UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
我们前面介绍的账户密码都是指定在我们的xml配置文件中,我们最终还是需要实现和数据库中的数据比较,那么我们就需要自定义认证逻辑的实现。我们还是一样先进行源码分析,系统认证是通过UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器实现的。表单提交参数public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter extendsAbstra
我们前面介绍的账户密码都是指定在我们的xml配置文件中,我们最终还是需要实现和数据库中的数据比较,那么我们就需要自定义认证逻辑的实现。
我们还是一样先进行源码分析,系统认证是通过UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器实现的。
表单提交参数
public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter extends
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter {
// ~ Static fields/initializers
//这就是表单提交的值
public static final String SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_USERNAME_KEY = "username";
public static final String SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_PASSWORD_KEY = "password";
private String usernameParameter = SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_USERNAME_KEY;
private String passwordParameter = SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_PASSWORD_KEY;
private boolean postOnly = true;
注意:
public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter() {
super(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/login", "POST"));
}
// ~ Methods
// ========================================================================================================
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(
"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
String username = obtainUsername(request);
String password = obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, password);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
前面我们提到过这个过滤器只能是post提交表单,如果不是post提交就会提出"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod())异常。
doFilter方法
因为UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter就是一个过滤器,所以我们要分析他的原理,肯定需要通过doFilter方法来开始,注意该方法在父类中。
public abstract class AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter extends GenericFilterBean
implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware, MessageSourceAware {
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
Assert.notNull(authenticationManager, "authenticationManager must be specified");
}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
if (!requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Request is to process authentication");
}
Authentication authResult;
try {
authResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response);
if (authResult == null) {
// return immediately as subclass has indicated that it hasn't completed
// authentication
return;
}
sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authResult, request, response);
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed) {
logger.error(
"An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.",
failed);
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
catch (AuthenticationException failed) {
// Authentication failed
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
// Authentication success
if (continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult);
}
}
因为UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter的父类AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter中的doFilter方法
这一句就是认证的核心代码了。
authResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response);
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(
"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
String username = obtainUsername(request);
String password = obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, password);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
先执行attemptAuthentication方法。这个方法会从request中读出用户名、密码,组成UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken对象,这个对象也是Authentication对象,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken是实现了Authentication。然后将Authentication对象传给AuthenticationManager进行登录认证。AuthenticationManager的认证过程是springsecurity认证的核心。大致记录下。
AuthenticationManager实际是ProviderManager,ProviderManager实现了AuthenticationManager接口。将认证的工作交给AuthenticationProvider,AuthenticationManager都会包含多个AuthenticationProvider对象,有任何一个AuthenticationProvider验证通过,都属于认证通过。AuthenticationManager和AuthenticationProvider在哪里来的呢?在spring-security.xml的配置中来的
this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
进入上面的方法
public interface AuthenticationManager {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
}
这是实现的接口,我们按ctrl+h进行查找
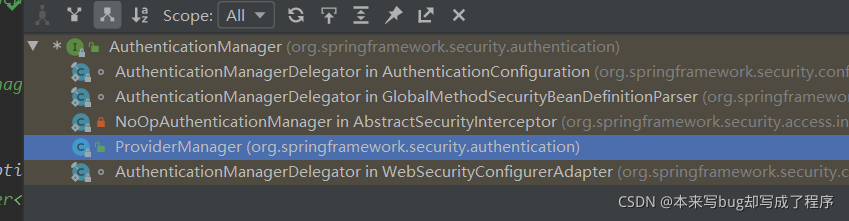
找到ProviderManager类
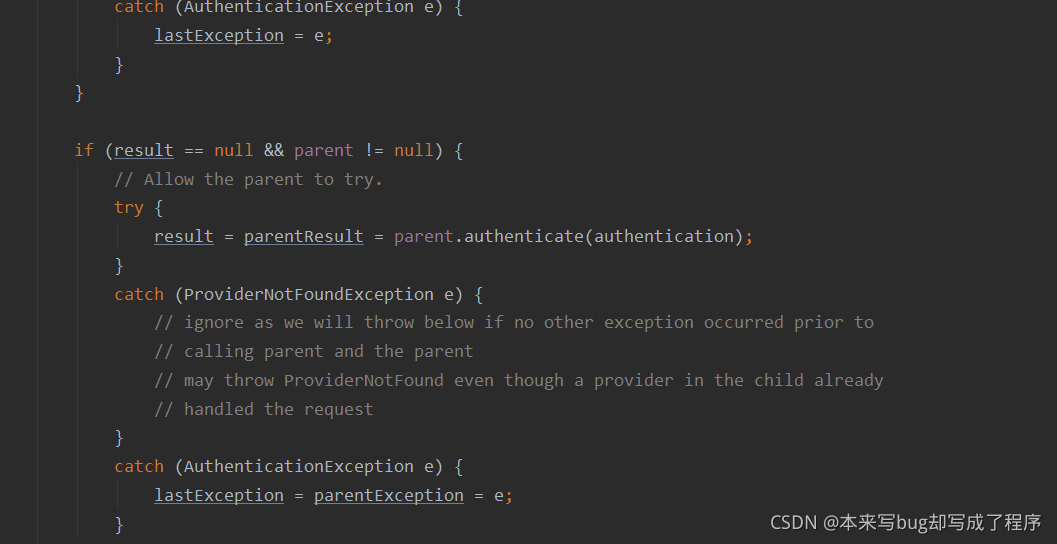
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
循环所有AuthenticationProvider,匹配当前认证类型。找到了对应认证类型就继续调用AuthenticationProvider对象完成认证业务
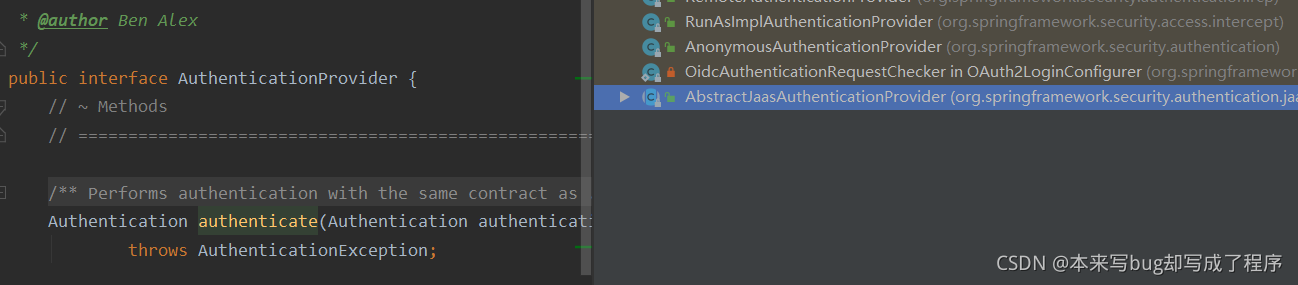
user = retrieveUser(username, (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
UserDetails认证账号对象!
UserDetails的实现
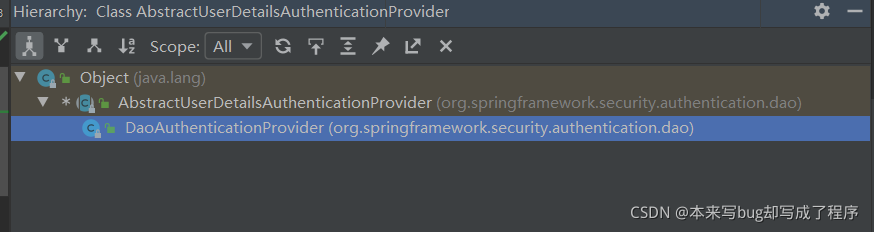
DaoAuthenticationProvider:它是AuthenticationProvider的的一个实现类,非常重要,它主要完成了两个工作,一个是retrieveUser方法,它返回UserDetails类.
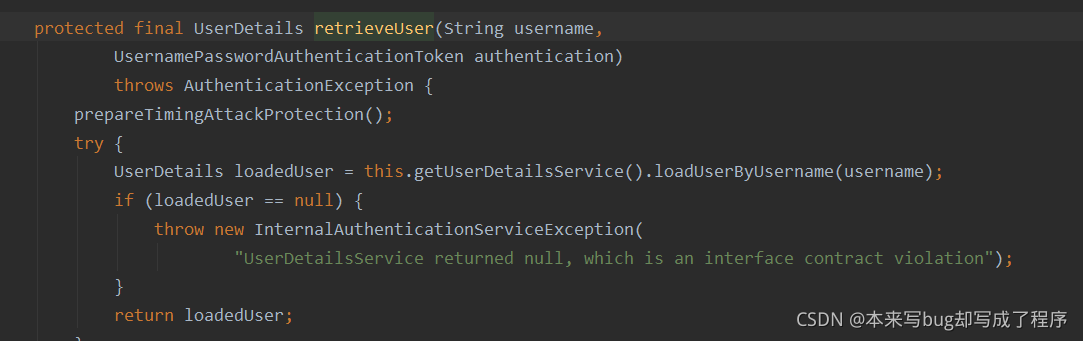
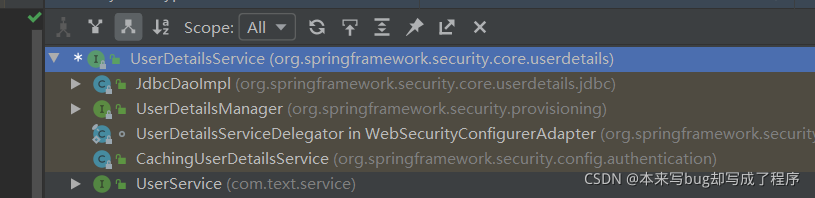
我们发现最终去做认证的是 UserDetailsService接口的实现去完成的,那么我们要自定义认证过程,也需要实现这个接口。
session的处理代码
sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authResult, request, response);
登录成功后
successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult);
自定义认证过程
1 准备好自己的MyBatils
2 导入相关依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>3.5.3</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId> <version>2.0.3</version> </dependency> <!-- mysql驱动包 --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.15</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.1.10</version> </dependency>
配置文件:db.properties
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/srm?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=123456
MyBatils配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <settings> <!-- 打印sql日志 MyBatis日志框架使用LOG4J --> <setting name="logImpl" value="LOG4J"/> </settings> </configuration>
和Spring的整合文件
<!-- 加载配置文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/>
<!-- 数据库连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"/>
<property name="maxActive" value="10"/>
<property name="minIdle" value="5"/>
</bean>
<!-- SqlSessionFactory -->
<!-- 让spring管理sqlsessionfactory 使用mybatis和spring整合包中的 -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<!-- 数据库连接池 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<!-- 加载mybatis的全局配置文件 -->
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"/>
<!--
映射文件和接口文件不在同一个目录下的时候
它的spring是不会去扫描jar包中的相应目录的,只会去他当前项目下获取。其实要改变这种情况很简单,
在classpath后面加一个*号,*号的作用是让spring的扫描涉及全个目录包括jar
-->
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath*:mapper/*.xml"/>
</bean>
<!-- Mapper映射文件的包扫描器 -->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.bruce.mapper"/>
</bean>
创建pojo,mapper接口,mapper的xml文件,映射文件
public interface UserDao {
UserPojo queryByUserName(@Param("userName") String userName);
}
<mapper namespace="com.text.mapper.UserDao">
<select id="queryByUserName" resultType="com.bruce.pojo.UserPojo">
select * from t_user where username = #{userName}
</select>
</mapper>
service serviceImpl 的实现 继承UserDetailsService 重写loadUserByusername
public interface UserService extends UserDetailsService{
}
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String s) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
// 根据账号去数据库中查询
UserPojo userPojo = this.queryByUserName(s);
if (userPojo != null) {
List<SimpleGrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>();
// 设置登录账号的角色
authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_USER"));
UserDetails user = new User(userPojo.getUsername(), "{noop}" + userPojo.getPassword(), authorities);
return user;
}
// 返回null 默认表示账号不存在
return null;
}
}
修改配置文件 ,既然连接了数据库那么我们的内存账号就不需要了。
<!--设置Spring Security认证用户信息的来源--> <security:authentication-manager> <security:authentication-provider user-service-ref="userServiceImpl"> </security:authentication-provider> </security:authentication-manager>
如果需要密码加密处理,security也提供了很多种加密算法
@Test
public void test2(){
Map<String, PasswordEncoder> encoders = new HashMap();
encoders.put("bcrypt", new BCryptPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("ldap", new LdapShaPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("MD4", new Md4PasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("MD5", new MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("MD5"));
encoders.put("noop", NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance());
encoders.put("pbkdf2", new Pbkdf2PasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("scrypt", new SCryptPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("SHA-1", new MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("SHA-1"));
encoders.put("SHA-256", new MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("SHA-256"));
encoders.put("sha256", new StandardPasswordEncoder());
}
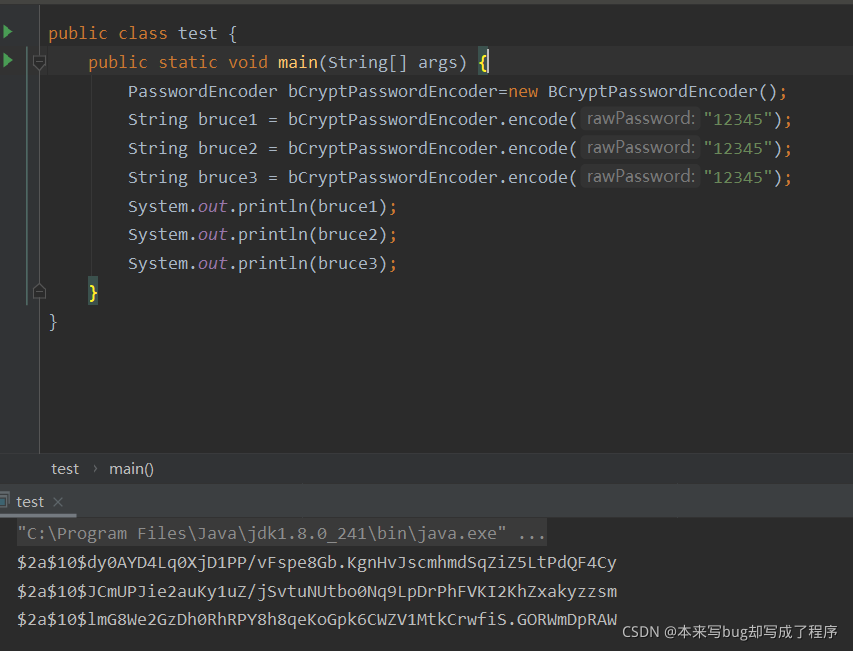
比较常用的就是BCryptPasswordEncoder来加密
我们会发现一个很神奇的事,他的三次加密同样的密码都不一样。
我们可以随便了解一下,其实他是一种加随机盐的算法,但是算法泰国高深,我也看不懂只能凭感觉分析,对比的过程并不是再次加密,过程:它的设计很巧妙,它能通过原来的密文和新的密码明文去判断是否能再次生成原来的密文。也就是说如果密码正确,那么我可以通过新密码再次得到之前的密文,如果得不到就是密码不对。也就是说虽然是随机盐,但是明文和密文之间是有关联存在的,但是关联我们也很难知晓,所以这就是他的牛逼之处。
在配置文件中设置加密格则
<!--加密算法对象--> <!--<bean id="passwordEncoder" class="org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder"/>--> <bean id="passwordEncoder" class="org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder"/> <security:authentication-manager> <security:authentication-provider user-service-ref="userServiceImpl"> <security:password-encoder ref="passwordEncoder"/> </security:authentication-provider> </security:authentication-manager>
再将数据库的密码修改成我们加密后的密码,此时我们就可以更安全的登录啦!!
oh 还有一步
将我们再serviceImpl中的密码前{noop}去掉。
认证状态判断
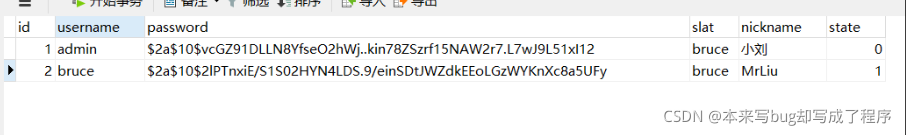
我们实际项目中因为用户不同,需要不同的操作,比如正常,冻结等。
SpringSecurity 也支持。
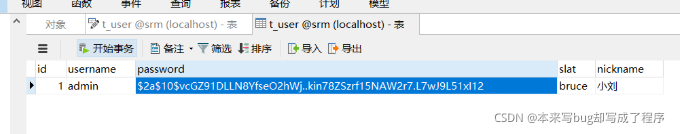
1 就是可用 0 为冻结
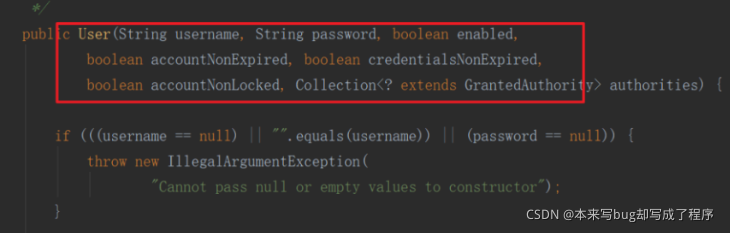
我们在认证的时候使用User对象的另一个构造器就可以了
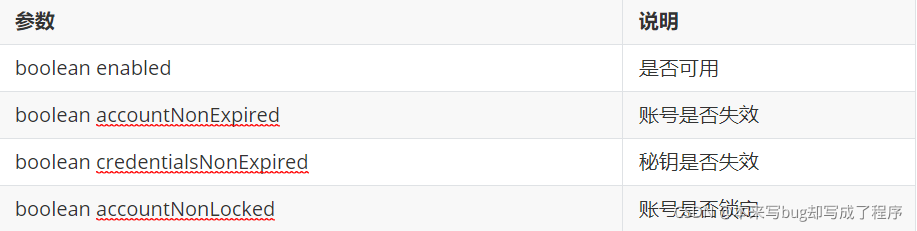
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String s) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//根据账号去数据库中查询
UserPojo userPojo = this.queryByUserName(s);
if (userPojo!=null){
ArrayList<SimpleGrantedAuthority> list = new ArrayList<>();
//设置登录账号角色
list.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_USER"));
UserDetails user = new User(userPojo.getUsername(), userPojo.getPassword(),userPojo.getState()==0,true,true,true, list);
return user;
}
//返回null 默认表示不存在
return null;
}
我们将状态设置成为0的记录就没有办法正常登录了。
注解授权
我们在前面提到,SpringSecurity中最重要最牛逼的就是认证和授权,我们前面提到了认证,现在我们来了解了解授权。
我们在控制器或者service中实现授权操作比较理想的方式就是通过相应的注解来实现。SpringSecurity可以通过注解的方式来控制类或者方法的访问权限。注解需要对应的注解支持,若注解放在controller类中,对应注解支持应该放在mvc配置文件中,因为controller类是有mvc配置文件扫描并创建的,同理,注解放在service类中,对应注解支持应该放在spring配置文件中。由于我们现在是模拟业务操作,并没有service业务代码,所以就把注解放在controller类中了。
我们下面给大家演示三种注解
但在实际开发中,一种就够了。
开启授权注解支持
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:security="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/security http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd"> <!-- 配置扫描路径--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.bruce.controller"></context:component-scan> <mvc:default-servlet-handler/> <mvc:annotation-driven/> <!-- 开启权限控制注解支持 jsr250-annotations="enabled"表示支持jsr250-api的注解,需要jsr250-api的jar包 pre-post-annotations="enabled"表示支持spring表达式注解 secured-annotations="enabled"这才是SpringSecurity提供的注解 --> <security:global-method-security jsr250-annotations="enabled" pre-post-annotations="enabled" secured-annotations="enabled"/> </beans>
在注解支持对应类或者方法上添加注解
jar包
创建相关的控制器
<dependency> <groupId>javax.annotation</groupId> <artifactId>jsr250-api</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> </dependency>
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RolesAllowed(value = {"ROLE_ADMIN"})
@RequestMapping("/find")
public String query(){
return "/success.jsp";
}
@RolesAllowed(value = {"ROLE_USER"})
@RequestMapping("/update")
public String update(){
return "/success.jsp";
}
}
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Resource
UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public UserPojo queryByUserName(String userName) {
return userMapper.queryUserPojoByUserName(userName);
}
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String s) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//根据账号去数据库中查询
UserPojo userPojo = this.queryByUserName(s);
if (userPojo!=null){
ArrayList<SimpleGrantedAuthority> list = new ArrayList<>();
//设置登录账号角色
list.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_USER"));
UserDetails user = new User(userPojo.getUsername(), userPojo.getPassword(),userPojo.getState()==0,true,true,true, list);
return user;
}
//返回null 默认表示不存在
return null;
}
}
这里的list.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_USER"));与@RolesAllowed(value = {"ROLE_USER"})对应就可以访问到了
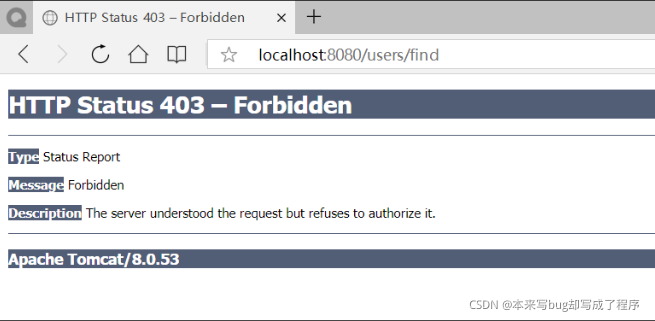
权限异常处理
方式一
<!--没有权限的异常处理页面--> <security:access-denied-handler error-page="/noreights.jsp"/>
或者配置web.xml
<error-page> <error-code>403</error-code> <location>/403.jsp</location> </error-page>
当然我们看到前端页面没有权限访问的也存在,看起来很不舒服,这时我们又有一种标签可以使没有权限访问的功能直接不展示。
<security:authorize access="hasAnyRole('ROLE_ADMIN')">
<a href="/user/find">用户查询</a><br/>
</security:authorize>
<security:authorize access="hasAnyRole('ROLE_USER')">
<a href="/user/update">用户更新</a><br/>
</security:authorize>
<security:authorize access="hasAnyRole('ROLE_USER')">
<a href="/order/find">订单查询</a><br/>
</security:authorize>
<security:authorize access="hasAnyRole('ROLE_CC')">
<a href="/order/update">订单更新</a><br/>
</security:authorize>
<security:authorize access="hasAnyRole('ROLE_ADMIN')">
<a href="/role/find">角色查询</a><br/>
</security:authorize>
<security:authorize access="hasAnyRole('ROLE_USER')">
<a href="/role/update">角色更新</a><br/>
</security:authorize>
进行验证码验证
package com.text.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.util.Random;
@RestController
public class CheckCodeController {
@RequestMapping("/getCode")
public void getCode(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
//生成对应宽高的初始图片
int width = 130;
int height = 45;
BufferedImage img = new BufferedImage(width, height, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_BGR);
//美化图片
Graphics g = img.getGraphics();
g.setColor(Color.white); //设置画笔颜色-验证码背景色
g.fillRect(0, 0, width, height);//填充背景
Random ran = new Random();
//产生4个随机验证码,12Ey
String checkCode = getCheckCode();
//将验证码放入HttpSession中
request.getSession().setAttribute("checkCode_session", checkCode);
System.out.println("系统生成的验证码是:" + checkCode);
Color color = new Color(ran.nextInt(256), ran.nextInt(256), ran.nextInt(256));//随机生成颜色
g.setColor(color);
//设置字体的小大
g.setFont(new Font("微软雅黑", Font.BOLD, 40));
//向图片上写入验证码
g.drawString(checkCode, 15, 33);
//画干扰线
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
// 设置随机颜色
Color color1 = new Color(ran.nextInt(256),
ran.nextInt(256), ran.nextInt(256));//随机生成颜色
g.setColor(color1);
// 随机画线
g.drawLine(ran.nextInt(width), ran.nextInt(height),
ran.nextInt(width), ran.nextInt(height));
}
//添加噪点
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
int x1 = ran.nextInt(width);
int y1 = ran.nextInt(height);
Color color2 = new Color(ran.nextInt(256), ran.nextInt(256), ran.nextInt(256));//随机生成颜色
g.setColor(color2);
g.fillRect(x1, y1, 2, 2);
}
//将图片输出页面展示
try {
ImageIO.write(img, "png", response.getOutputStream());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//生成随机验证码方法
private String getCheckCode() {
String base = "123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHJKLMNPQRSTUVWXYZ";
int size = base.length();
Random r = new Random();
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
//产生0到size-1的随机值
int index = r.nextInt(size);
//在base字符串中获取下标为index的字符
char c = base.charAt(index);
//将c放入到StringBuffer中去
sb.append(c);
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
进行前端页面比较
package com.text.filter;
import com.alibaba.druid.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.session.SessionAuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Objects;
@Component
public class CheckCodeFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
@Autowired
MyFailureHandler myFailureHandler;
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
if (StringUtils.equals("/login",request.getRequestURI())&&StringUtils.equalsIgnoreCase(request.getMethod(),"post")){
try{
validate(request);
}catch (AuthenticationException e){
//产生的异常交给myFilureHandle处理
myFailureHandler.onAuthenticationFailure(request,response,e);
return; //产生了异常不再向下执行。
}
}
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
}
private void validate(HttpServletRequest request) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
String checkCode = request.getParameter("checkCode");
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(checkCode)){
throw new SessionAuthenticationException("验证码能为空");
}
//获取session池中的验证码谜底,session中不存在的情况
String checkCode_session = (String) session.getAttribute("checkCode_session");
if (Objects.isNull(checkCode_session)){
throw new SessionAuthenticationException("验证码不存在");
}
//请求验证码校验
if (!StringUtils.equalsIgnoreCase(checkCode_session,checkCode)){
throw new SessionAuthenticationException("验证码错误");
}
}
}
package com.text.filter;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.session.SessionAuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@Component
public class MyFailureHandler extends SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler {
private String loginType="json";
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException, ServletException {
String errormsg = "用户名或者密码输入错误!";//返回的错误信息,默认是登录的错误
if (exception instanceof SessionAuthenticationException){
errormsg = exception.getMessage();
}
if (!loginType.equalsIgnoreCase("json")){
request.setAttribute("msg",errormsg);
request.getRequestDispatcher("/login.jsp").forward(request,response);
}else {
//跳转登录页面
super.onAuthenticationFailure(request, response, exception);
}
}
}
当然生成了验证码,我们需要在mvc中放开静态资源
<!--放开静态资源--> <mvc:default-servlet-handler/>
在spring-security配置文件中
<security:intercept-url pattern="/getCode" access="permitAll()"/>
这样就可以啦,每周保持三更!!加油加油!!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容








所有评论(0)