JS高级——防抖函数
防抖函数具体实现过程
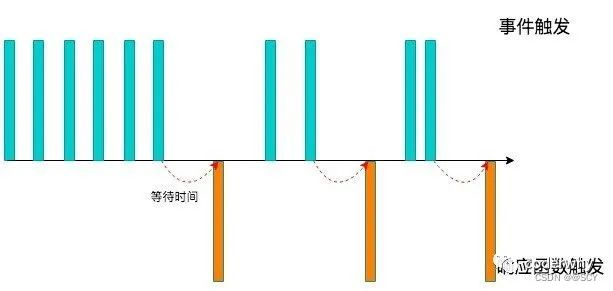
1、什么是防抖
在某设定的时间内,没有再次触发某个函数时,才真正的调用这个函数。
过程:
-
当事件触发时,相应的函数并不会立即触发,而是会等待一定的时间;
-
当事件密集触发时,函数的触发会被频繁的推迟;
-
只有等待了一段时间也没有事件触发,才会真正的执行响应函数;
2、防抖的应用场景
-
输入框中频繁的输入内容,搜索或者提交信息;
-
频繁的点击按钮,触发某个事件;
-
监听浏览器滚动事件,完成某些特定操作;
-
用户缩放浏览器的resize事件;
总之,密集的事件触发,我们只希望触发比较靠后发生的事件,就可以使用防抖函数;
3、防抖函数的实现
下面我们根据需求场景,一步一步深入实现防抖函数
3.1 防抖基本功能
防抖函数的核心思路如下:
-
当触发一个函数时,并不会立即执行这个函数,而是会延迟(通过定时器来延迟函数的执行)
-
如果在延迟时间内,有重新触发函数,那么取消上一次的函数执行(取消定时器);
-
如果在延迟时间内,没有重新触发函数,那么这个函数就正常执行(执行传入的函数);
-
接下来,就是将思路转成代码即可:
-
定义debounce函数要求传入两个参数
-
需要处理的函数fn;
-
延迟时间;
-
-
通过定时器来延迟传入函数fn的执行
-
如果在此期间有再次触发这个函数,那么clearTimeout取消这个定时器;
-
如果没有触发,那么在定时器的回调函数中执行即可;
-
代码实现 :
//debounce.js
/**
* @param {*} fn 要执行的函数
* @param {*} delay 延迟时间
* @returns
*/
function debounce(fn, delay) {
// 1.定义一个定时器, 保存上一次的定时器
let timer = null
// 2.真正执行的函数
const _debounce = function () {
// 取消上一次的定时器
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
// 延迟执行
timer = setTimeout(() => {
// 外部传入的真正要执行的函数
fn()
}, delay)
}
return _debounce
}代码调用:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text">
<button id="cancel">取消</button>
<script src="./debounce.js"></script>
<script>
const inputEl = document.querySelector("input")
const cancelBtn = document.querySelector("#cancel")
let counter = 0
//输入触发事件
const inputChange = function (event) {
console.log(`发送了第${++counter}次网络请求`)
}
inputEl.oninput = debounce(inputChange, 1000)
</script>
</body>
</html>3.2 绑定this和参数
我们知道在oninput事件触发时会有参数传递,并且触发的函数中this是指向当前的元素节点的
-
目前我们fn的执行是一个独立函数调用,它里面的this是window
-
我们需要将其修改为对应的节点对象,而返回的function中的this指向的是节点对象;
-
-
目前我们的fn在执行时是没有传递任何的参数的,它需要将触发事件时传递的参数传递给fn
-
而我们返回的function中的arguments正是我们需要的参数;
-
所以我们的代码可以进行如下的优化:
//debounce.js
/**
* @param {*} fn 要执行的函数
* @param {*} delay 延迟时间
* @returns
*/
function debounce(fn, delay) {
// 1.定义一个定时器, 保存上一次的定时器
let timer = null
// 2.真正执行的函数
const _debounce = function (...args) {
// 取消上一次的定时器
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
// 延迟执行
timer = setTimeout(() => {
// 外部传入的真正要执行的函数,绑定this和参数
fn.apply(this, args)
}, delay)
}
return _debounce
}代码调用:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text">
<button id="cancel">取消</button>
<script src="./debounce.js"></script>
<script>
const inputEl = document.querySelector("input")
const cancelBtn = document.querySelector("#cancel")
let counter = 0
//输入触发事件
const inputChange = function (event) {
console.log(`发送了第${++counter}次网络请求`, this, event)
}
inputEl.oninput = debounce(inputChange, 1000)
</script>
</body>
</html>3.3 防抖函数第一次触发,立即执行
目前我们的事件触发都要等到delay时间,但是某些场景是用户开始输入时的第一次是立即执行的,后续的输入才需要等待,我们可以如何优化呢?
-
我们可以让用户多传入一个参数:immediate
-
那么第一次就立即执行
-
后来的事件需要等待delay时间执行
-
immediate为false,或者不传,那么按照上面的防抖进行操作
-
immediate为true
-
-
我们可以根据是否传入immediate进行不同的处理方式:
//debounce.js
/**
* @param {*} fn 要执行的函数
* @param {*} delay 延迟时间
* @param {*} immediate 是否立即执行
* @returns
*/
function debounce(fn, delay, immediate = false) {
// 1.定义一个定时器, 保存上一次的定时器
let timer = null;
let isInvoke = false; //记录立即执行是否已执行过
// 2.真正执行的函数
const _debounce = function (...args) {
// 取消上一次的定时器
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer);
// 判断是否需要立即执行
if (immediate && !isInvoke) {
fn.apply(this, args);
isInvoke = true;
} else {
// 延迟执行
timer = setTimeout(() => {
// 外部传入的真正要执行的函数
fn.apply(this, args);
//没有这个步骤时,只有第一次输入是立即执行,即使后面延迟执行后再输入也是延迟执行;
// 有这个步骤时,第一次输入时立即执行,后面延迟执行后再输入也会有立即执行
isInvoke = false
timer = null
}, delay);
}
};
return _debounce;
}代码调用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text">
<button id="cancel">取消</button>
<script src="./debounce.js"></script>
<script>
const inputEl = document.querySelector("input")
const cancelBtn = document.querySelector("#cancel")
let counter = 0
//输入触发事件
const inputChange = function (event) {
console.log(`发送了第${++counter}次网络请求`, this, event)
}
inputEl.oninput = debounce(inputChange, 1000, true)
</script>
</body>
</html>3.4 当我们触发函数时,在未到执行时间,可以取消函数执行
有时候,在等待执行的过程中,可能需要取消之前的操作:
-
比如用户进行了搜索,但是还没有来得及发送搜索的情况下,退出了界面;
-
当用户退出时,之前的操作就可以取消掉;
我们这里将delay时间改长,并且在下方增加一个按钮:
-
在延迟时间内,我们点击按钮,就取消之前的函数执行:
//debounce.js
/**
* @param {*} fn 要执行的函数
* @param {*} delay 延迟时间
* @param {*} immediate 是否立即执行
* @returns
*/
function debounce(fn, delay, immediate = false) {
// 1.定义一个定时器, 保存上一次的定时器
let timer = null;
let isInvoke = false; //记录立即执行是否已执行过
// 2.真正执行的函数
const _debounce = function (...args) {
// 取消上一次的定时器
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer);
// 判断是否需要立即执行
if (immediate && !isInvoke) {
fn.apply(this, args);
isInvoke = true;
} else {
// 延迟执行
timer = setTimeout(() => {
// 外部传入的真正要执行的函数
fn.apply(this, args);
//没有这个步骤时,只有第一次输入是立即执行,即使后面延迟执行后再输入也是延迟执行;
// 有这个步骤时,第一次输入时立即执行,后面延迟执行后再输入也会有立即执行
isInvoke = false
timer = null
}, delay);
}
};
// 封装取消功能
_debounce.cancel = function () {
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
timer = null //重置
isInvoke = false //重置
}
return _debounce;
}代码调用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text">
<button id="cancel">取消</button>
<script src="./debounce.js"></script>
<script>
const inputEl = document.querySelector("input")
const cancelBtn = document.querySelector("#cancel")
let counter = 0
//输入触发事件
const debounceChange = debounce(inputChange, 2000, true)
inputEl.oninput = debounceChange
// 取消功能
cancelBtn.onclick = function () {
debounceChange.cancel()
}
</script>
</body>
</html>3.5 当触发的函数有返回值时,获取在防抖函数中执行的结果
有时候fn函数执行结束后还有返回值,如果我们希望拿到这个返回值应该怎么办呢?
先明确一个操作:
-
内部执行fn函数大多数情况是异步执行的(在setTimeout中执行)
-
所以通过return是无法拿到返回值的
异步的操作如何获取返回值呢?
-
方法一:通过回调函数
-
方法二:通过Promise的resolve
(1)给debounce函数,多添加一个参数,参数为一个回调函数:
//debounce.js
/**
* @param {*} fn 要执行的函数
* @param {*} delay 延迟时间
* @param {*} immediate 是否立即执行
* @param {*} resultCallback 用来操作返回值的函数
* @returns
*/
function debounce(fn, delay, immediate = false, resultCallback) {
// 1.定义一个定时器, 保存上一次的定时器
let timer = null;
let isInvoke = false; //记录立即执行是否已执行过
// 2.真正执行的函数
const _debounce = function (...args) {
// 取消上一次的定时器
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer);
// 判断是否需要立即执行
if (immediate && !isInvoke) {
const result = fn.apply(this, args)
if (resultCallback) resultCallback(result) //通过函数参数来返回值
isInvoke = true;
} else {
// 延迟执行
timer = setTimeout(() => {
// 外部传入的真正要执行的函数
const result = fn.apply(this, args)
if (resultCallback) resultCallback(result)
//没有这个步骤时,只有第一次输入是立即执行,即使后面延迟执行后再输入也是延迟执行;
// 有这个步骤时,第一次输入时立即执行,后面延迟执行后再输入也会有立即执行
isInvoke = false
timer = null
}, delay);
}
};
// 封装取消功能
_debounce.cancel = function () {
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
timer = null //重置
isInvoke = false //重置
}
return _debounce;
}代码调用:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text">
<button id="cancel">取消</button>
<script src="./debounce.js"></script>
<script>
const inputEl = document.querySelector("input")
const cancelBtn = document.querySelector("#cancel")
let counter = 0
const inputChange = function (event) {
console.log(`发送了第${++counter}次网络请求`, this, event)
// 返回值
return "aaaaaaaaaaaa"
}
// 方法一 通过添加一个函数参数来获取
const debounceChange = debounce(inputChange, 1000, true, (res) => {
console.log("函数参数返回的值:", res)
})
inputEl.oninput = debounceChange
// 取消功能
cancelBtn.onclick = function () {
debounceChange.cancel()
}
</script>
</body>
</html>(2)使用Promise来返回执行结果:
/**
* @param {*} fn 要执行的函数
* @param {*} delay 延迟时间
* @param {*} immediate 是否立即执行
* @returns
*/
function debounce(fn, delay, immediate = false) {
// 1.定义一个定时器, 保存上一次的定时器
let timer = null
let isInvoke = false
// 2.真正执行的函数
const _debounce = function (...args) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { //通过promise来返回值
// 取消上一次的定时器
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
// 判断是否需要立即执行
if (immediate && !isInvoke) {
const result = fn.apply(this, args)
resolve(result)
isInvoke = true
} else {
// 延迟执行
timer = setTimeout(() => {
// 外部传入的真正要执行的函数
const result = fn.apply(this, args)
resolve(result)
isInvoke = false
timer = null
}, delay)
}
})
}
// 封装取消功能
_debounce.cancel = function () {
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
timer = null
isInvoke = false
}
return _debounce
}代码调用:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text">
<button id="cancel">取消</button>
<script src="./debounce.js"></script>
<script>
const inputEl = document.querySelector("input")
const cancelBtn = document.querySelector("#cancel")
let counter = 0
const inputChange = function (event) {
console.log(`发送了第${++counter}次网络请求`, this, event)
// 返回值
return "aaaaaaaaaaaa"
}
// 方法二 返回一个promise
const debounceChange = debounce(inputChange, 3000, false)//相当于_debounce
const tempCallback = function (...args) {
debounceChange.apply(this, args).then(res => {//此时this绑定的是input对象
console.log("Promise的返回值结果:", res)
})
}
inputEl.oninput = tempCallback
// 取消功能
cancelBtn.onclick = function () {
debounceChange.cancel()
}
</script>
</body>
</html>更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容








所有评论(0)