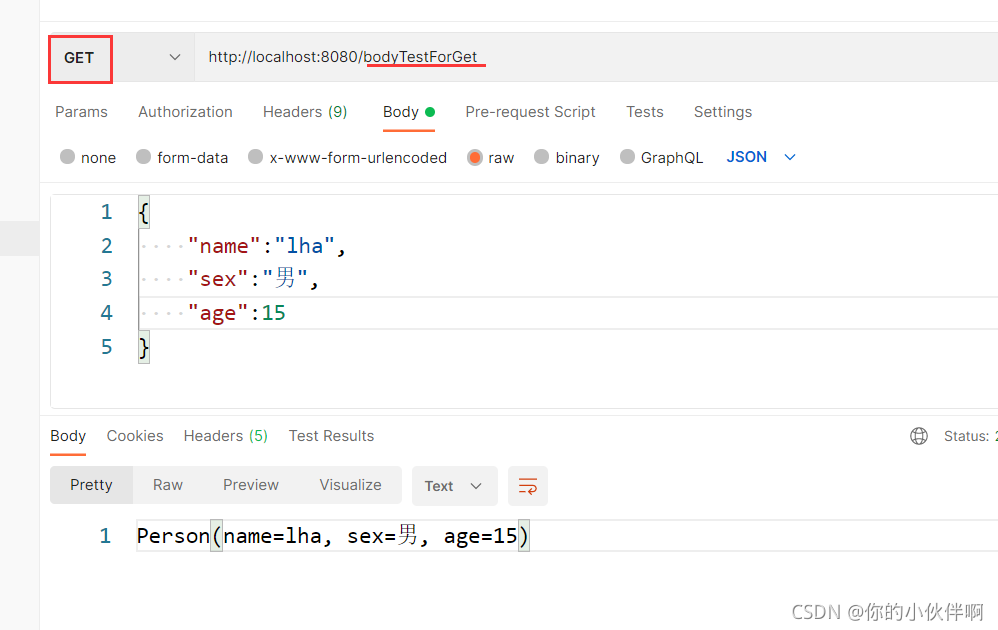
GET方式
请求路径:http://localhost:8080/bodyTestForGet
后端接收代码:
@GetMapping(path = "/bodyTestForGet")
public String bodyTestForGet(@RequestBody Person person) {
System.out.println(person.toString());
return person.toString();
}注:浏览器不支持get请求传body参数
postman请求效果:
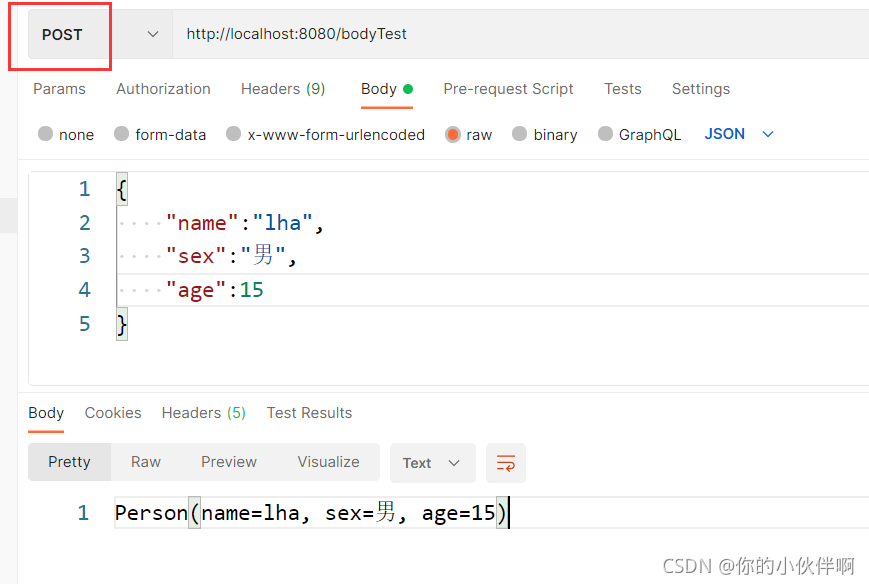
POST方式
请求路径:http://localhost:8080/bodyTest
后端接收代码:
@PostMapping(path = "/bodyTest")
public String bodyTest(@RequestBody Person person) {
System.out.println(person.toString());
return person.toString();
}postman请求效果:
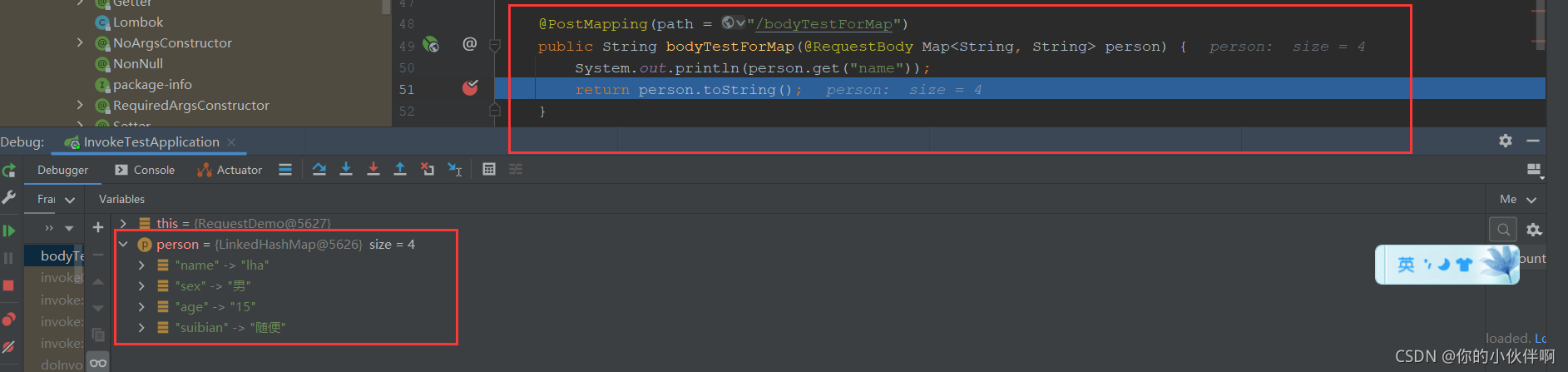
POST方式,不要实体类Person,而是通过Map来接收该对象:
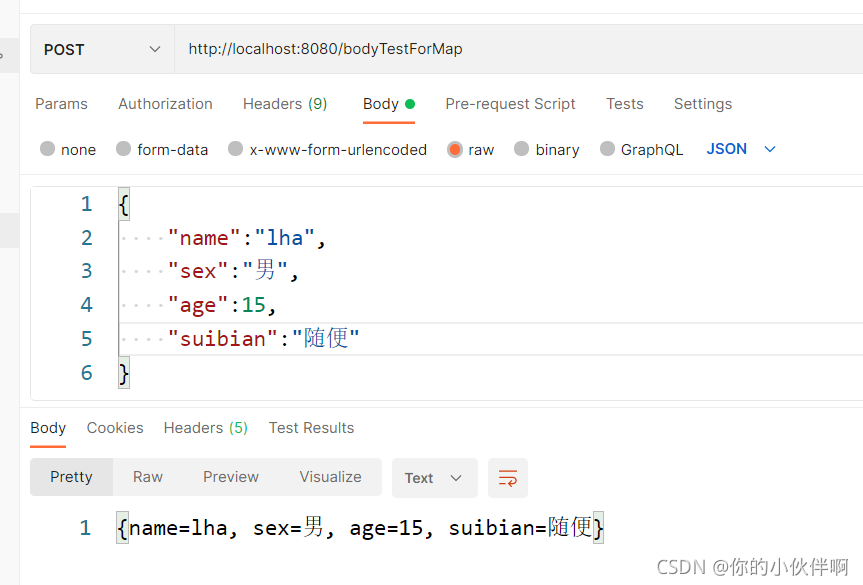
请求路径:http://localhost:8080/bodyTestForMap
后端代码如下:
@PostMapping(path = "/bodyTestForMap")
public String bodyTestForMap(@RequestBody Map<String, String> person) {
System.out.println(person.get("name"));
return person.toString();
}访问到后端如下,不需要实体类也能够正常接收到参数:
postman访问效果如下:
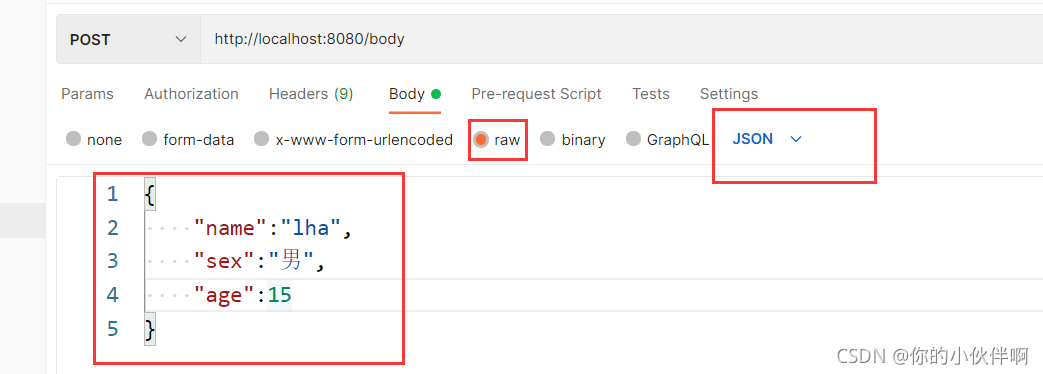
2.无注解
请求路径:http://localhost:8080/body
后端代码:
@PostMapping(path = "/body")
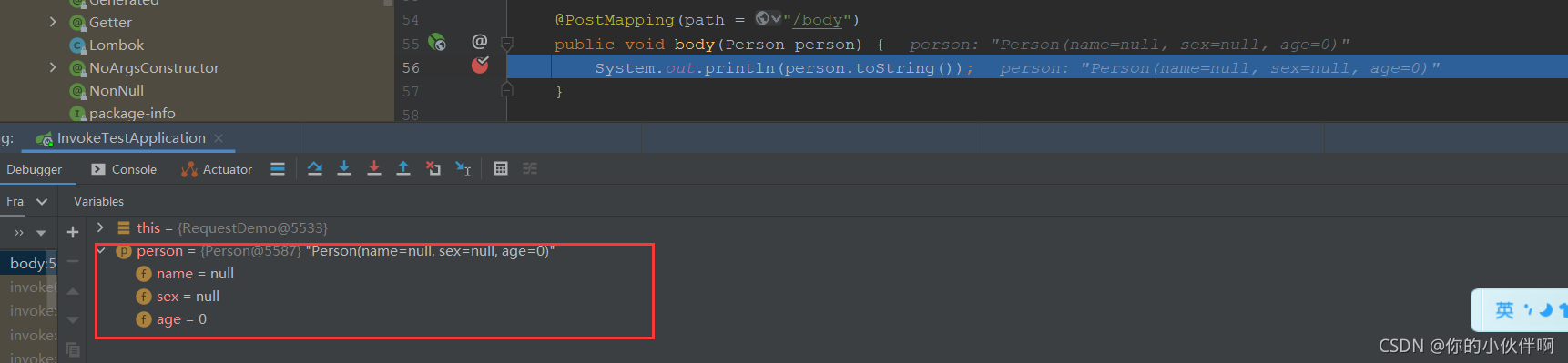
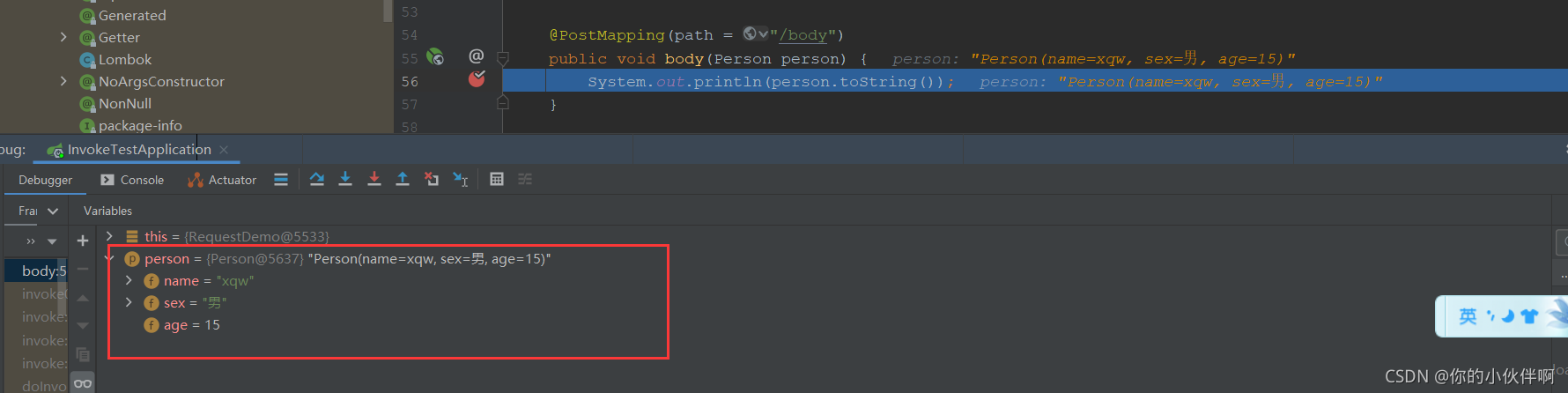
public void body(Person person) {
System.out.println(person.toString());
}
无@RequestBody注解时直接这样传递参数后端是收不到的
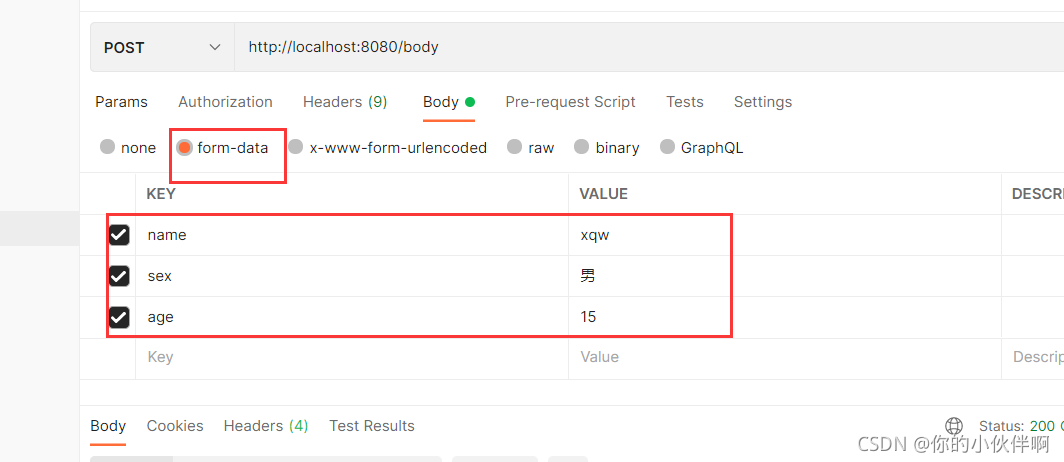
如下就传参就可以收到:
第三类:请求头参数以及Cookie
1、@RequestHeader
GET方式
GET/POST类似,不再重复写
请求地址:http://localhost:8080/RequestHeader
后端代码:
@GetMapping("/RequestHeader")
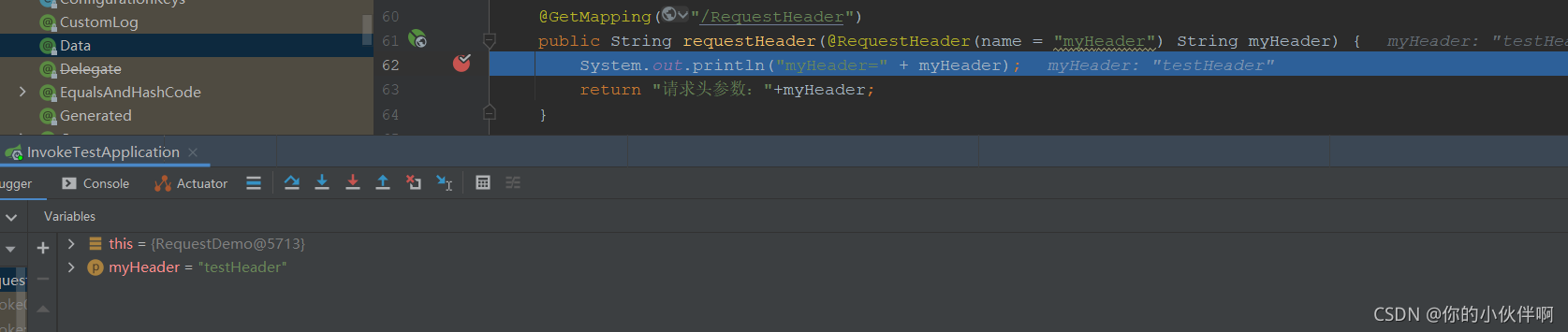
public String requestHeader(@RequestHeader(name = "myHeader") String myHeader) {
System.out.println("myHeader=" + myHeader);
return "请求头参数:"+myHeader;
}
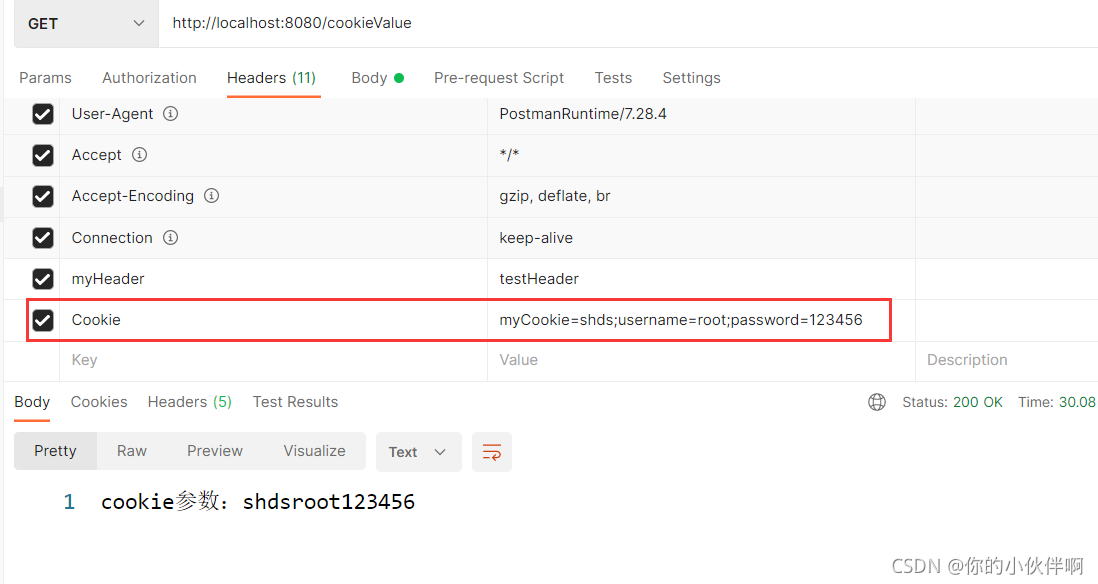
2、@CookieValue
请求地址:http://localhost:8080/cookieValue
后端接收代码:
@GetMapping("/cookieValue")
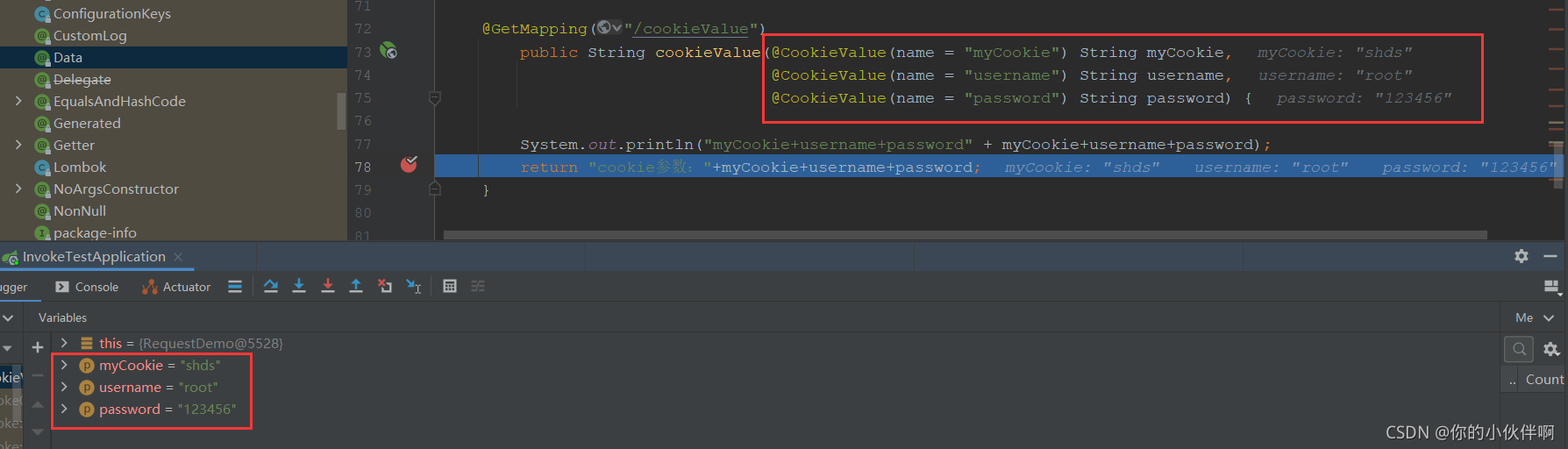
public String cookieValue(@CookieValue(name = "myCookie") String myCookie,
@CookieValue(name = "username") String username,
@CookieValue(name = "password") String password) {
System.out.println("myCookie+username+password" + myCookie+username+password);
return "cookie参数:"+myCookie+username+password;
}
postman响应结果:
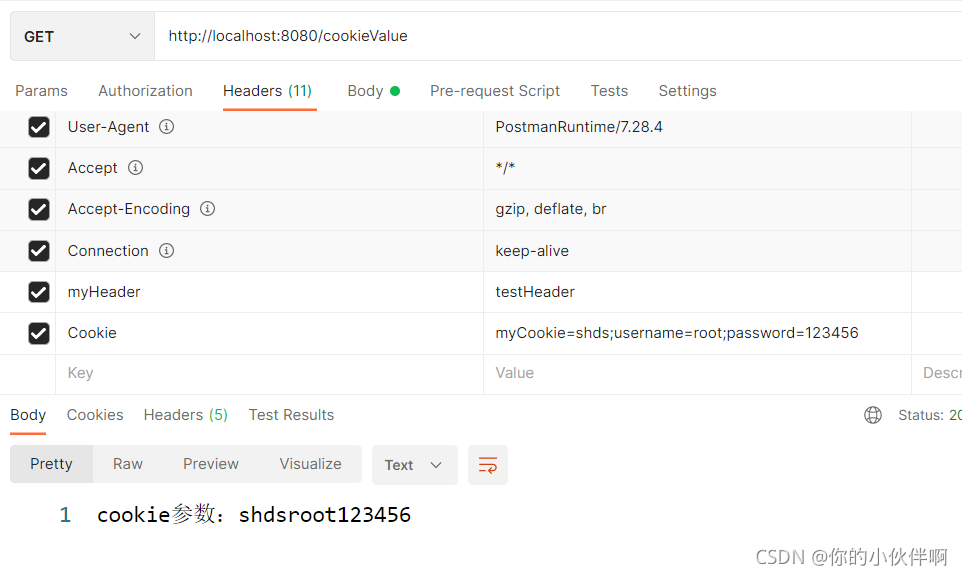
postman传cookie方式:
待补充...
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容






所有评论(0)