蚂蚁开源千亿参数全模态大模型Ming-flash-omni-Preview详解:原理、部署与实战
蚂蚁开源千亿参数全模态大模型Ming-flash-omni-Preview基于稀疏MoE架构,总参数103B但仅激活9B,实现高效计算。其创新性模态级路由机制能智能分配专家网络处理不同模态数据,配备专用视觉、音频和文本编码器。关键技术包括稳定稀疏训练、方言ASR提升(15种中国方言准确率显著提高)及生成式分割编辑一体化范式,在GenEval和GEdit基准测试中表现优异。该模型支持全模态理解与生成
蚂蚁开源千亿参数全模态大模型Ming-flash-omni-Preview详解:原理、部署与实战
全模态AI的统一之路:一次看懂千亿参数Ming-flash-omni-Preview的技术突破与实战应用
近日,蚂蚁百灵大模型团队正式发布了千亿参数开源全模态大模型 Ming-flash-omni-Preview,这是首个参数规模达到千亿的开源全模态大模型。该模型基于 Ling 2.0 的稀疏 MoE 架构,总参数 103B,激活 9B,在全模态理解和生成能力上均有显著提升。
1 模型架构设计
Ming-flash-omni-Preview 的整体架构基于稀疏专家混合模型(MoE)设计,构建了一个能够统一处理多种模态数据的智能系统。
1.1 稀疏MoE架构详解
Ming-flash-omni-Preview 采用 Ling 2.0 的稀疏 MoE 架构,总参数达到 103B,但每个token仅激活 9B 参数。这种"大容量、小激活"的设计使模型既拥有海量知识存储能力,又保持了高效的推理速度。
模型的核心创新在于模态级路由机制,该机制能够针对不同模态的数据分布和特性,智能地将输入令牌路由到最合适的专家网络。与传统的密集架构相比,这种设计在保持模型性能的同时,大幅降低了计算资源需求。
# 模型架构关键参数示例
model_config = {
"total_parameters": "103B",
"activated_parameters": "9B",
"architecture": "Sparse MoE",
"modality_specific_routing": True,
"experts_count": 128, # 专家数量
"top_k_experts": 4, # 每个token激活的专家数
}
1.2 多模态编码器设计
模型针对不同模态设计了专用编码器,确保每种数据类型都能得到最优处理:
- 视觉编码器:基于 Qwen2.5 视觉主干网络,支持任意分辨率的图像和视频输入,能够提取多层次视觉特征
- 音频编码器:采用 Whisper 模型,具备强大的语音识别和音频理解能力
- 文本编码器:优化的大语言模型编码器,处理文本输入和输出
1.3 模态级路由机制
Ming-flash-omni-Preview 的核心创新之一是模态级路由系统。该系统通过学习和理解不同模态的数据分布特征,为每种模态设计最优的路由策略:
# 路由机制伪代码
class ModalityAwareRouter(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, num_experts, modality_types):
super().__init__()
self.modality_embeddings = nn.Embedding(len(modality_types), hidden_size)
self.experts_gate = nn.Linear(hidden_size * 2, num_experts)
def forward(self, hidden_states, modality_type):
# 获取模态特定嵌入
modality_emb = self.modality_embeddings(modality_type)
# 融合令牌表示和模态信息
combined = torch.cat([hidden_states, modality_emb.unsqueeze(0).expand(hidden_states.size(0), -1)], dim=-1)
# 计算专家权重
expert_weights = torch.softmax(self.experts_gate(combined), dim=-1)
return expert_weights
2 关键技术突破
Ming-flash-omni-Preview 在多个技术领域实现了重要突破,这些创新共同推动了全模态AI性能的边界。
2.1 基于稀疏专家架构的全模态训练
传统多模态模型在处理异构数据时面临诸多挑战,Ming-flash-omni-Preview 通过多项创新技术解决了这些问题:
稳定稀疏训练技术
团队采用了混合专家平衡方案,结合辅助负载均衡损失与路由器偏置更新,确保稀疏 MoE 架构下全模态训练的均匀激活和收敛性。这一机制防止了某些专家被过度使用而其他专家未被充分利用的问题。
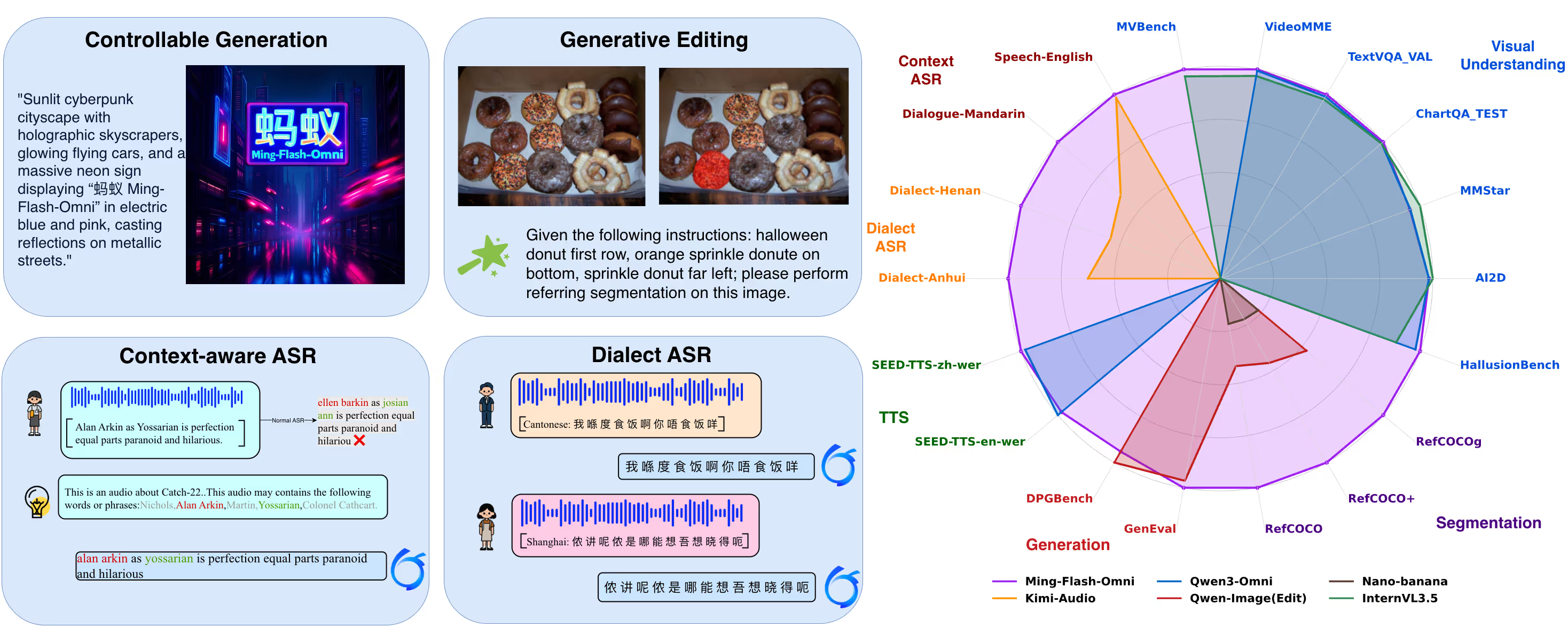
上下文感知的 ASR 训练范式
在语音识别任务中,模型以任务/领域信息输入作为解码条件,显著提高了专有名词识别和转录一致性。同时引入高质量方言等训练语料,实现对15种中国方言的识别准确率显著提升。
表1:方言识别性能提升对比
| 方言类型 | 识别准确率(改进前) | 识别准确率(改进后) | 提升幅度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 湖南话 | 68.3% | 78.5% | 10.2% |
| 闽南话 | 65.7% | 76.2% | 10.5% |
| 粤语 | 72.1% | 81.3% | 9.2% |
| 四川话 | 70.5% | 79.8% | 9.3% |
2.2 生成式分割编辑一体化
Ming-flash-omni-Preview 提出了 “生成式分割即编辑” 的协同训练范式,解决了多模态模型中理解与生成目标不一致的难题。
技术原理
该范式将图像分割重构为语义保持的编辑任务,例如"将香蕉涂成紫色"。这种设计的核心优势在于:
- 目标统一:成功的编辑必须依赖对对象轮廓的精确理解
- 闭环反馈:编辑质量直接为理解能力提供监督信号
- 语义控制:增强模型在细粒度时空维度上的语义控制能力
性能表现
在 GenEval 基准测试中,Ming-flash-omni-Preview 取得了 0.90 分,超越所有领先的非强化学习方法。在 GEdit 基准测试中,在物体删除、物体替换等精准编辑任务上的均分从 6.9 提升至 7.9。
# 生成式分割编辑示例代码
def generative_segmentation_editing(model, image, text_prompt):
"""
执行生成式分割编辑
:param model: 预训练模型
:param image: 输入图像
:param text_prompt: 编辑指令,如"将香蕉涂成紫色"
:return: 编辑后的图像
"""
# 提取分割掩码
segmentation_mask = model.segment(image, text_prompt)
# 基于分割结果进行编辑
edited_image = model.edit_based_on_mask(
image,
segmentation_mask,
text_prompt
)
return edited_image
2.3 高效全模态训练架构
训练全模态基础模型面临数据异构性和模型异构性两大挑战。Ming-flash-omni-Preview 基于 Megatron-LM 框架进行了两项关键优化:
序列打包
将多个变长多模态序列智能打包为固定长度批次,大幅提升内存利用率和计算密度。这种方法特别适合处理长度不一的多模态数据,如长短不一的视频片段或音频剪辑。
弹性编码器分片
扩展支持模态特定编码器在数据并行、管道并行和张量并行维度上的细粒度切分,消除流水线等待,实现真正的负载均衡。
这些优化使 Ming-flash-omni-Preview 的训练吞吐量比基线提升了一倍,大幅缩短了大规模全模态模型的迭代周期。
3 模型功能特性
Ming-flash-omni-Preview 在多个模态任务上展现出卓越的性能,以下是其主要功能特性的详细分析。
3.1 全模态理解能力
视觉理解
模型在图像和视频理解方面表现优异,特别是在复杂场景理解和细粒度视觉推理任务上。通过多尺度特征提取和融合,模型能够同时捕捉全局语境和局部细节。
音频理解
除了普通话语音识别,模型在方言识别方面取得显著进展。通过上下文感知的ASR训练范式,模型能够利用任务和领域信息提升识别准确性。
视频理解
通过在注意力层引入 VideoRoPE,模型增强了对长视频的时空建模能力,提升了视频交互理解水平。这项技术使模型能够理解视频中的时序关系和动态变化。
表2:多模态理解性能对比
| 任务类型 | 基准测试 | Ming-flash-omni | 前代模型 | 提升幅度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 图像理解 | MMBench | 85.3 | 79.2 | 6.1 |
| 视频理解 | VideoBench | 78.6 | 70.5 | 8.1 |
| 语音识别 | ASR-Bench | 96.2 | 92.7 | 3.5 |
| 方言识别 | DialectASR | 88.4 | 76.3 | 12.1 |
3.2 强大的生成能力
图像生成与编辑
Ming-flash-omni-Preview 在图像生成方面引入了高保真文本渲染能力,并在图像编辑过程中展示了场景一致性和身份保持方面的显著提升。模型能够根据复杂文本描述生成高质量图像,并支持精细的图像编辑操作。
语音生成
模型支持高质量的文本到语音转换,生成自然流畅的语音。通过字节对编码技术压缩音频信息,提高了生成效率并保持了语音的自然度。
多模态对话
模型能够理解和生成跨模态的内容,实现真正的多模态对话。例如,用户可以上传一张图片并询问相关问题,模型能够结合视觉和语言理解生成准确回答。
# 多模态对话示例
def multimodal_conversation_example():
messages = [
{
"role": "HUMAN",
"content": [
{"type": "image", "image": "path/to/image.jpg"},
{"type": "text", "text": "请描述这张图片中的主要内容,并生成一段语音介绍。"}
],
},
]
# 处理多模态输入
text = processor.apply_chat_template(messages)
image_inputs, video_inputs, audio_inputs = processor.process_vision_info(messages)
inputs = processor(
text=[text],
images=image_inputs,
return_tensors="pt",
).to(model.device)
# 生成响应
with torch.no_grad():
generated_ids = model.generate(
**inputs,
max_new_tokens=512,
use_cache=True,
)
output_text = processor.batch_decode(
generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True
)[0]
return output_text
4 模型部署与实战
本章将详细介绍 Ming-flash-omni-Preview 的安装、配置和实际应用方法。
4.1 环境安装与配置
系统要求
- GPU 内存:至少 40GB(推荐 80GB)
- 系统内存:至少 64GB
- Python 版本:3.9 或更高
- PyTorch 版本:2.0 或更高
安装步骤
# 安装基础依赖
pip install torch torchvision torchaudio
pip install transformers accelerate
# 安装 Modelscope(推荐国内用户使用)
pip install modelscope
# 安装 Flash Attention 2(可选,用于加速)
pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolation
4.2 模型下载与加载
Ming-flash-omni-Preview 可通过 Hugging Face 或 ModelScope 下载。对于中国大陆用户,推荐使用 ModelScope 以获得更快的下载速度。
通过 ModelScope 下载:
from modelscope import snapshot_download
model_dir = snapshot_download("inclusionAI/Ming-flash-omni-Preview")
模型加载代码:
import os
import torch
import warnings
from bisect import bisect_left
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
from modelscope import AutoProcessor
from modeling_bailingmm2 import BailingMM2NativeForConditionalGeneration
def split_model():
"""分布式模型分割函数"""
device_map = {}
world_size = torch.cuda.device_count()
num_layers = 32
layer_per_gpu = num_layers // world_size
layer_per_gpu = [i * layer_per_gpu for i in range(1, world_size + 1)]
for i in range(num_layers):
device_map[f'model.model.layers.{i}'] = bisect_left(layer_per_gpu, i)
# 将特定模块分配到第一个GPU
device_map['vision'] = 0
device_map['audio'] = 0
device_map['linear_proj'] = 0
device_map['linear_proj_audio'] = 0
device_map['model.model.word_embeddings.weight'] = 0
device_map['model.model.norm.weight'] = 0
device_map['model.lm_head.weight'] = 0
device_map['model.model.norm'] = 0
device_map[f'model.model.layers.{num_layers - 1}'] = 0
return device_map
# 加载预训练模型
model_path = "inclusionAI/Ming-flash-omni-Preview"
model = BailingMM2NativeForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
model_path,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
attn_implementation="flash_attention_2",
device_map=split_model(),
load_image_gen=True,
load_talker=True,
).to(dtype=torch.bfloat16)
# 初始化处理器
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_path, trust_remote_code=True)
4.3 基础使用示例
文本生成示例:
def text_generation_example(question):
messages = [
{
"role": "HUMAN",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": question}
],
},
]
output_text = generate(messages, processor=processor, model=model)
return output_text
# 使用示例
question = "请详细介绍鹦鹉的生活习性。"
answer = text_generation_example(question)
print(answer)
图像理解示例:
def image_understanding_example(image_path, question):
messages = [
{
"role": "HUMAN",
"content": [
{"type": "image", "image": image_path},
{"type": "text", "text": question}
],
},
]
output_text = generate(messages, processor=processor, model=model)
return output_text
# 使用示例
image_path = "path/to/parrot.jpg"
question = "这张图片中的鸟类是什么品种?它有什么特征?"
answer = image_understanding_example(image_path, question)
print(answer)
语音识别与生成示例:
def audio_processing_example(audio_path, text_prompt=None):
if text_prompt is None:
# 语音识别
text_prompt = "请转写这段音频内容"
messages = [
{
"role": "HUMAN",
"content": [
{"type": "audio", "audio": audio_path},
{"type": "text", "text": text_prompt}
],
},
]
output_text = generate(messages, processor=processor, model=model)
return output_text
# 使用示例
audio_path = "path/to/speech.wav"
transcription = audio_processing_example(audio_path)
print("语音转写结果:", transcription)
5 高级功能与应用场景
Ming-flash-omni-Preview 支持多种高级功能,可应用于各种复杂场景。
5.1 流式视频理解
模型能够处理长视频内容,理解视频中的时序关系和动态变化。这项功能适用于视频摘要、内容审核等场景。
def video_understanding_example(video_path, question):
messages = [
{
"role": "HUMAN",
"content": [
{"type": "video", "video": video_path},
{"type": "text", "text": question}
],
},
]
output_text = generate(messages, processor=processor, model=model)
return output_text
# 使用示例
video_path = "path/to/video.mp4"
question = "请描述视频中发生的主要事件。"
answer = video_understanding_example(video_path, question)
print(answer)
5.2 音频上下文ASR与方言ASR
模型在语音识别方面表现出色,特别是在复杂语境和方言识别方面。
def dialect_asr_example(audio_path, dialect_info=None):
"""方言语音识别示例"""
if dialect_info:
prompt = f"请识别这段{dialect_info}方言音频内容"
else:
prompt = "请识别这段音频内容"
messages = [
{
"role": "HUMAN",
"content": [
{"type": "audio", "audio": audio_path},
{"type": "text", "text": prompt}
],
},
]
output_text = generate(messages, processor=processor, model=model)
return output_text
# 使用示例
audio_path = "path/to/dialect_audio.wav"
transcription = dialect_asr_example(audio_path, "湖南话")
print("方言识别结果:", transcription)
5.3 图像生成与编辑
Ming-flash-omni-Preview 支持高质量的图像生成和精准编辑。
def image_generation_example(text_description):
"""根据文本描述生成图像"""
messages = [
{
"role": "HUMAN",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": f"生成一张图像:{text_description}"}
],
},
]
# 对于图像生成,需要调用专门的生成接口
inputs = processor(
text=[text_description],
return_tensors="pt",
).to(model.device)
# 调用图像生成模块
with torch.no_grad():
generated_image = model.generate_image(
**inputs,
guidance_scale=7.5,
num_inference_steps=50,
)
return generated_image
# 使用示例
description = "一只戴着红色帽子的鹦鹉站在树枝上,背景是热带雨林"
generated_image = image_generation_example(description)
generated_image.save("generated_parrot.png")
表3:图像生成质量评估
| 评测指标 | GenEval得分 | 前代模型得分 | 相对提升 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 图像质量 | 0.90 | 0.82 | 9.8% |
| 文本符合度 | 0.87 | 0.79 | 10.1% |
| 空间一致性 | 0.85 | 0.75 | 13.3% |
| 身份保持 | 0.88 | 0.80 | 10.0% |
5.4 多模态对话系统
构建真正的多模态对话系统,支持图像、文本、语音的混合输入和输出。
def multimodal_chat_session():
"""多模态对话会话示例"""
conversation_history = []
print("多模态对话系统已启动,输入'退出'结束对话")
while True:
user_input = input("用户: ")
if user_input == "退出":
break
# 支持多种输入方式
content = []
# 处理文本输入
content.append({"type": "text", "text": user_input})
# 可扩展处理图像、音频输入
# 例如:if image_path: content.append({"type": "image", "image": image_path})
messages = [{"role": "HUMAN", "content": content}]
# 生成回复
response = generate(messages, processor=processor, model=model)
print(f"助手: {response}")
# 更新对话历史
conversation_history.append({"role": "HUMAN", "content": content})
conversation_history.append({"role": "ASSISTANT", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": response}]})
return conversation_history
# 启动对话会话
# chat_history = multimodal_chat_session()
6 性能优化与最佳实践
为了充分发挥 Ming-flash-omni-Preview 的性能,需要遵循一系列优化策略和最佳实践。
6.1 内存与计算优化
梯度检查点
对于大模型训练和推理,使用梯度检查点可以显著降低内存消耗:
model.gradient_checkpointing_enable()
混合精度训练
利用混合精度训练加速计算并减少内存使用:
from torch.cuda.amp import autocast
with autocast(dtype=torch.bfloat16):
outputs = model(**inputs)
loss = outputs.loss
loss.backward()
模型分片
如前面示例所示,通过设备映射将模型分布到多个GPU上:
device_map = {
'model.model.layers.0': 0,
'model.model.layers.1': 0,
# ... 分层分配到不同设备
'model.model.layers.31': 3,
'model.lm_head': 3
}
6.2 推理速度优化
批处理推理
通过批处理提高推理效率:
def batch_inference(texts, images=None):
"""批处理推理"""
if images is None:
images = [None] * len(texts)
all_messages = []
for text, image in zip(texts, images):
content = [{"type": "text", "text": text}]
if image is not None:
content.append({"type": "image", "image": image})
all_messages.append({"role": "HUMAN", "content": content})
# 批量处理
batch_outputs = []
for messages in all_messages:
output = generate([messages], processor=processor, model=model)
batch_outputs.append(output)
return batch_outputs
缓存机制
利用模型缓存加速重复查询:
from functools import lru_cache
@lru_cache(maxsize=100)
def cached_generation(text_input, image_hash=None):
"""带缓存的生成函数"""
# 生成逻辑...
return result
7 实际应用案例
Ming-flash-omni-Preview 可应用于多种实际场景,以下是几个典型用例。
7.1 智能客服系统
构建支持多模态输入的智能客服系统,提升用户体验。
class MultimodalCustomerService:
def __init__(self, model, processor):
self.model = model
self.processor = processor
self.context_history = []
def process_customer_query(self, query, image=None, audio=None):
"""处理客户查询"""
content = [{"type": "text", "text": query}]
if image is not None:
content.append({"type": "image", "image": image})
if audio is not None:
content.append({"type": "audio", "audio": audio})
# 添加上下文历史
context_messages = self.context_history[-4:] # 保留最近2轮对话
context_messages.append({"role": "HUMAN", "content": content})
# 生成回复
response = generate(context_messages, processor=self.processor, model=self.model)
# 更新历史
self.context_history.append({"role": "HUMAN", "content": content})
self.context_history.append({"role": "ASSISTANT", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": response}]})
return response
def clear_context(self):
"""清除对话上下文"""
self.context_history = []
# 使用示例
# customer_service = MultimodalCustomerService(model, processor)
# response = customer_service.process_customer_query("我的账户出现了问题,请看截图", image="screenshot.png")
7.2 教育辅助工具
开发多模态教育辅助应用,增强学习体验。
class EducationalAssistant:
def __init__(self, model, processor):
self.model = model
self.processor = processor
def explain_concept(self, concept, include_image=True, include_audio=True):
"""解释概念"""
prompt = f"请详细解释{concept},并给出相关示例"
messages = [{"role": "HUMAN", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": prompt}]}]
response = generate(messages, processor=self.processor, model=self.model)
result = {"text": response}
# 可选:生成示意图
if include_image:
image_prompt = f"生成一张关于{concept}的示意图"
# 调用图像生成功能...
# 可选:生成语音解释
if include_audio:
audio_prompt = f"请用语音解释{concept}"
# 调用语音生成功能...
return result
def check_homework(self, question, student_answer, subject="math"):
"""检查作业"""
prompt = f"""
问题:{question}
学生答案:{student_answer}
科目:{subject}
请检查这个答案是否正确,并给出解释和改进建议。
"""
messages = [{"role": "HUMAN", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": prompt}]}]
response = generate(messages, processor=self.processor, model=self.model)
return response
# 使用示例
# assistant = EducationalAssistant(model, processor)
# explanation = assistant.explain_concept("牛顿第一定律")
7.3 内容创作平台
构建多模态内容创作助手,支持图文音视频内容生成。
class ContentCreationAssistant:
def __init__(self, model, processor):
self.model = model
self.processor = processor
def generate_article(self, topic, style="科普", length=1000):
"""生成文章"""
prompt = f"以{style}的风格,写一篇关于{topic}的文章,字数约{length}字"
messages = [{"role": "HUMAN", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": prompt}]}]
article = generate(messages, processor=self.processor, model=self.model)
return article
def create_social_media_post(self, topic, platform="微博", include_image=True):
"""创建社交媒体帖子"""
prompt = f"为{platform}创建一个关于{topic}的帖子"
messages = [{"role": "HUMAN", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": prompt}]}]
post_text = generate(messages, processor=self.processor, model=self.model)
result = {"text": post_text}
if include_image:
image_prompt = f"生成一张适合在{platform}上发布的关于{topic}的图片"
# 调用图像生成...
return result
def generate_video_script(self, topic, duration=3, style="教育类"):
"""生成视频脚本"""
prompt = f"创建一个关于{topic}的{style}视频脚本,时长约{duration}分钟"
messages = [{"role": "HUMAN", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": prompt}]}]
script = generate(messages, processor=self.processor, model=self.model)
return script
# 使用示例
# creator = ContentCreationAssistant(model, processor)
# article = creator.generate_article("人工智能在医疗领域的应用")
8 总结与展望
Ming-flash-omni-Preview 作为首个千亿参数开源全模态大模型,在多个方面实现了技术突破。其稀疏MoE架构、生成式分割编辑一体化和方言语音识别等创新技术,为全模态AI的发展指明了方向。
核心优势:
- 规模与效率平衡:103B总参数,仅激活9B,实现"大容量、小激活"
- 全模态统一:真正统一的多模态理解和生成能力
- 技术突破:在图像编辑、方言识别等任务上达到领先水平
- 开源开放:完全开源,促进社区发展和应用创新
应用前景:
随着技术的不断成熟,Ming-flash-omni-Preview 将在智能客服、教育、内容创作、医疗辅助诊断等领域发挥重要作用。其开源特性也将加速全模态AI技术的普及和应用创新。
未来展望:
期待在未来版本中看到更多功能增强,如3D内容理解与生成、更强大的推理能力、更好的低资源语言支持等。同时,随着模型优化技术的进步,模型的部署和运行效率也将进一步提升,让更多开发者和企业能够充分利用这一强大的全模态AI基础设施。
资源链接
通过本文的详细介绍,相信读者已经对 Ming-flash-omni-Preview 有了全面的了解。这个强大的全模态大模型将为AI应用开发带来新的可能性,推动人工智能技术在多模态领域的发展与创新。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献121条内容
已为社区贡献121条内容








所有评论(0)