树的几种遍历方法介绍
与线性数据结构(如数组、链表、队列、栈)只有一种遍历逻辑方法不同,树可以通过不同的方法进行遍历。常见的树的遍历方法包括:中序遍历(InOrder Traversal)、前序遍历(PreOrder Traversal)及后序遍历(PostOrder Traversal)。
·
本文主要介绍数据结构“树(tree)”的几种常见的遍历方式,同时给出相应的示例代码。
1 概述
与线性数据结构(如数组、链表、队列、栈)只有一种遍历逻辑方法不同,树可以通过不同的方法进行遍历。
常见的树的遍历方法包括:中序遍历(InOrder Traversal)、前序遍历(PreOrder Traversal)及后序遍历(PostOrder Traversal)。
下图给出了这几种遍历方法访问到节点的顺序:
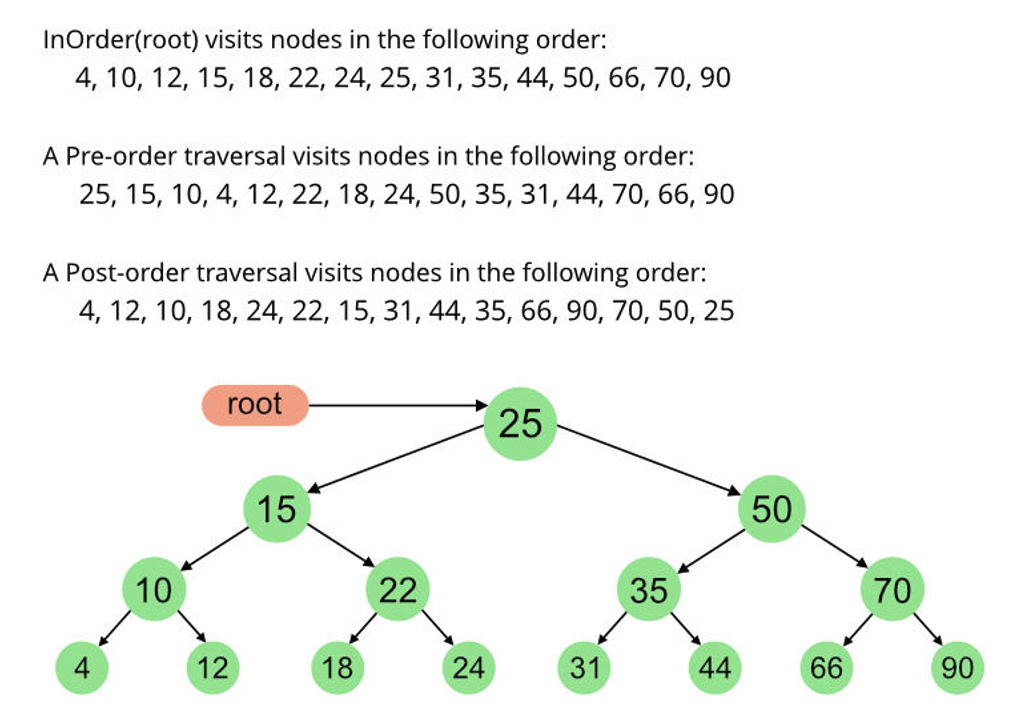
2 前序遍历(PreOrder Traversal)
2.1 算法
前序遍历的算法实现为:
- Visit the root;
- Traverse the left subtree, i.e., call Preorder(left->subtree);
- Traverse the right subtree, i.e., call Preorder(right->subtree) .
2.2 使用场景
前序遍历可用于创建树的拷贝,同时也可用于获取表达树的前缀表达式。
2.3 示例代码
下面通过一道LeetCode题来演示前序遍历的代码。
题目信息:
Given the root of an n-ary tree, return the preorder traversal of its nodes' values.
Nary-Tree input serialization is represented in their level order traversal. Each group of children is separated by the null value (See examples).
Example:
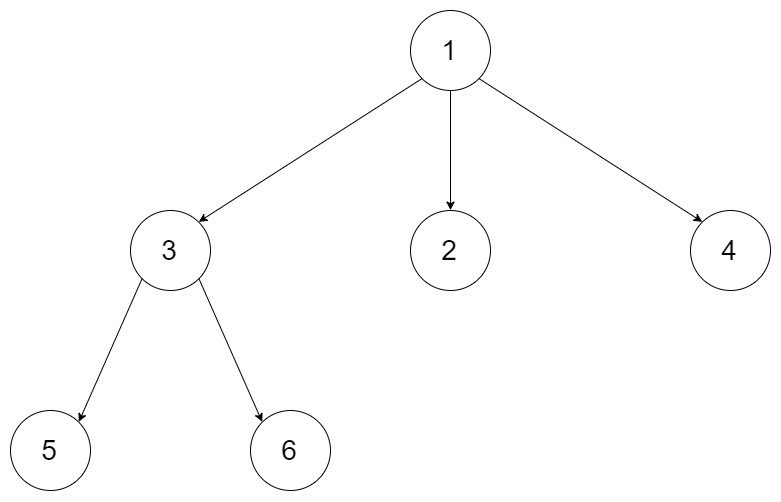
Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
Output: [1,3,5,6,2,4]
解法:
此题可通过递归法以“Depth-First Search”方式解决,相关代码如下:
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorder(Node* root) {
vector<int> result;
traverse(root, result);
return result;
}
private:
// traverse tree elements recursively
void traverse(Node* root, vector<int>& result) {
// if root is empty
if (nullptr == root) {
return;
}
// store the root of the tree first
result.push_back(root->val);
// store the children of the tree
for (auto node:(root->children)) {
traverse(node, result);
}
return;
}
};3 中序遍历(InOrder Traversal)
3.1 算法
中序遍历的算法实现为:
- Traverse the left subtree, i.e., call Inorder(left->subtree);
- Visit the root;
- Traverse the right subtree, i.e., call Inorder(right->subtree).
3.2 使用场景
对于二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree),中序遍历可以获取到该树的非降序节点序列,当然,通过反转操作,就可以获取对应的非升序节点序列。
3.3 示例代码
下面通过一道LeetCode题(98. Validate Binary Search Tree)来演示中序遍历的代码。
题目信息:
Given the root of a binary tree, determine if it is a valid binary search tree (BST).
A valid BST is defined as follows:
1. The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key;
2. The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node's key;
3. Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example:
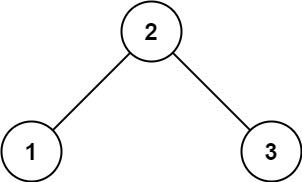
Input: root = [2,1,3]
Output: true
解法:
此题可通过递归法解决,相关代码如下:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
// store elements of node to vector by inorder traversal way
void inOrder(TreeNode* node) {
if (!node) {
return;
}
inOrder(node->left);
vecValue.push_back(node->val);
inOrder(node->right);
}
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return true;
}
inOrder(root);
for (int i = 1; i < vecValue.size(); i++) {
if (vecValue[i - 1] >= vecValue[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
private:
vector<int> vecValue;
};更多推荐
 已为社区贡献6条内容
已为社区贡献6条内容









所有评论(0)